Abstract
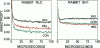
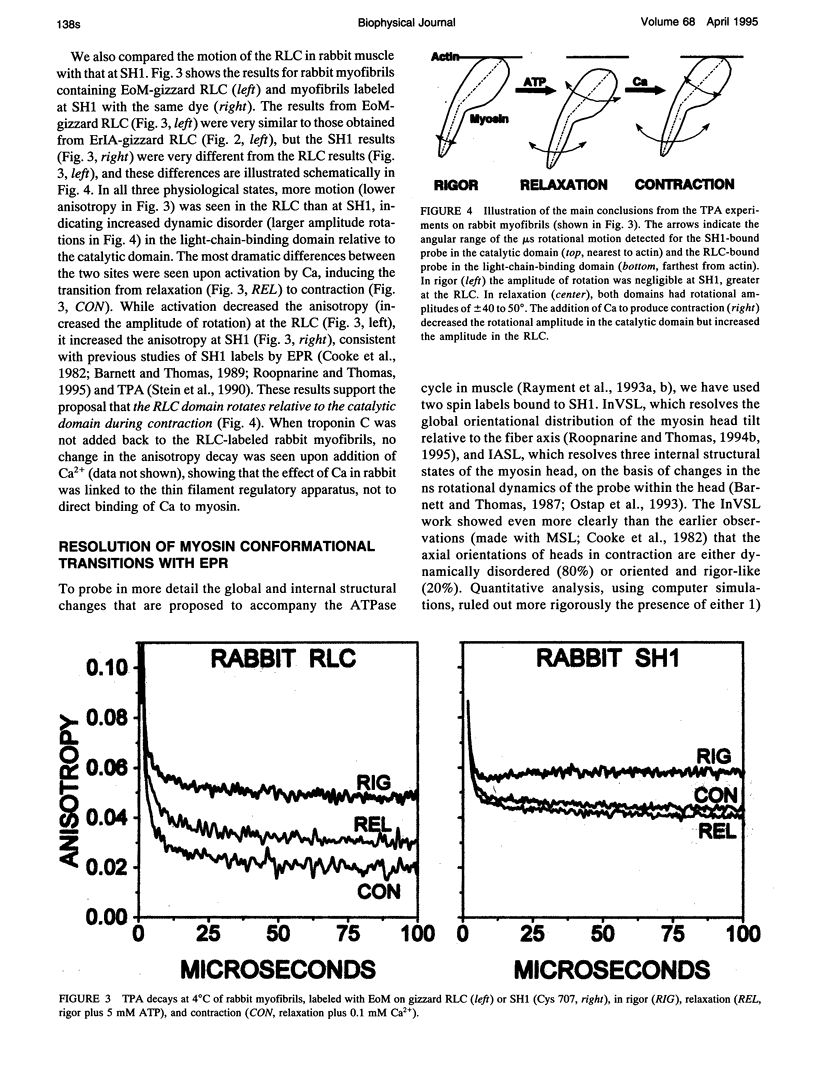
We propose a molecular mechanism of force generation in muscle, based primarily on site-specific spectroscopic probe studies of myosin heads in contracting muscle fibers and myofibrils. Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) and time-resolved phosphorescence anisotropy (TPA) of probes attached to SH1 (Cys 707, in the catalytic domain of the head) have consistently shown that most myosin heads in contracting muscle are dynamically disordered, undergoing large-amplitude rotations in the microsecond time range. Some of these disordered heads are bound to actin, especially in the early (weak-binding, preforce) phase of the ATPase cycle. The small ordered population (10-20%) is rigidly oriented precisely as in rigor, with no other distinct angle observed in contraction or in the presence of intermediate states trapped by nucleotide analogs. These results are not consistent with the classical model in which the entire head undergoes a 45 degree transition between two distinct orientations. Therefore, it has been proposed that the catalytic domain of the myosin head has only one stereospecific (rigor-like) actin-binding angle, and that the head's internal structure changes during force generation, causing the distal light-chain-binding domain to rotate. To test this model, we have performed EPR and TPA studies of probes attached to regulatory light chains (RLCs) in rabbit and scallop myofibrils and fibers. The RLC results confirm the predominance of dynamic (microsecond) rotational disorder in both relaxation and contraction, and show that the different mechanisms of calcium regulation in the two muscles produce different rotational dynamics. In rabbit myofibrils, RLC probes are more dynamically disordered than SH1 probes, especially in rigor and contraction,indicating that the light-chain-binding domain undergoes rotational motions relative to the catalytic domain when myosin heads interact with actin. An SH1-bound spin label, which is sensitive to myosin's internal dynamics, resolves three distinct conformations during contraction, and time-resolved EPR shows that these transitions are coupled to specific steps in the ATPase cycle. We propose that force is generated during contraction by a disorder-to-order transition, in which myosin heads first attach weakly to actin in a nonstereospecific mode characterized by large-scale dynamic disorder, then undergo at least two conformational transitions involving large-scale structural (rotational) changes within the head, culminating in a highly ordered strong-binding state that bears force.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arata T. Orientation of spin-labeled light chain 2 of myosin heads in muscle fibers. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jul 20;214(2):471–478. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90194-Q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett V. A., Thomas D. D. Microsecond rotational motion of spin-labeled myosin heads during isometric muscle contraction. Saturation transfer electron paramagnetic resonance. Biophys J. 1989 Sep;56(3):517–523. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82698-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett V. A., Thomas D. D. Resolution of conformational states of spin-labeled myosin during steady-state ATP hydrolysis. Biochemistry. 1987 Jan 13;26(1):314–323. doi: 10.1021/bi00375a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger C. L., Svensson E. C., Thomas D. D. Photolysis of a photolabile precursor of ATP (caged ATP) induces microsecond rotational motions of myosin heads bound to actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8753–8757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger C. L., Thomas D. D. Rotational dynamics of actin-bound intermediates in the myosin ATPase cycle. Biochemistry. 1991 Nov 19;30(46):11036–11045. doi: 10.1021/bi00110a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger C. L., Thomas D. D. Rotational dynamics of actin-bound intermediates of the myosin adenosine triphosphatase cycle in myofibrils. Biophys J. 1994 Jul;67(1):250–261. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80476-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger C. L., Thomas D. D. Rotational dynamics of actin-bound myosin heads in active myofibrils. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 13;32(14):3812–3821. doi: 10.1021/bi00065a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R., Crowder M. S., Thomas D. D. Orientation of spin labels attached to cross-bridges in contracting muscle fibres. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):776–778. doi: 10.1038/300776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R. The mechanism of muscle contraction. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1986;21(1):53–118. doi: 10.3109/10409238609113609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowder M. S., Cooke R. The effect of myosin sulphydryl modification on the mechanics of fibre contraction. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1984 Apr;5(2):131–146. doi: 10.1007/BF00712152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajer P. G., Fajer E. A., Brunsvold N. J., Thomas D. D. Effects of AMPPNP on the orientation and rotational dynamics of spin-labeled muscle cross-bridges. Biophys J. 1988 Apr;53(4):513–524. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83131-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajer P. G., Fajer E. A., Schoenberg M., Thomas D. D. Orientational disorder and motion of weakly attached cross-bridges. Biophys J. 1991 Sep;60(3):642–649. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82093-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajer P. G., Fajer E. A., Thomas D. D. Myosin heads have a broad orientational distribution during isometric muscle contraction: time-resolved EPR studies using caged ATP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5538–5542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hambly B., Franks K., Cooke R. Orientation of spin-labeled light chain-2 exchanged onto myosin cross-bridges in glycerinated muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1991 Jan;59(1):127–138. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82205-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hambly B., Franks K., Cooke R. Paramagnetic probes attached to a light chain on the myosin head are highly disordered in active muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1992 Nov;63(5):1306–1313. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81717-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley H. E., Kress M. Crossbridge behaviour during muscle contraction. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1985 Apr;6(2):153–161. doi: 10.1007/BF00713057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludescher R. D., Thomas D. D. Microsecond rotational dynamics of phosphorescent-labeled muscle cross-bridges. Biochemistry. 1988 May 3;27(9):3343–3351. doi: 10.1021/bi00409a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostap E. M., White H. D., Thomas D. D. Transient detection of spin-labeled myosin subfragment 1 conformational states during ATP hydrolysis. Biochemistry. 1993 Jul 6;32(26):6712–6720. doi: 10.1021/bi00077a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raucher D., Fajer P. G. Orientation and dynamics of myosin heads in aluminum fluoride induced pre-power stroke states: an EPR study. Biochemistry. 1994 Oct 4;33(39):11993–11999. doi: 10.1021/bi00205a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayment I., Holden H. M., Whittaker M., Yohn C. B., Lorenz M., Holmes K. C., Milligan R. A. Structure of the actin-myosin complex and its implications for muscle contraction. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):58–65. doi: 10.1126/science.8316858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayment I., Rypniewski W. R., Schmidt-Bäse K., Smith R., Tomchick D. R., Benning M. M., Winkelmann D. A., Wesenberg G., Holden H. M. Three-dimensional structure of myosin subfragment-1: a molecular motor. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):50–58. doi: 10.1126/science.8316857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roopnarine O., Thomas D. D. A spin label that binds to myosin heads in muscle fibers with its principal axis parallel to the fiber axis. Biophys J. 1994 Oct;67(4):1634–1645. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80636-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellers J. R., Chantler P. D., Szent-Györgyi A. G. Hybrid formation between scallop myofibrils and foreign regulatory light-chains. J Mol Biol. 1980 Dec 15;144(3):223–245. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90088-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobieszek A., Bremel R. D. Preparation and properties of vertebrate smooth-muscle myofibrils and actomyosin. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun 16;55(1):49–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R. A., Ludescher R. D., Dahlberg P. S., Fajer P. G., Bennett R. L., Thomas D. D. Time-resolved rotational dynamics of phosphorescent-labeled myosin heads in contracting muscle fibers. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 30;29(43):10023–10031. doi: 10.1021/bi00495a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson E. C., Thomas D. D. ATP induces microsecond rotational motions of myosin heads crosslinked to actin. Biophys J. 1986 Nov;50(5):999–1002. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83541-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Cooke R. Orientation of spin-labeled myosin heads in glycerinated muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1980 Dec;32(3):891–906. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85024-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Ishiwata S., Seidel J. C., Gergely J. Submillisecond rotational dynamics of spin-labeled myosin heads in myofibrils. Biophys J. 1980 Dec;32(3):873–889. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85023-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D. Spectroscopic probes of muscle cross-bridge rotation. Annu Rev Physiol. 1987;49:691–709. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.49.030187.003355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie X., Harrison D. H., Schlichting I., Sweet R. M., Kalabokis V. N., Szent-Györgyi A. G., Cohen C. Structure of the regulatory domain of scallop myosin at 2.8 A resolution. Nature. 1994 Mar 24;368(6469):306–312. doi: 10.1038/368306a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]