Abstract
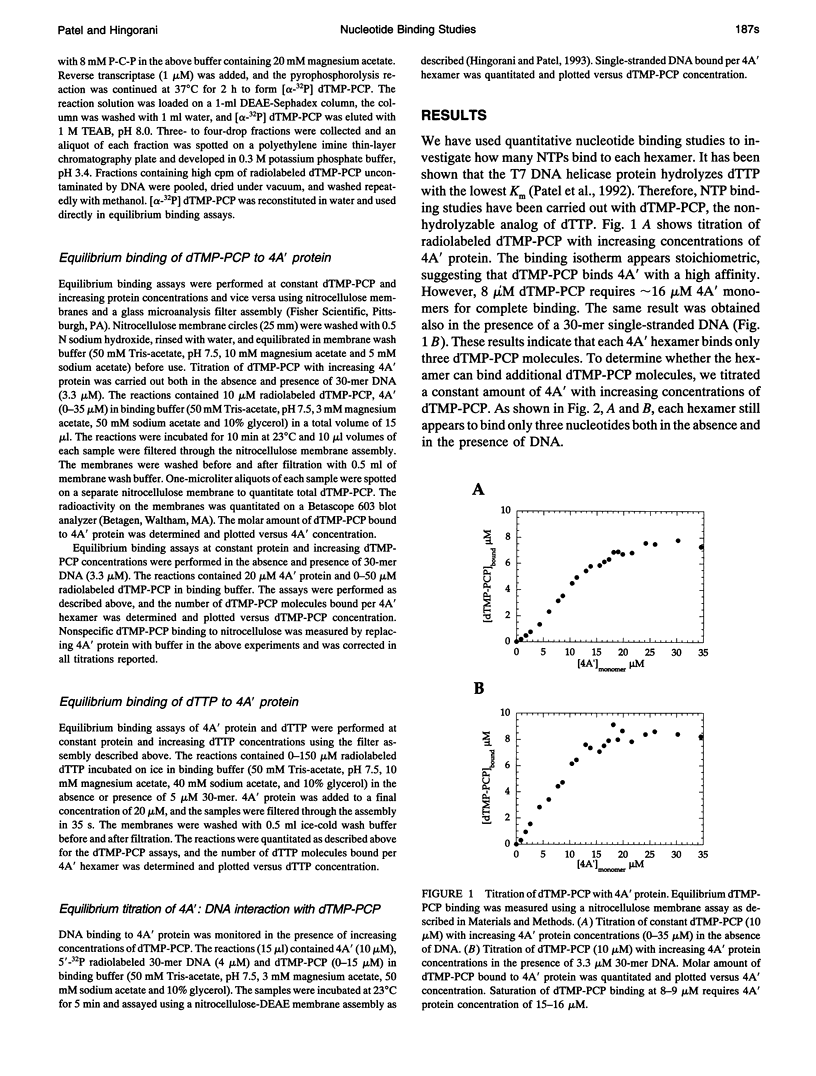
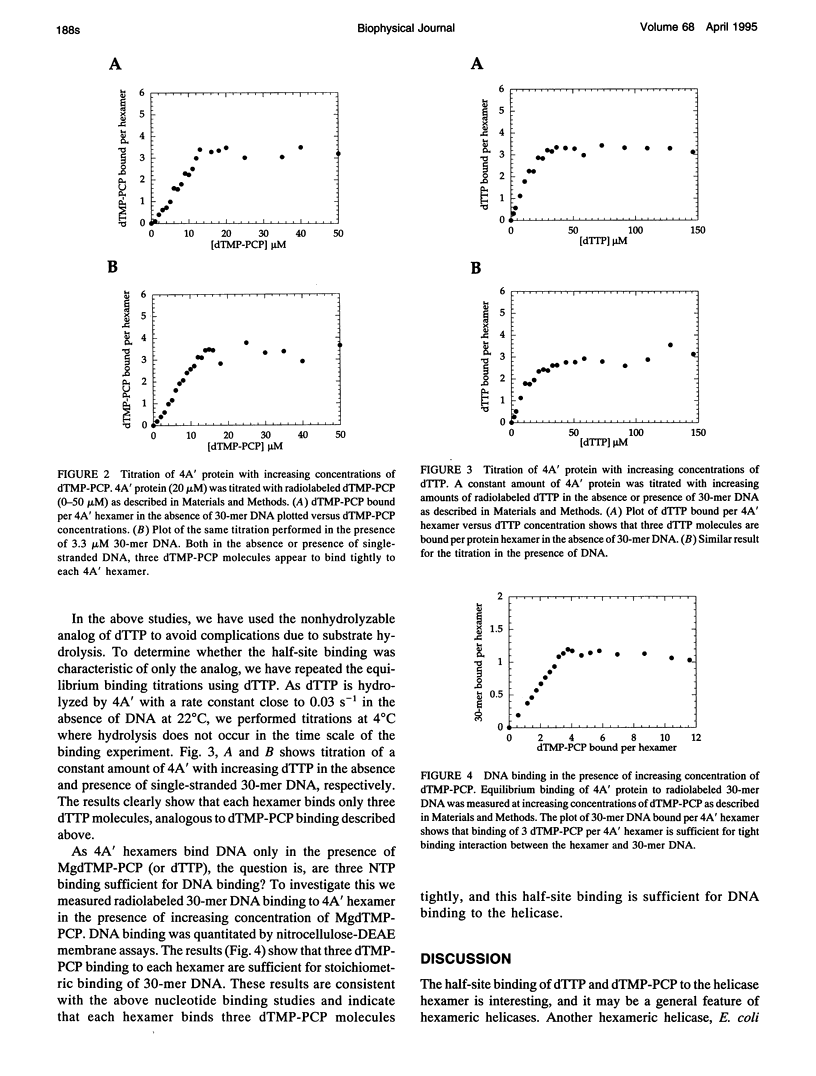
Bacteriophage T7 DNA helicase protein is a hexameric protein that contains identical subunits arranged in a ring-like structure. Single-stranded DNA binds through the hole of the ring, and the helicase protein translocates and unwinds duplex DNA using nucleoside triphosphate (NTP) hydrolysis. In our efforts to understand how NTP hydrolysis may be coupled to movement of the helicase on the DNA, we have quantitated the equilibrium binding of deoxythymidine triphosphate and thymidine 5'-(beta,gamma-methylenetriphosphate) using nitrocellulose binding assays. Even though the helicase consists of six identical subunits, each hexamer was found to bind only three NTP molecules. These results indicate half-site binding or negative cooperativity in NTP binding by the hexamer. Interestingly, binding of three NTP molecules to the hexamer was sufficient for stoichiometric binding of a single-stranded oligodeoxynucleotide. Similar negative cooperativity in NTP binding has also been observed for other helicases, suggesting that it may be a general feature of hexameric helicases. The significance of half-site binding, however, is not understood at the present time.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bujalowski W., Klonowska M. M. Negative cooperativity in the binding of nucleotides to Escherichia coli replicative helicase DnaB protein. Interactions with fluorescent nucleotide analogs. Biochemistry. 1993 Jun 8;32(22):5888–5900. doi: 10.1021/bi00073a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Complete nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage T7 DNA and the locations of T7 genetic elements. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):477–535. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80282-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hingorani M. M., Patel S. S. Interactions of bacteriophage T7 DNA primase/helicase protein with single-stranded and double-stranded DNAs. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 23;32(46):12478–12487. doi: 10.1021/bi00097a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohman T. M. Escherichia coli DNA helicases: mechanisms of DNA unwinding. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jan;6(1):5–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb00831.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohman T. M. Helicase-catalyzed DNA unwinding. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2269–2272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel S. S., Hingorani M. M., Ng W. M. The K318A mutant of bacteriophage T7 DNA primase-helicase protein is deficient in helicase but not primase activity and inhibits primase-helicase protein wild-type activities by heterooligomer formation. Biochemistry. 1994 Jun 28;33(25):7857–7868. doi: 10.1021/bi00191a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel S. S., Hingorani M. M. Oligomeric structure of bacteriophage T7 DNA primase/helicase proteins. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 15;268(14):10668–10675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel S. S., Rosenberg A. H., Studier F. W., Johnson K. A. Large scale purification and biochemical characterization of T7 primase/helicase proteins. Evidence for homodimer and heterodimer formation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):15013–15021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. H., Patel S. S., Johnson K. A., Studier F. W. Cloning and expression of gene 4 of bacteriophage T7 and creation and analysis of T7 mutants lacking the 4A primase/helicase or the 4B helicase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):15005–15012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. Template recognition sequence for RNA primer synthesis by gene 4 protein of bacteriophage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):205–209. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


