Abstract
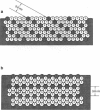
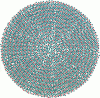
Collagen fibrils resemble smectic, liquid crystals in being highly ordered axially but relatively disordered laterally. In some connective tissues, x-ray diffraction reveals three-dimensional crystallinity in the molecular packing within fibrils, although the continued presence of diffuse scatter indicates significant underlying disorder. In addition, several observations from electron microscopy suggest that the molecular packing is organized concentrically about the fibril core. In the present work, theoretical equatorial x-ray diffraction patterns for a number of models for collagen molecular packing are calculated and compared with the experimental data from tendon fibrils. None of the models suggested previously can account for both the crystalline Bragg peaks and the underlying diffuse scatter. In addition, models in which any of the nearest-neighbor, intermolecular vectors are perpendicular to the radial direction are inconsistent with the observed radial orientation of the principal approximately 4 nm Bragg spacing. Both multiple-start spiral and concentric ring models are devised in which one of the nearest-neighbor vectors is along the radial direction. These models are consistent with the radial orientation of the approximately 4 nm spacing, and energy minimization results in radially oriented crystalline domains separated by disordered grain boundaries. Theoretical x-ray diffraction patterns show a combination of sharp Bragg peaks and underlying diffuse scatter. Close agreement with the observed equatorial diffraction pattern is obtained. The concentric ring model is consistent with the observation that the diameters of collagen fibrils are restricted to discrete values.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brodsky B., Eikenberry E. F. Characterization of fibrous forms of collagen. Methods Enzymol. 1982;82(Pt A):127–174. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)82062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman J. A. The regulation of size and form in the assembly of collagen fibrils in vivo. Biopolymers. 1989 Aug;28(8):1367–1382. doi: 10.1002/bip.360280803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eikenberry E. F., Childs B., Sheren S. B., Parry D. A., Craig A. S., Brodsky B. Crystalline fibril structure of type II collagen in lamprey notochord sheath. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jun 25;176(2):261–277. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90424-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franc S. Ultrastructural evidences of a distinct axial domain within native rat tail tendon collagen fibrils. J Submicrosc Cytol Pathol. 1993 Jan;25(1):85–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser R. D., MacRae T. P., Miller A. Molecular packing in type I collagen fibrils. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jan 5;193(1):115–125. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90631-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser R. D., MacRae T. P., Miller A., Suzuki E. Molecular conformation and packing in collagen fibrils. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 25;167(2):497–521. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80347-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fratzl P., Fratzl-Zelman N., Klaushofer K. Collagen packing and mineralization. An x-ray scattering investigation of turkey leg tendon. Biophys J. 1993 Jan;64(1):260–266. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81362-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynpas M. Three-dimensional packing of collagen in bone. Nature. 1977 Jan 27;265(5592):381–382. doi: 10.1038/265381a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. F., Chapman J. A., Prockop D. J., Kadler K. E. Growing tips of type I collagen fibrils formed in vitro are near-paraboloidal in shape, implying a reciprocal relationship between accretion and diameter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9855–9859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulmes D. J. A possible mechanism for the regulation of collagen fibril diameter in vivo. Coll Relat Res. 1983 Jul;3(4):317–321. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(83)80013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulmes D. J., Holmes D. F., Cummings C. Crystalline regions in collagen fibrils. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 5;184(3):473–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90295-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulmes D. J., Jesior J. C., Miller A., Berthet-Colominas C., Wolff C. Electron microscopy shows periodic structure in collagen fibril cross sections. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3567–3571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulmes D. J., Miller A. Quasi-hexagonal molecular packing in collagen fibrils. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):878–880. doi: 10.1038/282878a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulmes D. J. The collagen superfamily--diverse structures and assemblies. Essays Biochem. 1992;27:49–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinski L. W., Sullivan C. E., Torchia D. A. 2H NMR study of molecular motion in collagen fibrils. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):531–534. doi: 10.1038/284531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. Y., Miller A. Analysis of structural design features in collagen. J Mol Biol. 1991 Mar 5;218(1):209–219. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90885-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jésior J. C., Miller A., Berthet-Colominas C. Crystalline three-dimensional packing is a general characteristic of type I collagen fibrils. FEBS Lett. 1980 May 5;113(2):238–240. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80600-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft J. H. Ruthenium red and violet. II. Fine structural localization in animal tissues. Anat Rec. 1971 Nov;171(3):369–415. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091710303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayne R., Brewton R. G. New members of the collagen superfamily. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;5(5):883–890. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90039-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao K., Bashey R. I. Fine structure of collagen fibrils as revealed by ruthenium red. Exp Mol Pathol. 1972 Aug;17(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(72)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piez K. A., Trus B. L. A new model for packing of type-I collagen molecules in the native fibril. Biosci Rep. 1981 Oct;1(10):801–810. doi: 10.1007/BF01114803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAMACHANDRAN G. N., SASISEKHARAN V. Cylindrical lattice structure of collagen. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1956 Jul;63(1):255–257. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(56)90029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raspanti M., Ottani V., Ruggeri A. Different architectures of the collagen fibril: morphological aspects and functional implications. Int J Biol Macromol. 1989 Dec;11(6):367–371. doi: 10.1016/0141-8130(89)90009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri A., Benazzo F., Reale E. Collagen fibrils with straight and helicoidal microfibrils: a freeze-fracture and thin-section study. J Ultrastruct Res. 1979 Jul;68(1):101–108. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(79)90146-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver D., Miller J., Harrison R., Prockop D. J. Helical model of nucleation and propagation to account for the growth of type I collagen fibrils from symmetrical pointed tips: a special example of self-assembly of rod-like monomers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9860–9864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Rest M., Garrone R. Collagen family of proteins. FASEB J. 1991 Oct;5(13):2814–2823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]