Abstract
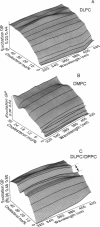
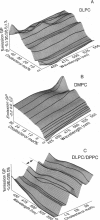
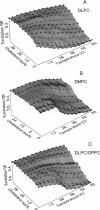
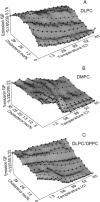
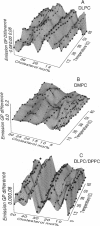
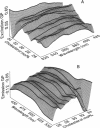
The fluorescence generalized polarization (GP) of 2-dimethylamino-6-lauroylnaphthalene (Laurdan) reveals different effects of cholesterol on the phase behavior of phospholipid bilayers. Phospholipid vesicles composed of gel, liquid-crystalline, and coexisting domains of the two phases have been studied at temperatures from 1 to 65 degrees C, without cholesterol and with cholesterol concentrations of 3-50 mol %. Laurdan GP measurements show the general effect of cholesterol of increasing the molecular dynamics of the gel and of decreasing the molecular dynamics of the liquid-crystalline phase. In the liquid-crystalline phase, the increased order yields Laurdan GP values close to those obtained in the gel phase. At cholesterol concentrations > 15 mol % a phase transition cannot be detected. Using the wavelength dependence of the excitation and emission GP spectra we determine that differences between the two phospholipid phases cannot be detected. In particular, in vesicles composed of coexisting gel and liquid-crystalline phases the GP wavelength dependence characteristic of coexisting domains cannot be observed at cholesterol concentrations > or = 15 mol %. Cholesterol causes the decrease in both the polarity and the dipolar relaxation effects on the neighborhood of the fluorescent naphthalene moiety of Laurdan. Probably because of a cholesterol-induced increase in the bilayer packing, these effects do not occur continuously with the increase of cholesterol concentration in the bilayer. Cholesterol concentrations inducing higher Laurdan GP values have been determined at about 5, 10, 15, 30, and 45 mol % with respect to phospholipids. We propose that the formation of ordered molecular microdomains at critical cholesterol concentrations can explain the occurrence of the observed discontinuities.
Full text
PDF


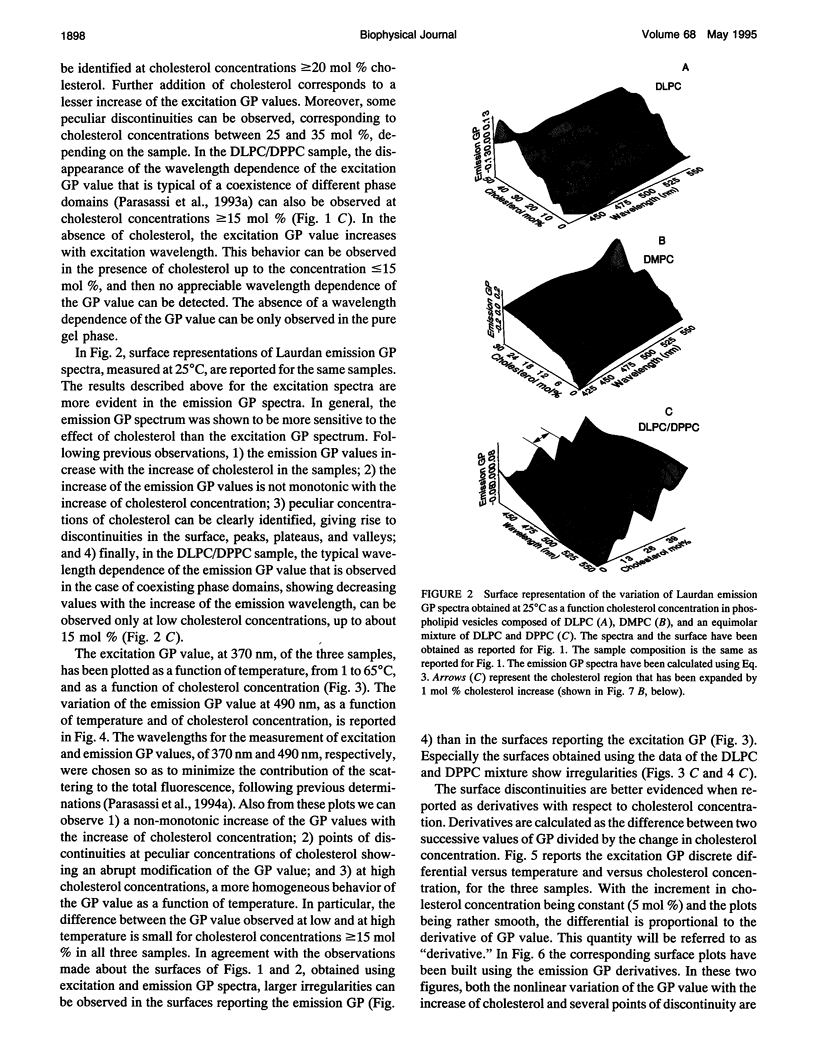
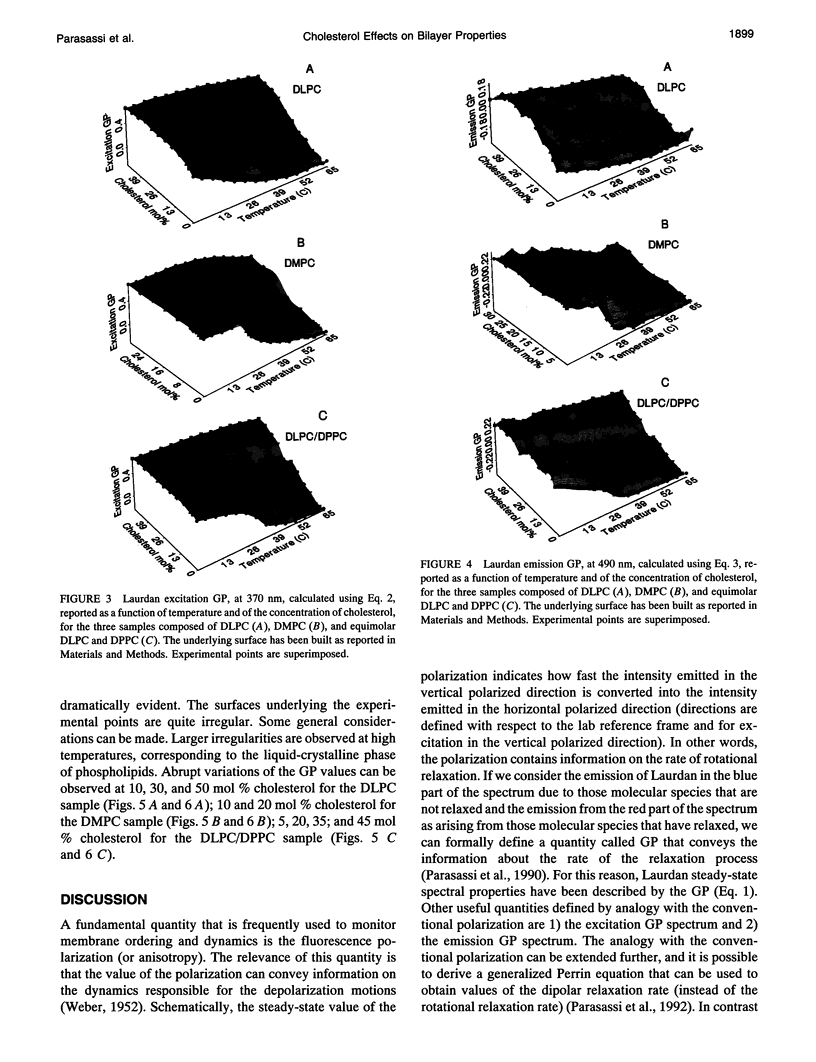


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almeida P. F., Vaz W. L., Thompson T. E. Percolation and diffusion in three-component lipid bilayers: effect of cholesterol on an equimolar mixture of two phosphatidylcholines. Biophys J. 1993 Feb;64(2):399–412. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81381-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong P. L. Effects of hydrostatic pressure on the location of PRODAN in lipid bilayers and cellular membranes. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 12;27(1):399–404. doi: 10.1021/bi00401a060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ipsen J. H., Karlström G., Mouritsen O. G., Wennerström H., Zuckermann M. J. Phase equilibria in the phosphatidylcholine-cholesterol system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Nov 27;905(1):162–172. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ipsen J. H., Mouritsen O. G., Zuckermann M. J. Theory of thermal anomalies in the specific heat of lipid bilayers containing cholesterol. Biophys J. 1989 Oct;56(4):661–667. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82713-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabrey S., Mateo P. L., Sturtevant J. M. High-sensitivity scanning calorimetric study of mixtures of cholesterol with dimyristoyl- and dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholines. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 13;17(12):2464–2468. doi: 10.1021/bi00605a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchior D. L., Scavitto F. J., Steim J. M. Dilatometry of dipalmitoyllecithin-cholesterol bilayers. Biochemistry. 1980 Oct 14;19(21):4828–4834. doi: 10.1021/bi00562a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouritsen O. G. Theoretical models of phospholipid phase transitions. Chem Phys Lipids. 1991 Mar;57(2-3):179–194. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(91)90075-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parasassi T., De Stasio G., Ravagnan G., Rusch R. M., Gratton E. Quantitation of lipid phases in phospholipid vesicles by the generalized polarization of Laurdan fluorescence. Biophys J. 1991 Jul;60(1):179–189. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82041-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parasassi T., De Stasio G., d'Ubaldo A., Gratton E. Phase fluctuation in phospholipid membranes revealed by Laurdan fluorescence. Biophys J. 1990 Jun;57(6):1179–1186. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82637-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parasassi T., Di Stefano M., Loiero M., Ravagnan G., Gratton E. Cholesterol modifies water concentration and dynamics in phospholipid bilayers: a fluorescence study using Laurdan probe. Biophys J. 1994 Mar;66(3 Pt 1):763–768. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(94)80852-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parasassi T., Di Stefano M., Loiero M., Ravagnan G., Gratton E. Influence of cholesterol on phospholipid bilayers phase domains as detected by Laurdan fluorescence. Biophys J. 1994 Jan;66(1):120–132. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80763-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parasassi T., Giusti A. M., Gratton E., Monaco E., Raimondi M., Ravagnan G., Sapora O. Evidence for an increase in water concentration in bilayers after oxidative damage of phospholipids induced by ionizing radiation. Int J Radiat Biol. 1994 Mar;65(3):329–334. doi: 10.1080/09553009414550391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parasassi T., Loiero M., Raimondi M., Ravagnan G., Gratton E. Absence of lipid gel-phase domains in seven mammalian cell lines and in four primary cell types. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Dec 12;1153(2):143–154. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(93)90399-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parasassi T., Ravagnan G., Rusch R. M., Gratton E. Modulation and dynamics of phase properties in phospholipid mixtures detected by Laurdan fluorescence. Photochem Photobiol. 1993 Mar;57(3):403–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1993.tb02309.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sankaram M. B., Thompson T. E. Interaction of cholesterol with various glycerophospholipids and sphingomyelin. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 27;29(47):10670–10675. doi: 10.1021/bi00499a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon S. A., McIntosh T. J., Latorre R. Influence of cholesterol on water penetration into bilayers. Science. 1982 Apr 2;216(4541):65–67. doi: 10.1126/science.7063872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerharju P. J., Virtanen J. A., Eklund K. K., Vainio P., Kinnunen P. K. 1-Palmitoyl-2-pyrenedecanoyl glycerophospholipids as membrane probes: evidence for regular distribution in liquid-crystalline phosphatidylcholine bilayers. Biochemistry. 1985 May 21;24(11):2773–2781. doi: 10.1021/bi00332a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tampé R., von Lukas A., Galla H. J. Glycophorin-induced cholesterol-phospholipid domains in dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine bilayer vesicles. Biochemistry. 1991 May 21;30(20):4909–4916. doi: 10.1021/bi00234a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang D., Chong P. L. E/M dips. Evidence for lipids regularly distributed into hexagonal super-lattices in pyrene-PC/DMPC binary mixtures at specific concentrations. Biophys J. 1992 Oct;63(4):903–910. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81672-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vist M. R., Davis J. H. Phase equilibria of cholesterol/dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine mixtures: 2H nuclear magnetic resonance and differential scanning calorimetry. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 16;29(2):451–464. doi: 10.1021/bi00454a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBER G. Polarization of the fluorescence of macromolecules. I. Theory and experimental method. Biochem J. 1952 May;51(2):145–155. doi: 10.1042/bj0510145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeagle P. L. Cholesterol and the cell membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Dec 9;822(3-4):267–287. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(85)90011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]