Abstract
Natural abundance 13C solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy was used to investigate the effect of the incorporation of cholesterol on the dynamics of dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine (DMPC) bilayers in the liquid-crystalline phase. In particular, the use of a combination of the cross-polarization and magic angle spinning techniques allows one to obtain very high resolution spectra from which can be distinguished several resonances attributed to the polar head group, the glycerol backbone, and the acyl chains of the lipid molecule. To examine both the fast and slow motions of the lipid bilayers, 1H spin-lattice relaxation times as well as proton and carbon spin-lattice relaxation times in the rotating frame were measured for each resolved resonance of DMPC. The use of the newly developed ramped-amplitude cross-polarization technique results in a significant increase in the stability of the cross-polarization conditions, especially for molecular groups undergoing rapid motions. The combination of T1 and T1 rho measurements indicates that the presence of cholesterol significantly decreases the rate and/or amplitude of both the high and low frequency motions in the DMPC bilayers. This effect is particularly important for the lipid acyl chains and the glycerol backbone region.
Full text
PDF
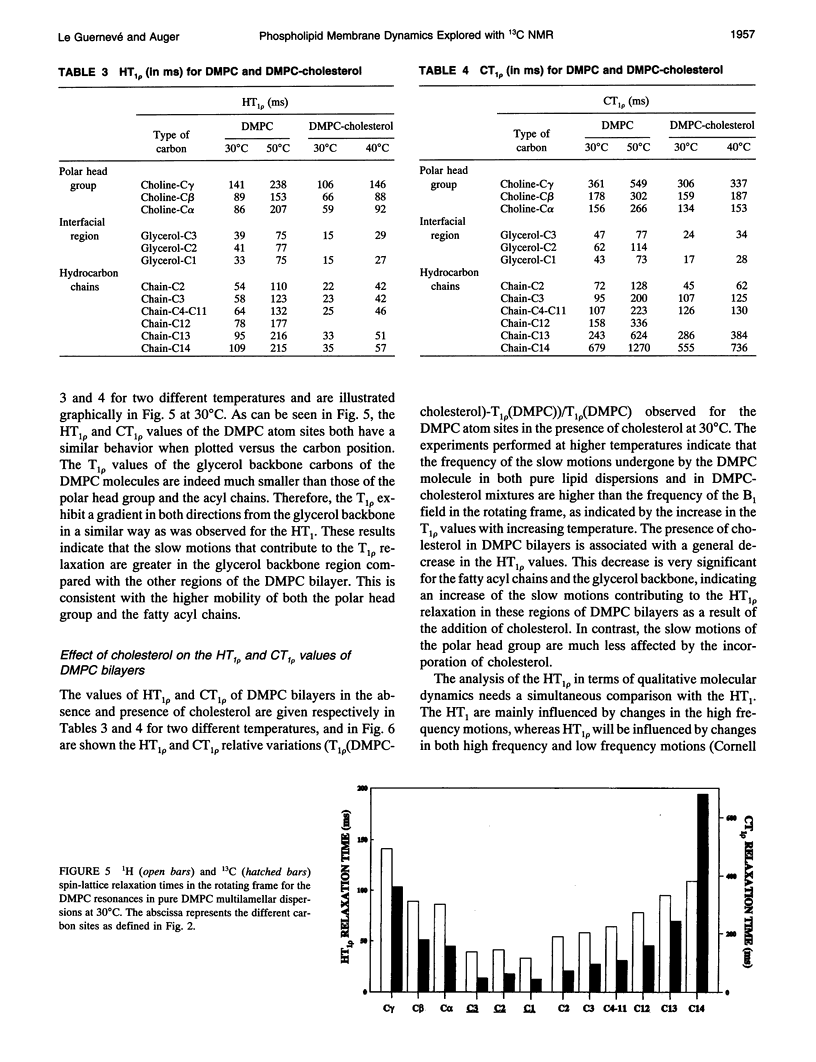
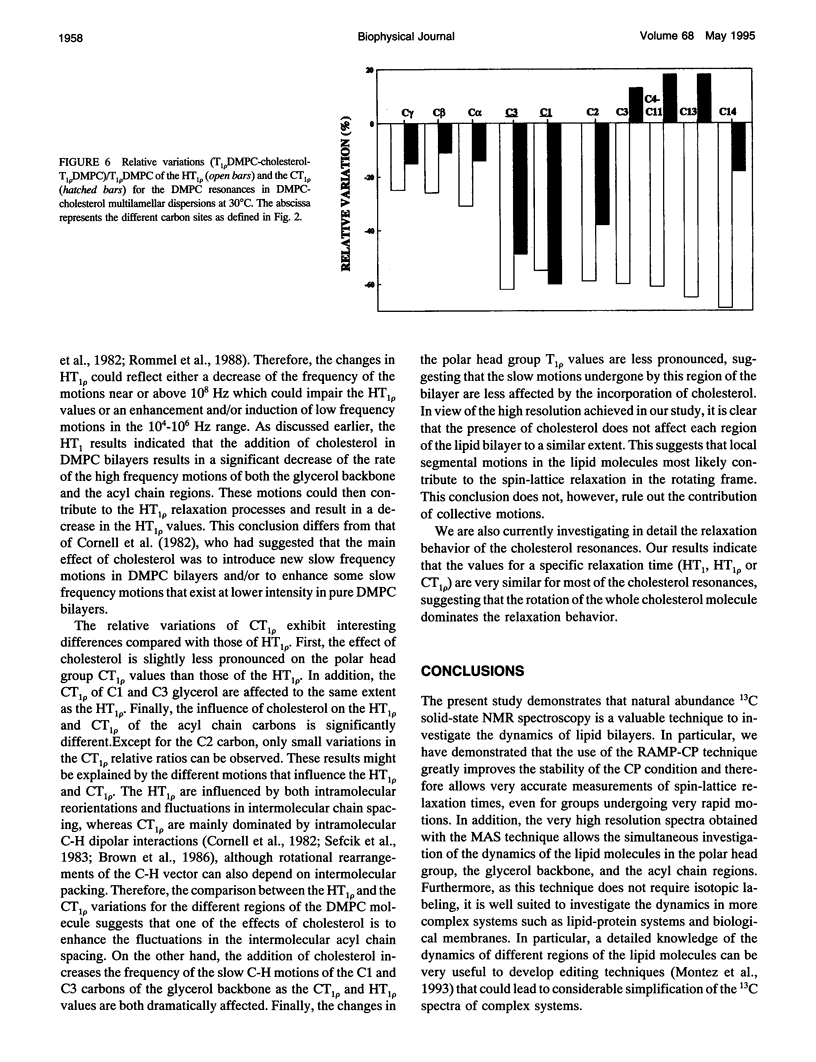

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adebodun F., Chung J., Montez B., Oldfield E., Shan X. Spectroscopic studies of lipids and biological membranes: carbon-13 and proton magic-angle sample-spinning nuclear magnetic resonance study of glycolipid-water systems. Biochemistry. 1992 May 12;31(18):4502–4509. doi: 10.1021/bi00133a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M., Evans E., Mouritsen O. G. Physical properties of the fluid lipid-bilayer component of cell membranes: a perspective. Q Rev Biophys. 1991 Aug;24(3):293–397. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500003735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braach-Maksvytis V. L., Cornell B. A. Chemical shift anisotropies obtained from aligned egg yolk phosphatidylcholine by solid-state 13C nuclear magnetic resonance. Biophys J. 1988 May;53(5):839–843. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83163-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brainard J. R., Cordes E. H. Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance studies of cholesterol-egg yolk phosphatidylcholine vesicles. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 4;20(16):4607–4617. doi: 10.1021/bi00519a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell B. A., Davenport J. B., Separovic F. Low-frequency motion in membranes. The effect of cholesterol and proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jul 28;689(2):337–345. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90267-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell B. A., Hiller R. G., Raison J., Separovic F., Smith R., Vary J. C., Morris C. Biological membranes are rich in low-frequency motion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jul 27;732(2):473–478. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90065-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. H. The description of membrane lipid conformation, order and dynamics by 2H-NMR. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):117–171. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90015-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin R. G. Solid state nuclear magnetic resonance of lipid bilayers. Methods Enzymol. 1981;72:108–174. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)72010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancée-Hermkens A. W., de Kruijff B. 13 C NMR measurements of unsonicated phosphatidylcholine bilayers of different fatty acid and sterol composition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Oct 17;470(2):141–151. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90095-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. G., Birdsall N. J., Metcalfe J. C., Warren G. B., Roberts G. C. A determination of the mobility gradient in lipid bilayers by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1976 May 18;193(1112):253–274. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1976.0045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montez B., Oldfield E., Urbina J. A., Pekerar S., Husted C., Patterson J. Editing 13C-NMR spectra of membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Nov 7;1152(2):314–318. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(93)90263-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldfield E., Adebodun F., Chung J., Montez B., Park K. D., Le H. B., Phillips B. Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of lipids: differential line broadening due to cross-correlation effects as a probe of membrane structure. Biochemistry. 1991 Nov 19;30(46):11025–11028. doi: 10.1021/bi00110a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldfield E., Meadows M., Rice D., Jacobs R. Spectroscopic studies of specifically deuterium labeled membrane systems. Nuclear magnetic resonance investigation of the effects of cholesterol in model systems. Biochemistry. 1978 Jul 11;17(14):2727–2740. doi: 10.1021/bi00607a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng Z. Y., Simplaceanu V., Dowd S. R., Ho C. Effects of cholesterol or gramicidin on slow and fast motions of phospholipids in oriented bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8758–8762. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen N. O., Chan S. I. More on the motional state of lipid bilayer membranes: interpretation of order parameters obtained from nuclear magnetic resonance experiments. Biochemistry. 1977 Jun 14;16(12):2657–2667. doi: 10.1021/bi00631a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefcik M. D., Schaefer J., Stejskal E. O., McKay R. A., Ellena J. F., Dodd S. W., Brown M. F. Lipid bilayer dynamics and rhodopsin-lipid interactions: new approach using high-resolution solid-state 13C NMR. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Aug 12;114(3):1048–1055. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90668-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siminovitch D. J., Ruocco M. J., Olejniczak E. T., Das Gupta S. K., Griffin R. G. Anisotropic 2H-nuclear magnetic resonance spin-lattice relaxation in cerebroside- and phospholipid-cholesterol bilayer membranes. Biophys J. 1988 Sep;54(3):373–381. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)82970-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Kruijff B. 13C NMR studies on [4-13C] cholesterol incorporated in sonicated phosphatidylcholine vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jan 19;506(2):173–182. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90388-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


