Abstract
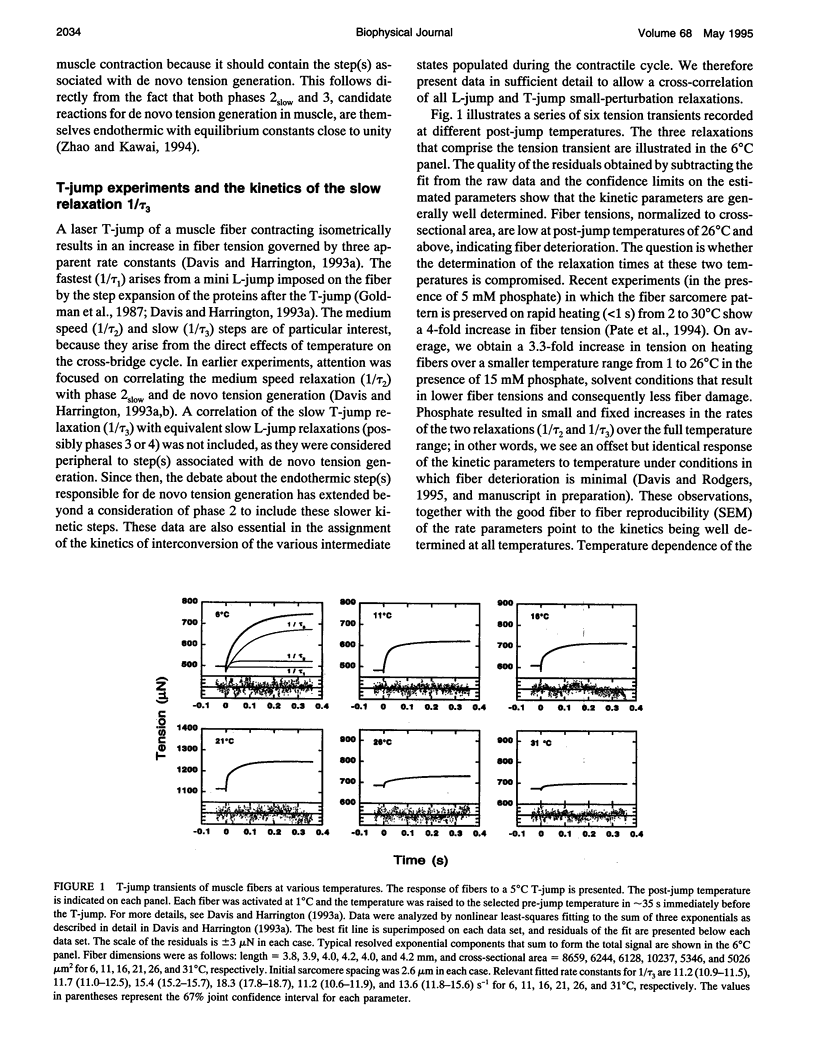
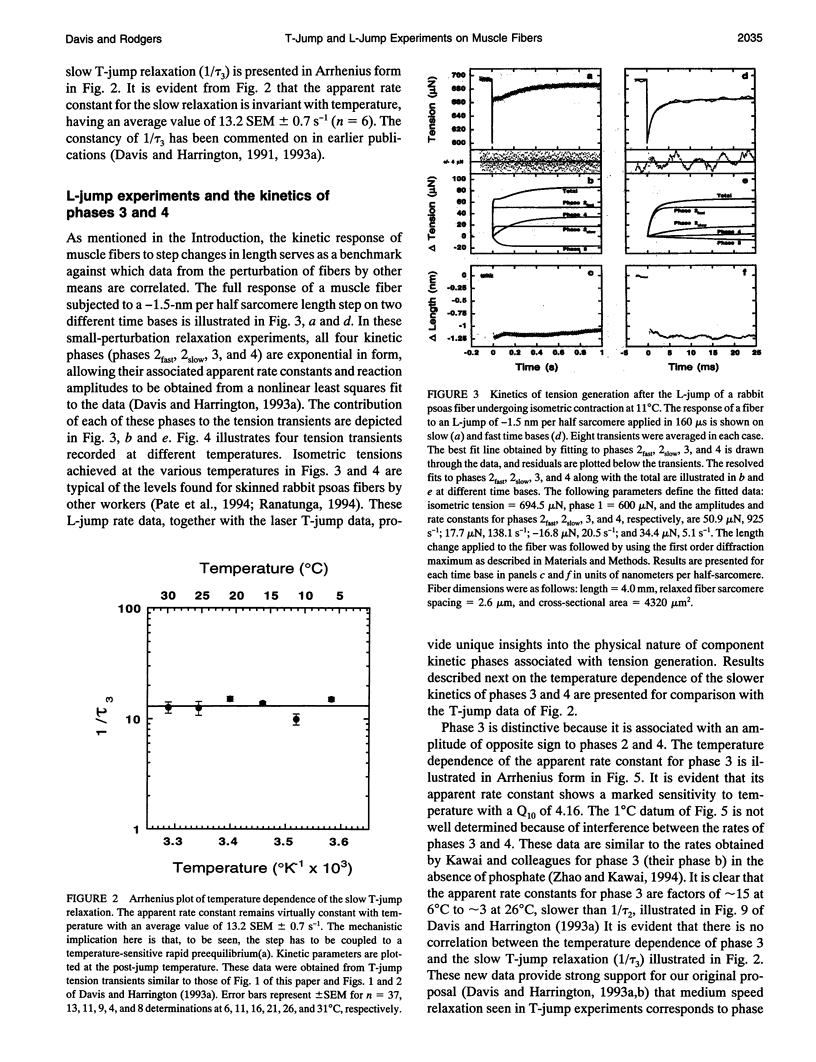
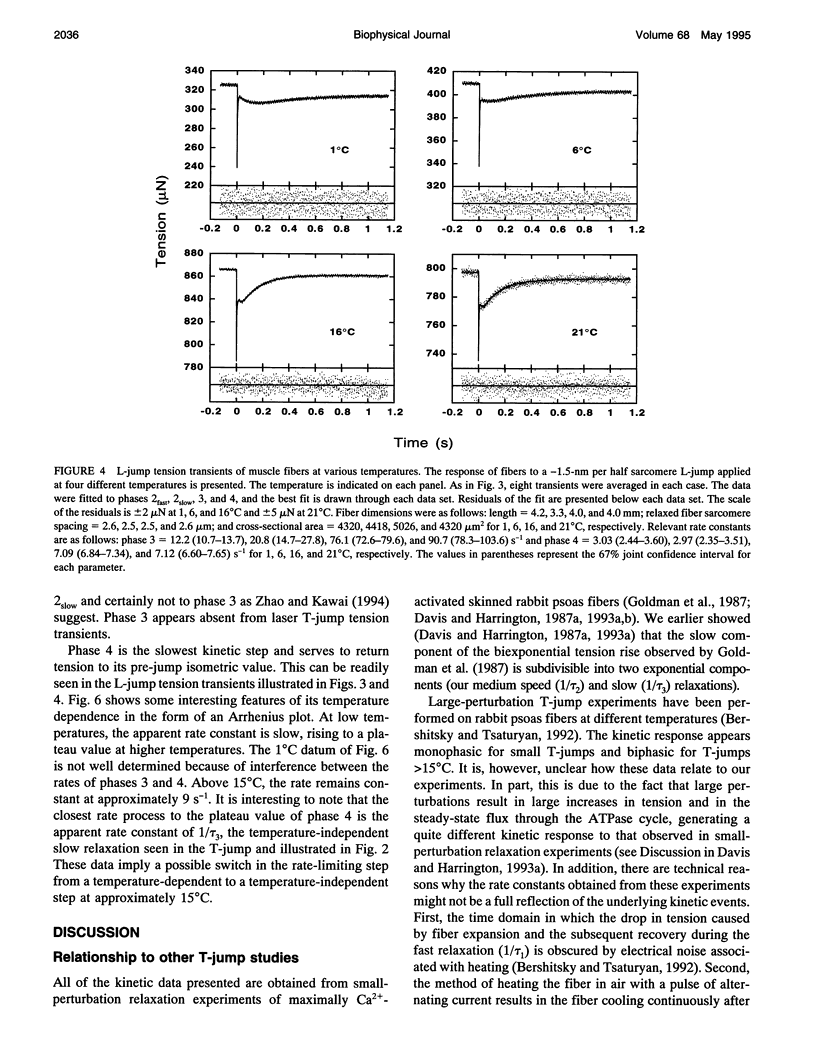
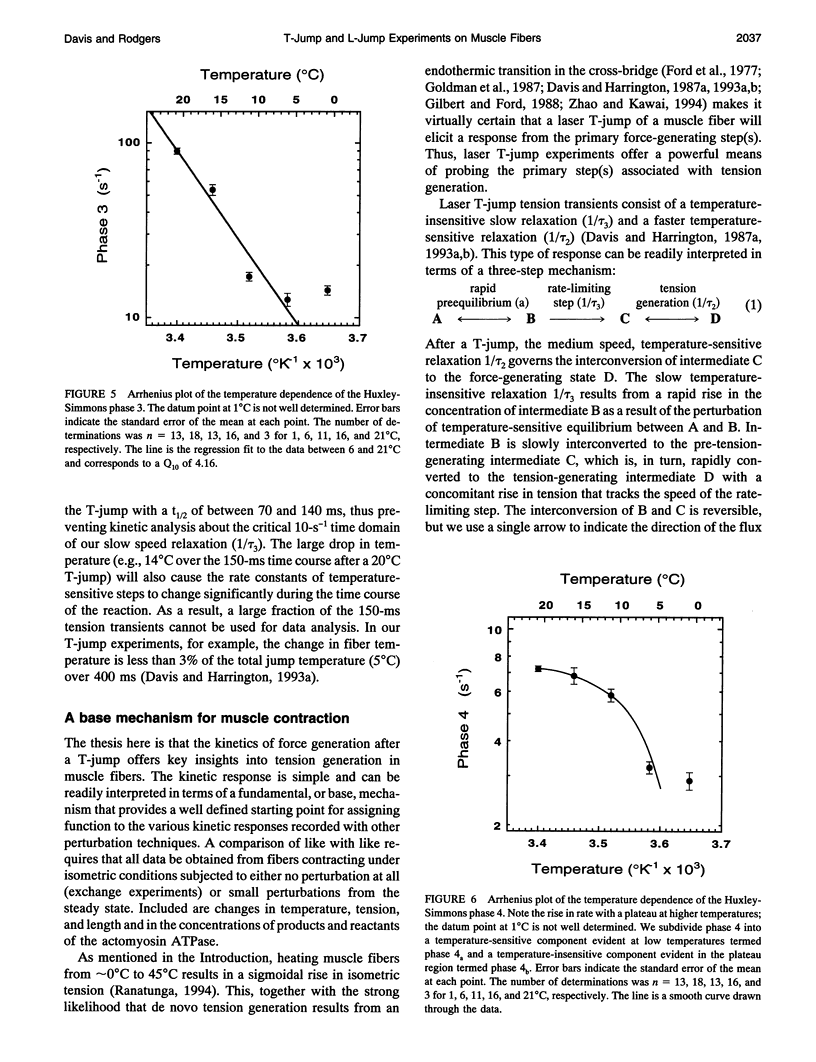
Muscle tension rises with increasing temperature. The kinetics that govern the tension rise of maximally Ca(2+)-activated, skinned rabbit psoas fibers over a temperature range of 0-30 degrees C was characterized in laser temperature-jump experiments. The kinetic response is simple and can be readily interpreted in terms of a basic three-step mechanism of contraction, which includes a temperature-sensitive rapid preequilibrium(a) linked to a temperature-insensitive rate-limiting step and followed by a temperature-sensitive tension-generating step. These data and mechanism are compared and contrasted with the more complex length-jump Huxley-Simmons phases in which all states that generate tension or bear tension are perturbed. The rate of the Huxley-Simmons phase 4 is temperature sensitive at low temperatures but plateaus at high temperatures, indicating a change in rate-limiting step from a temperature-sensitive (phase 4a) to a temperature-insensitive reaction (phase 4b); the latter appears to correlate with the slow, temperature-insensitive temperature-jump relaxation. Phase 3 is absent in the temperature-jump, which excludes it from tension generation. We confirm that de novo tension generation occurs as an order-disorder transition during phase 2slow and the equivalent, temperature-sensitive temperature-jump relaxation.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bershitsky S. Y., Tsaturyan A. K. Tension responses to joule temperature jump in skinned rabbit muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1992 Feb;447:425–448. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B., Eisenberg E. Rate of force generation in muscle: correlation with actomyosin ATPase activity in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3542–3546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. Technique for stabilizing the striation pattern in maximally calcium-activated skinned rabbit psoas fibers. Biophys J. 1983 Jan;41(1):99–102. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84411-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase P. B., Kushmerick M. J. Effects of pH on contraction of rabbit fast and slow skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1988 Jun;53(6):935–946. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83174-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. S., Harrington W. F. A single order-disorder transition generates tension during the Huxley-Simmons phase 2 in muscle. Biophys J. 1993 Nov;65(5):1886–1898. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81259-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. S., Harrington W. F. Force generation by muscle fibers in rigor: a laser temperature-jump study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):975–979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. S., Harrington W. F. Kinetic and physical characterization of force generation in muscle: a laser temperature-jump and length-jump study on activated and contracting rigor fibers. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1993;332:513–526. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-2872-2_47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. S., Harrington W. F. Laser temperature-jump apparatus for the study of force changes in fibers. Anal Biochem. 1987 Mar;161(2):543–549. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90487-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenczi M. A. Phosphate burst in permeable muscle fibers of the rabbit. Biophys J. 1986 Sep;50(3):471–477. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83484-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenczi M. A., Simmons R. M., Sleep J. A. General considerations of cross-bridge models in relation to the dependence on MgATP concentration of mechanical parameters of skinned fibers from frog muscles. Soc Gen Physiol Ser. 1982;37:91–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford L. E., Huxley A. F., Simmons R. M. Proceedings: Mechanism of early tension recovery after a quick release in tetanized muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1974 Jul;240(2):42P–43P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford L. E., Huxley A. F., Simmons R. M. Tension responses to sudden length change in stimulated frog muscle fibres near slack length. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;269(2):441–515. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford L. E., Huxley A. F., Simmons R. M. Tension transients during steady shortening of frog muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1985 Apr;361:131–150. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert S. H., Ford L. E. Heat changes during transient tension responses to small releases in active frog muscle. Biophys J. 1988 Oct;54(4):611–617. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)82996-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman Y. E., Hibberd M. G., Trentham D. R. Initiation of active contraction by photogeneration of adenosine-5'-triphosphate in rabbit psoas muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:605–624. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman Y. E., McCray J. A., Ranatunga K. W. Transient tension changes initiated by laser temperature jumps in rabbit psoas muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1987 Nov;392:71–95. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman Y. E., Simmons R. M. Control of sarcomere length in skinned muscle fibres of Rana temporaria during mechanical transients. J Physiol. 1984 May;350:497–518. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley A. F., Simmons R. M. Proposed mechanism of force generation in striated muscle. Nature. 1971 Oct 22;233(5321):533–538. doi: 10.1038/233533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai M., Halvorson H. R. Two step mechanism of phosphate release and the mechanism of force generation in chemically skinned fibers of rabbit psoas muscle. Biophys J. 1991 Feb;59(2):329–342. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82227-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai M., Zhao Y. Cross-bridge scheme and force per cross-bridge state in skinned rabbit psoas muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1993 Aug;65(2):638–651. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81109-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Z., Moss R. L., Walker J. W. Tension transients initiated by photogeneration of MgADP in skinned skeletal muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1993 Jun;101(6):867–888. doi: 10.1085/jgp.101.6.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pate E., Wilson G. J., Bhimani M., Cooke R. Temperature dependence of the inhibitory effects of orthovanadate on shortening velocity in fast skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1994 May;66(5):1554–1562. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80947-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranatunga K. W. Thermal stress and Ca-independent contractile activation in mammalian skeletal muscle fibers at high temperatures. Biophys J. 1994 May;66(5):1531–1541. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80944-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranatunga K. W., Wylie S. R. Temperature-dependent transitions in isometric contractions of rat muscle. J Physiol. 1983 Jun;339:87–95. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweeney H. L., Corteselli S. A., Kushmerick M. J. Measurements on permeabilized skeletal muscle fibers during continuous activation. Am J Physiol. 1987 May;252(5 Pt 1):C575–C580. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.252.5.C575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao Y., Kawai M. Kinetic and thermodynamic studies of the cross-bridge cycle in rabbit psoas muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1994 Oct;67(4):1655–1668. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80638-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


