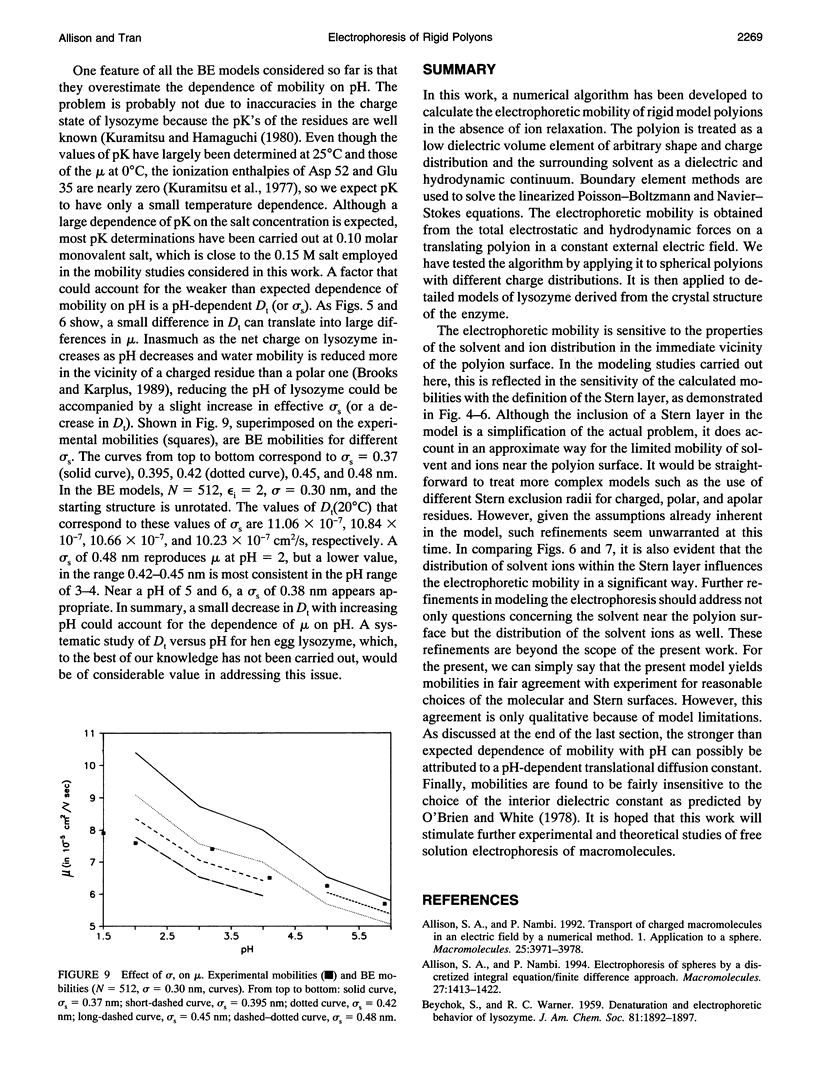
Abstract
An algorithm is developed to determine the electrophoretic mobility of a rigid polyion modeled as a low dielectric volume element of arbitrary shape containing an arbitrary charge distribution. The solvent is modeled as a high dielectric continuum with salt distributed according to the linearized Poisson Boltzmann equation. Account is also taken of a Stern layer that separates the molecular surface and the surface of hydrodynamic shear, or Stern surface. Relaxation of the ion atmosphere because of the presence of the external field is ignored. The electrostatic and hydrodynamic problems are both solved by boundary element methods. The procedure is first applied to spherical polyions containing monopolar, dipolar, and quadrupolar charge distributions, and calculated mobilities are found to be in excellent agreement with the theory of Yoon and Kim. It is then applied to lysozyme by using models that account for the detailed shape and charge distribution of the enzyme. For reasonable choices of the molecular and Stern surfaces, calculated and experimental mobilities are found to be in fair agreement with each other. However, if a pH independent Stern layer (or, equivalently, translational diffusion constant, Dt) is assumed, the calculated mobilities exhibit a stronger pH dependence than is observed experimentally. A small increase in Dt with increasing pH could correct this discrepancy.
Full text
PDF



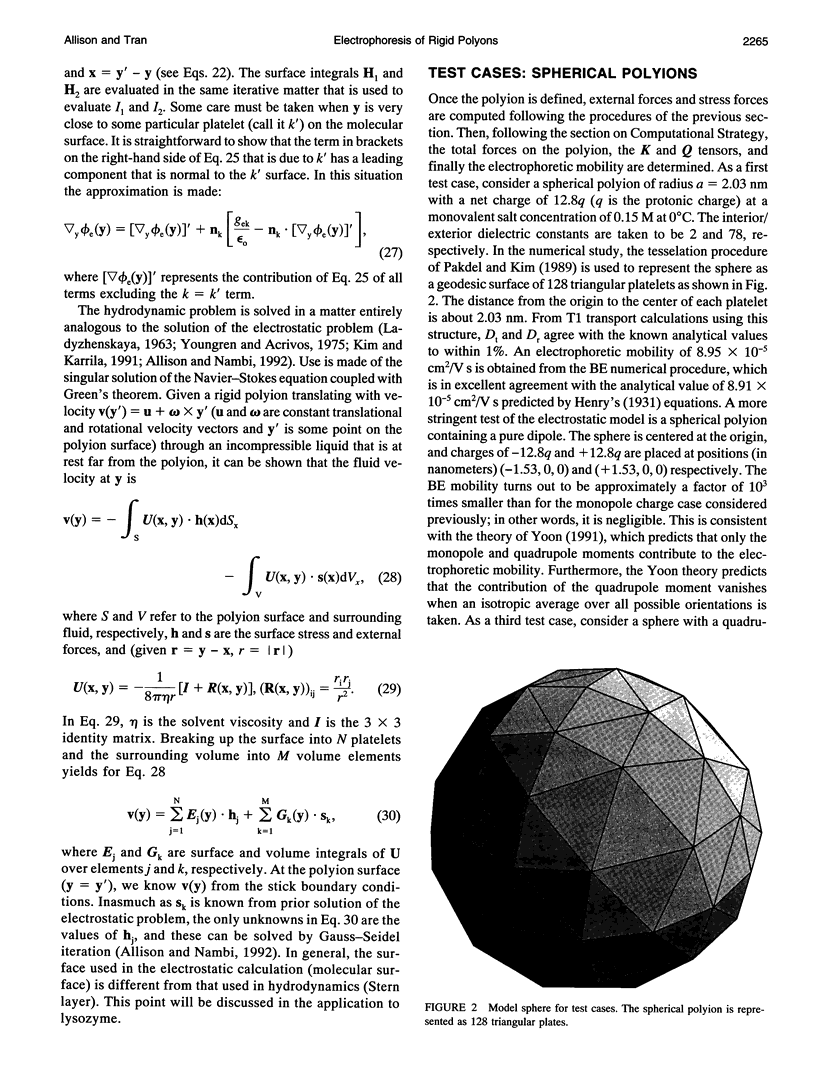

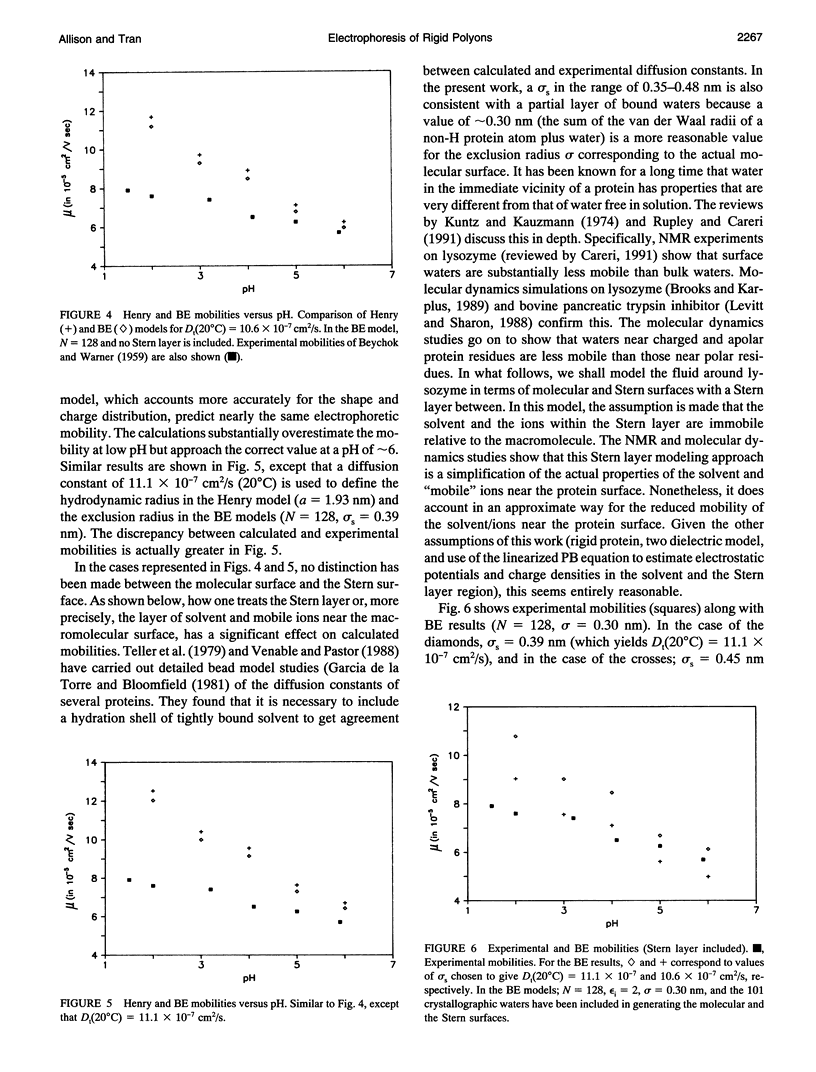
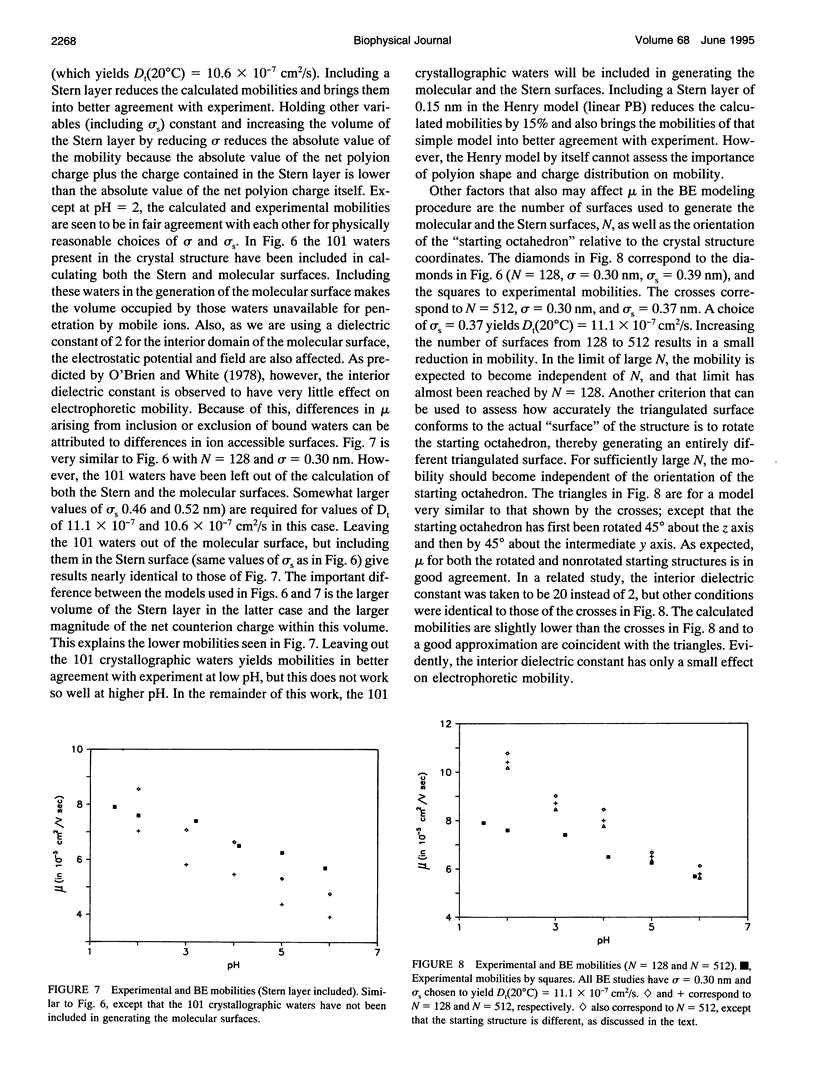

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brooks C. L., 3rd, Karplus M. Solvent effects on protein motion and protein effects on solvent motion. Dynamics of the active site region of lysozyme. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jul 5;208(1):159–181. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90093-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brune D., Kim S. Predicting protein diffusion coefficients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):3835–3839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.3835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubin S. B., Lunacek J. H., Benedek G. B. Observation of the spectrum of light scattered by solutions of biological macromolecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 May;57(5):1164–1171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.5.1164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia de la Torre J. G., Bloomfield V. A. Hydrodynamic properties of complex, rigid, biological macromolecules: theory and applications. Q Rev Biophys. 1981 Feb;14(1):81–139. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. L., Stellwagen N. C. Estimation of polyacrylamide gel pore size from Ferguson plots of normal and anomalously migrating DNA fragments. I. Gels containing 3% N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide. Electrophoresis. 1991 Apr;12(4):253–263. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150120405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuntz I. D., Jr, Kauzmann W. Hydration of proteins and polypeptides. Adv Protein Chem. 1974;28:239–345. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60232-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramitsu S., Hamaguchi K. Analysis of the acid-base titration curve of hen lysozyme. J Biochem. 1980 Apr;87(4):1215–1219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramitsu S., Ikeda K., Hamaguchi K. Effects of ionic strength and temperature on the ionization of the catalytic groups, Asp 52 and Glu 35, in hen lysozyme. J Biochem. 1977 Aug;82(2):585–597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt M., Sharon R. Accurate simulation of protein dynamics in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7557–7561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupley J. A., Careri G. Protein hydration and function. Adv Protein Chem. 1991;41:37–172. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOPHIANOPOULOS A. J., VANHOLDE K. E. PHYSICAL STUDIES OF MURAMIDASE (LYSOZYME). II. PH-DEPENDENT DIMERIZATION. J Biol Chem. 1964 Aug;239:2516–2524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellman J. A. Electrical double layer, zeta potential, and electrophoretic charge of double-stranded DNA. Biopolymers. 1977 Jul;16(7):1415–1434. doi: 10.1002/bip.1977.360160704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squire P. G., Himmel M. E. Hydrodynamics and protein hydration. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Aug;196(1):165–177. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90563-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teller D. C., Swanson E., de Haën C. The translational friction coefficient of proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1979;61:103–124. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)61010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venable R. M., Pastor R. W. Frictional models for stochastic simulations of proteins. Biopolymers. 1988 Jun;27(6):1001–1014. doi: 10.1002/bip.360270609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou H. X. Boundary element solution of macromolecular electrostatics: interaction energy between two proteins. Biophys J. 1993 Aug;65(2):955–963. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81094-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]