Abstract
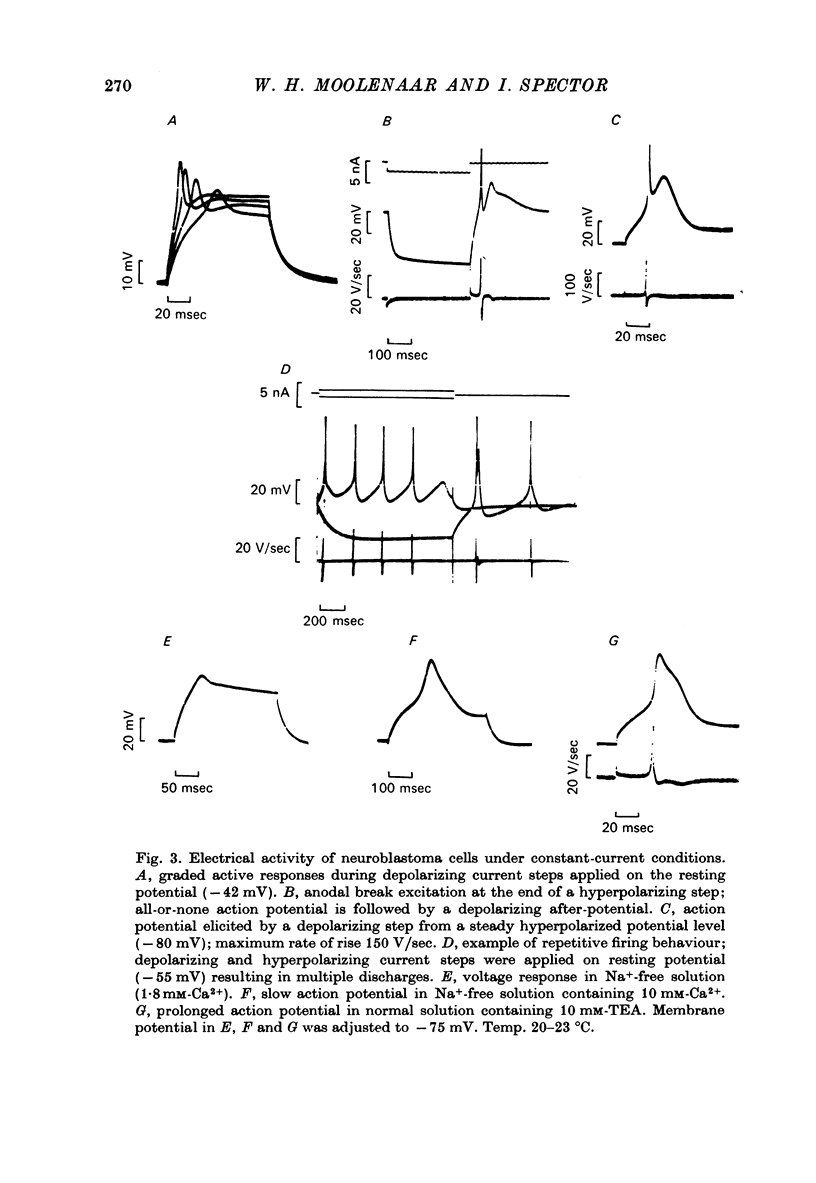
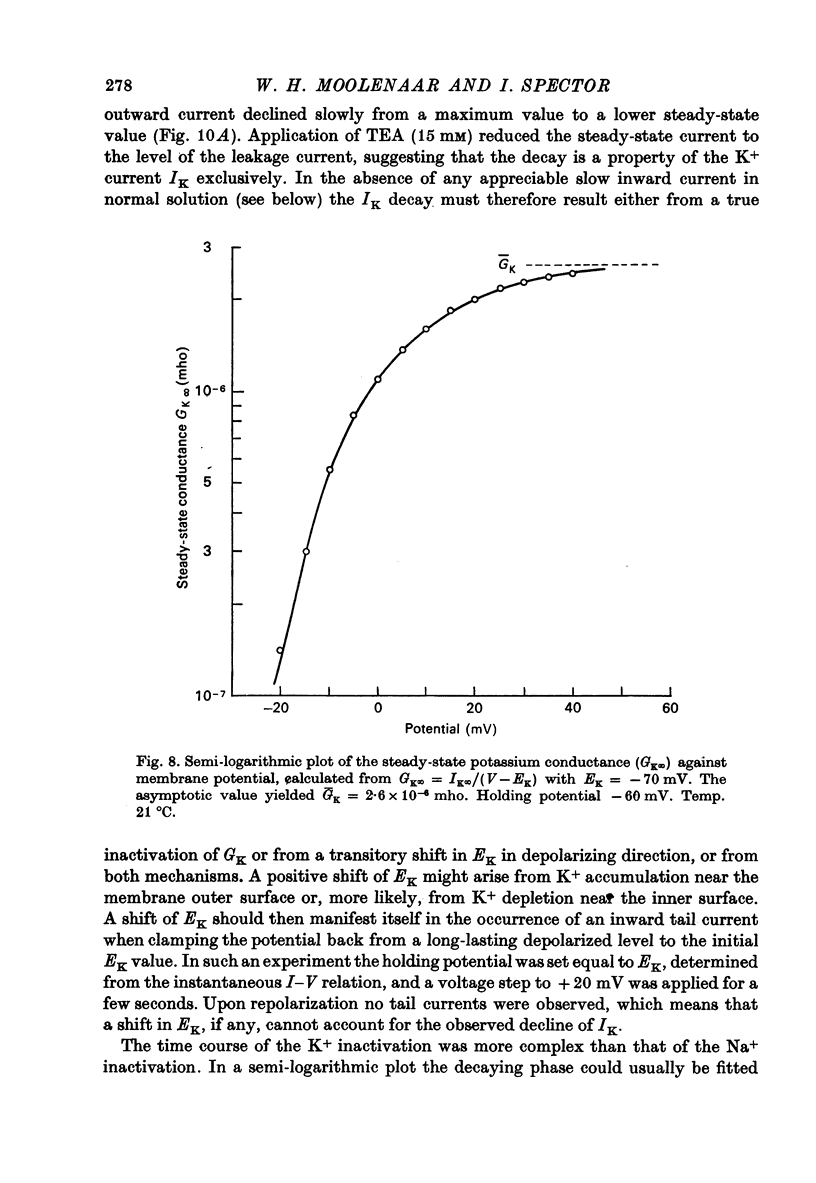
1. Ionic currents in differentiated cells of mouse neuroblastoma clone N1E-115 have been studied under voltage-clamp conditions. 2. Depolarizing voltage steps from a holding potential of -85 mV to levels more positive than -40 mV produced fast transient inward currents followed by delayed outward currents. 3. The fast inward current is carried by Na+: it is blocked by tetrodotoxin and is absent in Na+-free solutions. Its kinetic behaviour resembles that of the Na+ current in squid giant axon. A mean value of 85 mmho/cm2 was found for the maximum Na+ conductance (GNa).4. The delayed outward current is carried primarily by K+: it is blocked by externally applied tetraethylammonium (TEA, 15 mM) and has a reversal potential (mean -71 mV) close to the theoretical K+ equilibrium potential. Its instantaneous I--V curve is linear. By analogy with the formulation of Hodgkin & Huxley (1952c), the outward current can be described by IK = -GKn2(V--EK) where GK = 12 mmho/mc2. 5. During prolonged depolarizations the delayed outward current declines. This decline, which occurs in two phases, represents a partial inactivation of the K+ conductance. 6. A weak inward current with slow activation and inactivation kinetics appears in Na+-free solution containing 10 mM-Ca2+. It is activated at a membrane potential of -55 mV and reaches its maximum at -20 mV with a time to peak of about 10 msec. This current is tetrodotoxin-resistant, reversibly blocked by Co2+ (5mM) and is suggested to be carried by Ca2+. 7. An increase in the external divalent cation concentration results in a parallel shift of the steady-state I--V curve along the voltage axis in positive direction. The activation of delayed outward currents is suggested not to depend on Ca2+ influx. 8. It is concluded that separate voltage-dependent Na+, K+ and Ca2+ channels exist in the differentiated neuroblastoma membrane with kinetic and pharmacological properties similar to those observed in non-mammalian preparations.
Full text
PDF



















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARAKI T., TERZUOLO C. A. Membrane currents in spinal motoneurons associated with the action potential and synaptic activity. J Neurophysiol. 1962 Nov;25:772–789. doi: 10.1152/jn.1962.25.6.772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amano T., Richelson E., Nirenberg M. Neurotransmitter synthesis by neuroblastoma clones (neuroblast differentiation-cell culture-choline acetyltransferase-acetylcholinesterase-tyrosine hydroxylase-axons-dendrites). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):258–263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baccaglini P. I., Spitzer N. C. Developmental changes in the inward current of the action potential of Rohon-Beard neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;271(1):93–117. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Hodgkin A. L., Ridgway E. B. Depolarization and calcium entry in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1971 Nov;218(3):709–755. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett E. F., Barret J. N. Separation of two voltage-sensitive potassium currents, and demonstration of a tetrodotoxin-resistant calcium current in frog motoneurones. J Physiol. 1976 Mar;255(3):737–774. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begenisich T., Lynch C. Effects of internal divalent cations on voltage-clamped squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Jun;63(6):675–689. doi: 10.1085/jgp.63.6.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp studies of a transient outward membrane current in gastropod neural somata. J Physiol. 1971 Feb;213(1):21–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dichter M. A., Fischbach G. D. The action potential of chick dorsal root ganglion neurones maintained in cell culture. J Physiol. 1977 May;267(2):281–298. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Lux H. D. A voltage-sensitive persistent calcium conductance in neuronal somata of Helix. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(1):129–151. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B. A QUANTITATIVE DESCRIPTION OF POTASSIUM CURRENTS IN MYELINATED NERVE FIBRES OF XENOPUS LAEVIS. J Physiol. 1963 Nov;169:424–430. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):218–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANK K., FUORTES M. G., NELSON P. G. Voltage clamp of motoneuron soma. Science. 1959 Jul 3;130(3366):38–39. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3366.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. L., Ehrenstein G. Effect of divalent cations on potassium conductance of squid axons: determination of surface charge. Biophys J. 1969 Mar;9(3):447–463. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86396-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman L., Schauf C. L. Quantitative description of sodium and potassium currents and computed action potentials in Myxicola giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Mar;61(3):361–384. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.3.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGIWARA S., SAITO N. Voltage-current relations in nerve cell membrane of Onchidium verruculatum. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:161–179. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. Currents carried by sodium and potassium ions through the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):449–472. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. The dual effect of membrane potential on sodium conductance in the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):497–506. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Takahashi K. Surface density of calcium ions and calcium spikes in the barnacle muscle fiber membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Jan;50(3):583–601. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.3.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyer C. B., Lux H. D. Control of the delayed outward potassium currents in bursting pace-maker neurones of the snail, Helix pomatia. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(2):349–382. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Charges and potentials at the nerve surface. Divalent ions and pH. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Feb;51(2):221–236. doi: 10.1085/jgp.51.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidokoro Y. Sodium and calcium components of the action potential in a developing skeletal muscle cell line. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(1):145–159. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimhi Y., Palfrey C., Spector I., Barak Y., Littauer U. Z. Maturation of neuroblastoma cells in the presence of dimethylsulfoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):462–466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinhaus A. L., Prichard J. W. Calcium dependent action potentials produced in leech Retzius cells by tetraethylammonium chloride. J Physiol. 1975 Mar;246(2):351–369. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koketsu K., Nishi S. Calcium and action potentials of bullfrog sympathetic ganglion cells. J Gen Physiol. 1969 May;53(5):608–623. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.5.608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Steinberg I. Z., Walton K. Presynaptic calcium currents and their relation to synaptic transmission: voltage clamp study in squid giant synapse and theoretical model for the calcium gate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2918–2922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda Y., Yoshida S., Yonezawa T. A Ca- dependent regenerative response in rodent dorsal root ganglion cells cultured in vitro. Brain Res. 1976 Oct 15;115(2):334–338. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90519-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W., Standen N. B. Potassium activation in Helix aspersa neurones under voltage clamp: a component mediated by calcium influx. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):211–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Spector I. Membrane currents examined under voltage clamp in cultured neuroblastoma cells. Science. 1977 Apr 15;196(4287):331–333. doi: 10.1126/science.557842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NARAHASHI T., MOORE J. W., SCOTT W. R. TETRODOTOXIN BLOCKAGE OF SODIUM CONDUCTANCE INCREASE IN LOBSTER GIANT AXONS. J Gen Physiol. 1964 May;47:965–974. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.5.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narahashi T. Chemicals as tools in the study of excitable membranes. Physiol Rev. 1974 Oct;54(4):813–889. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1974.54.4.813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E. Two fast transient current components during voltage clamp on snail neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Jul;58(1):36–53. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. G. Nerve and muscle cells in culture. Physiol Rev. 1975 Jan;55(1):1–61. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1975.55.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Takahashi K., Yamashita N. Ionic currents through the membrane of the mammalian oocyte and their comparison with those in the tunicate and sea urchin. J Physiol. 1977 May;267(2):465–495. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Takahashi K., Yoshii M. Membrane currents of the tunicate egg under the voltage-clamp condition. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(3):607–638. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad K. N. Differentiation of neuroblastoma cells in culture. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1975 May;50(2):129–165. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1975.tb01055.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. Divalent cations as charge carriers in excitable membranes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1973;26:1–43. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(73)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz J. R., Vogel W. Potassium inactivation in single myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis. Pflugers Arch. 1971;330(1):61–73. doi: 10.1007/BF00588735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwindt P., Crill W. E. A persistent negative resistance in cat lumbar motoneurons. Brain Res. 1977 Jan 14;120(1):173–178. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90510-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector I., Kimhi Y., Nelson P. G. Tetrodotoxin and cobalt blockade of neuroblastoma action potentials. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 28;246(152):124–126. doi: 10.1038/newbio246124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B. Voltage-clamp studies of the calcium inward current in an identified snail neurone: comparison with the sodium inward current. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):253–268. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TASAKI I., HAGIWAR A. S. Demonstration of two stable potential states in the squid giant axon under tetraethylammonium chloride. J Gen Physiol. 1957 Jul 20;40(6):859–885. doi: 10.1085/jgp.40.6.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. H. Three pharmacologically distinct potassium channels in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(2):465–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


