Abstract
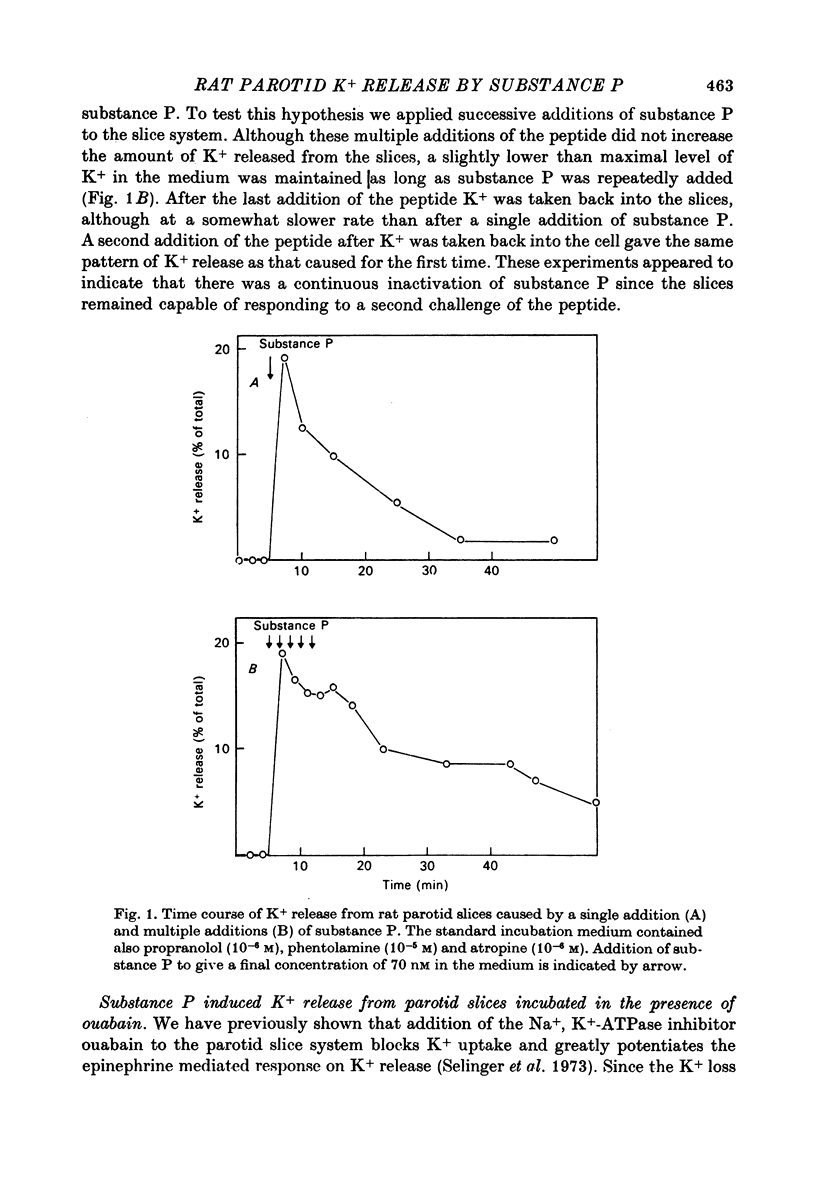
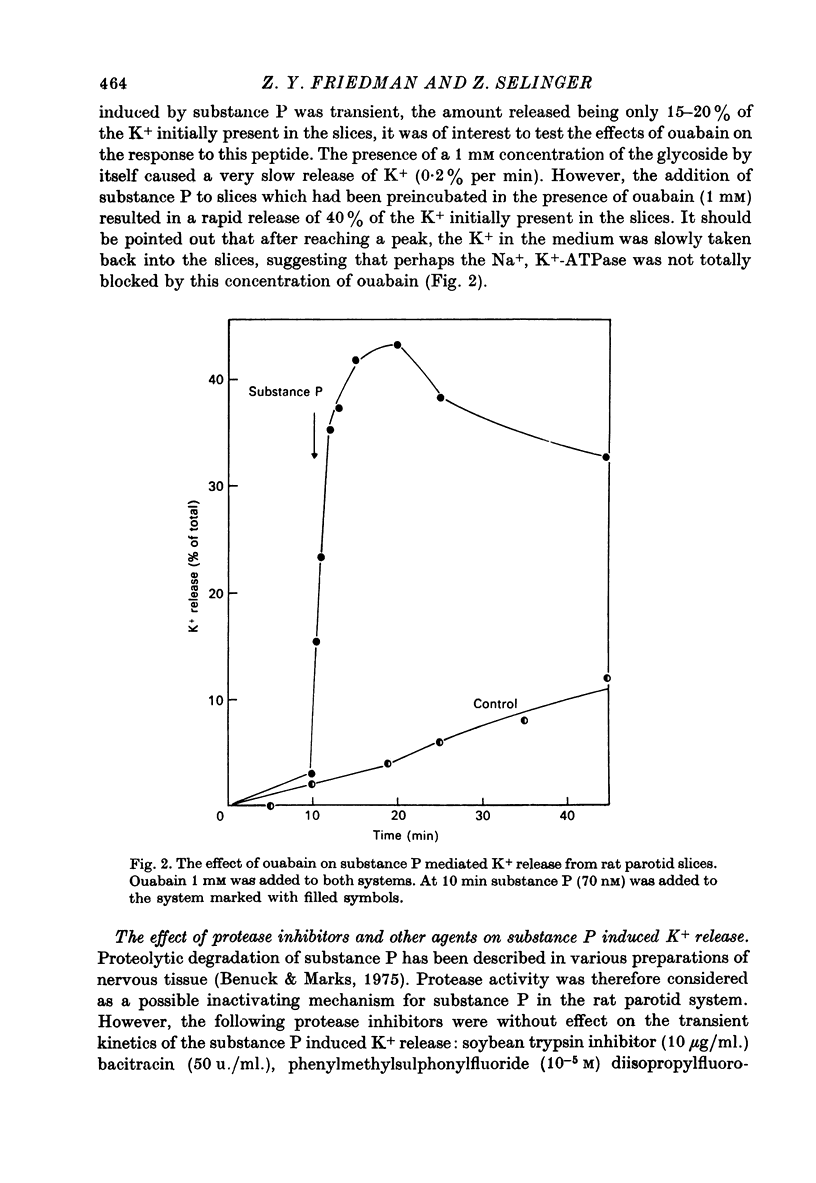
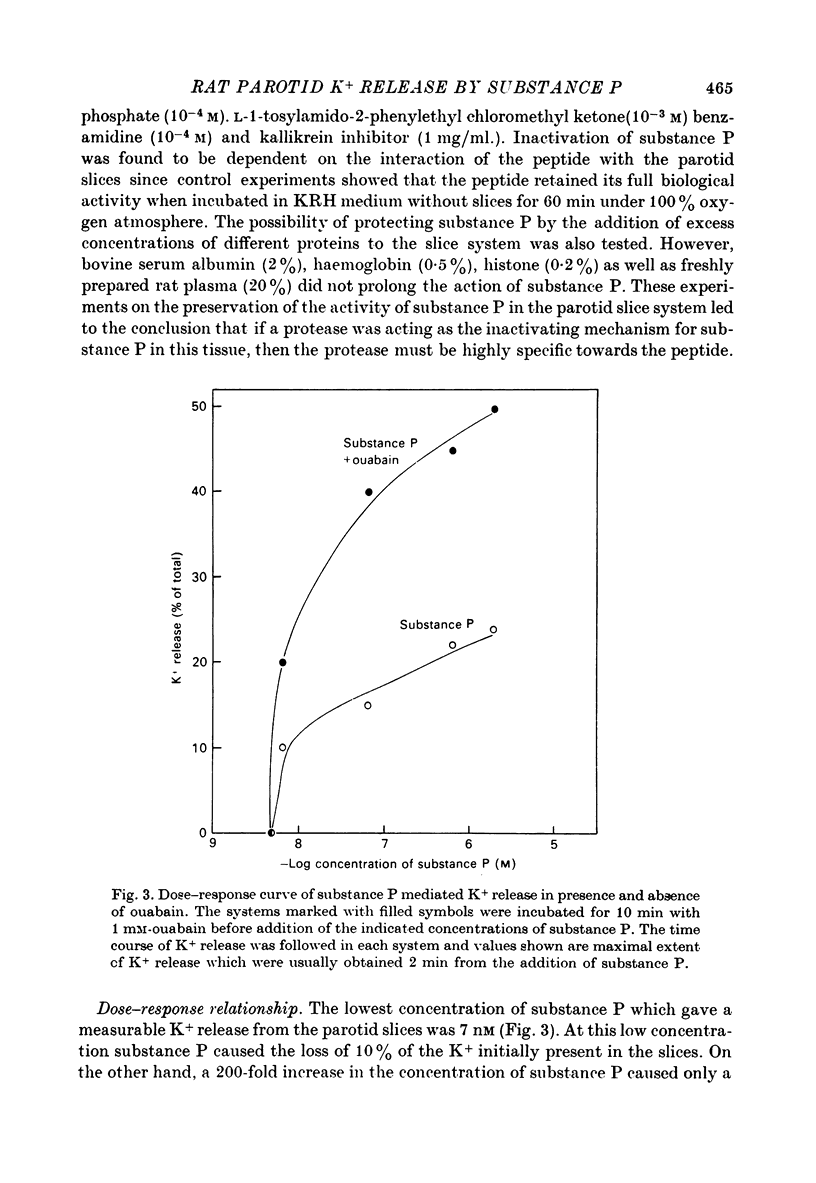
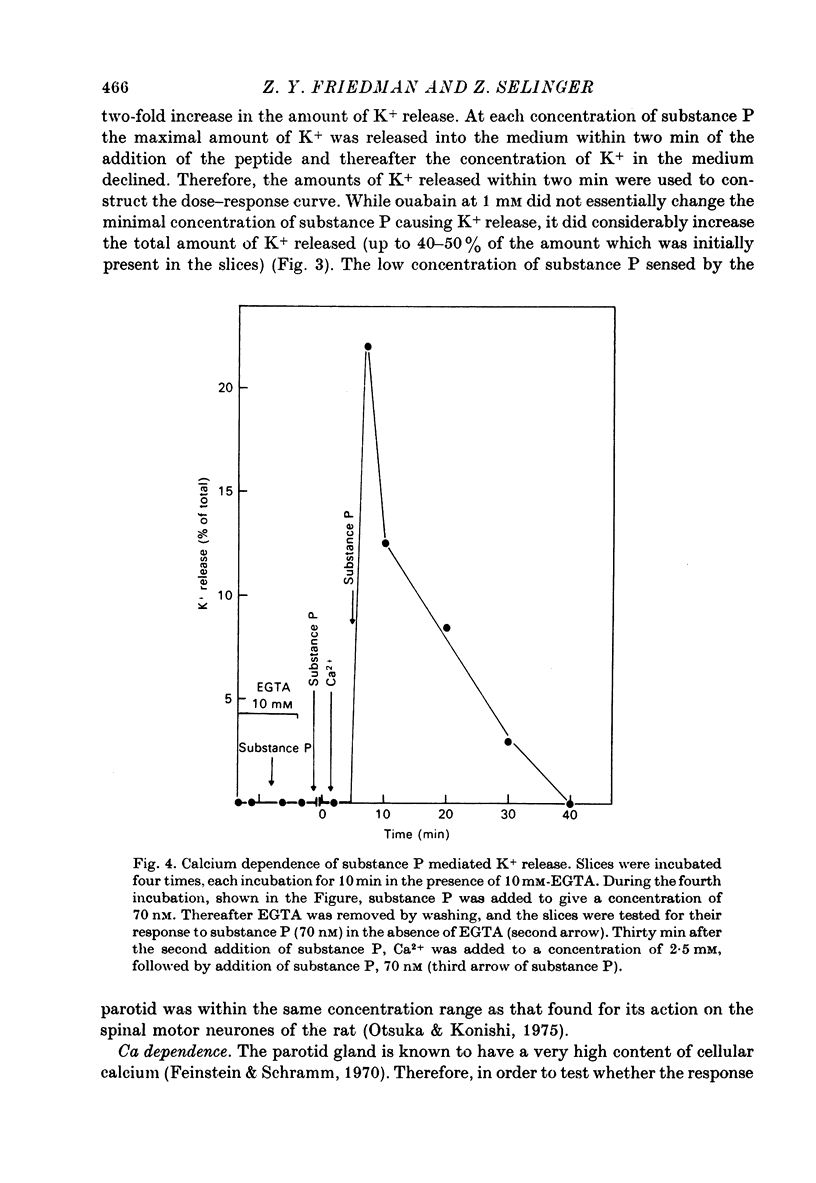
Substance P (a peptide of eleven amino acids) caused a Ca-dependent release of K+ from rat parotid slices. The response to substance P differed from the alpha-adrenergic and the cholinergic responses in that it was transient, of smaller extent, and was not inhibited by phentolamine and atropine. Substance P caused little, if any, amylase secretion. Successive additions of the peptide to the slice system maintained the effect of C+ release indicating that the transient response to a single addition of the peptide was due to inactivation of substance P and not due to a decline in the response of the tissue.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batzri S., Selinger Z. Enzyme secretion mediated by the epinephrine -receptor in rat parotid slices. Factors governing efficiency of the process. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):356–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benuck M., Marks N. Enzymatic inactivation of substance P by a partially purified enzyme from rat brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jul 8;65(1):153–160. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M. M., Leeman S. E. Isolation of a sialogogic peptide from bovine hypothalamic tissue and its characterization as substance P. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 25;245(18):4784–4790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M. M., Leeman S. E., Niall H. D. Amino-acid sequence of substance P. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 21;232(29):86–87. doi: 10.1038/newbio232086a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen L. L. Catecholamine uptake processes. Br Med Bull. 1973 May;29(2):130–135. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEMBECK F. Zur Frage der zentralen Ubertragung afferenter Impulse. III. Das Vorkommen und die Bedeutung der Substanz P in den dorsalen Wurzeln des Rückenmarks. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1953;219(3):197–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeman S. E., Hammerschlag R. Stimulation of salivary secretion by a factor extracted from hypothalamic tissue. Endocrinology. 1967 Oct;81(4):803–810. doi: 10.1210/endo-81-4-803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka M., Konishi S. Substance P and excitatory transmitter of primary sensory neurons. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:135–143. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudich L., Butcher F. R. Effect of substance P and eledoisin on K+ efflux, amylase release and cyclic nucleotide levels in slices of rat parotid gland. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 22;444(3):704–711. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90317-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramm M., Selinger Z. Enzyme secretion and K+ release mediated by beta and alpha adrenergic receptors in rat parotid slices. Methods Enzymol. 1975;39:461–466. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(75)39041-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramm M., Selinger Z. The function of alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptors and a cholinergic receptor in the secretory cell of rat parotid gland. Adv Cytopharmacol. 1974;2:29–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramm M., Selinger Z. The functions of cyclic AMP and calcium as alternative second messengers in parotid gland and pancreas. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;1(4):181–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selinger Z., Batzri S., Eimerl S., Schramm M. Calcium and energy requirements for K + release mediated by the epinephrine -receptor in rat parotid slices. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):369–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- V Euler U. S., Gaddum J. H. An unidentified depressor substance in certain tissue extracts. J Physiol. 1931 Jun 6;72(1):74–87. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1931.sp002763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITBY L. G., AXELROD J., WEIL-MALHERBE H. The fate of H3-norepinephrine in animals. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1961 May;132:193–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


