Abstract
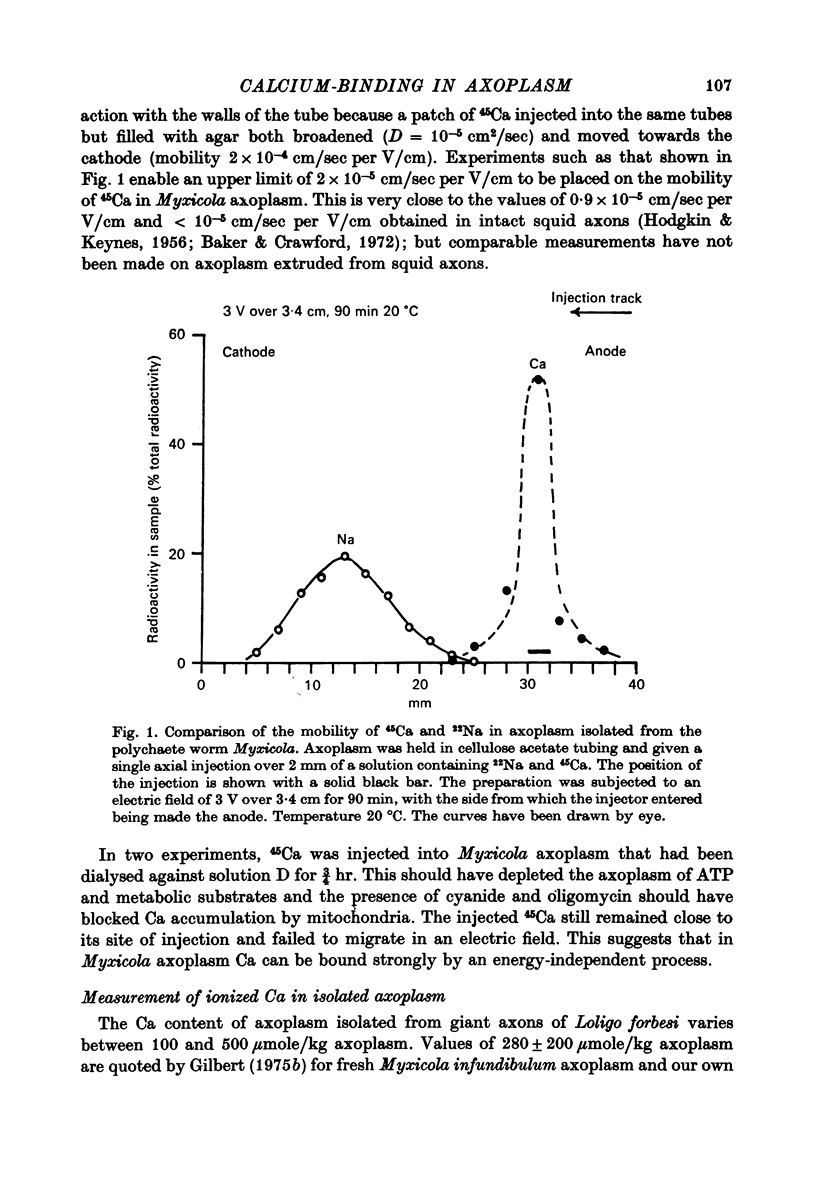
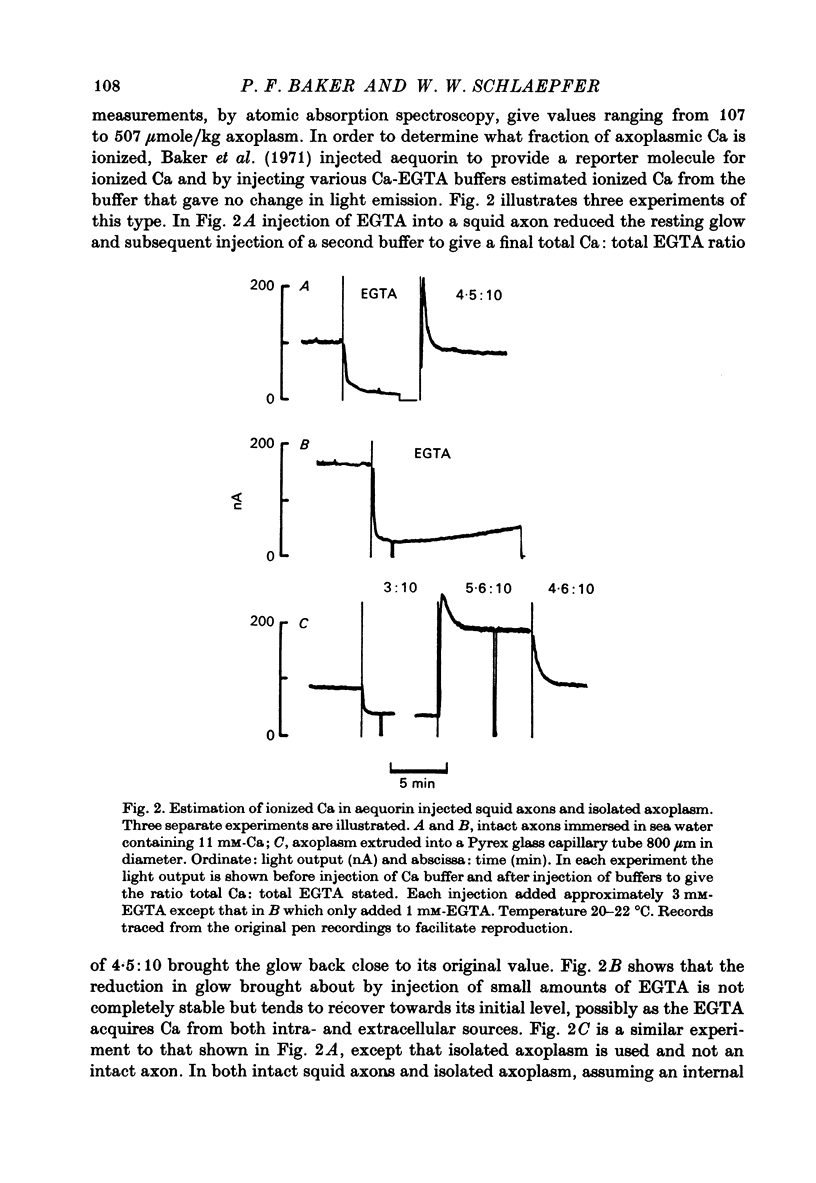
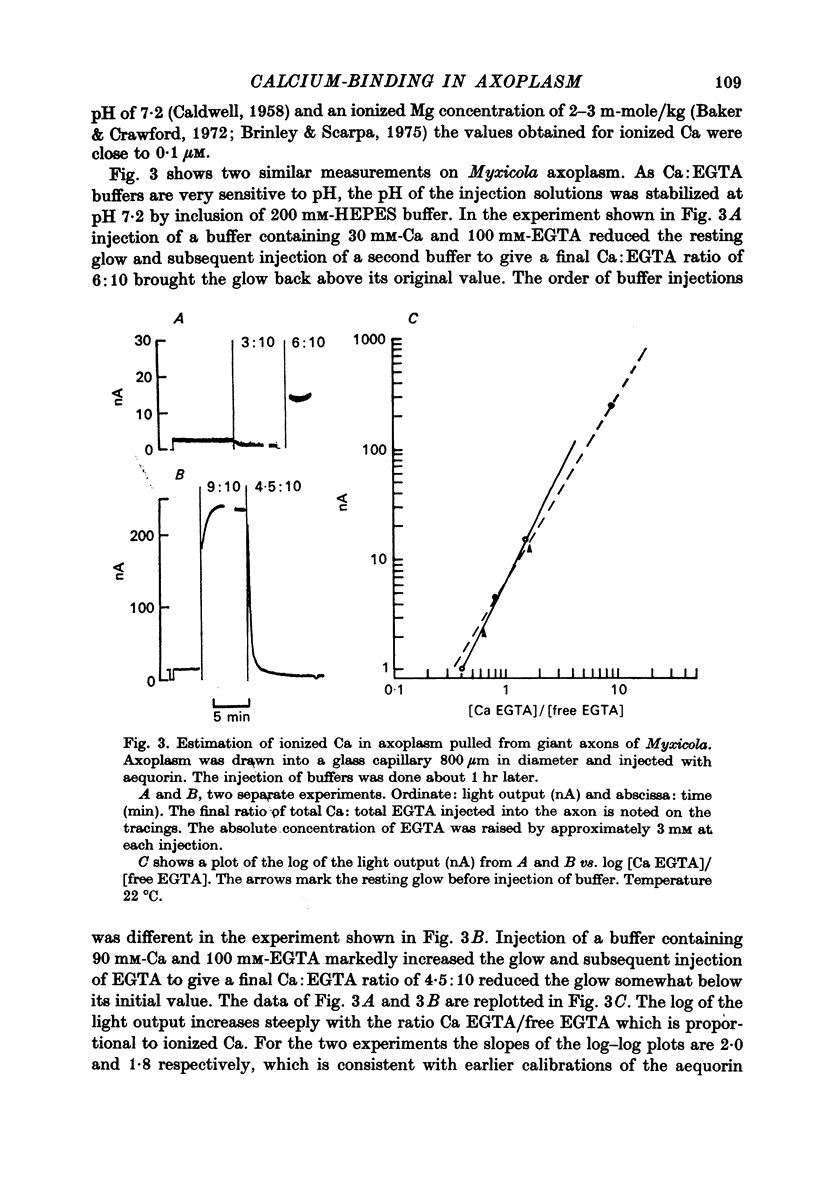
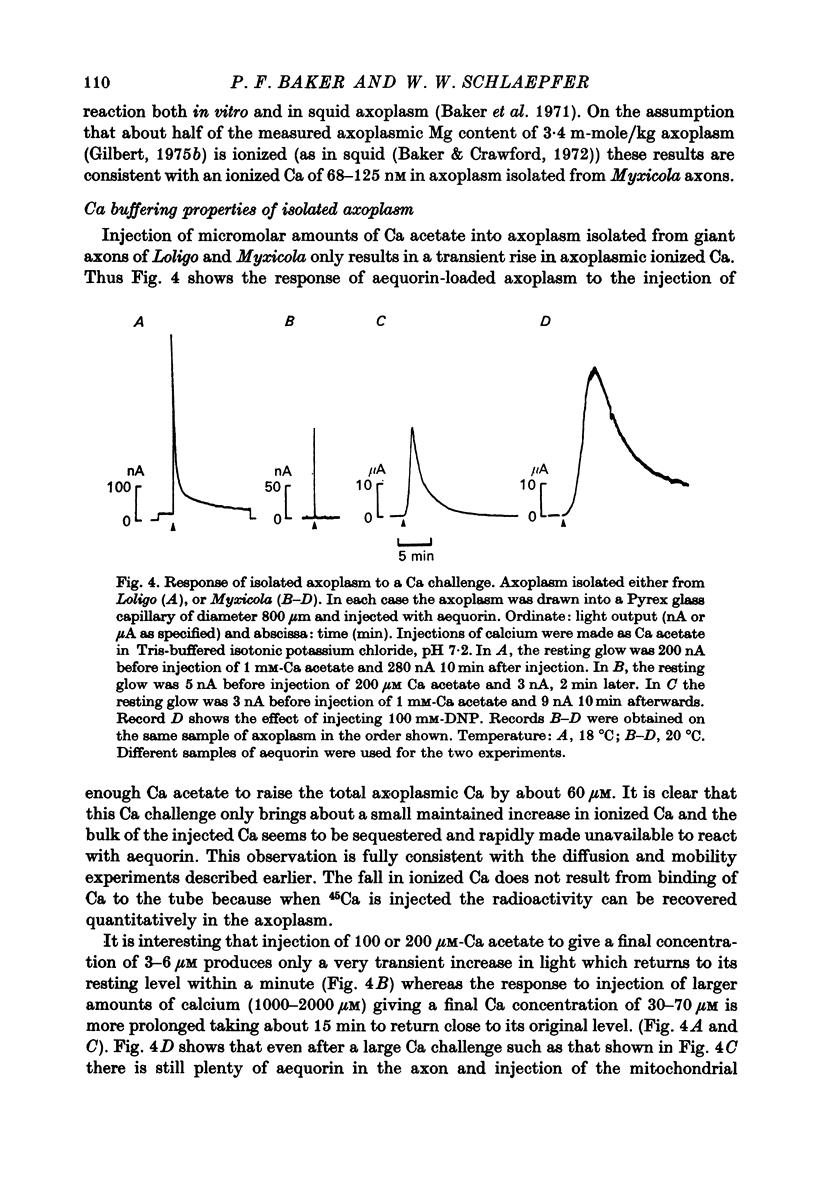
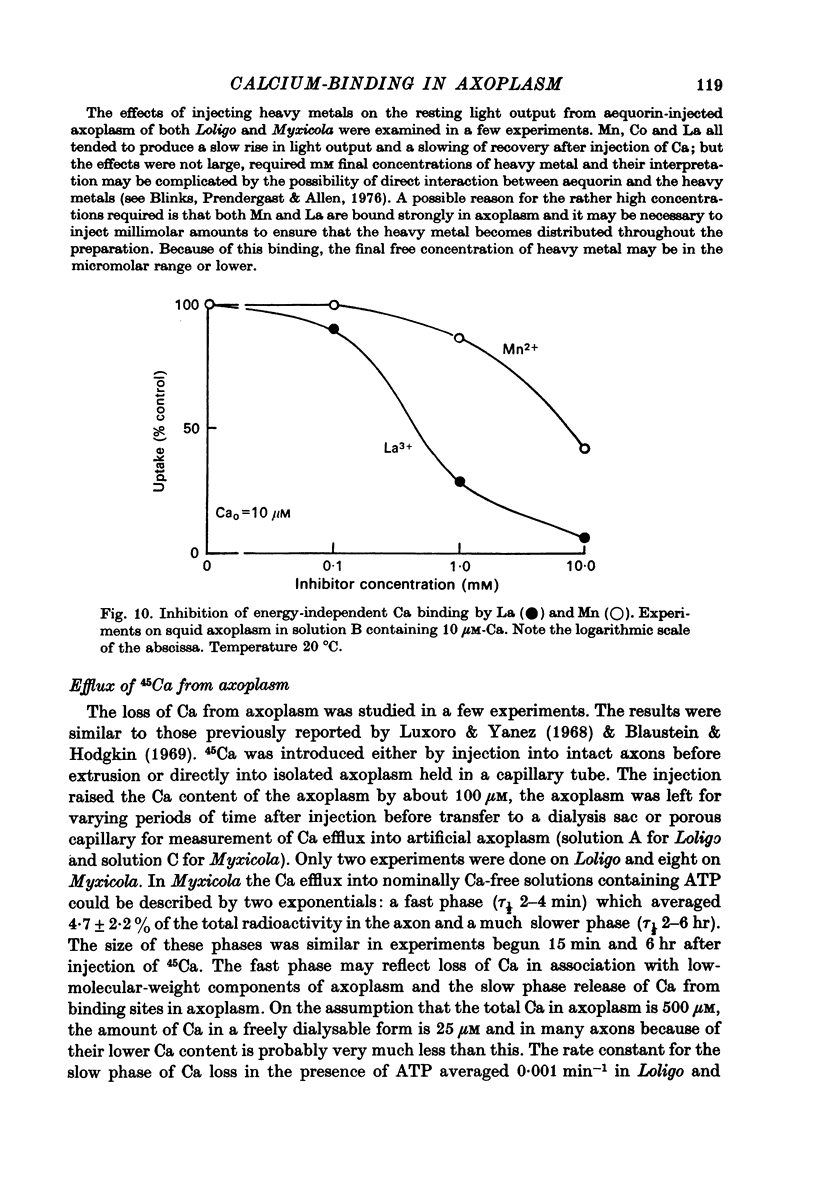
1. Axoplasm isolated from giant axons of the squid Loligo and of the polychaete worm Myxicola continues to bind Ca and maintain an ionized Ca concentration close to 0.1 microgram which is similar to that seen in intact axons. 2. Injection of Ca into isolated axoplasm only produces a transient rise in ionized Ca showing that axoplasm can buffer a Ca challenge. 3. In order to characterize the Ca-binding systems isolated axoplasm was placed in small dialysis tubes and exposed to a variety of artificial axoplasms containing 45Ca. 4. In the presence of ATP, orthophosphate and succinate, Ca uptake appreciable and after 4 hr exposure of Loligo axoplasm to 0.1 microgram-Ca, approximately 100 mumole Ca/kg axoplasm was bound. Binding could be divided operationally into two distinct processes, one that requires ATP or succinate togeth with orthophosphate and is blocked by cyanide and oligomyocin, and one that is unaffected by these reagents. 5. Energy-dependent binding has a large capacity, but a rather low affinity for Ca, being half-maximal between 20 and 60 microgram-Ca. In Loligo, its properties closely parallel those of a crude mitochondrial preparation isolated from axoplasm; but there are some interesting differences in Myxicola. Energy-independent binding is half-maximal at ionized Ca concentrations between 80 and 160 nM but is readily saturated and has a capacity of 6-60 mumole/kg axoplasm. 6. Ca binding by Loligo is greatest in media containing roughly physiological concentrations of K and is reduced by isosmotic replacement of K by Na. This effect seems to be confined to the energy-dependent, presumed mitochondrial, component of binding. 7. Ca binding by Loligo axoplasm is reduced by both La and Mn ions.
Full text
PDF



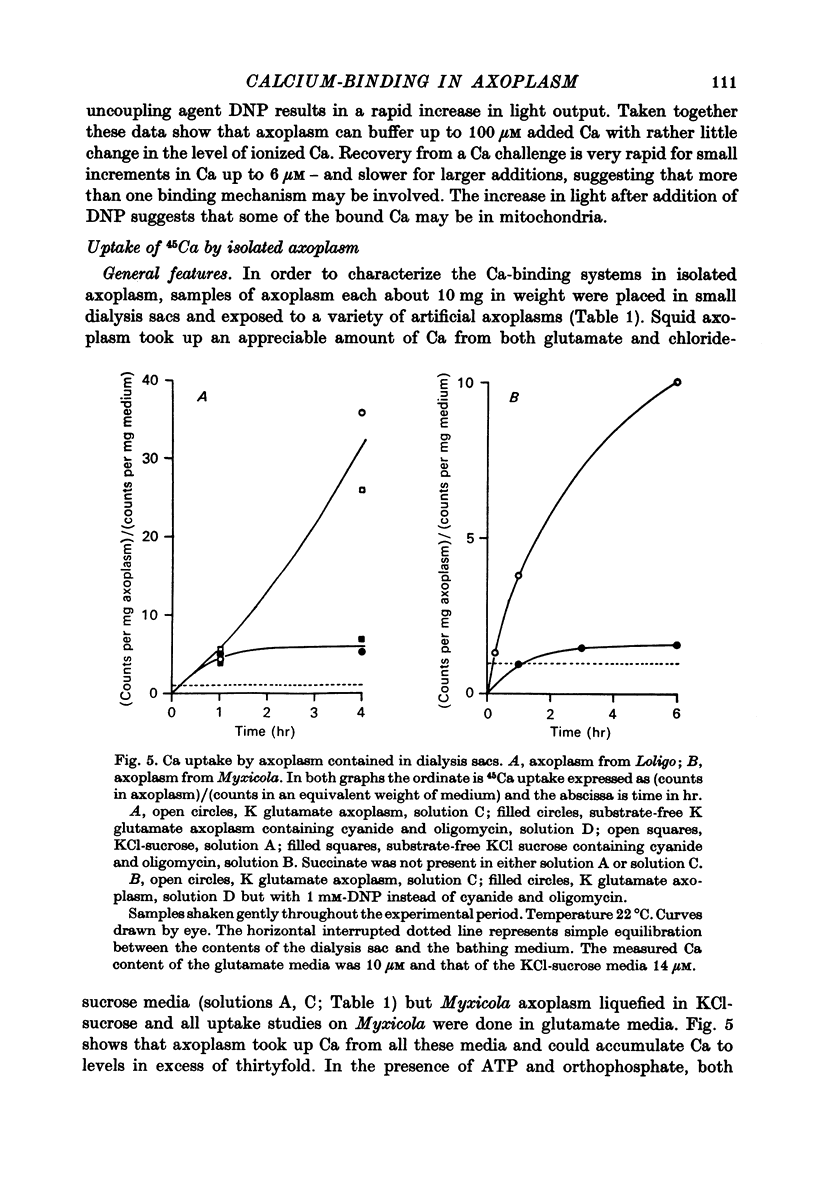
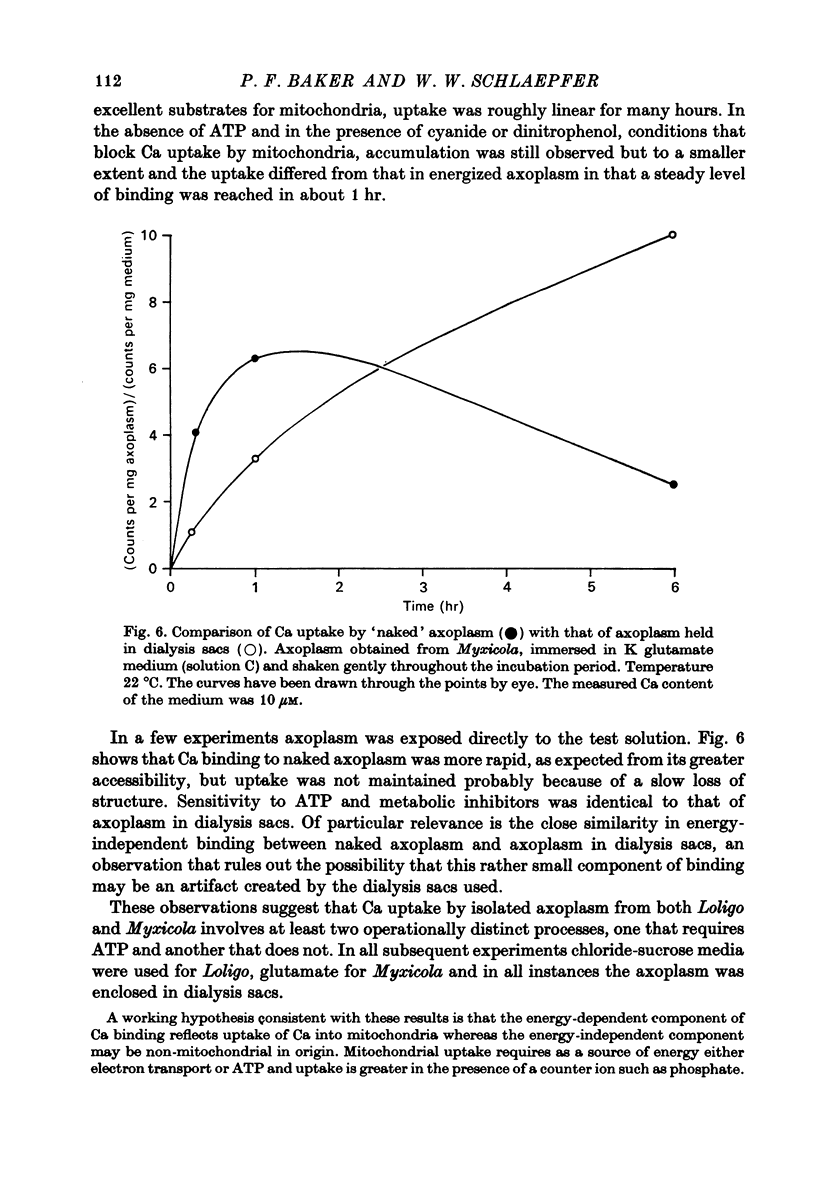

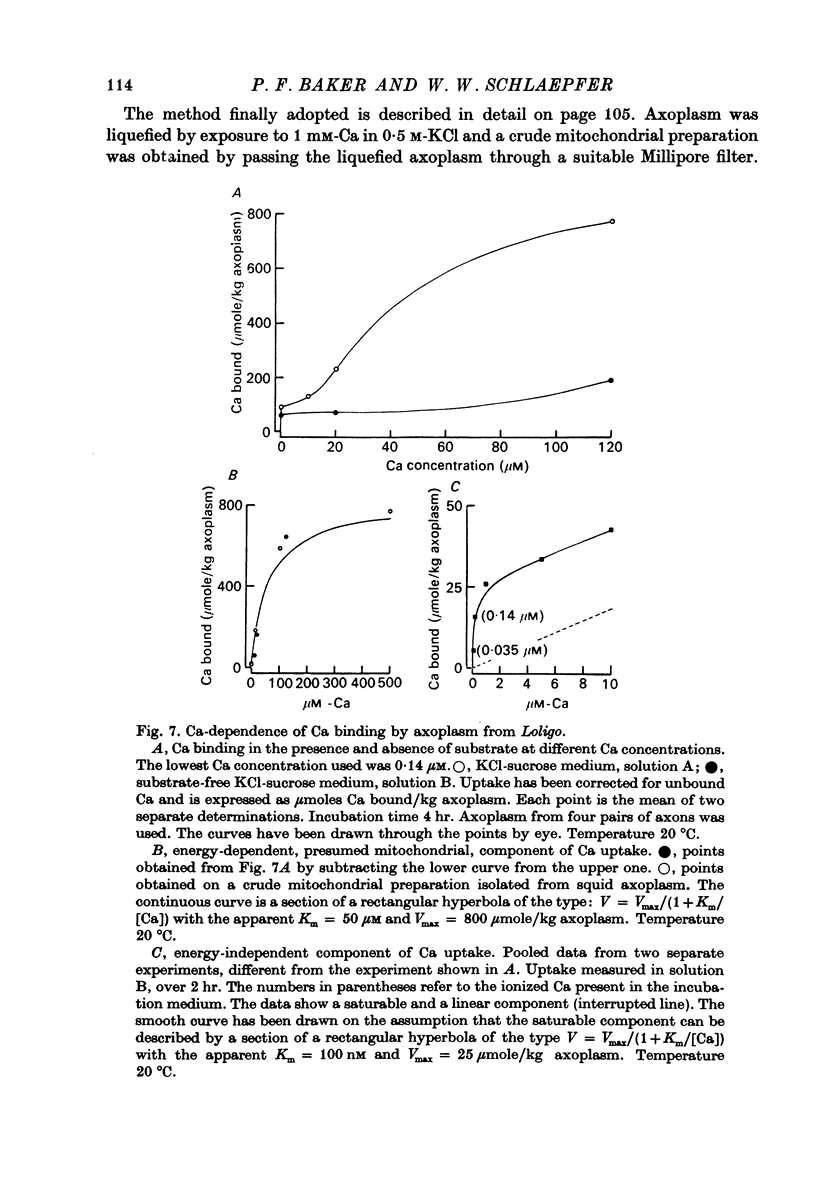
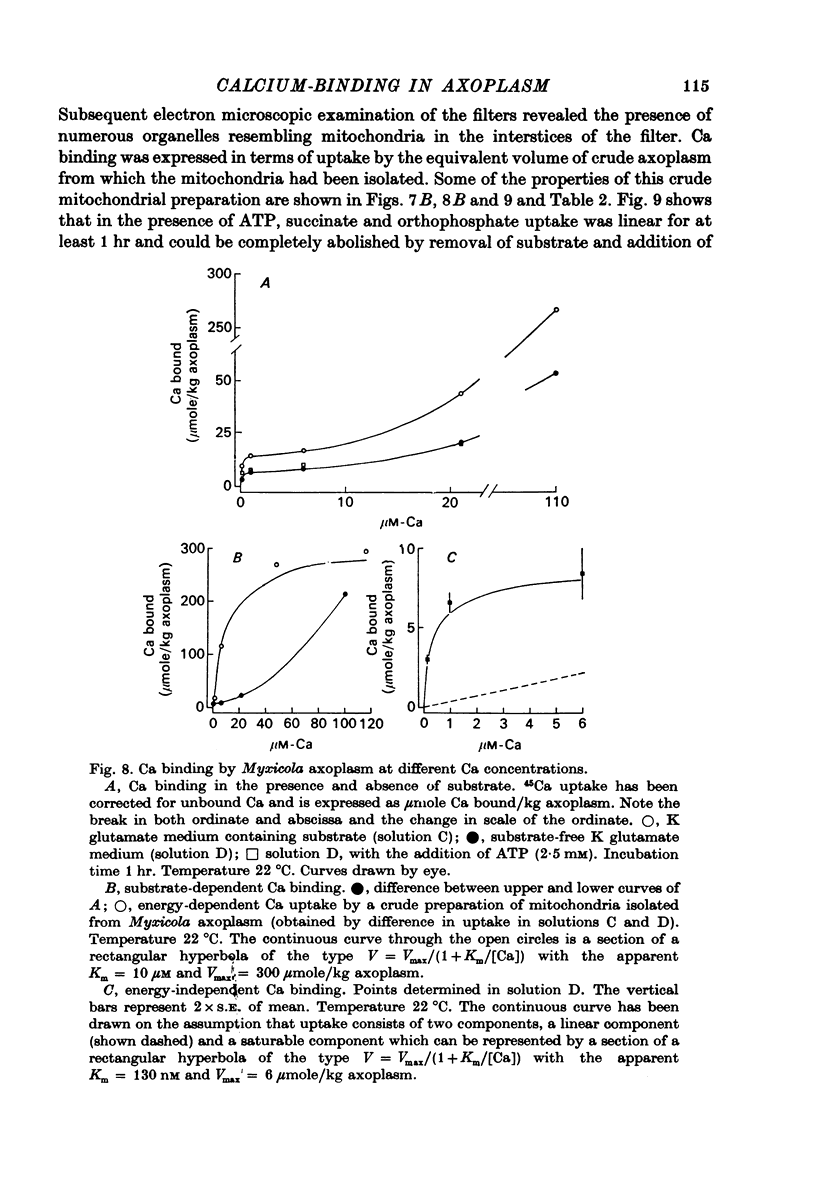
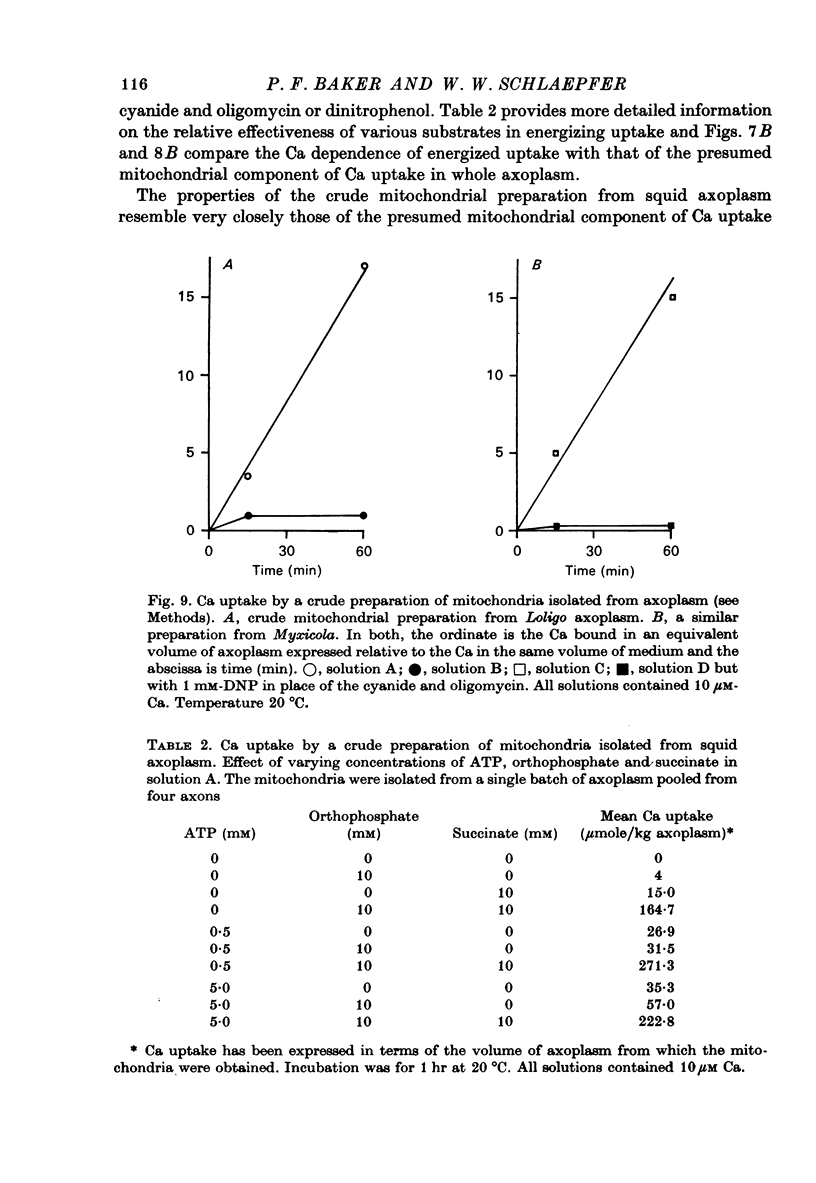








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alemà S., Calissano P., Rusca G., Giuditta A. Identification of a calcium-binding, brain specific protein in the axoplasm of squid giant axons. J Neurochem. 1973 Mar;20(3):681–689. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb00028.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Crawford A. C. A note of the mechanism by which inhibitors of the sodium pump accelerate spontaneous release of transmitter from motor nerve terminals. J Physiol. 1975 May;247(1):209–226. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Crawford A. C. Mobility and transport of magnesium in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(3):855–874. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Hodgkin A. L., Ridgway E. B. Depolarization and calcium entry in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1971 Nov;218(3):709–755. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Knight D. E., Pattni D. D. Porous cellulose acetate tubing provides a suitable support for isolated protoplasm during studies under controlled conditions [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1977 Mar;266(1):6P–6P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Ladds M., Rubinson K. A. Measurement of the flow properties of isolated axoplasm in a defined chemical environment [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;269(1):10P–11P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F. Regulation of intracellular Ca and Mg in squid axons. Fed Proc. 1976 Dec;35(14):2589–2595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Schapira A. H. Measurement of ionic diffusion and mobility in axoplasm isolated from giant axons of Myxicola [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1977 Mar;266(1):5P–5P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Schlaepfer W. Proceedings: Calcium uptake by axoplasm extruded from giant axons of Loligo. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(1):37P–38P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Shaw T. I. A comparison of the phosphorus metabolism of intact squid nerve with that of the isolated axoplasm and sheath. J Physiol. 1965 Sep;180(2):424–438. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birks R. I., Cohen M. W. The action of sodium pump inhibitors on neuromuscular transmission. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1968 Jul 9;170(1021):381–399. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1968.0046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Hodgkin A. L. The effect of cyanide on the efflux of calcium from squid axons. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(2):497–527. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinks J. R., Prendergast F. G., Allen D. G. Photoproteins as biological calcium indicators. Pharmacol Rev. 1976 Mar;28(1):1–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinley F. J., Jr, Scarpa A. Ionized magnesium concentration in axoplasm of dialyzed squid axons. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jan 15;50(1):82–85. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)81046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CALDWELL P. C. Studies on the internal pH of large muscle and nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1958 Jun 18;142(1):22–62. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calissano P., Moore B. W., Friesen A. Effect of calcium ion on S-100, a protein of the nervous system. Biochemistry. 1969 Nov;8(11):4318–4326. doi: 10.1021/bi00839a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E., Tiozzo R., Lugli G., Crovetti F., Kratzing C. The release of calcium from heart mitochondria by sodium. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1974 Aug;6(4):361–371. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(74)90077-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. M., Goldman R. D. The localization of actin-like fibers in cultured neuroblastoma cells as revealed by heavy meromyosin binding. J Cell Biol. 1973 Jun;57(3):867–874. doi: 10.1083/jcb.57.3.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford A. C. Lithium ions and the release of transmitter at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1975 Mar;246(1):109–142. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dipolo R., Requena J., Brinley F. J., Jr, Mullins L. J., Scarpa A., Tiffert T. Ionized calcium concentrations in squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Apr;67(4):433–467. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.4.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dravid A. R., Hammerschlag R. Axoplasmic transport of proteins in vitro in primary afferent neurons of frog spinal cord: effect of Ca2+-free incubation conditions. J Neurochem. 1975 Apr;24(4):711–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine R. E., Bray D. Actin in growing nerve cells. Nat New Biol. 1971 Nov 24;234(47):115–118. doi: 10.1038/newbio234115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. S. Axoplasm architecture and physical properties as seen in the Myxicola giant axon. J Physiol. 1975 Dec;253(1):257–301. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. S. Axoplasm chemical composition in Myxicola and solubility properties of its structural proteins. J Physiol. 1975 Dec;253(1):303–319. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. S., Newby B. J. Neurofilament disguise, destruction and discipline. Nature. 1975 Aug 14;256(5518):586–589. doi: 10.1038/256586a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of calcium on the axoplasm of giant nerve fibers. J Exp Biol. 1949 Oct;26(3):292-4, pl. doi: 10.1242/jeb.26.3.292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. Movements of labelled calcium in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;138(2):253–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. N., Lasek R. J. The slow component of axonal transport. Identification of major structural polypeptides of the axon and their generality among mammalian neurons. J Cell Biol. 1975 Aug;66(2):351–366. doi: 10.1083/jcb.66.2.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo I. C., Coffee C. J. Purification and characterization of a troponin-C-like protein from bovine adrenal medulla. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 25;251(6):1603–1609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaepfer W. W. Calcium-induced degeneration of axoplasm in isolated segments of rat peripheral nerve. Brain Res. 1974 Apr 5;69(2):203–215. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90002-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


