Abstract
1. The catecholamines adrenaline (A), noradrenaline (NA) and dopamine (DA) were determined in plasma samples of man and various animal species using a highly sensitive radioenzymatic method.
2. Basal values were determined under conditions producing virtually no physical or psychic stress in blood obtained through acutely inserted venous catheters in human volunteers, rabbits and cows, through chronic indwelling catheters in cats and rats, and by cubital venipuncture in trained dogs.
3. Basal values (pg/ml.) for A, NA, and DA were respectively 64, 203 and 98 in man, 73, 609 and 276 in cats, 166, 392 and 216 in rabbits, 56, 152 and 91 in cows, 204, 376 and 173 in dogs, and 175, 509, and 84 in SPF rats. The NA concentrations were always higher than those of A and DA.
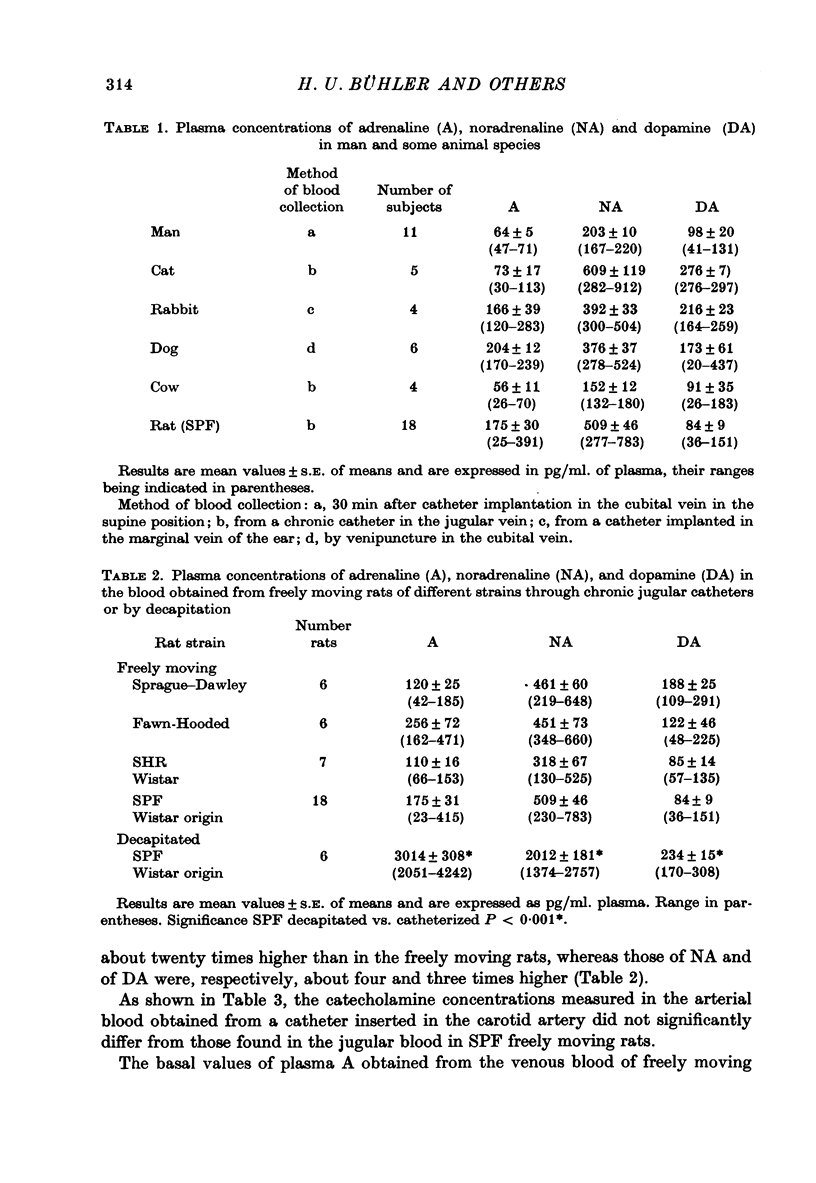
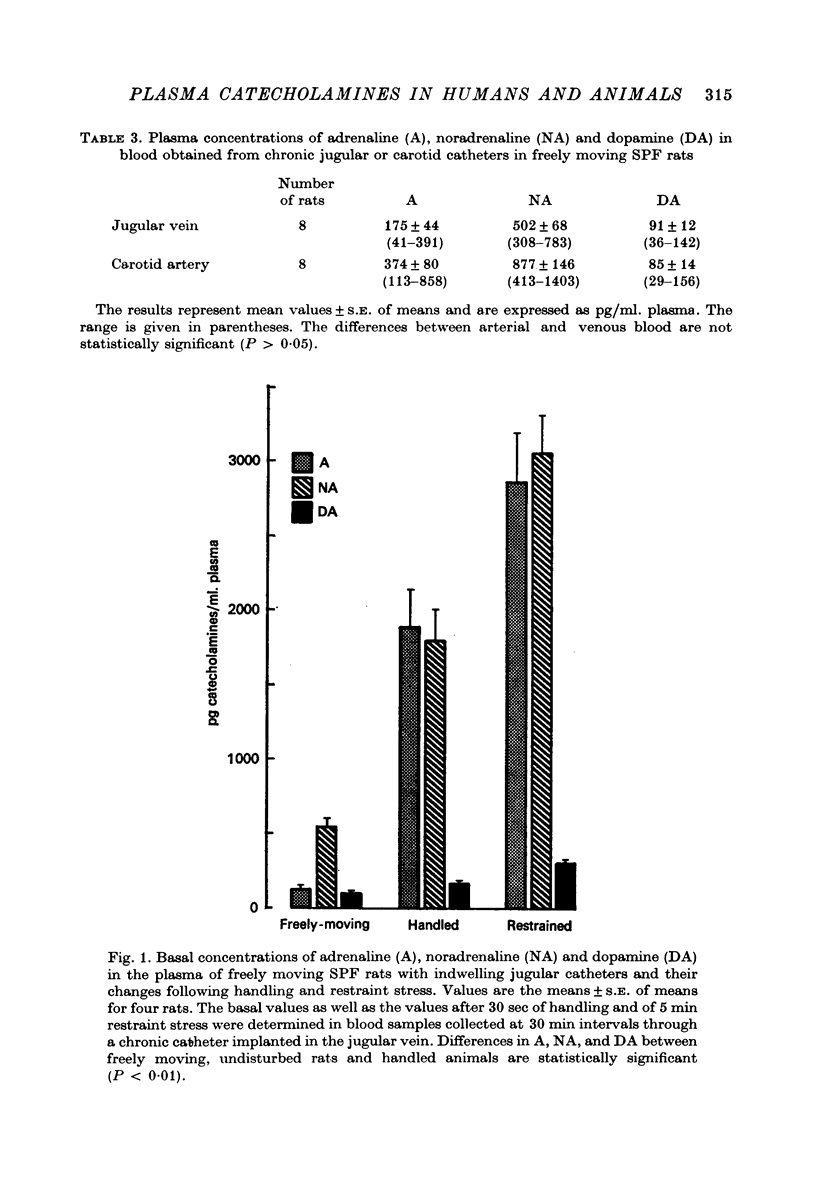
4. Gentle handling of rats for 30 sec greatly increased the levels of all catecholamines, especially of A. Even more marked rises were observed during and up to 5 min after restraint stress.
5. Blood from the trunk of decapitated rats contained about 20 times more A and 3-4 times more DA and NA than venous blood from catheters in the absence of handling.
6. Basal values of plasma catecholamines in small animals can only be obtained through indwelling catheters and in the absence of handling. Most of the previously reported values are too high and are experimental artifacts.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANTON A. H., SAYRE D. F. A study of the factors affecting the aluminum oxide-trihydroxyindole procedure for the analysis of catecholamines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1962 Dec;138:360–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Jonathan N., Porter J. C. A sensitive radioenzymatic assay for dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine in plasma and tissue. Endocrinology. 1976 Jun;98(6):1497–1507. doi: 10.1210/endo-98-6-1497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. R., Hedge G. A. Thyroid secretion in the unanesthetized, stress-free rat and its suppression by pentobarbital. Neuroendocrinology. 1972;9(3):158–174. doi: 10.1159/000122047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callingham B. A., Barrand M. A. Catecholamines in blood. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1976 Apr;28(4 Suppl):356–360. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1976.tb04179.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen N. J. A sensitive assay for the determination of dopamine in plasma. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1973 May;31(3):343–346. doi: 10.3109/00365517309082441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Da Prada M., Zürcher Simultaneous radioenzymatic determination of plasma and tissue adrenaline, noradrenaline and dopamine within the femtomole range. Life Sci. 1976 Oct 15;19(8):1161–1174. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90251-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dargie H. J., Franklin S. S., Reid J. L. Proceedings: The sympathetic nervous system and renovascular hypertension in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Mar;56(3):365P–365P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depocas F., Behrens W. A. Effects of handling, decapitation, anesthesia, and surgery on plasma noradrenaline levels in the white rat. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1977 Apr;55(2):212–219. doi: 10.1139/y77-031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eleftheriou B. E. Circadian rhythm in blood and brain biogenic amines and other biochemical changes in rabbits. Brain Res. 1974 Jul 19;75(1):145–152. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90776-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green R. D., 3rd, Miller J. W. Catecholamine Concentrations: Changes in Plasma of Rats during Estrous Cycle and Pregnancy. Science. 1966 Feb 18;151(3712):825–826. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3712.825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grobecker G., Roizen M. F., Weise V., Saavedra J. M., Kopin I. J. Letter: Sympathoadrenal medullary activity in young, spontaneously hypertensive rats. Nature. 1975 Nov 20;258(5532):267–268. doi: 10.1038/258267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grobecker H., Roizen M. F., Kopin I. J. Effect of tyramine and guanethidine on dopamine-beta-hydroxylase activity and norepinephrine concentrations in vesicular fraction of the heart and plasma of rats. Life Sci. 1977 Mar 15;20(6):1009–1015. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90288-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempel K., Männl H. F. Resting secretion of dopamine from the adrenal glands of the cat in vivo. Experientia. 1967 Nov 15;23(11):919–920. doi: 10.1007/BF02136219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M., Sharman D. F., Tegerdine P. Dopamine in the blood of the ruminant. J Physiol. 1970 Sep;210(2):130P–130P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lishajko F. Dopamine secretion from the isolated perfused sheep adrenal. Acta Physiol Scand. 1970 Jul;79(3):405–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1970.tb04740.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLAR R. A., KEENER E. B., BENFEY B. G. Plasma adrenaline and noradrenaline after phenoxybenzamine administration, and during haemorrhagic hypotension, in normal and adrenalectomized dogs. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):9–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00921.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin L. E., Harrison C. An automated method for determination of noradrenaline and adrenaline in tissues and biological fluids. Anal Biochem. 1968 Jun;23(3):529–545. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90244-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagaoka A., Lovenberg W. Plasma norepinephrine and dopamine-beta-hydroxylase in genetic hypertensive rats. Life Sci. 1976 Jul 1;19(1):29–34. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90370-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizen M. F., Moss J., Henry D. P., Kopin I. J. Effects of halothane on plasma catecholamines. Anesthesiology. 1974 Nov;41(5):432–439. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197411000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizen M. F., Weise V., Moss J., Kopin I. J. Plasma catecholamines: arterial-venous difference and the influence of body temperature. Life Sci. 1975 Apr 1;16(7):1133–1143. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90197-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Street D. M., Roberts D. J. The presence of dopamine in cat spleen and blood. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1969 Mar;21(3):199–201. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1969.tb08230.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weise V. K., Kopin I. J. Assay of cathecholamines in human plasma: studies of a single isotope radioenzymatic procedure. Life Sci. 1976 Dec 1;19(11):1673–1685. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90073-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


