Abstract
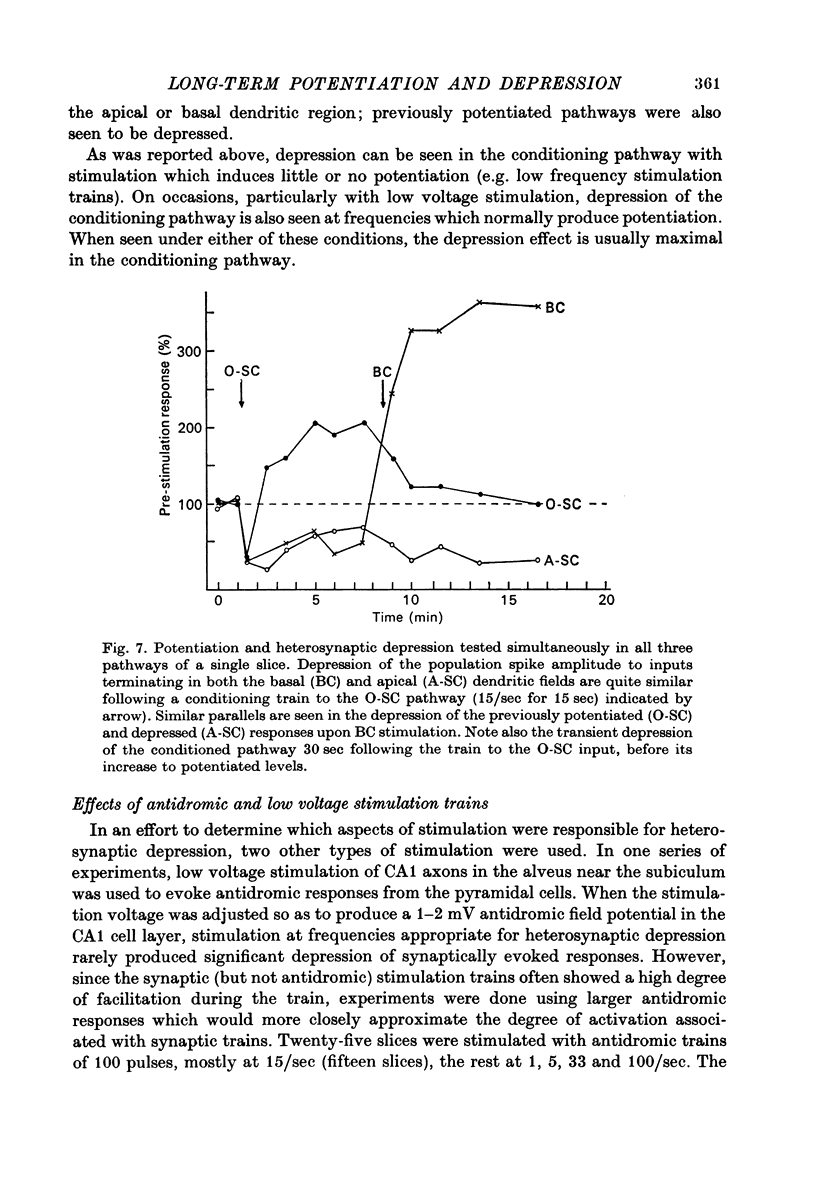
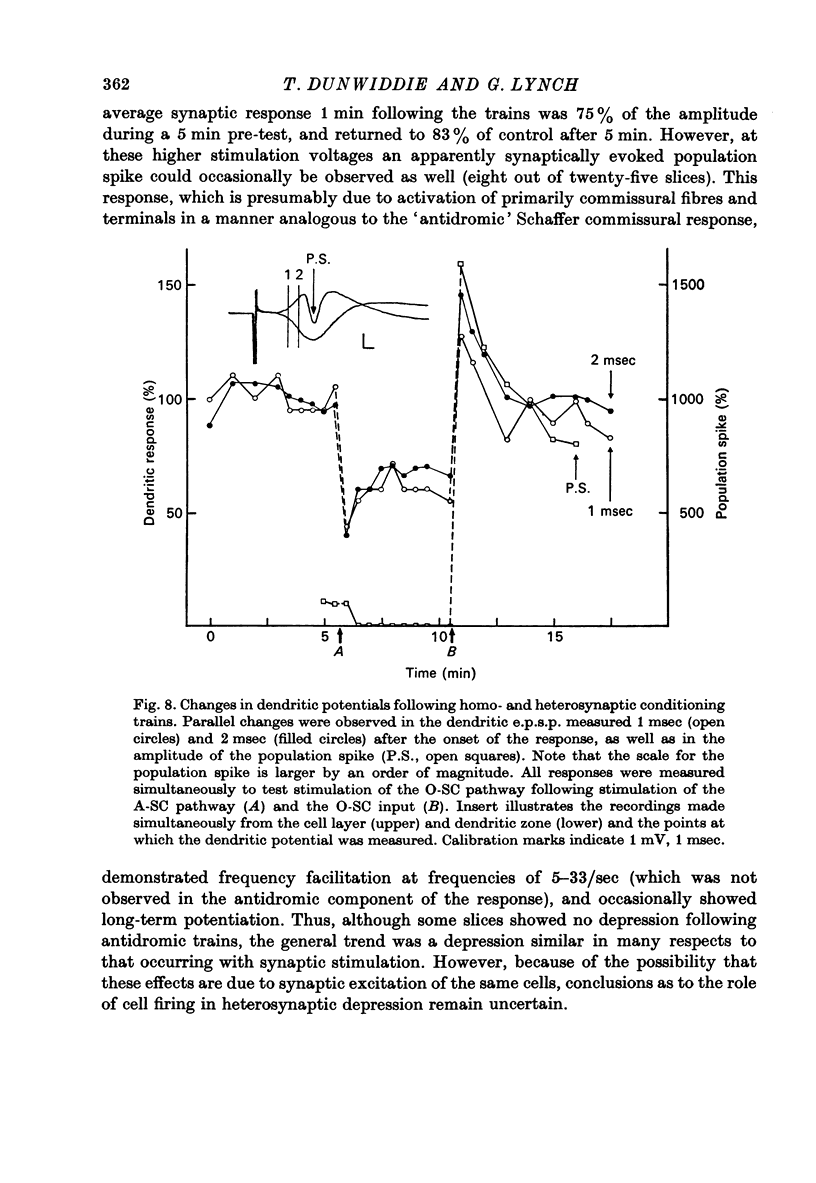
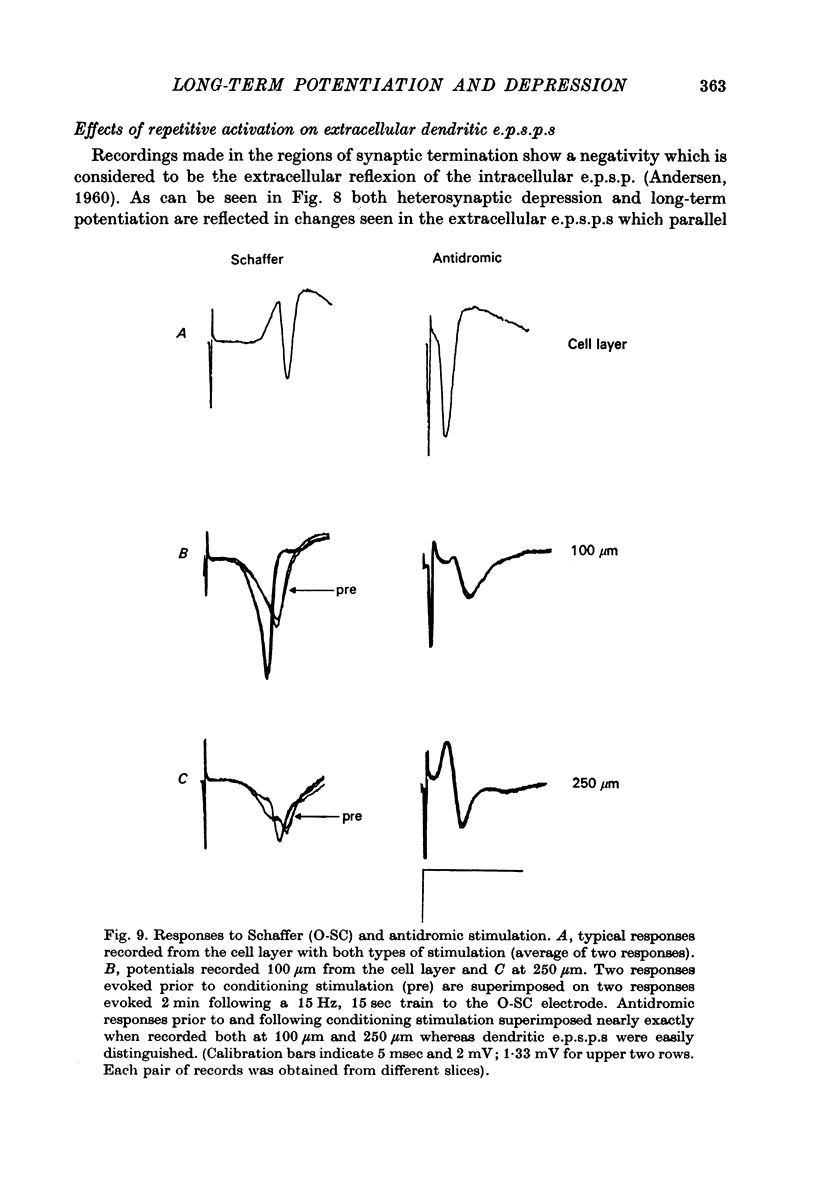
1. The consequences of repetitive activation of excitatory synaptic inputs to the CA1 pyramidal cells of rat hippocampus have been studied using in vitro techniques. 2. Single stimulation trains of 100 pulses at rates of 5-100/sec resulted in potentiation of population spike amplitudes lasting the duration of a 5 min test period in thirty-four out of thirty-five cases. Trains of 100 pulses delivered at 1/sec resulted in depression of the stimulated pathway in ten out of twelve experiments. 3. Responses to test stimulation of other excitatory inputs to the same cell population were depressed following conditioning trains at frequencies in the range 1-100/sec. Depression was seen both in the population spike amplitude (reflecting synchronous cell discharge) as well as the extracellularly recorded population e.p.s.p., and appeared to be maximal at lower frequencies. 4. Trains of antidromic stimulation of the CA1 cell population produced subsequent decreases in synaptically evoked responses, indicating that repetitive firing of pyramidal neurones or interneurones do not cause potentiation, but may be involved in heterosynaptic depression. 5. The results suggest that potentiation and heterosynaptic depression arise from different mechanisms, and that potentiation is confined to the set of terminals activated by a conditioning train, whereas the depression is generalized to the whole neurone.
Full text
PDF

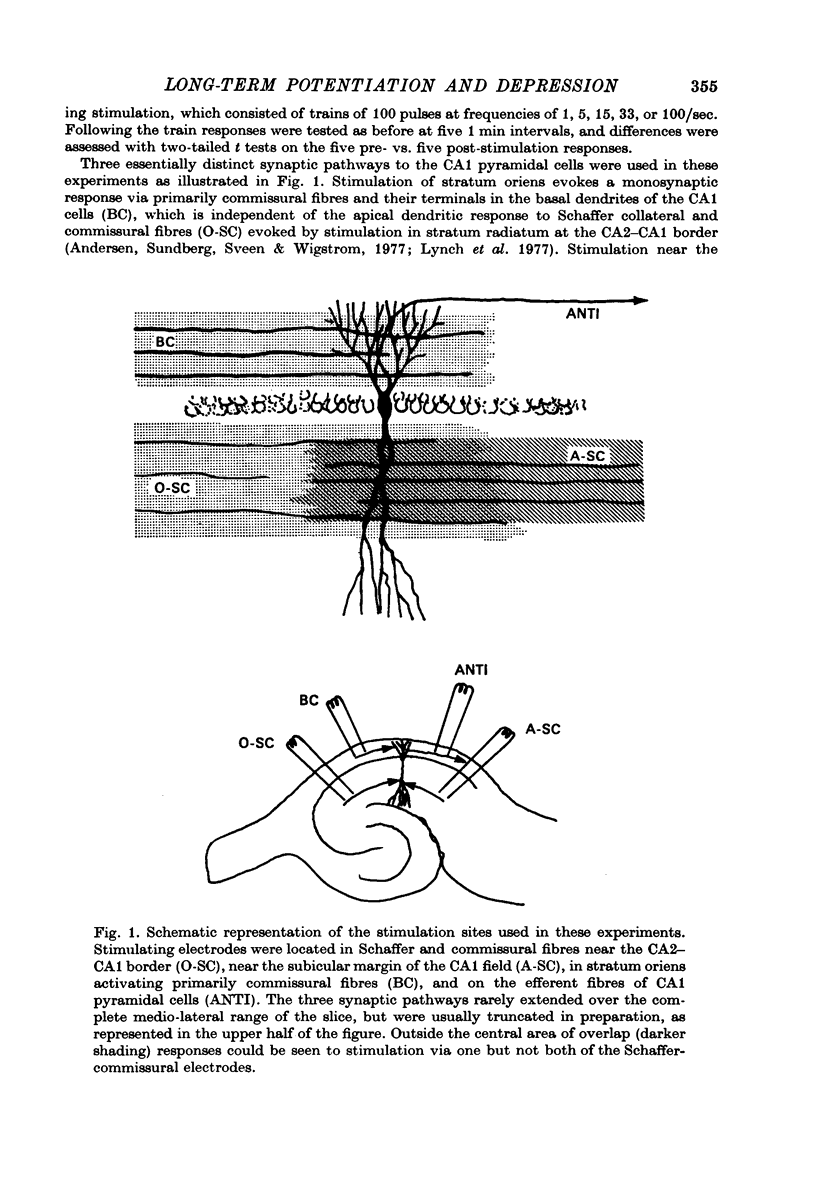

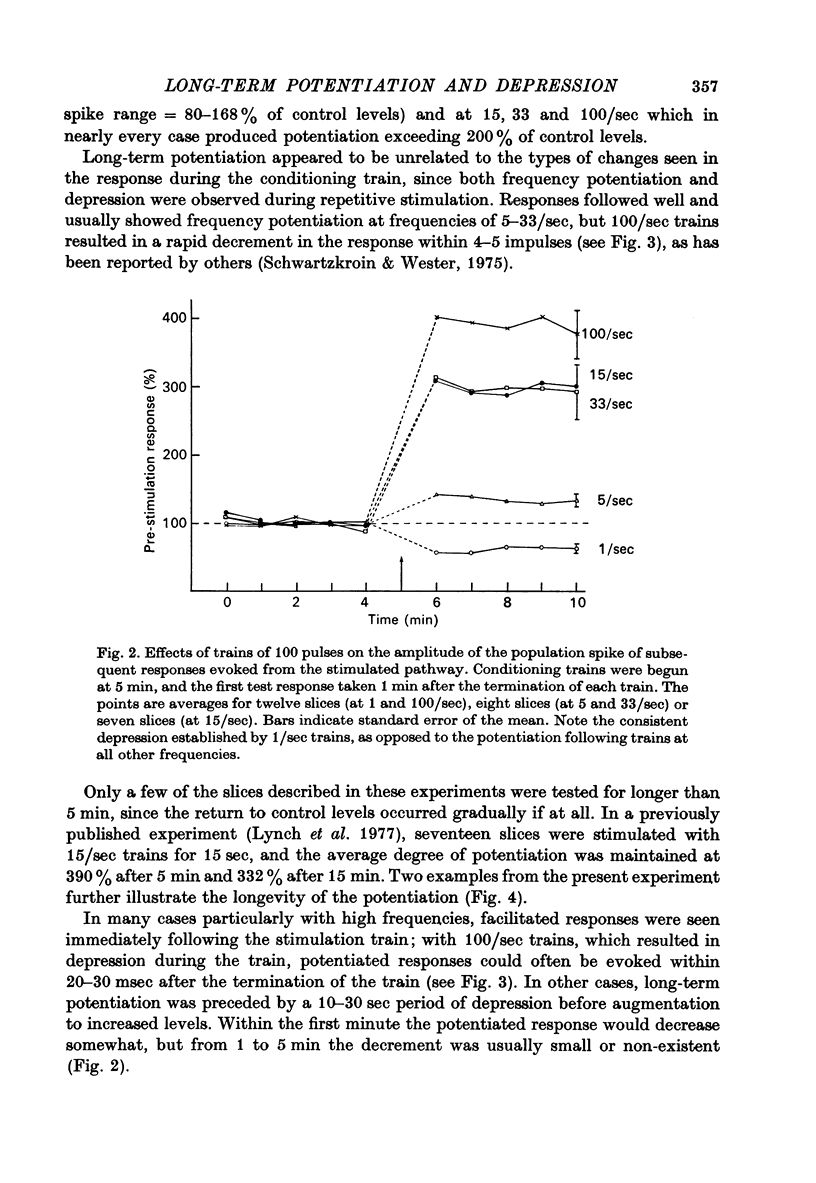

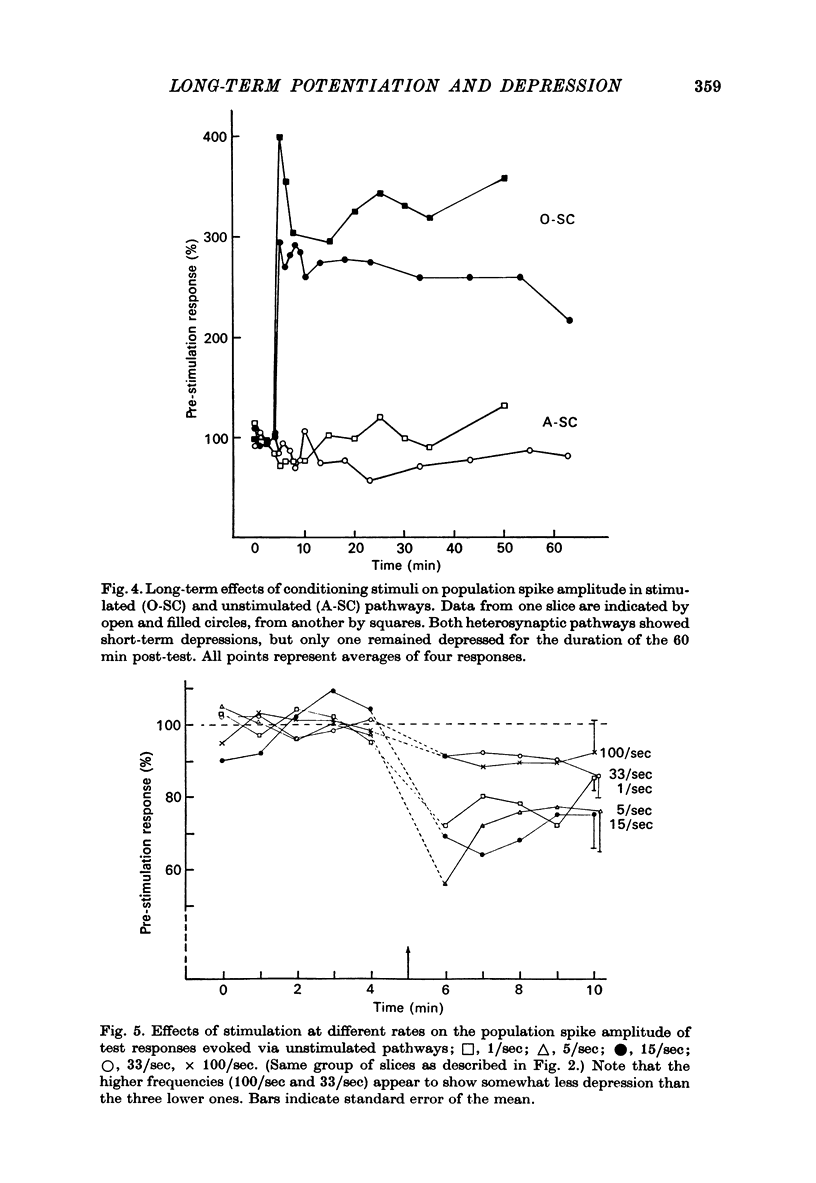
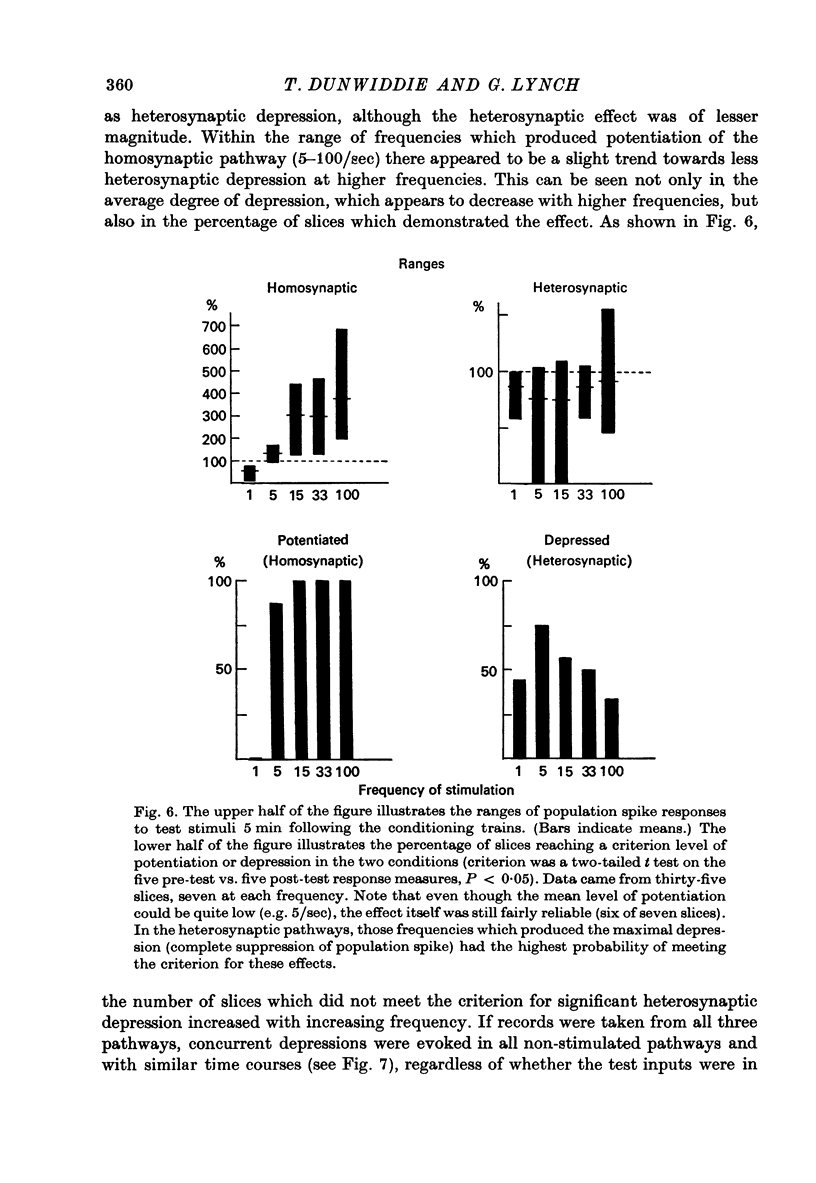




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSEN P. Interhippocampal impulses. II. Apical dendritic activation of CAI neurons. Acta Physiol Scand. 1960 Mar 18;48:178–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1960.tb01858.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alger B. E., Teyler T. J. A monosynaptic fiber track studied in vitro: evidence of a hippocampal CA1 associational system? Brain Res Bull. 1977 Sep-Oct;2(5):355–365. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(77)90069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alger B. E., Teyler T. J. Long-term and short-term plasticity in the CA1, CA3, and dentate regions of the rat hippocampal slice. Brain Res. 1976 Jul 16;110(3):463–480. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90858-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Sundberg S. H., Sveen O., Wigström H. Specific long-lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission in hippocampal slices. Nature. 1977 Apr 21;266(5604):736–737. doi: 10.1038/266736a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bliss T. V., Gardner-Medwin A. R. Long-lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission in the dentate area of the unanaestetized rabbit following stimulation of the perforant path. J Physiol. 1973 Jul;232(2):357–374. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bliss T. V., Lomo T. Long-lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission in the dentate area of the anaesthetized rabbit following stimulation of the perforant path. J Physiol. 1973 Jul;232(2):331–356. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas R. M., Goddard G. V. Long-term potentiation of the perforant path-granule cell synapse in the rat hippocampus. Brain Res. 1975 Mar 21;86(2):205–215. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90697-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz L. C., Gardner-Medwin A. R. The effect of synaptic activation on the extracellular potassium concentration in the hippocampal dentate area, in vitro. Brain Res. 1976 Aug 6;112(1):183–187. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90348-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch G. S., Dunwiddie T., Gribkoff V. Heterosynaptic depression: a postsynaptic correlate of long-term potentiation. Nature. 1977 Apr 21;266(5604):737–739. doi: 10.1038/266737a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch G. S., Gribkoff V. K., Deadwyler S. A. Long term potentiation is accompanied by a reduction in dendritic responsiveness to glutamic acid. Nature. 1976 Sep 9;263(5573):151–153. doi: 10.1038/263151a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert P., Lee K., West M., Deadwyler S., Lynch G. Stimulation-dependent release of 3H-adenosine derivatives from central axon terminals to target neurones. Nature. 1976 Apr 8;260(5551):541–542. doi: 10.1038/260541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzkroin P. A., Wester K. Long-lasting facilitation of a synaptic potential following tetanization in the in vitro hippocampal slice. Brain Res. 1975 May 16;89(1):107–119. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90138-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M., Bloom F. E. The action of norepinephrine in the rat hippocampus. I. Iontophoretic studies. Brain Res. 1974 May 31;72(1):79–97. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90652-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siggins G. R., Hoffer B. J., Bloom F. E. Studies on norepinephrine-containing afferents to Purkinje cells of rat cerebellum. 3. Evidence for mediation of norepinephrine effects by cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate. Brain Res. 1971 Feb 5;25(3):535–553. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90459-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer H. J., Gribkoff V. K., Cotman C. W., Lynch G. S. GDEE antagonism of iontophoretic amino acid excitations in the intact hippocampus and in the hippocampal slice preparation. Brain Res. 1976 Apr 9;105(3):471–481. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90594-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


