Abstract
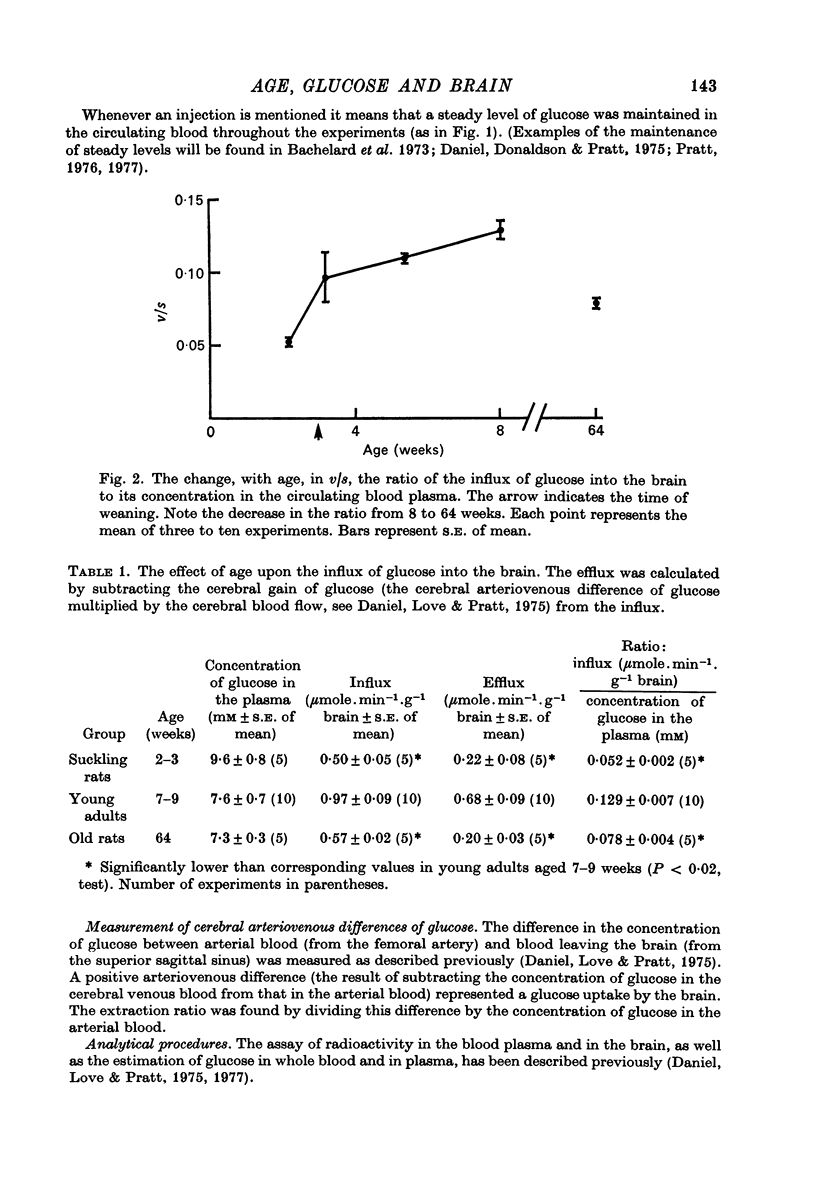
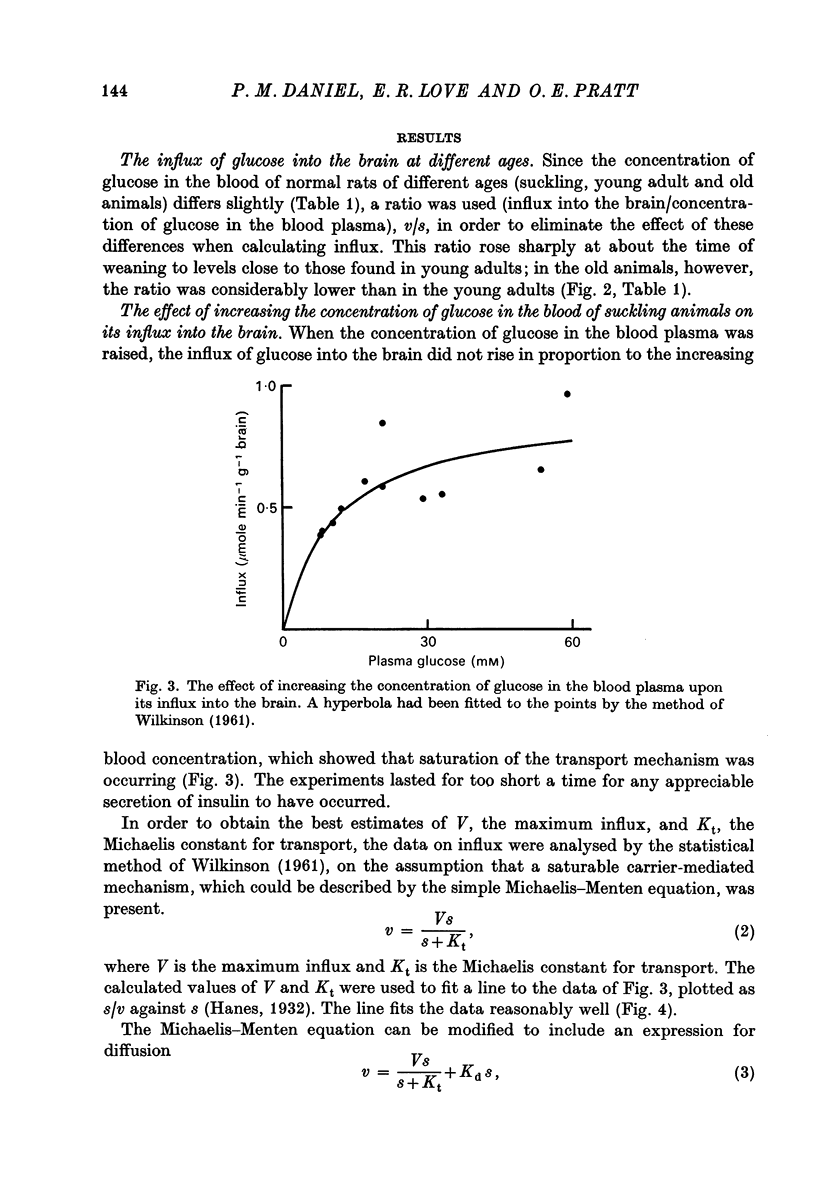
1. Rats aged from 1 to 116 weeks were studied. 2. Influx of glucose into the brain is low in suckling rats but rises after weaning, to reach its highest level in the young adult, thenceforward declining slowly as age increases. 3. The blood-brain barrier for glucose is fully developed in the rat by the age of 18 days and glucose enters the brain, at this stage, by carrier-mediated transport, as in the adult. 4. The results show that the low influx of glucose into the brain of the suckling animal is due to a low maximum rate of transport of glucose rather than to a low affinity of the carrier-molecule for glucose. 5. In the young adult rat, efflux of glucose back from the brain into the blood is greater than in either the suckling or the old animals. Thus the margin of safety, i.e. the extent to which the blood glucose can be reduced without affecting the utilization of glucose by the brain, is highest in the young adult. 6. The lower margin of safety in the suckling animals is compensated for by the high influx of the ketone bodies which provide an alternative source of energy at this age. In the old animals there is no alternative source of energy, so that the older brain is at greatest risk in hypoglycaemia.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachelard H. S., Daniel P. M., Love E. R., Pratt O. E. The transport of glucose into the brain of the rat in vivo. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1973 Feb 27;183(1070):71–82. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1973.0005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz A. L., Gilboe D. D., Yudilevich D. L., Drewes L. R. Kinetics of unidirectional glucose transport into the isolated dog brain. Am J Physiol. 1973 Sep;225(3):586–592. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.225.3.586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer J. E., Braun L. D., Oldendorf W. H. Changes during development in transport processes of the blood-brain barrier. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 2;448(4):633–637. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90120-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crone C. Facilitated transfer of glucose from blood into brain tissue. J Physiol. 1965 Nov;181(1):103–113. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel P. M., Donaldson J., Pratt O. E. A method for injecting substances into the circulation to reach rapidly and to maintain a steady level. With examples of its application in the study of carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism. Med Biol Eng. 1975 Mar;13(2):214–227. doi: 10.1007/BF02477731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel P. M., Donaldson J., Pratt O. E. Infusion schedules for prescribed blood concentration time courses. J Appl Physiol. 1976 Oct;41(4):608–608. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1976.41.4.608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
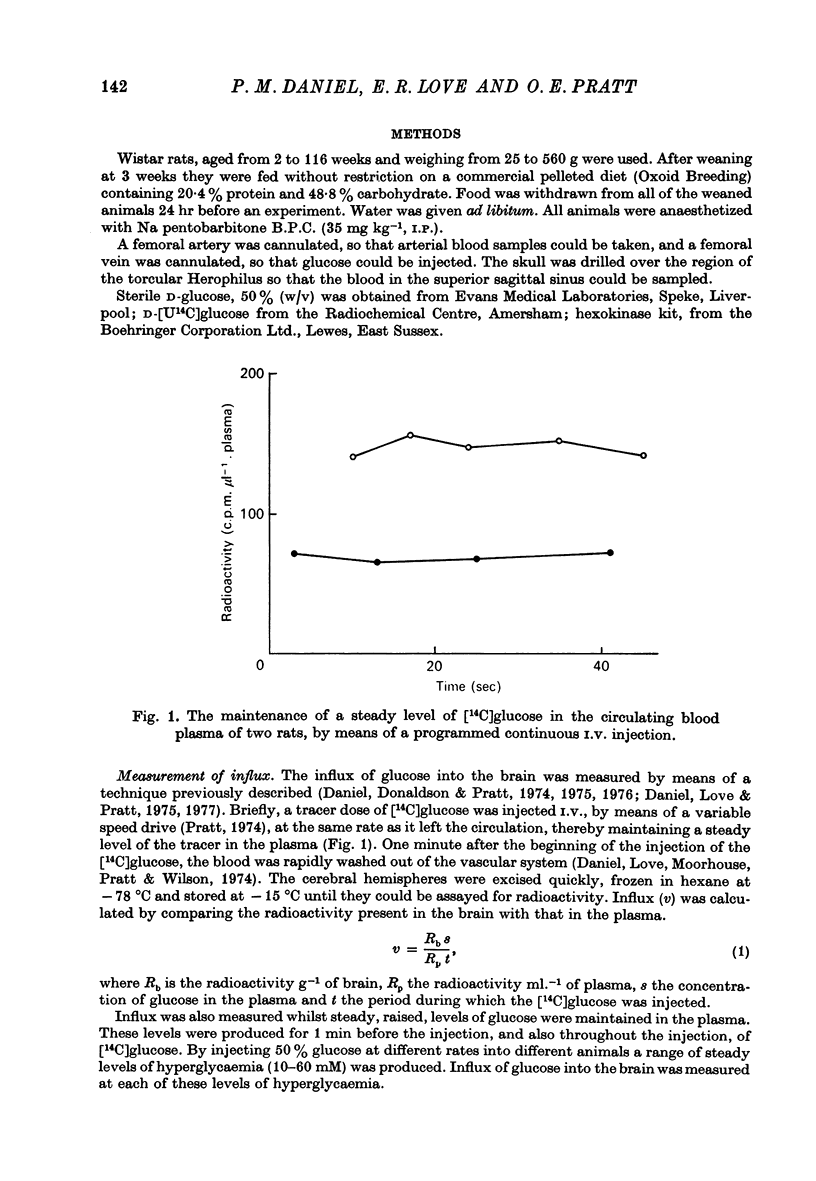
- Daniel P. M., Donaldson J., Pratt O. E. The rapid achievement and maintenance of a steady level of an injected substance in the blood plasma. J Physiol. 1974 Mar;237(2):8P–9P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel P. M., Love E. R., Moorehouse S. R., Pratt O. E., Wilson P. Factors influencing utilisation of ketone-bodies by brain in normal rats and rats with ketoacidosis. Lancet. 1971 Sep 18;2(7725):637–638. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)80073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel P. M., Love E. R., Moorhouse S. R., Pratt O. E., Wilson P. A method for rapidly washing the blood out of an organ or tissue of the anaesthetized living animal. J Physiol. 1974 Mar;237(2):11P–12P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel P. M., Love E. R., Moorhouse S. R., Pratt O. E., Wilson P. The movement of ketone bodies, glucose, pyruvate and lactate between the blood and the brain of rats. J Physiol. 1972 Feb;221(1):22P–23P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel P. M., Love E. R., Pratt O. E. Insulin and the way the brain handles glucose. J Neurochem. 1975 Oct;25(4):471–476. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1975.tb04352.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel P. M., Love E. R., Pratt O. E. The influence of insulin upon the metabolism of glucose by the brain. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Feb 11;196(1122):85–104. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaitonde M. K., Richter D. Changes with age in the utilization of glucose carbon in liver and brain. J Neurochem. 1966 Dec;13(12):1309–1316. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb04293.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
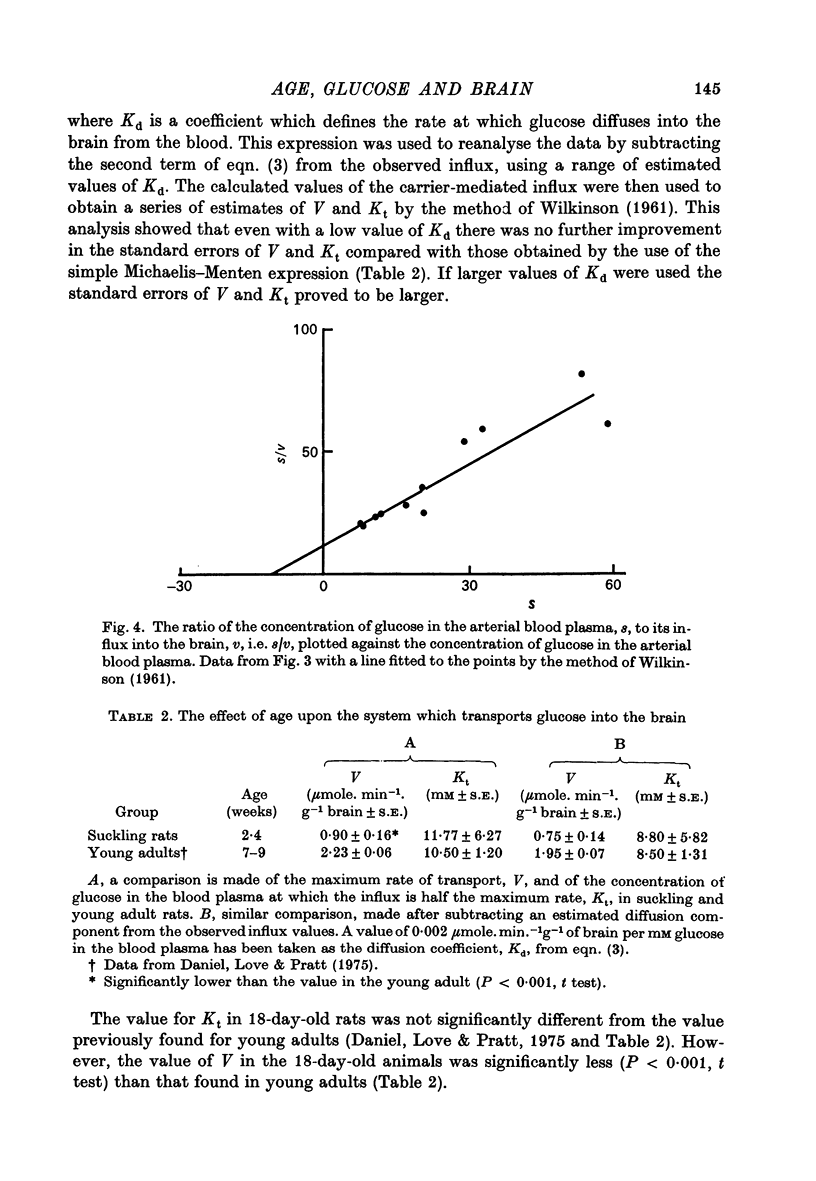
- Hanes C. S. Studies on plant amylases: The effect of starch concentration upon the velocity of hydrolysis by the amylase of germinated barley. Biochem J. 1932;26(5):1406–1421. doi: 10.1042/bj0261406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins R. A., Williamson D. H., Krebs H. A. Ketone-body utilization by adult and suckling rat brain in vivo. Biochem J. 1971 Mar;122(1):13–18. doi: 10.1042/bj1220013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus H., Schlenker S., Schwedesky D. Developmental changes of cerebral ketone body utilization in human infants. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1974 Feb;355(2):164–170. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1974.355.1.164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore T. J., Lione A. P., Sugden M. C., Regen D. M. Beta-hydroxybutyrate transport in rat brain: developmental and dietary modulations. Am J Physiol. 1976 Mar;230(3):619–630. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.3.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldendorf W. H. Brain uptake of radiolabeled amino acids, amines, and hexoses after arterial injection. Am J Physiol. 1971 Dec;221(6):1629–1639. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.6.1629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardridge W. M., Oldendorf W. H. Kinetics of blood-brain transport of hexoses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;382(3):377–392. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90279-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt O. E. An electronically controlled syringe drive for giving an injection at a variable rate according to a preset programme. J Physiol. 1974 Mar;237(2):5P–6P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON G. N. Statistical estimations in enzyme kinetics. Biochem J. 1961 Aug;80:324–332. doi: 10.1042/bj0800324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


