Abstract
1. Intracellular recordings were made from the presynaptic regions of the photoreceptors of the median ocellus of the giant barnacle, Balanus nubilus.
2. Millivolt changes in membrane potential near the dark resting level in the terminals elicit post-synaptic activity and consequently must be sufficient to modulate transmitter release from these endings.
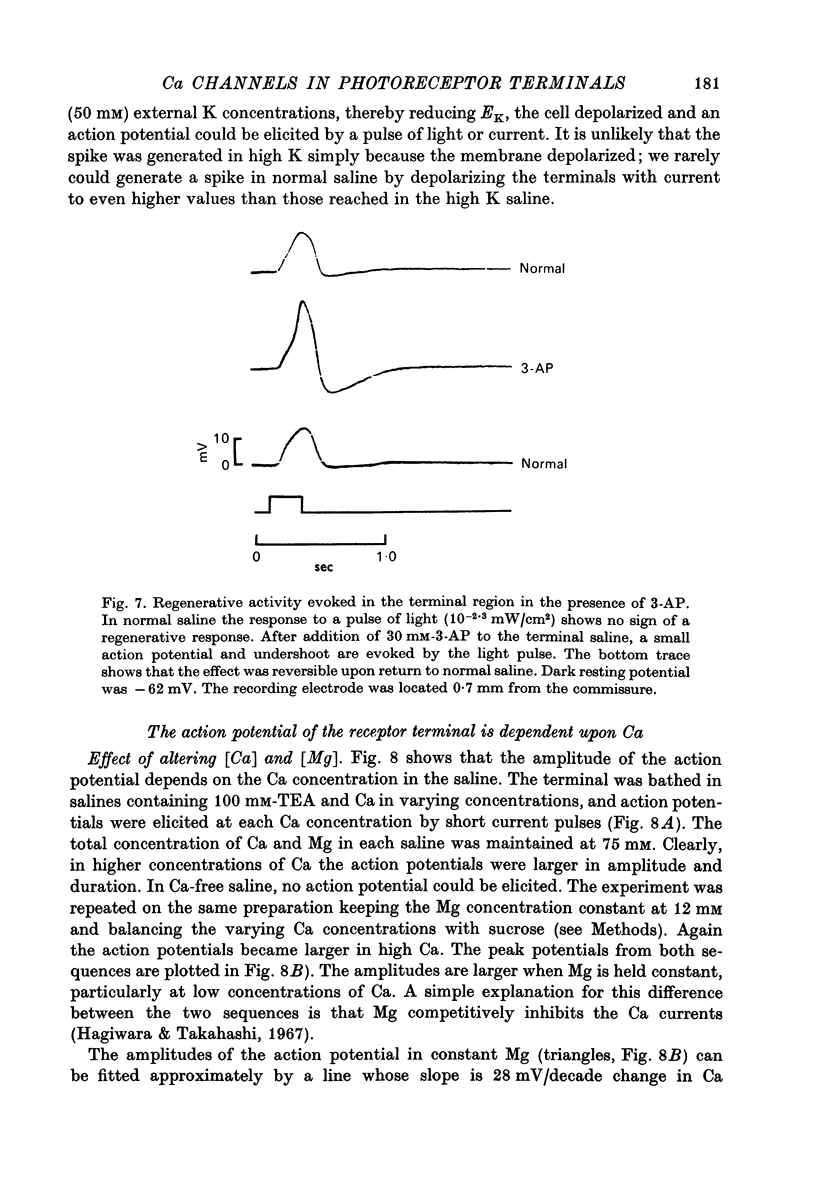
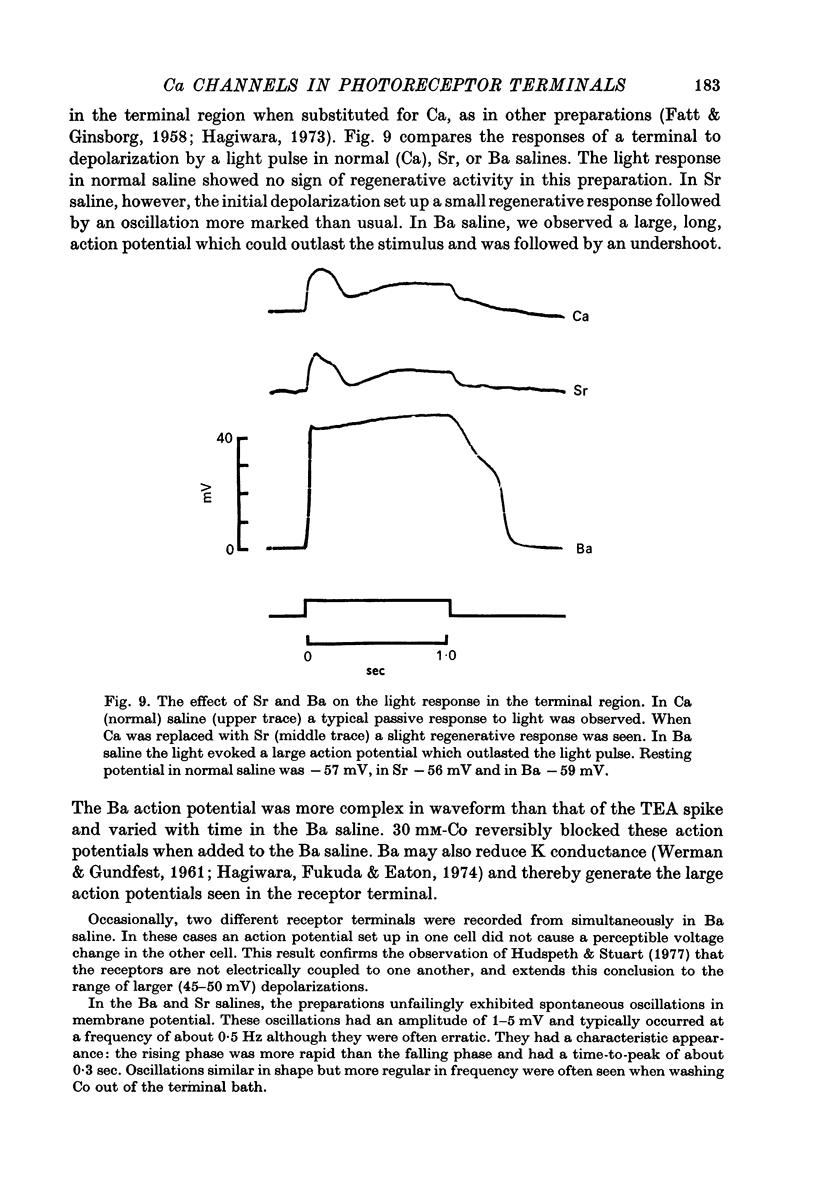
3. In normal saline the terminal voltage usually changes in a graded manner to increasing intensities of illumination of the cell. When the terminal region is superfused with saline containing TEA, 3-AP or high concentrations of K, an all-or-none action potential can be elicited consistently by light or injected current.
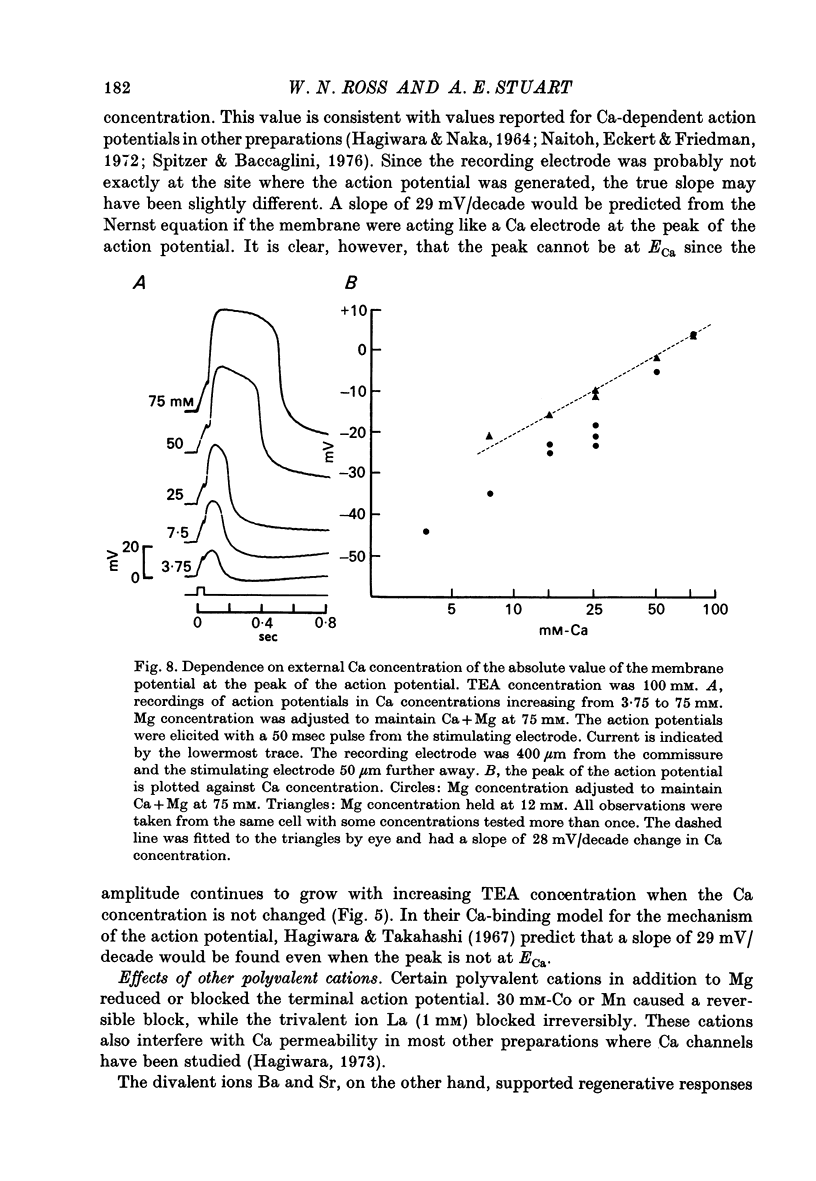
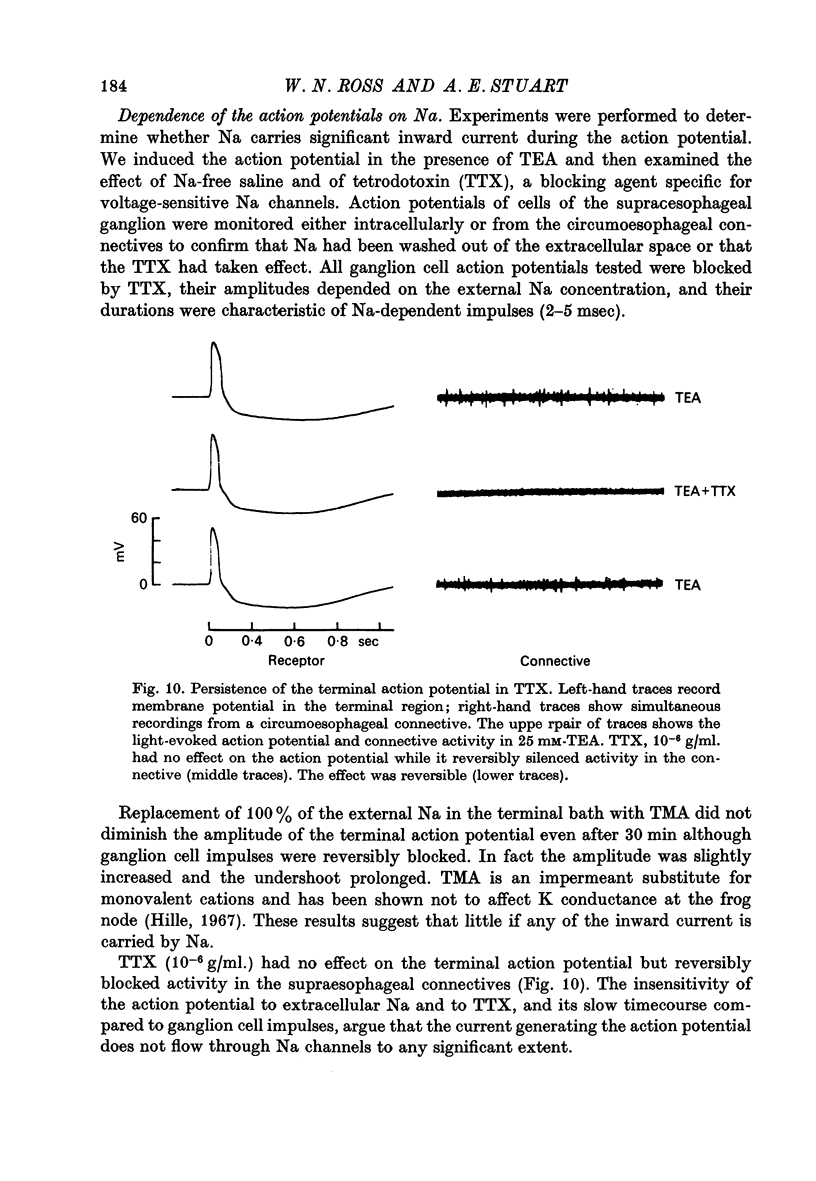
4. The peak value of this action potential depends on the Ca concentration in the saline. The action potential can be generated if Sr or Ba ions replace Ca, but is reduced or blocked if Mg, Co, or Mn ions are added to the saline. It is virtually unaffected by TTX or replacement of Na with TMA ions in the saline. These results suggest that Ca carries most or all of the inward current during the action potential.
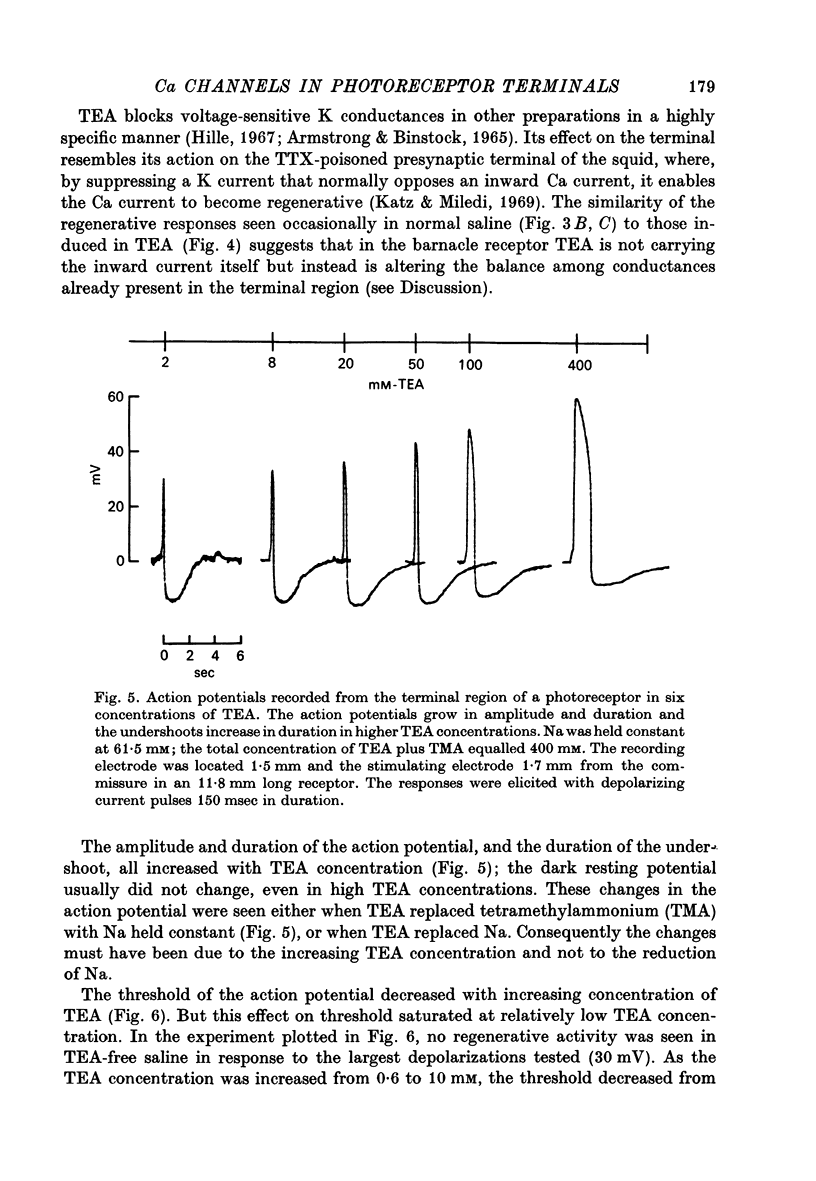
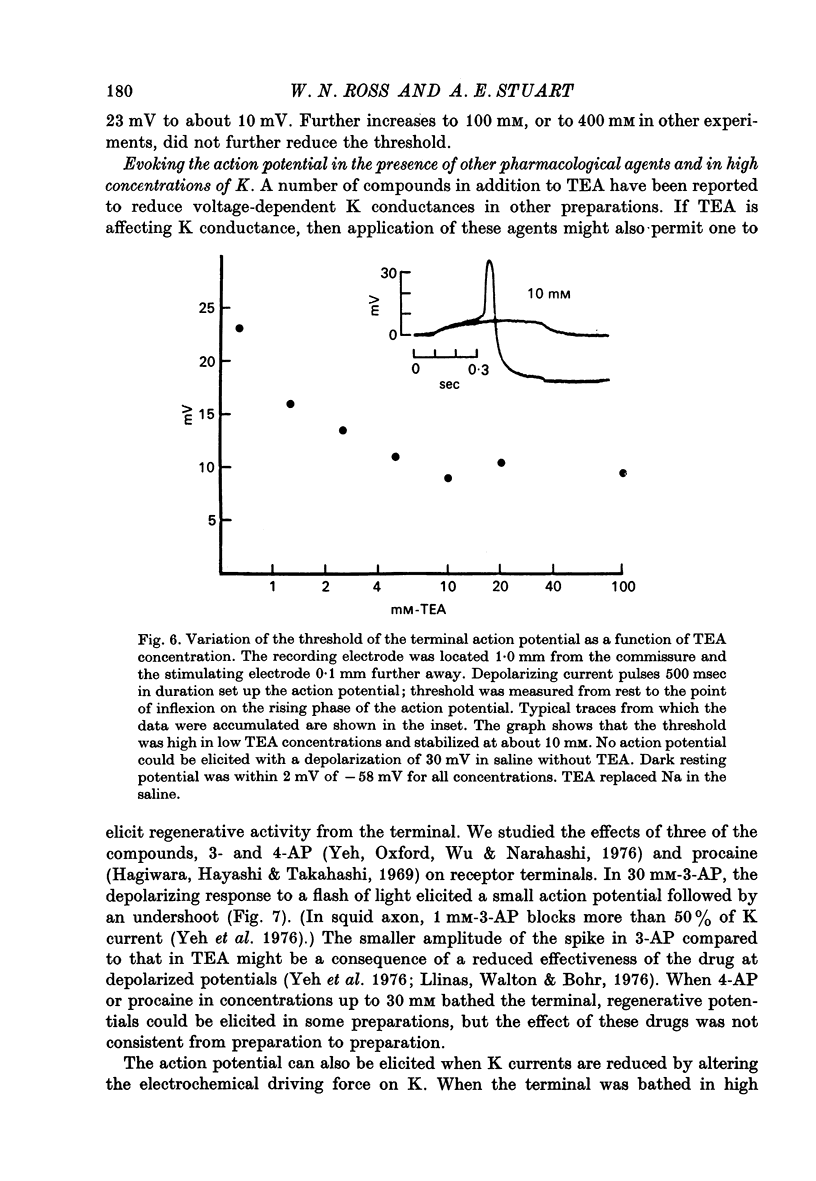
5. The action potential is followed by a large undershoot which can last several seconds. The amplitude and duration of the action potential and the duration of the undershoot all grow in increasing concentrations of TEA up to 400 mM, the highest concentration tested. The threshold for the action potential decreases as the concentration of TEA is increased to 10 mM; increasing the concentration further has no effect on the threshold. These observations suggest that TEA blocks a voltage-sensitive potassium conductance at low concentrations but has less effect on the current responsible for the undershoot.
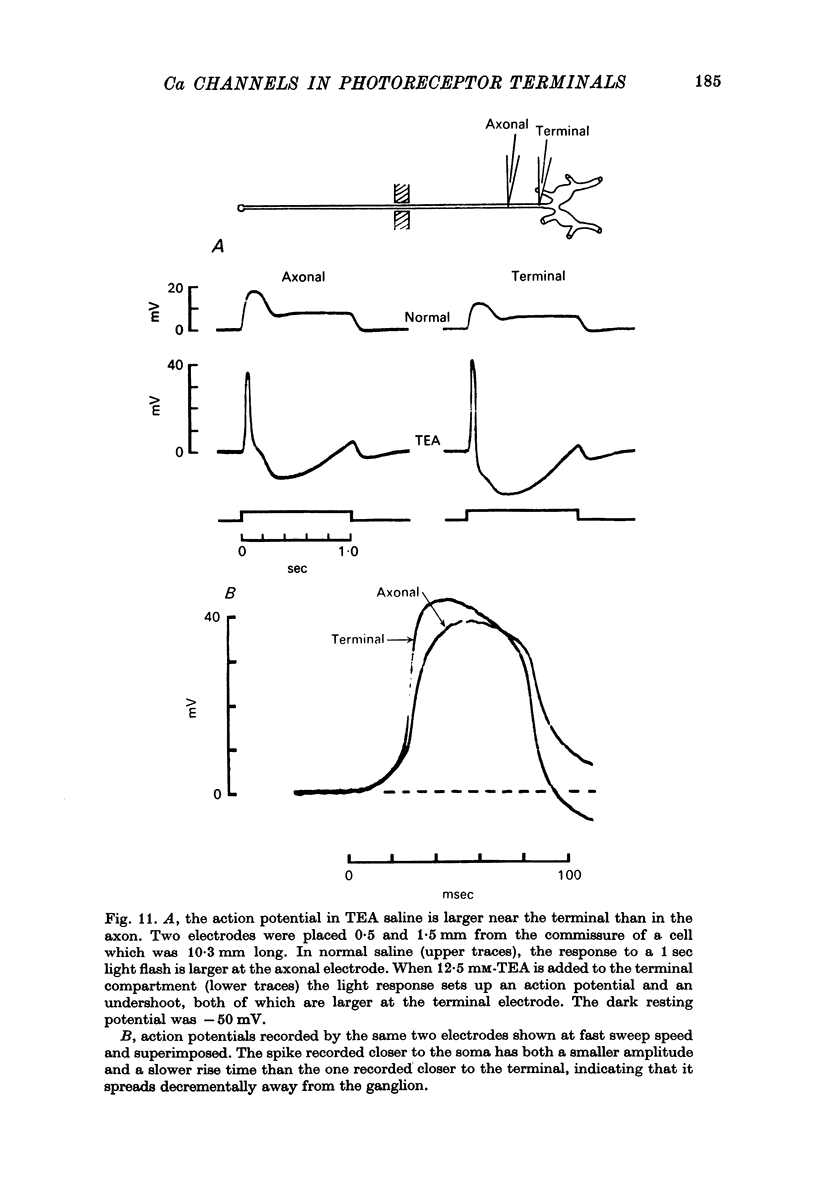
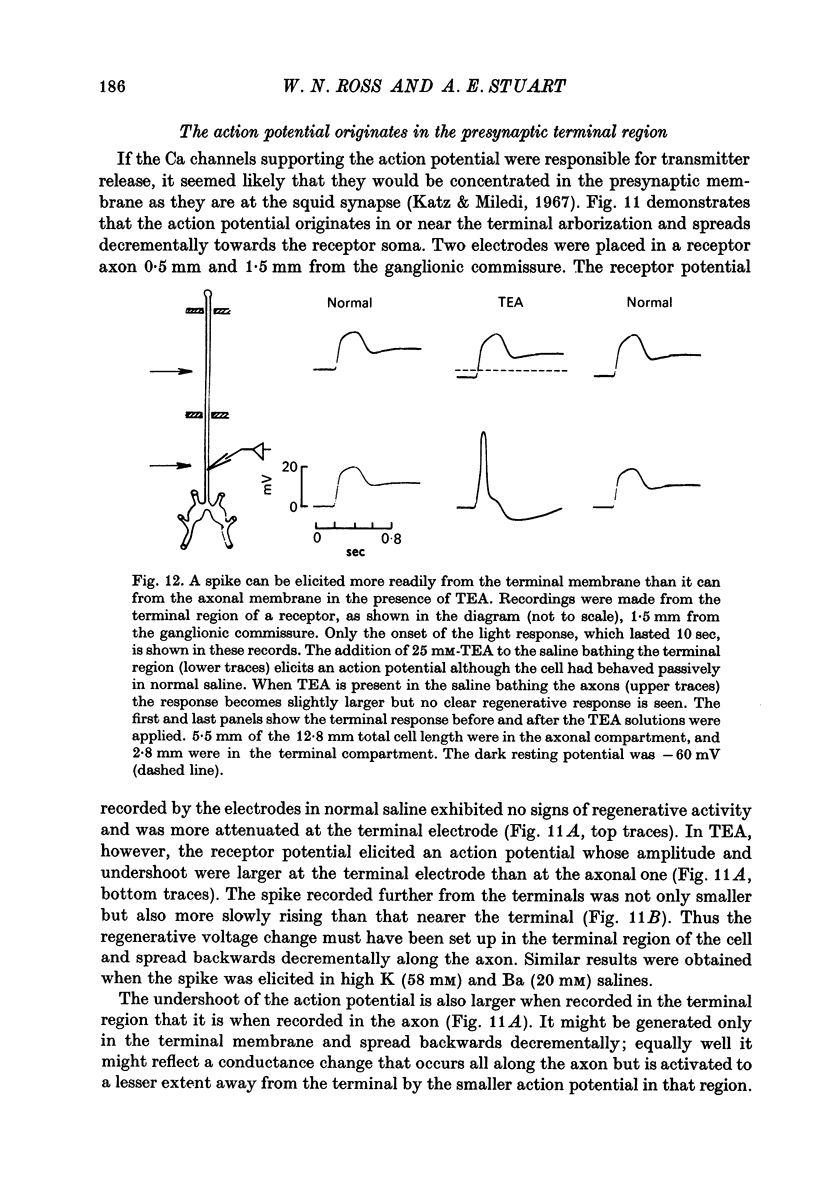
6. Electrophysiological and pharmacological evidence suggests that the Ca channels are concentrated in the presynaptic terminals of this photoreceptor.
Full text
PDF

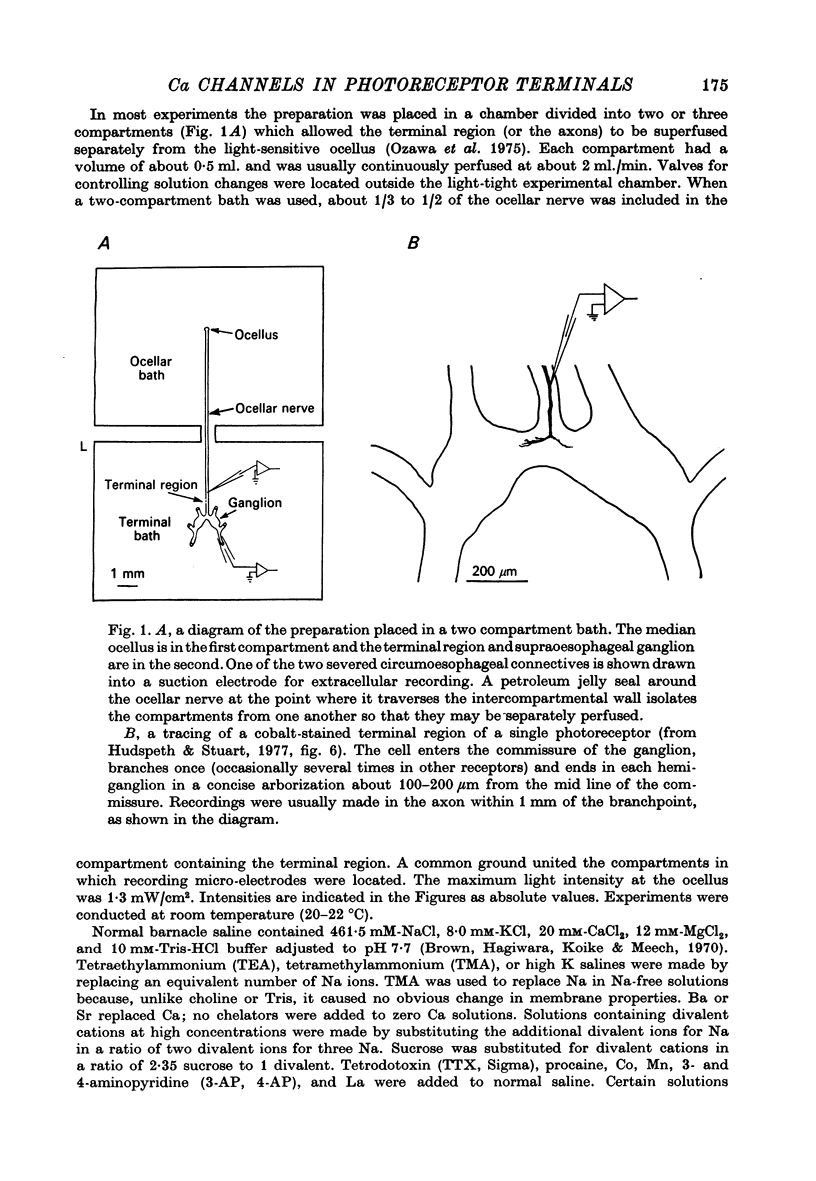
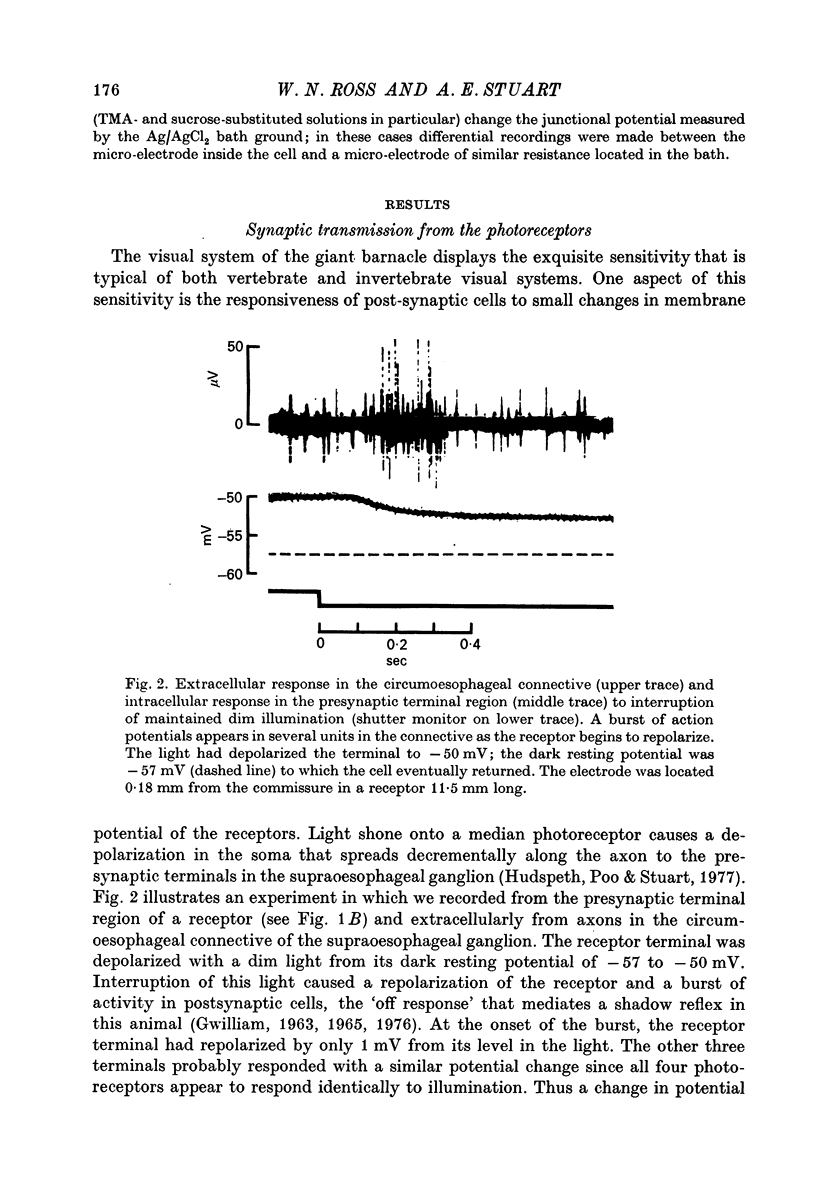
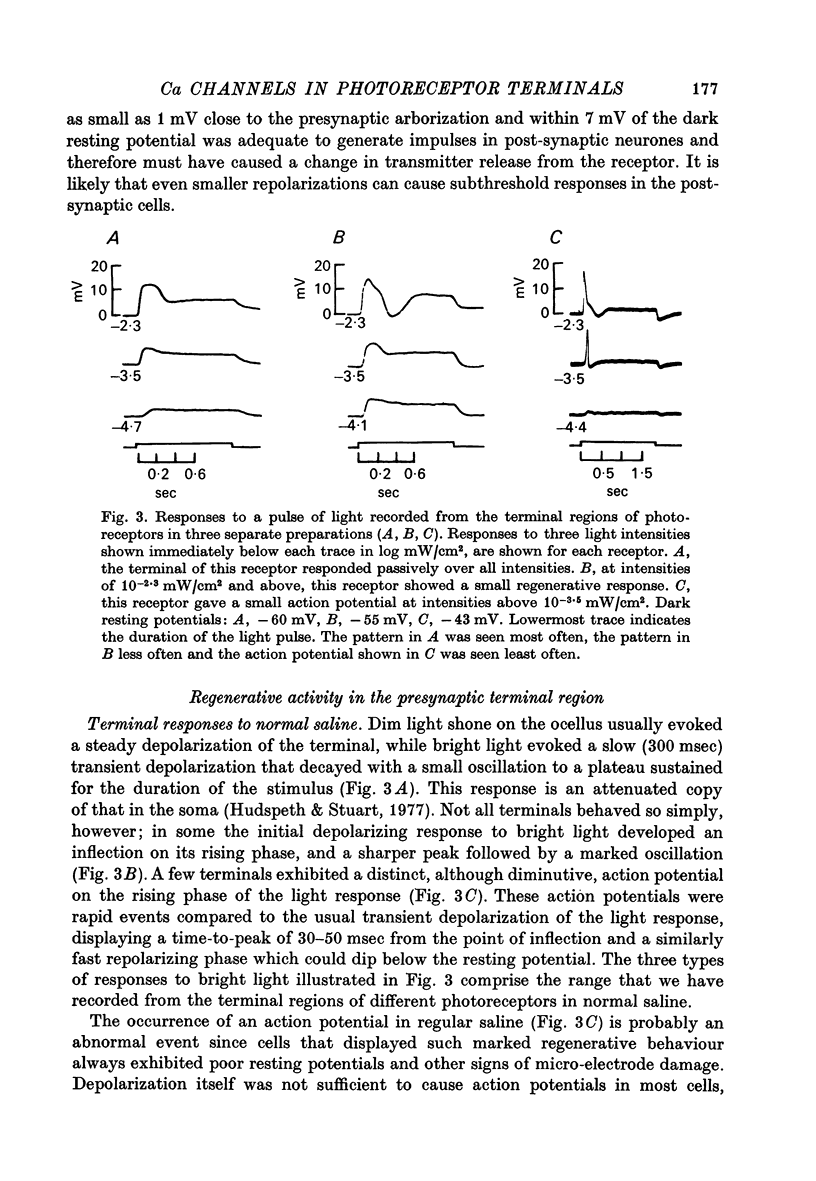
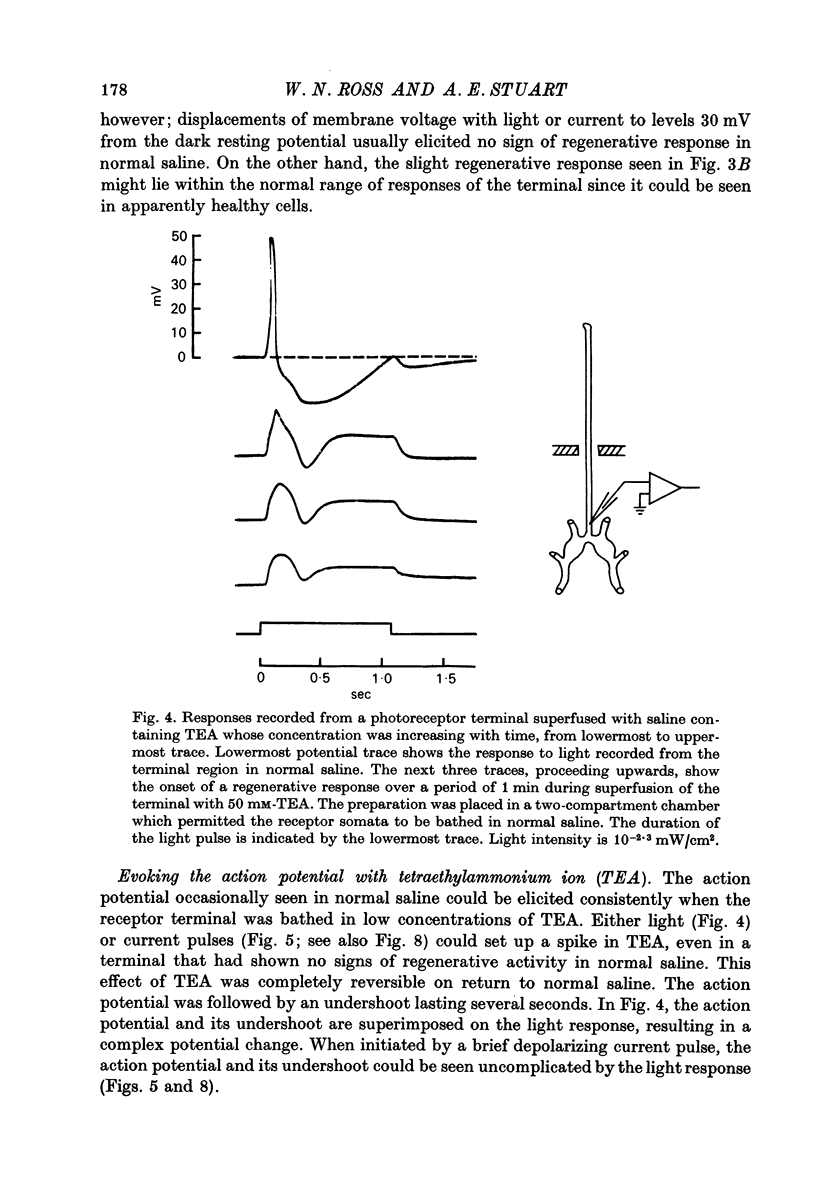





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARMSTRONG C. M., BINSTOCK L. ANOMALOUS RECTIFICATION IN THE SQUID GIANT AXON INJECTED WITH TETRAETHYLAMMONIUM CHLORIDE. J Gen Physiol. 1965 May;48:859–872. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.5.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashmore J. F., Falk G. Absolute sensitivity of rod bipolar cells in a dark-adapted retina. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):248–249. doi: 10.1038/263248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auerbach A. A., Bennett M. V. Chemically mediated transmission at a giant fiber synapse in the central nervous system of a vertebrate. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Feb;53(2):183–210. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.2.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULLOCK T. H., HAGIWARA S. Intracellular recording from the giant synapse of the squid. J Gen Physiol. 1957 Mar 20;40(4):565–577. doi: 10.1085/jgp.40.4.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Meves H., Ridgway E. B. Calcium entry in response to maintained depolarization of squid axons. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):527–548. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett E. F., Barret J. N. Separation of two voltage-sensitive potassium currents, and demonstration of a tetrodotoxin-resistant calcium current in frog motoneurones. J Physiol. 1976 Mar;255(3):737–774. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Fettiplace R. Transmission of signals from photoreceptors to ganglion cells in the eye of the turtle. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:529–536. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown H. M., Hagiwara S., Koike H., Meech R. M. Membrane properties of a barnacle photoreceptor examined by the voltage clamp technique. J Physiol. 1970 Jun;208(2):385–413. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush B. M., Cannone A. J. A stretch reflex in crabs evoked by muscle receptor potentials in non-impulsive afferents. J Physiol. 1973 Jul;232(2):95P–96P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., GINSBORG B. L. The ionic requirements for the production of action potentials in crustacean muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1958 Aug 6;142(3):516–543. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain G. L., Granda A. M., Maxwell J. M. Voltage signal of photoreceptors at visual threshold. Nature. 1977 Jan 13;265(5590):181–183. doi: 10.1038/265181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S. Ca spike. Adv Biophys. 1973;4:71–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Fukuda J., Eaton D. C. Membrane currents carried by Ca, Sr, and Ba in barnacle muscle fiber during voltage clamp. J Gen Physiol. 1974 May;63(5):564–578. doi: 10.1085/jgp.63.5.564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Hayashi H., Takahashi K. Calcium and potassium currents of the membrane of a barnacle muscle fibre in relation to the calcium spike. J Physiol. 1969 Nov;205(1):115–129. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Takahashi K. Surface density of calcium ions and calcium spikes in the barnacle muscle fiber membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Jan;50(3):583–601. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.3.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The selective inhibition of delayed potassium currents in nerve by tetraethylammonium ion. J Gen Physiol. 1967 May;50(5):1287–1302. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.5.1287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudspeth A. J., Poo M. M., Stuart A. E. Passive signal propagation and membrane properties in median photoreceptors of the giant barnacle. J Physiol. 1977 Oct;272(1):25–43. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudspeth A. J., Stuart A. E. Morphology and responses to light of the somata, axons, and terminal regions of individual photoreceptors of the giant barnacle. J Physiol. 1977 Oct;272(1):1–23. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. A study of synaptic transmission in the absence of nerve impulses. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(2):407–436. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Tetrodotoxin-resistant electric activity in presynaptic terminals. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(2):459–487. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusano K., Livengood D. R., Werman R. Correlation of transmitter release with membrane properties of the presynaptic fiber of the squid giant synapse. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Dec;50(11):2579–2601. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.11.2579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Steinberg I. Z., Walton K. Presynaptic calcium currents and their relation to synaptic transmission: voltage clamp study in squid giant synapse and theoretical model for the calcium gate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2918–2922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Walton K., Bohr V. Synaptic transmission in squid giant synapse after potassium conductance blockage with external 3- and 4-aminopyridine. Biophys J. 1976 Jan;16(1):83–86. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85664-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin A. R., Ringham G. L. Synaptic transfer at a vertebrate central nervous system synapse. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(2):409–426. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W., Standen N. B. Potassium activation in Helix aspersa neurones under voltage clamp: a component mediated by calcium influx. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):211–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson M. Oscillator neurons in crustacean ganglia. Science. 1971 Mar 19;171(3976):1170–1173. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3976.1170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naitoh Y., Eckert R., Friedman K. A regenerative calcium response in Paramecium. J Exp Biol. 1972 Jun;56(3):667–681. doi: 10.1242/jeb.56.3.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa S., Hagiwara S., Nicolaysen K., Stuart A. E. Signal transmission from photoreceptors to ganglion cells in the visual system of the giant barnacle. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:563–570. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson K. G., Fourtner C. R. Nonspiking interneurons in walking system of the cockroach. J Neurophysiol. 1975 Jan;38(1):33–52. doi: 10.1152/jn.1975.38.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ripley S. H., Bush B. M., Roberts A. Crab muscle receptor which responds without impulses. Nature. 1968 Jun 22;218(5147):1170–1171. doi: 10.1038/2181170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt R. O., Dev P., Smith B. H. Electrotonic processing of information by brain cells. Science. 1976 Jul 9;193(4248):114–120. doi: 10.1126/science.180598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw S. R. Decremental conduction of the visual signal in barnacle lateral eye. J Physiol. 1972 Jan;220(1):145–175. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzer N. C., Baccaglini P. I. Development of the action potential in embryo amphibian neurons in vivo. Brain Res. 1976 May 14;107(3):610–616. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90148-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. H. Three pharmacologically distinct potassium channels in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(2):465–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WERMAN R., GRUNDFEST H. Graded and all-or-none electrogenesis in arthropod muscle. II. The effects of alkali-earth and onium ions on lobster muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1961 May;44:997–1027. doi: 10.1085/jgp.44.5.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh J. Z., Oxford G. S., Wu C. H., Narahashi T. Dynamics of aminopyridine block of potassium channels in squid axon membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Nov;68(5):519–535. doi: 10.1085/jgp.68.5.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


