Abstract
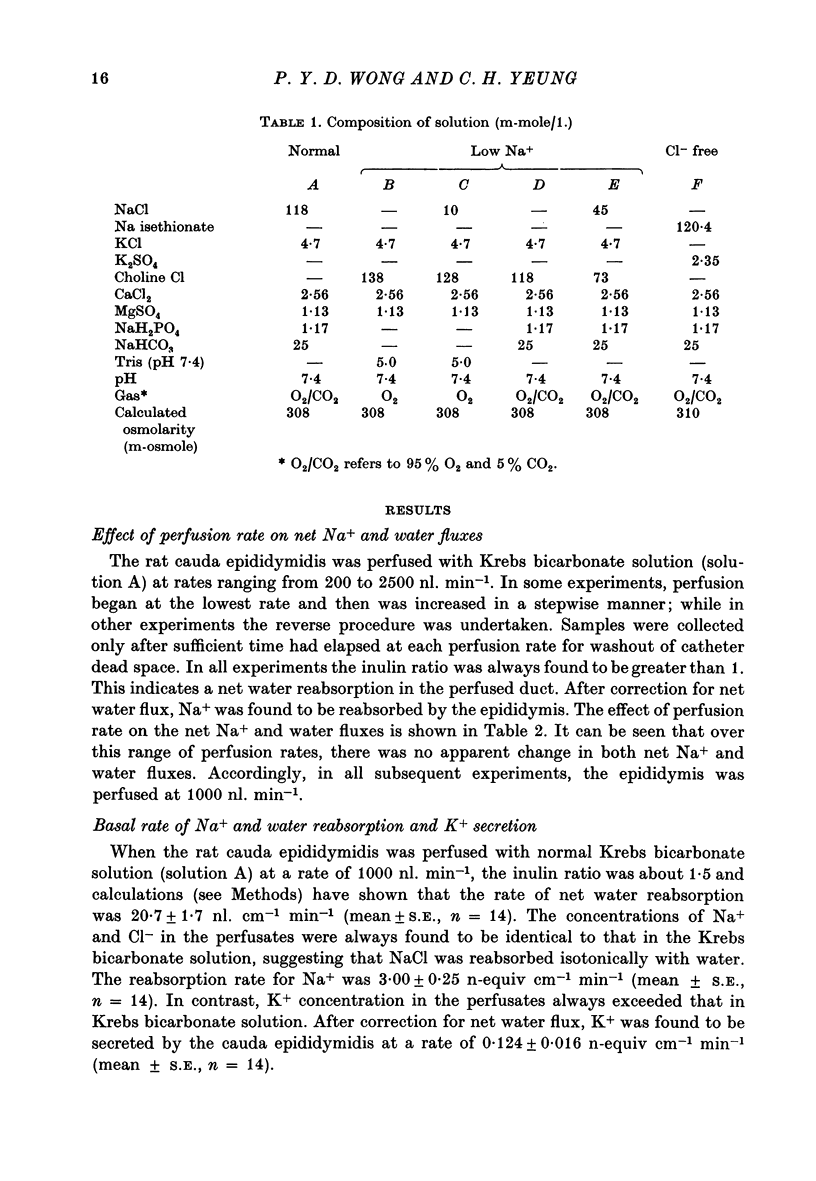
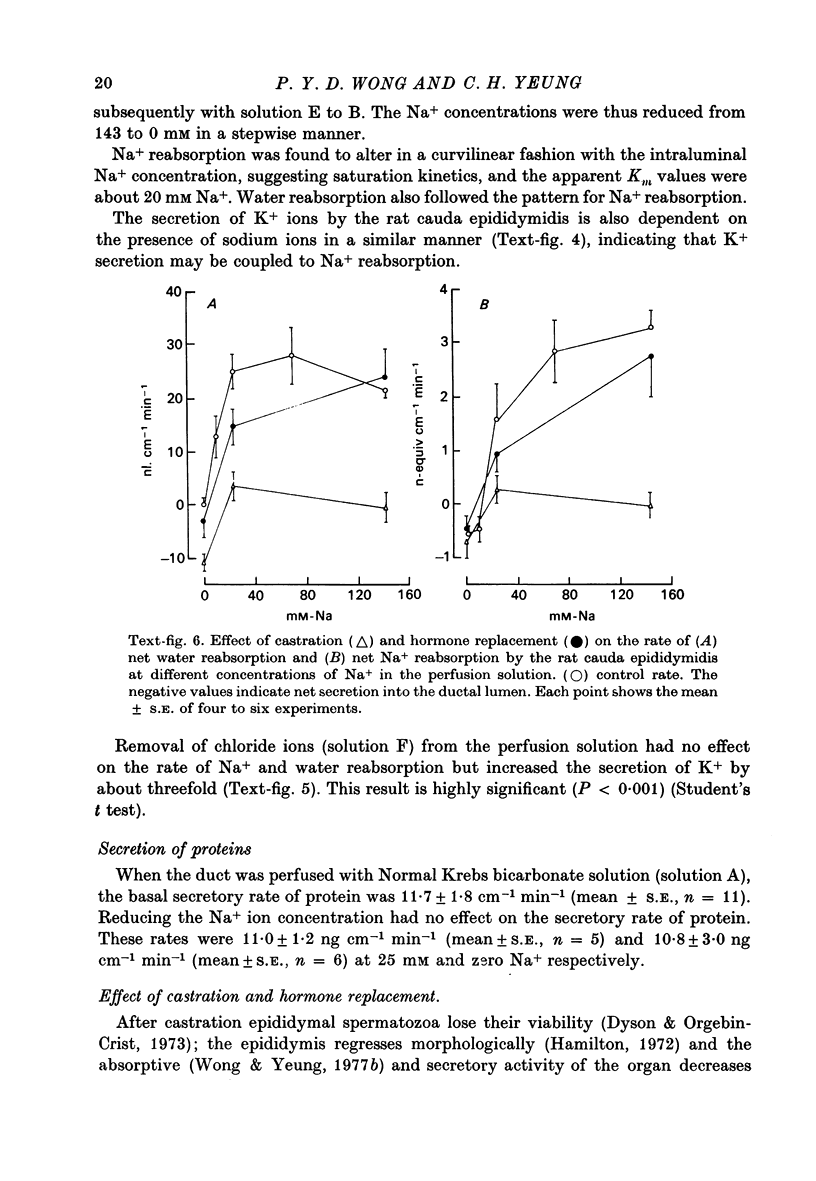
1. A microperfusion technique has been developed to study transport processes in the rat cauda epididymidis in vivo. 2. Na+ and water were found to be reabsorbed by the perfused rat cauda epididymidis at the rates of 3.000 +/- 0.25 n-equiv cm-1 min-1 (mean +/- S.E., n = 14) and 20.7 +/- 1.7 nl. cm-1 min-1 (mean +/- S.E., n = 14) respectively. Reabsorption of Na+ was isotonic. 3. K+ was found to be secreted into the ductal lumen at the rate of 0.124 +/- 0.016 n-equiv cm-1 min-1 (mean +/- S.E., n = 14). 4. Na+ reabsorption and water reabsorption were abolished by removing Na+ ions from the perfusion medium. The dependence of rate of net Na+ reabsorption on the intraluminal Na+ ion concentration showed saturation kinetics, with the apparent Km values of about 20 mM Na+. The dependence of water reabsorption on the intraluminal Na+ ion concentration also followed closely that of Na+. 5. Application of amiloride 10(-4) M) to the perfusion fluid abolished both Na+ and water reabsorption by the rat cauda epididymidis. 6. Removal of chloride from the perfusion fluid had no effect on Na+ and water reabsorption but increased the K+ secretion rate by threefold. 7. Proteins were also found to be secreted by the rat cauda epididymidis at a rate of 11.7 +/- 1.8 ng cm-1 min-1 (mean +/- S.E., n = 11). The secretory rate was not dependent on the intraluminal Na+ ion concentration. 8. Castration in rats abolished the reabsorption of Na+ and water and secretion of K+ and proteins by the rate cauda epididymidis. These effects could be reversed by injecting testosterone propionate into castrated rats. 9. The possible role of these transport processes in sperm maturation is discussed.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed K., Williams-Ashman H. G. Studies on the microsoml sodium-plus-potassium ion-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase system in rat ventral prostate. Biochem J. 1969 Aug;113(5):829–836. doi: 10.1042/bj1130829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amann R. P., Killian G. J., Benton A. W. Differences in the electrophoretic characteristics of bovine rete testis fluid and plasma from the cauda epididymidis. J Reprod Fertil. 1973 Nov;35(2):321–330. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0350321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammon H. V., Phillips S. F. Inhibition of ileal water absorption by intraluminal fatty acids. Influence of chain length, hydroxylation, and conjugation of fatty acids. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jan;53(1):205–210. doi: 10.1172/JCI107539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry H., Flower R. J. The assay of endogenous cholecystokinin and factors influencing its release in the dog and cat. Gastroenterology. 1971 Mar;60(3):409–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R. Hormones of the gastrointestinal tract. Br Med Bull. 1974 Jan;30(1):62–67. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boden G., Essa N., Owen O. E. Effects of intraduodenal amino acids, fatty acids, and sugars on secretin concentrations. Gastroenterology. 1975 Apr;68(4 Pt 1):722–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böttger I., Dobbs R., Faloona G. R., Unger R. H. The effects of triglyceride absorption upon glucagon, insulin, and gut glucagon-like immunoreactivity. J Clin Invest. 1973 Oct;52(10):2532–2541. doi: 10.1172/JCI107444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CEREIJIDO M., HERRERA F. C., FLANIGAN W. J., CURRAN P. F. THE INFLUENCE OF NA CONCENTRATION ON NA TRANSPORT ACROSS FROG SKIN. J Gen Physiol. 1964 May;47:879–893. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.5.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRABO B., GUSTAFSSON B. DISTRIBUTION OF SODIUM AND POTASSIUM AND ITS RELATION TO SPERM CONCENTRATION IN THE EPIDIDYMAL PLASMA OF THE BULL. J Reprod Fertil. 1964 Jun;7:337–345. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0070337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURRAN P. F., SOLOMON A. K. Ion and water fluxes in the ileum of rats. J Gen Physiol. 1957 Sep 20;41(1):143–168. doi: 10.1085/jgp.41.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameo M. S., Blaquier J. A. Androgen-controlled specific proteins in rat epididymis. J Endocrinol. 1976 Apr;69(1):47–55. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0690047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavarzan A., Teixeira A. S., Sarles H., Palasciano G., Tiscornia O. Action of intragastric ethanol on the pancreatic secretion of conscious rats. Digestion. 1975;13(3):145–152. doi: 10.1159/000197703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung Y. M., Hwang J. C., Wong P. Y. In vitro measurement of rate of fluid secretion in rat isolated seminiferous tubules: effects of metabolic inhibitors and ions. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;269(1):1–15. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung Y. M., Hwang J. C., Wong P. Y. Proceedings: In vitro measurement of the secretory rate in isolated seminiferous tubules of rats. J Physiol. 1976 May;257(1):17P–18P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline W. S., Lorenzsonn V., Benz L., Bass P., Olsen W. A. The effects of sodium ricinoleate on small intestinal function and structure. J Clin Invest. 1976 Aug;58(2):380–390. doi: 10.1172/JCI108482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W., Wong P. Y. The effect of metal ions and antidiuretic hormone on oxygen consumption in toad bladder. J Physiol. 1971 Dec;219(1):39–56. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEBRAY C., DE LA TOUR J., VAILLE C., ROZE C., SOUCHARD M. [Contribution to the study of the biliary and external pancreatic secretion in the rat]. J Physiol (Paris) 1962 May-Jun;54:459–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIAMOND J. M. The reabsorptive function of the gall-bladder. J Physiol. 1962 May;161:442–473. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. M., Tormey J. M. Studies on the structural basis of water transport across epithelial membranes. Fed Proc. 1966 Sep-Oct;25(5):1458–1463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyck W. P. Influence of intrajejunal glucose on pancreatic exocrine function in man. Gastroenterology. 1971 May;60(5):864–869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyck W. P., Texter E. C., Jr, Lasater J. M., Hightower N. C., Jr Influence of glucagon on pancreatic exocrine secretion in man. Gastroenterology. 1970 Apr;58(4):532–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson A. L., Orgebin-Crist M. C. Effect of hypophysectomy, castration and androgen replacement upon the fertilizing ability of rat epididymal spermatozoa. Endocrinology. 1973 Aug;93(2):391–402. doi: 10.1210/endo-93-2-391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds C. J., Marriott J. C. The effect of aldosterone and adrenalectomy on the electrical potential difference of rat colon and on the transport of sodium, potassium, chloride and bicarbonate. J Endocrinol. 1967 Dec;39(4):517–531. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0390517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frame C. M. The contribution of the distal gastrointestinal tract to glucagon-like immunoreactivity secretion in the rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1976 Sep;152(4):667–670. doi: 10.3181/00379727-152-39464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giebisch G. Functional organization of proximal and distal tubular electrolyte transport. Nephron. 1969;6(3):260–281. doi: 10.1159/000179733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green G. M., Lyman R. L. Feedback regulation of pancreatic enzyme secretion as a mechanism for trypsin inhibitor-induced hypersecretion in rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 May;140(1):6–12. doi: 10.3181/00379727-140-36384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hage G., Tiscornia O., Palasciano G., Sarles H. Inhibition of pancreatic exocrine secretion by intra-colonic oleic acid infusion in the dog. Biomedicine. 1974 Jun 10;21(6):263–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotz J., Zwicker M., Minne H., Ziegler R. Pancreatic enzyme secretion in the conscious rat. Method and application. Pflugers Arch. 1975;353(2):171–189. doi: 10.1007/BF00599877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howards S. S., Jessee S. J., Johnson A. L. Micropuncture studies of the blood-seminiferous tubule barrier. Biol Reprod. 1976 Apr;14(3):264–269. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod14.3.264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessee S. J., Howards S. S. A survey of sperm, potassium and sodium concentrations in the tubular fluid of the hamster epididymis. Biol Reprod. 1976 Dec;15(5):626–631. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod15.5.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. Absorption and secretion in the cauda epididymidis of the rabbit and the effects of degenerating spermatozoa on epididymal plasma after castration. J Endocrinol. 1974 Oct;63(1):157–165. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0630157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R., Glover T. D. The collection and composition of epididymal plasma from the cauda epididymidis of the rabbit. J Reprod Fertil. 1973 Sep;34(3):395–403. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0340395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konturek S. J., Pucher A., Radecki T. Comparison of vasoactive intestinal peptide and secretin in stimulation of pancreatic secretion. J Physiol. 1976 Feb;255(2):497–509. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskimies A. I., Kormano M. Proteins in fluids from different segments of the rat epididymis. J Reprod Fertil. 1975 May;43(2):345–348. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0430345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskimies A. I., Kormano M. The proteins in fluids from the seminiferous tubules and rete testis of the rat. J Reprod Fertil. 1973 Sep;34(3):433–434. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0340433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laporte J. C., Trémolières J. Action de la trypsine et des inhibiteurs trypsiques sur la sécrétion pancréatique. Nutr Metab. 1973;15(3):192–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laugier R., Sarles H. Action of oleic acid on the exocrine pancreatic secretion of the conscious rat: evidence for an anti-cholecystokinin-pancreozymin factor. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;271(1):81–92. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leaf A. Transepithelial transport and its hormonal control in toad bladder. Ergeb Physiol. 1965;56:216–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine N., Marsh D. J. Micropuncture studies of the electrochemical aspects of fluid and electrolyte transport in individual seminiferous tubules, the epididymis and the vas deferens in rats. J Physiol. 1971 Mar;213(3):557–570. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARQUIS N. R., FRITZ I. B. EFFECTS OF TESTOSTERONE ON THE DISTRIBUTION OF CARNITINE, ACETYLCARNITINE, AND CARNITINE ACETYLTRANSFERASE IN TISSUES OF THE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OF THE MALE RAT. J Biol Chem. 1965 May;240:2197–2200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malnic G., Klose R. M., Giebisch G. Micropuncture study of distal tubular potassium and sodium transport in rat nephron. Am J Physiol. 1966 Sep;211(3):529–547. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.3.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J. H., Jones R. S. Canine pancreatic responses to intestinally perfused fat and products of fat digestion. Am J Physiol. 1974 May;226(5):1178–1187. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.226.5.1178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mott C. B., Sarles H., Tiscornia O. Action différente des triglycérides à chaines courtes, moyennes ou longues sur la sécrétion pancréatique exocrine de l'homme. Biol Gastroenterol (Paris) 1972;5(1):79–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse A. G., Polak J. M., Bloom S. R. The newer gut hormones. Cellular sources, physiology, pathology, and clinical aspects. Gastroenterology. 1977 Apr;72(4 Pt 1):746–761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajalakshmi M., Prasad M. R. Changes in sialic acid in the testis and epididymis of the rat during the onset of puberty. J Endocrinol. 1969 Jul;44(3):379–385. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0440379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez J., Hubel K. A., Clifton J. A. Intestinal factors affecting pancreatic exocrine secretion in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jul;211(1):260–263. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.1.260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOTT T. W., WALES R. G., WALLACE J. C., WHITE I. G. COMPOSITION OF RAM EPIDIDYMAL AND TESTICULAR FLUID AND THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF GLYCERYLPHOSPHORYLCHOLINE BY THE RABBIT EPIDIDYMIS. J Reprod Fertil. 1963 Aug;6:49–59. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0060049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sum P. T., Preshaw R. M. Intraduodenal glucose infusion and pancreatic secretion in man. Lancet. 1967 Aug 12;2(7511):340–341. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)90176-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuck R. R., Setchell B. P., Waites G. M., Young J. A. The composition of fluid collected by micropuncture and catheterization from the seminiferous tubules and rete testis of rats. Pflugers Arch. 1970;318(3):225–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00593663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner T. T., Hartmann P. K., Howards S. S. In vivo sodium, potassium, and sperm concentrations in the rat epididymis. Fertil Steril. 1977 Feb;28(2):191–194. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)42382-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waele B. D., Desmul A., Wissocq P., Kiekens R. La sécrétion pancréatique chez le rat. Influence de l'intervention chirurgicale, de la narcose, de l'hypothermie et de la dérivation du suc gastrique ou du suc pancréatique. Biol Gastroenterol (Paris) 1974;7(4):253–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. Y., Yeung C. H. Fluid reabsorption in the isolated duct of the rat cauda epididymidis. J Reprod Fertil. 1977 Jan;49(1):77–81. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0490077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. Y., Yeung C. H. Inhibition by amiloride of sodium-dependent fluid reabsorption in the rat isolated caudal epididymis. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Dec;58(4):529–531. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1976.tb08620.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. A., Frömter E., Schögel E., Hamann K. F. A microperfusion investigation of sodium resorption and potassium secretion by the main excretory duct of the rat submaxillary gland. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1967;295(2):157–172. doi: 10.1007/BF00362747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



