Abstract
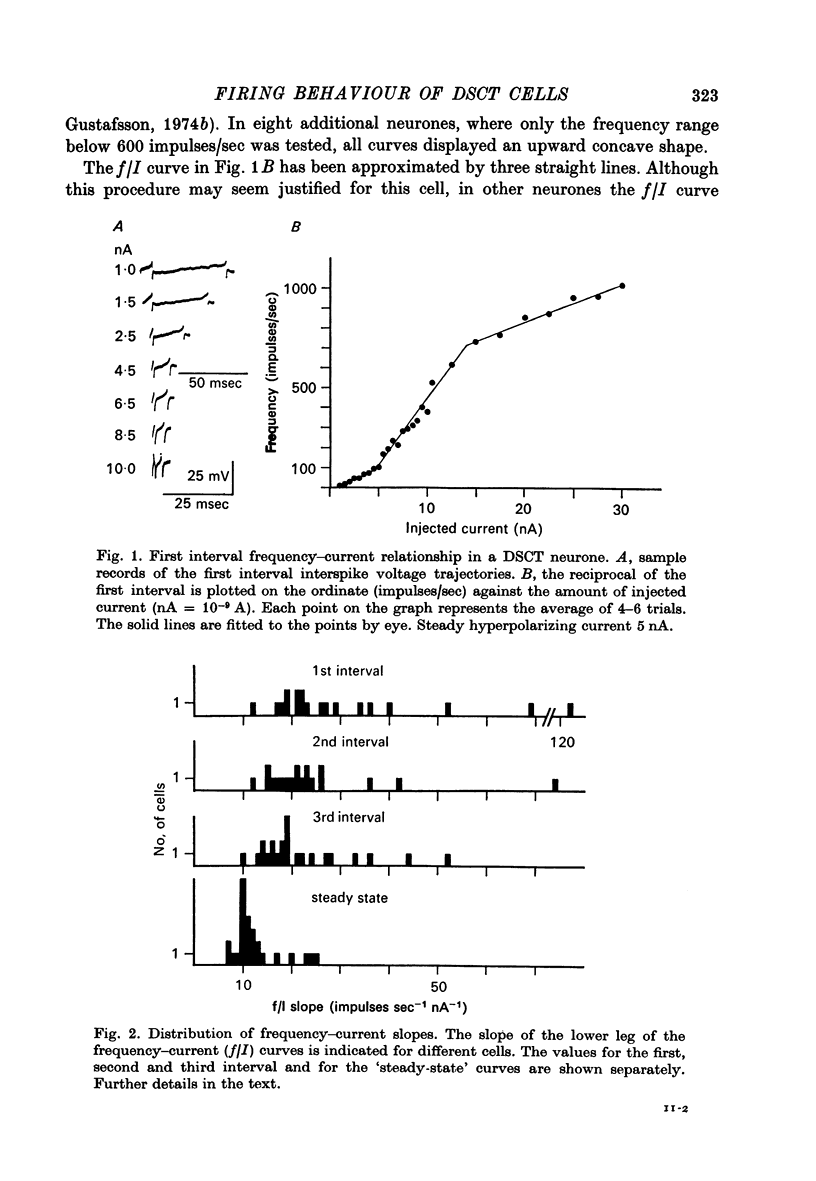
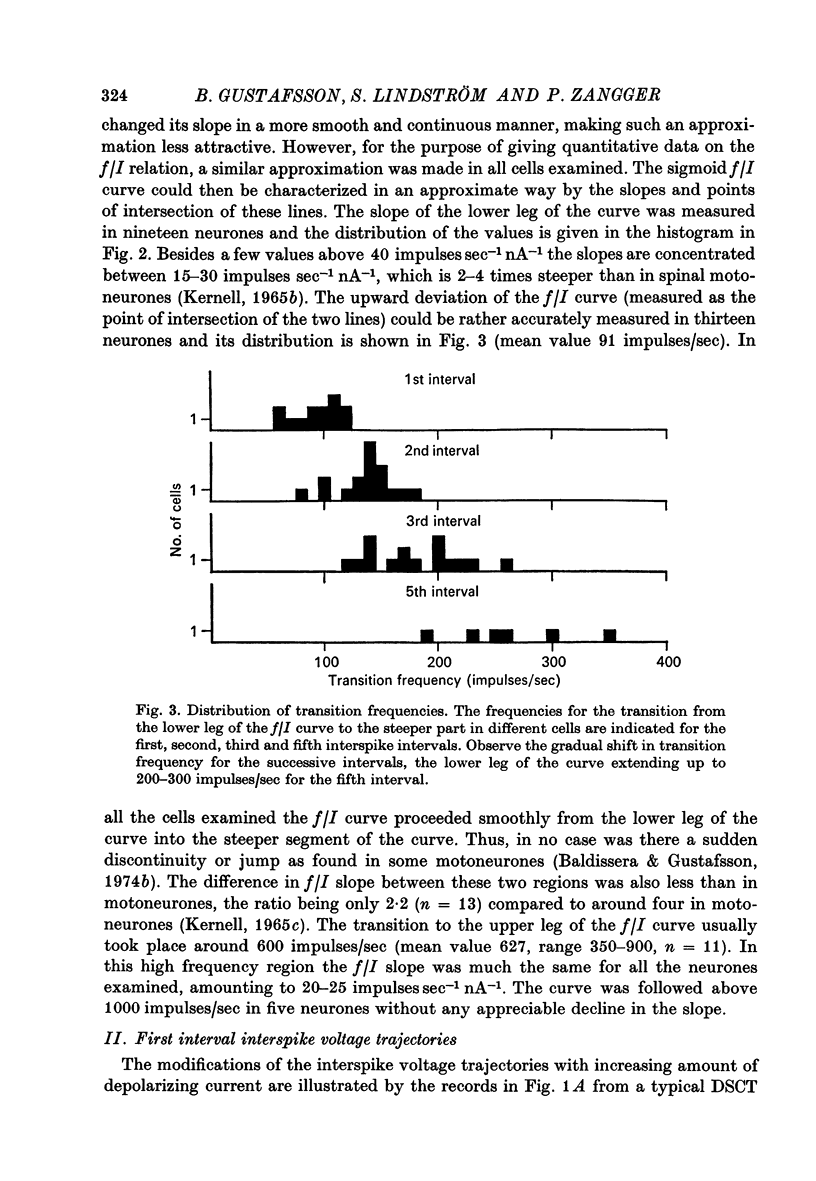
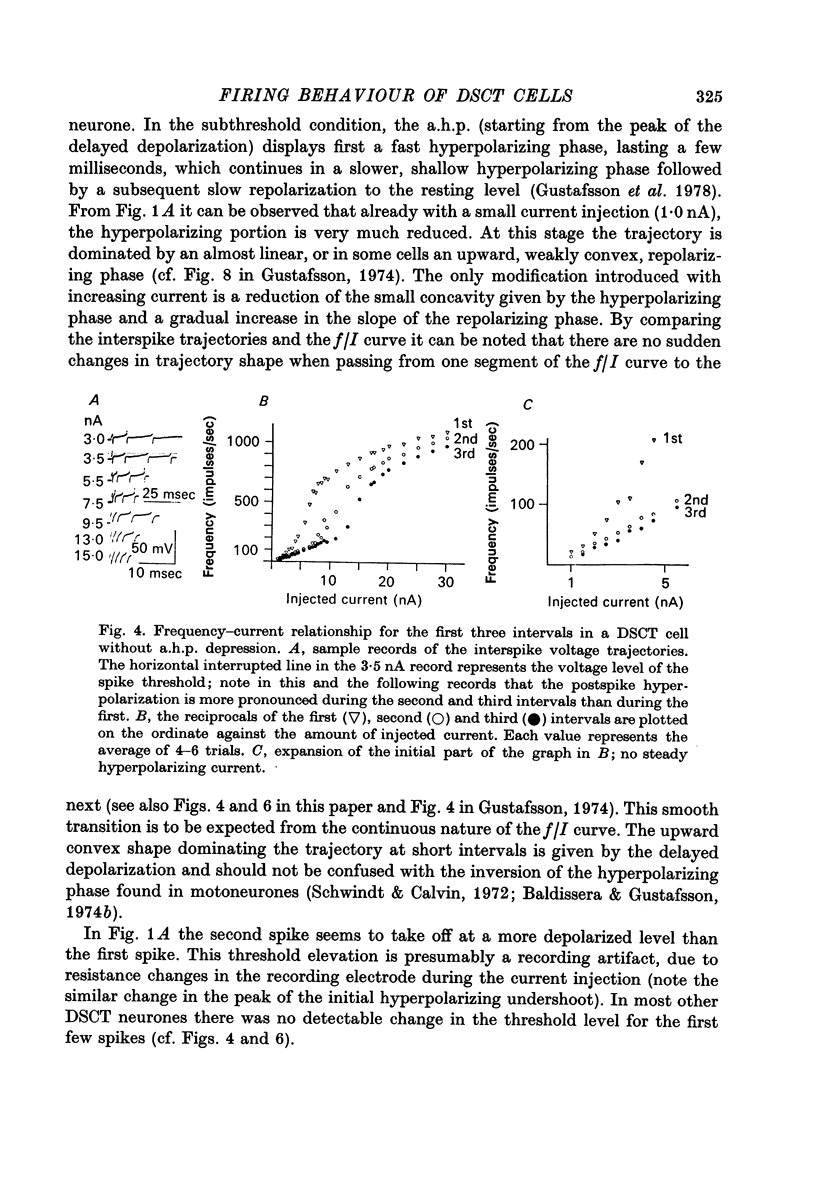
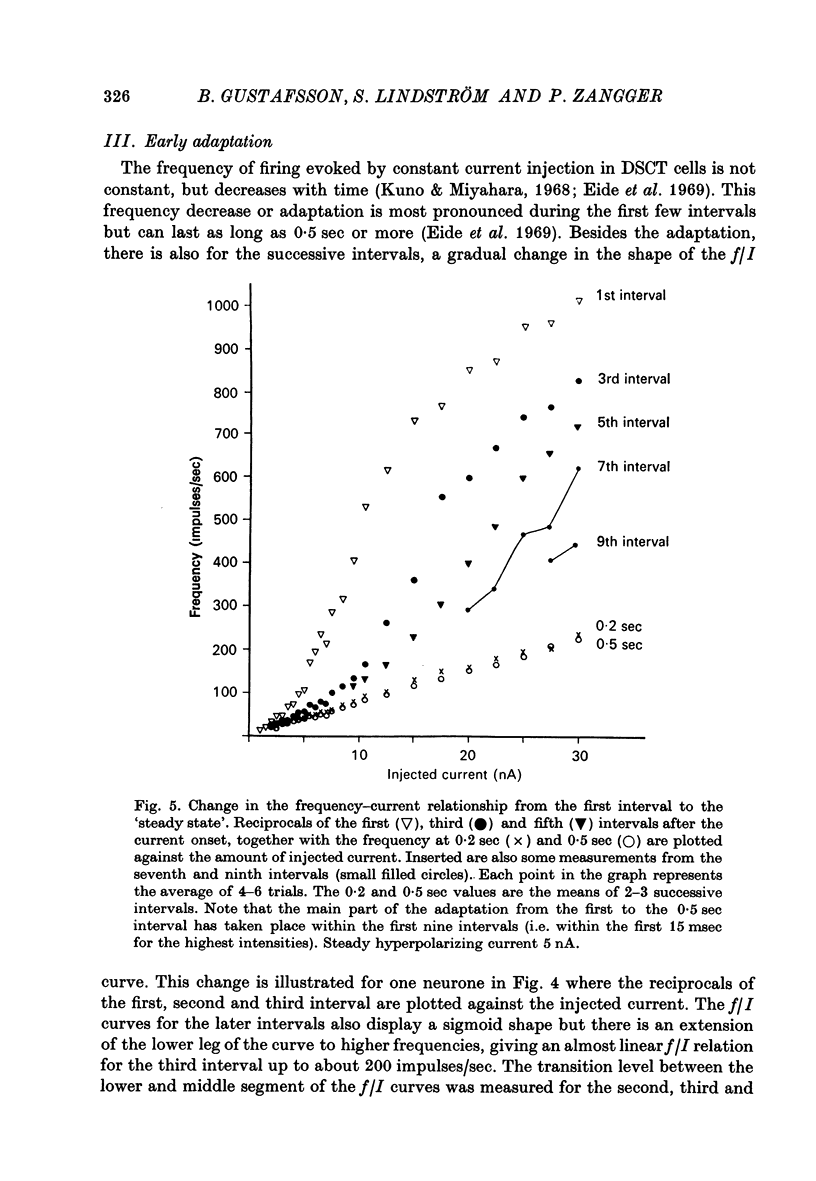
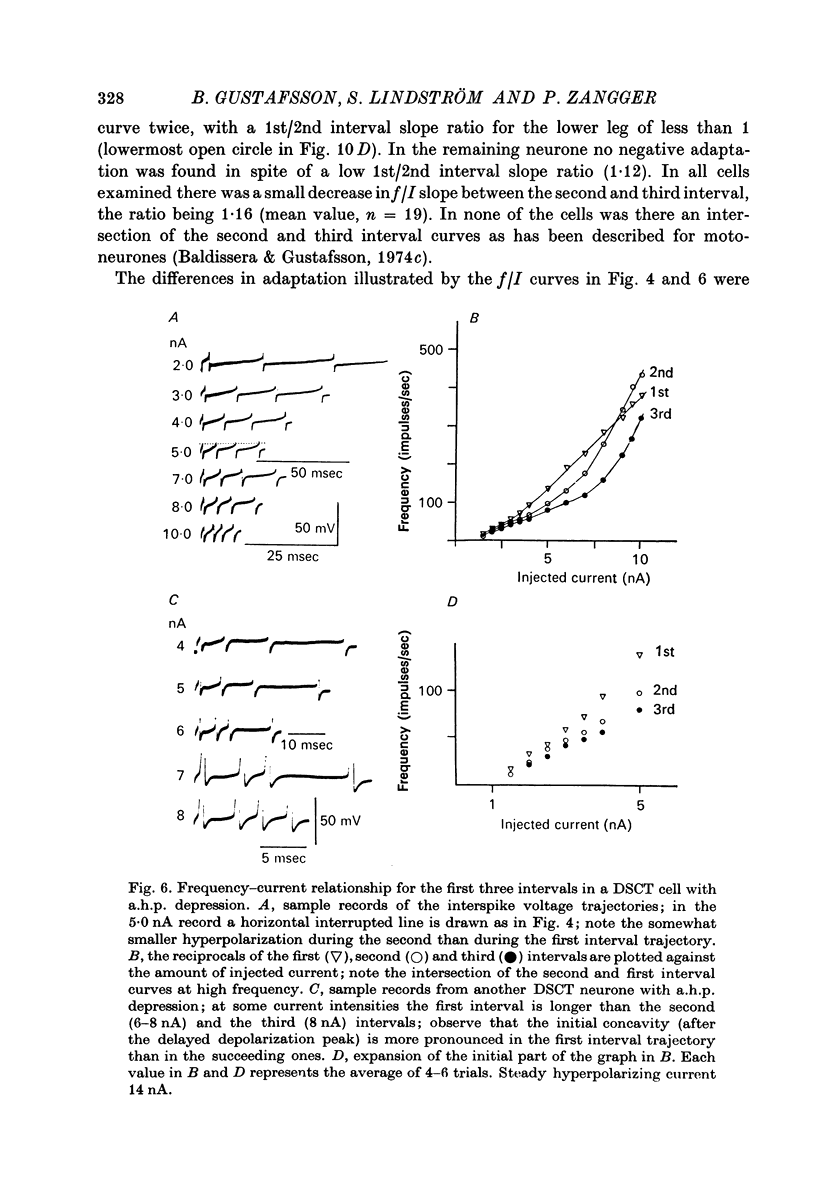
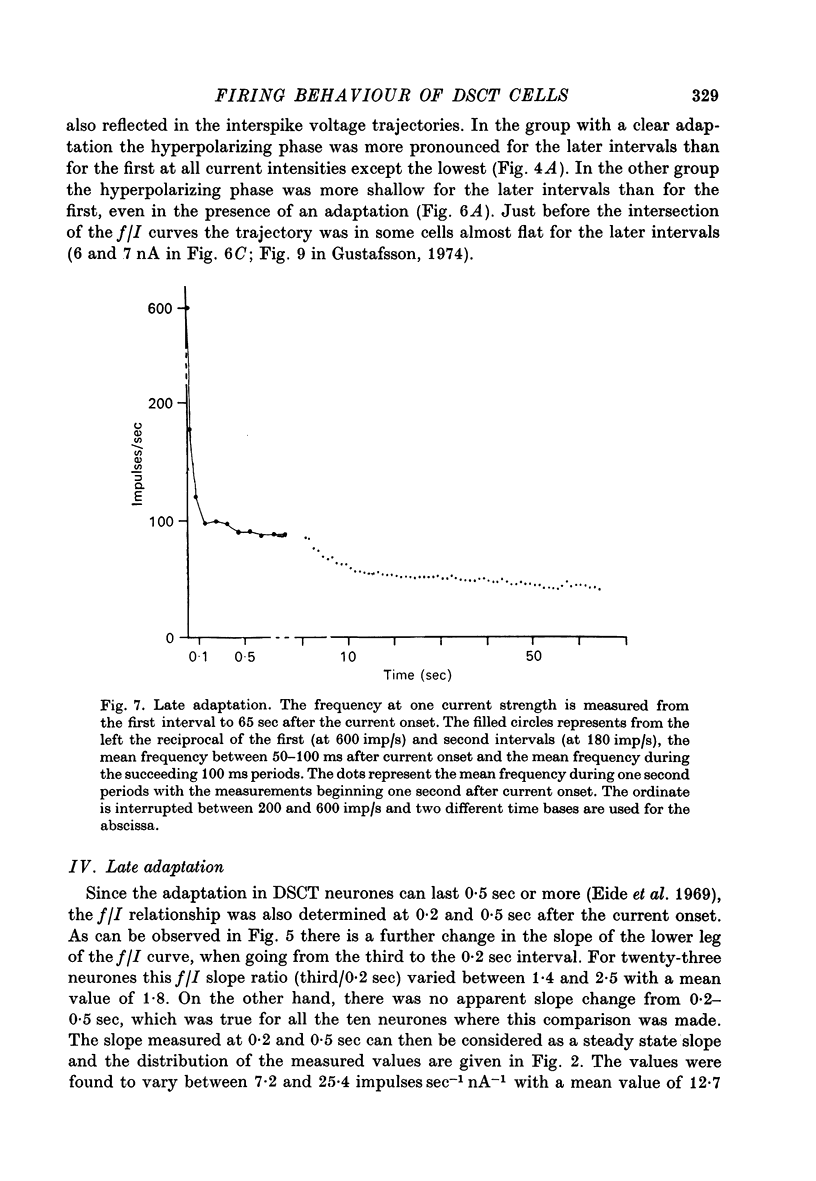
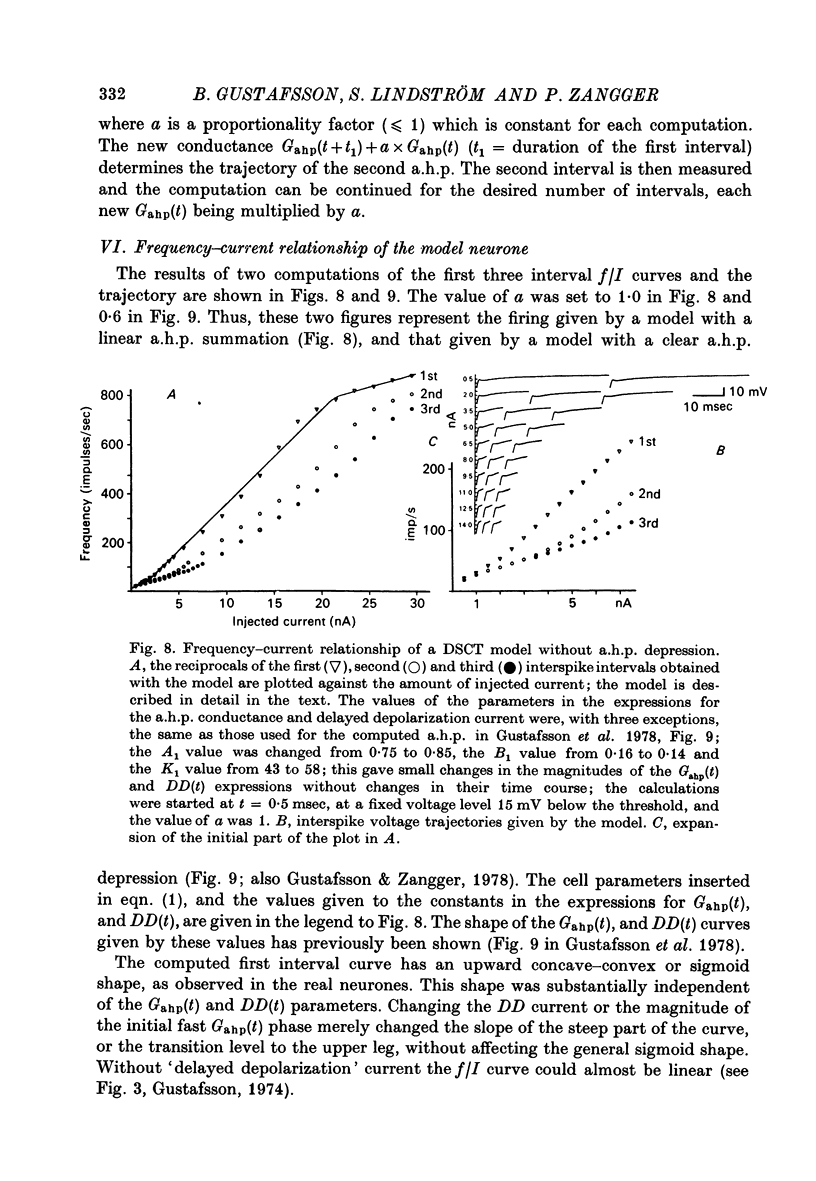
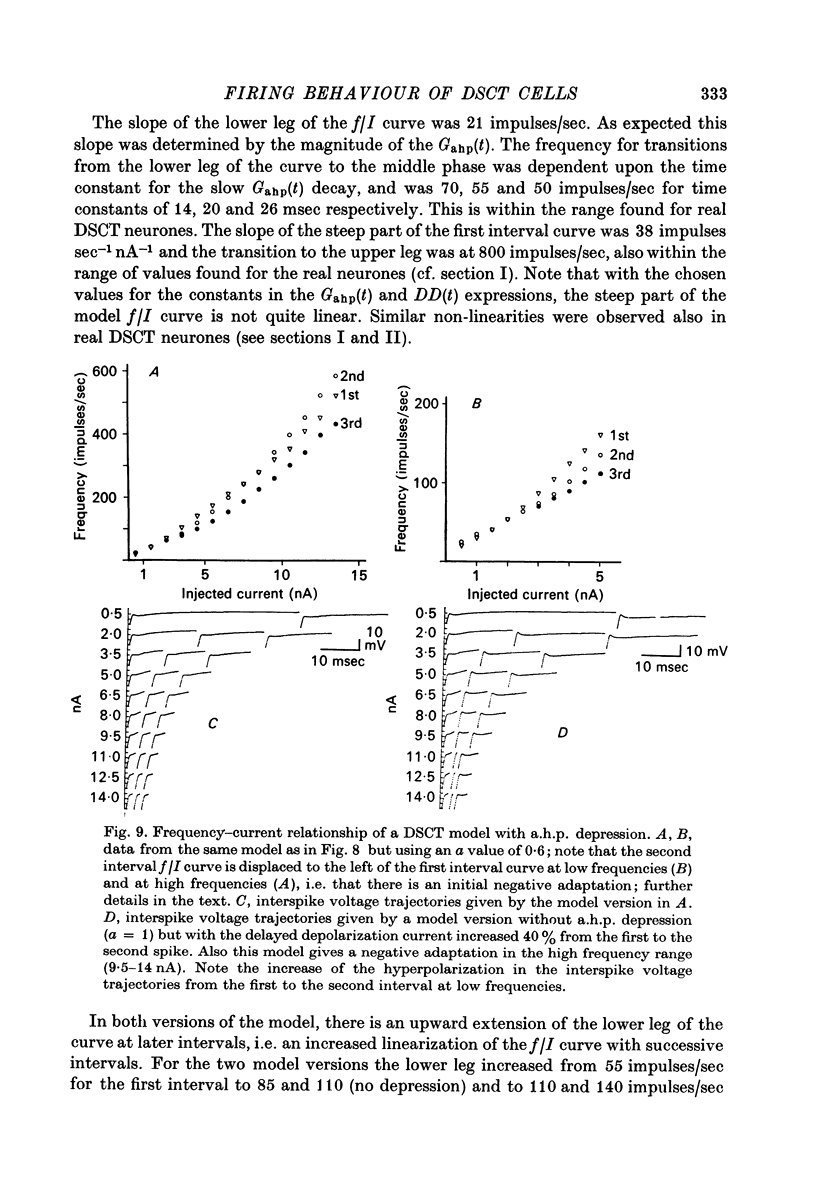
1. The repetitive discharge evoked by constant current injection from an intracellular micropipette has been studied in dorsal spinocerebellar tract cells of the cat. 2. The discharge frequency decreased with time, the decrease being more pronounced at high current intensities. Most of the frequency change occurred during the first ten intervals but the decrease continued slowly for several seconds. In some cells the frequency rose initially, the first interspike interval being larger than immediately succeeding ones. 3. The frequency-current (f/I) curves for the first interspike intervals were S-shaped, as found in spinal motoneurones. With successive intervals the lower leg of the f/I curve extended to higher frequencies, giving a progressive linearization of the f/I curves. In almost all cells this linearization was completed at 200 msec after current onset. 4. The experimental f/I curves were compared with the f/I curves obtained with a simple neurone model based on the properties of the postspike afterhyperpolarization. For the first interspike interval there was a good agreement between the experimental and calculated f/I curves of individual neurones up to frequencies of several hundred impulses per second. In the high frequency range, it was necessary to compensate for changes in initial postspike voltage trajectories caused by the injected current. Other aspects of the firing of real neurones, such as the progressive linearization of the f/I curves, the negative adaptation and the changes in the interspike voltage trajectories with increasing current were also reproduced by the neurone model. 5. It is concluded that the conductance process underlying the postspike afterhyperpolarization is a major factor in the regulation of repetitive firing in dorsal spinocerebellar tract neurones.
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian E. D., Zotterman Y. The impulses produced by sensory nerve-endings: Part II. The response of a Single End-Organ. J Physiol. 1926 Apr 23;61(2):151–171. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1926.sp002281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldissera F., Gustafsson B. Afterhyperpolarization conductance time course in lumbar motoneurones of the cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 Aug;91(4):512–527. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05707.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldissera F., Gustafsson B. Firing behaviour of a neurone model based on the afterhyperpolarization conductance time course and algebraical summation. Adaptation and steady state firing. Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 Sep;92(1):27–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05720.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldissera F., Gustafsson B. Firing behaviour of a neurone model based on the afterhyperpolarization conductance time course. First interval firing. Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 Aug;91(4):528–544. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05708.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvin W. H., Sypert G. W. Fast and slow pyramidal tract neurons: an intracellular analysis of their contrasting repetitive firing properties in the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Mar;39(2):420–434. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.2.420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eide E., Fedina L., Jansen J., Lundberg A., Vyklický L. Properties of Clarke's column neurones. Acta Physiol Scand. 1969 Sep-Oct;77(1):125–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1969.tb04558.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., KERNELL D., SHORTESS G. K. QUANTITATIVE ASPECTS OF REPETITIVE FIRING OF MAMMALIAN MOTONEURONES, CAUSED BY INJECTED CURRENTS. J Physiol. 1963 Oct;168:911–931. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granit R., Kernell D., Lamarre Y. Algebraical summation in synaptic activation of motoneurones firing within the 'primary range' to injected currents. J Physiol. 1966 Nov;187(2):379–399. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granit R., Kernell D., Lamarre Y. Synaptic stimulation superimposed on motoneurones firing in the 'secondary range' to injected current. J Physiol. 1966 Nov;187(2):401–415. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Lindstrom S., Takata M. Repetitive firing in dorsal spinocerebellar tract neurones. Brain Res. 1972 Dec 12;47(2):506–509. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90659-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Linström S., Takata M. Afterhyperpolarization mechanism in the dorsal spinocerebellar tract cells of the cat. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:283–301. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Zangger P. Effect of repetitive activation on the afterhyperpolarization in dorsal spinocerebellar tract neurones. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:303–319. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito M., Oshima T. Electrical behaviour of the motoneurone membrane during intracellularly applied current steps. J Physiol. 1965 Oct;180(3):607–635. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERNELL D. SYNAPTIC INFLUENCE ON THE REPETITIVE ACTIVITY ELICITED IN CAT LUMBOSACRAL MOTONEURONES BY LONG-LASTING INJECTED CURRENTS. Acta Physiol Scand. 1965 Mar;63:409–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1965.tb04081.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernell D. Effects of synapses of dendrites and soma on the repetitive impulse firing of a compartmental neuron model. Brain Res. 1971 Dec 24;35(2):551–555. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90499-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernell D., Sjöholm H. Repetitive impulse firing: comparisons between neurone models based on 'voltage clamp equations' and spinal motoneurones. Acta Physiol Scand. 1973 Jan;87(1):40–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1973.tb05364.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernell D. The repetitive impulse discharge of a simple neurone model compared to that of spinal motoneurones. Brain Res. 1968 Dec;11(3):685–687. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(68)90157-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike H., Mano N., Okada Y., Oshima T. Repetitive impulses generated in fast and slow pyramidal tract cells by intracellularly applied current steps. Exp Brain Res. 1970;11(3):263–281. doi: 10.1007/BF01474386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno M., Miyahara J. T. Factors responsible for multiple discharge of neurons in Clarke's column. J Neurophysiol. 1968 Jul;31(4):624–638. doi: 10.1152/jn.1968.31.4.624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor R. J., Sharpless S. K. Repetitive discharge rate of a simple neuron model with accumulation of after-hyperpolarization conductance. Brain Res. 1973 Dec 21;64:387–390. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90192-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauritz K. H., Schlue W. R., Richter D. W., Nacimiento A. C. Membrane conductance course during spike intervals and repetitive firing in cat spinal motoneurones. Brain Res. 1974 Aug 16;76(2):223–233. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90456-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwindt P. C., Calvin W. H. Equivalence of synaptic and injected current in determining the membrane potential trajectory during motoneuron rhythmic firing. Brain Res. 1973 Sep 14;59:389–394. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90278-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwindt P. C., Calvin W. H. Membrane-potential trajectories between spikes underlying motoneuron firing rates. J Neurophysiol. 1972 May;35(3):311–325. doi: 10.1152/jn.1972.35.3.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwindt P. C., Calvin W. H. Nature of conductances underlying rhythmic firing in cat spinal motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1973 Nov;36(6):955–973. doi: 10.1152/jn.1973.36.6.955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwindt P. C. Membrane-potential trajectories underlying motoneuron rhythmic firing at high rates. J Neurophysiol. 1973 May;36(3):434–439. doi: 10.1152/jn.1973.36.3.434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walloe L., Jansen J. K., Nygaard K. A computer simulated model of a second order sensory neurone. Kybernetik. 1969 Sep;6(4):130–141. doi: 10.1007/BF00274106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


