Abstract
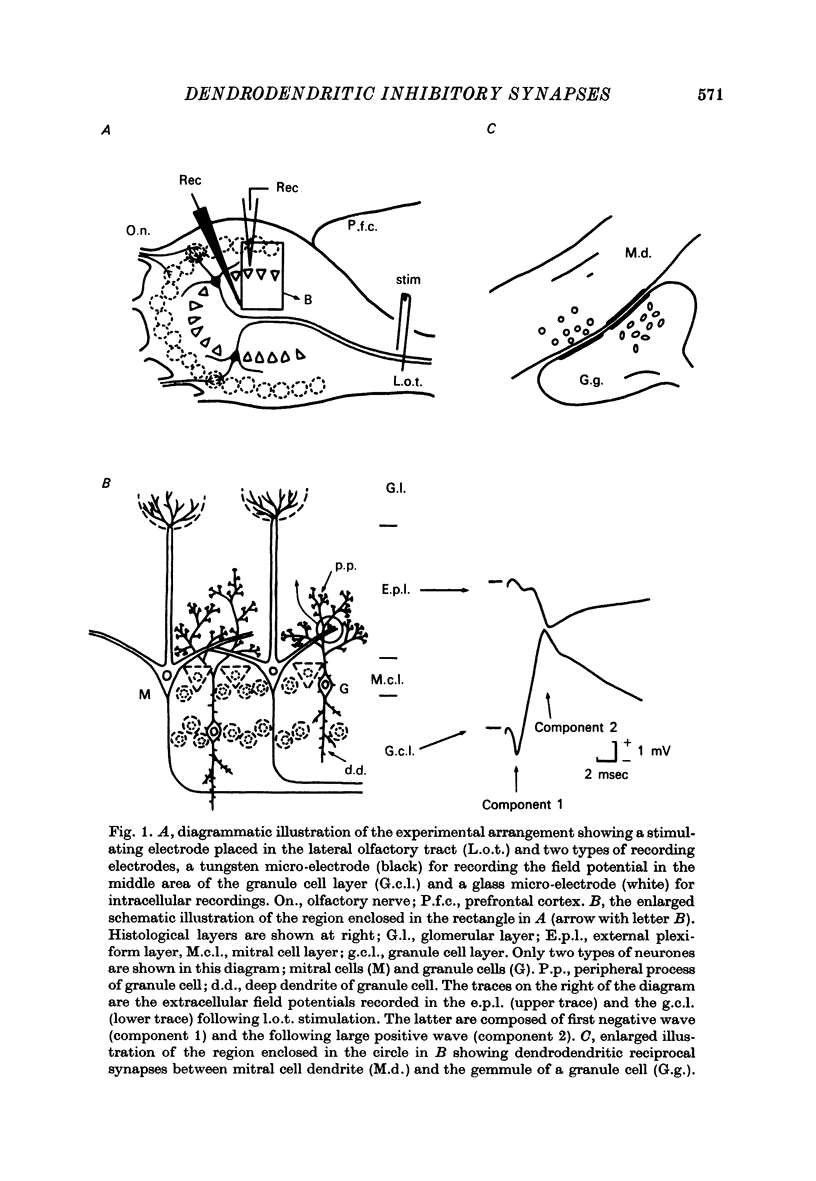
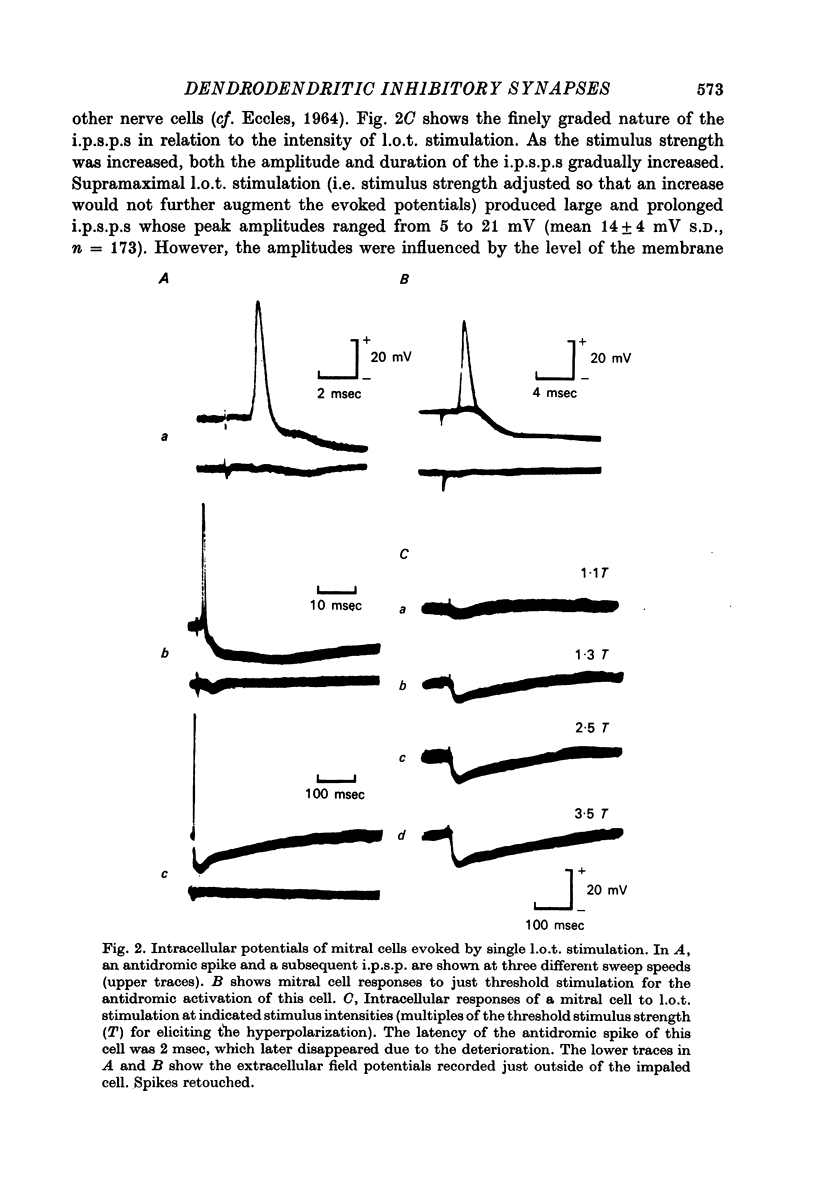
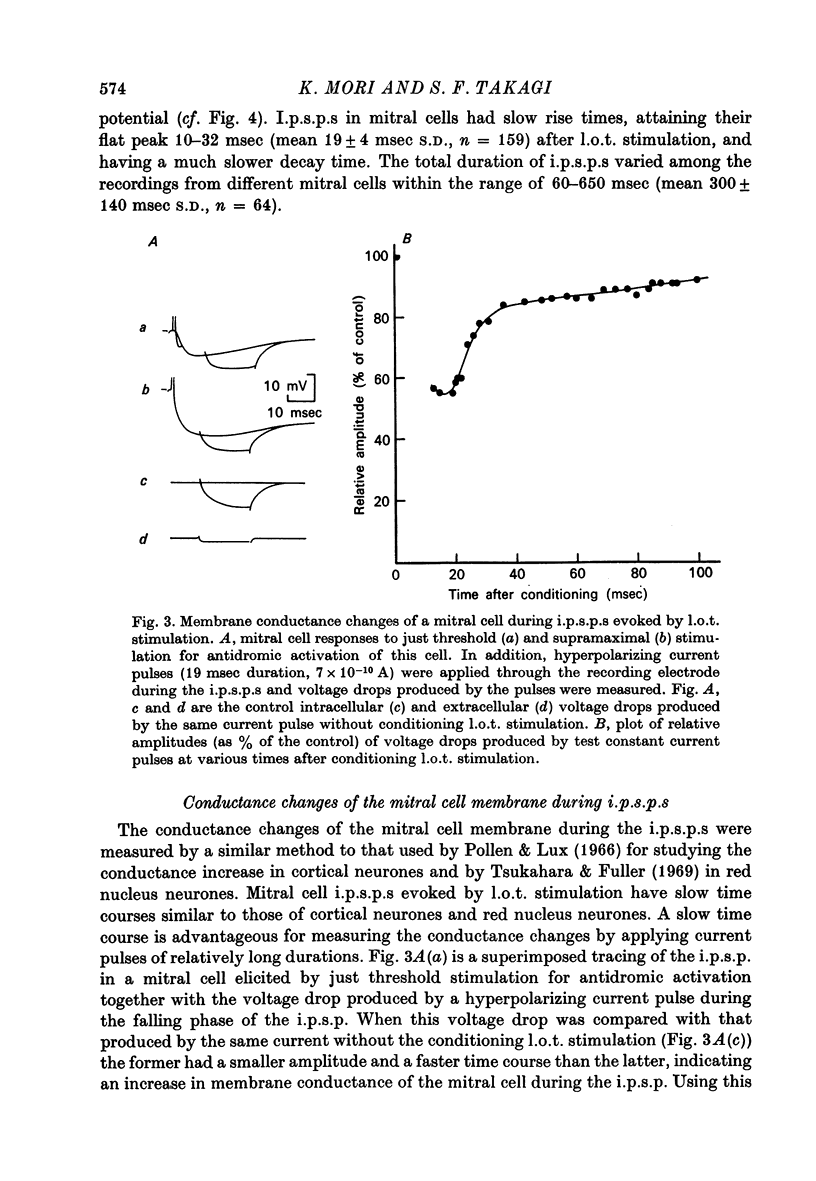
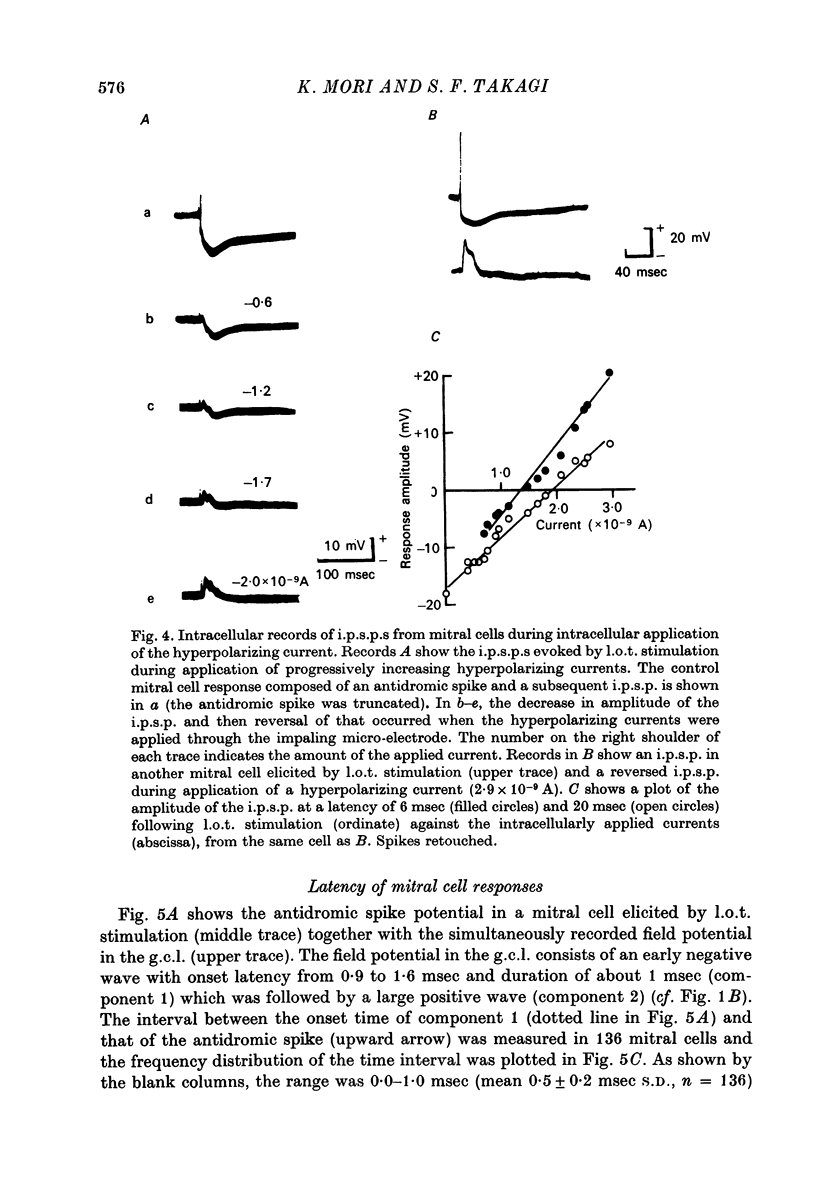
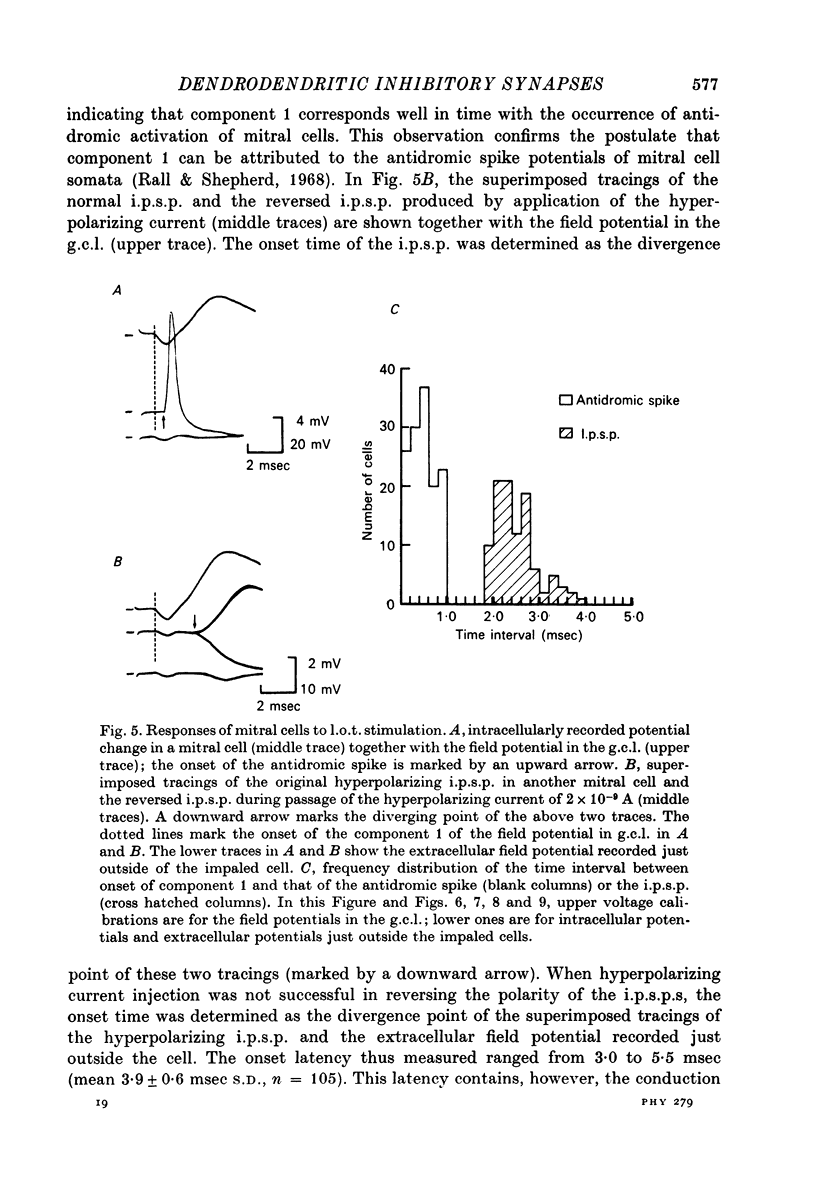
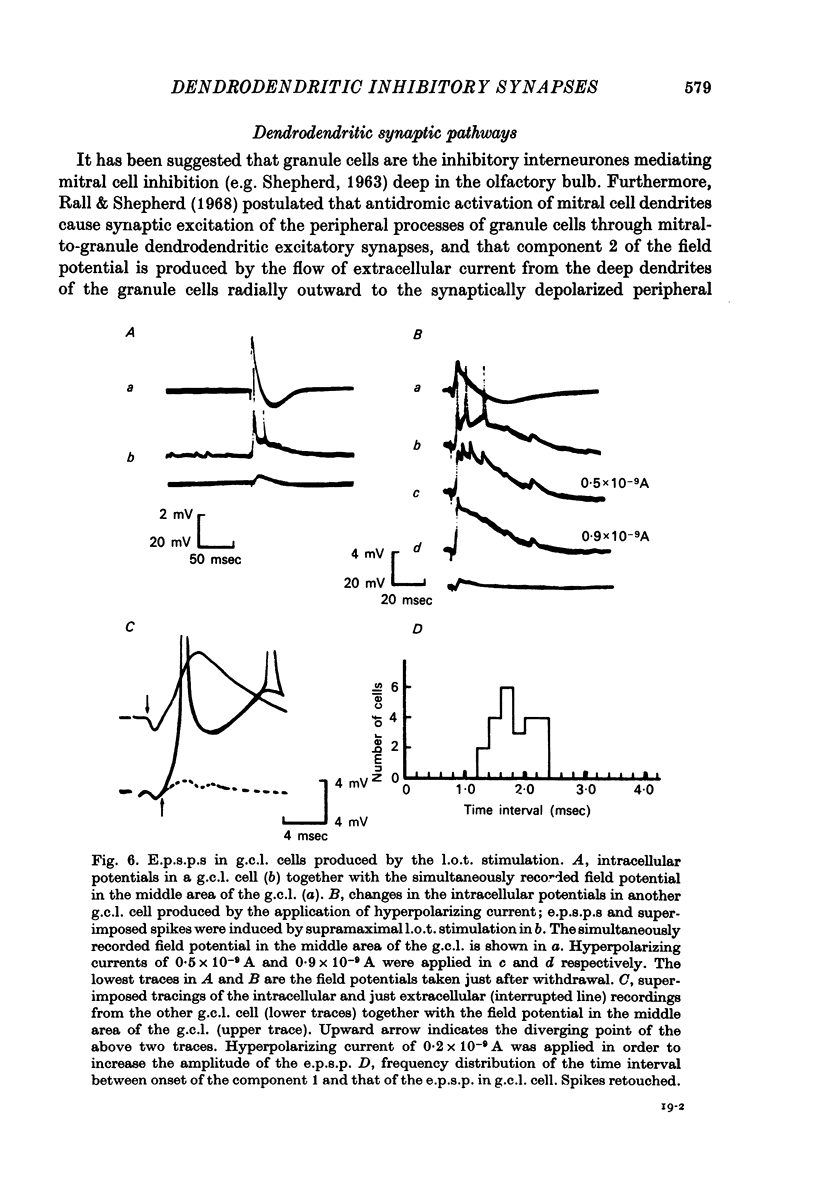
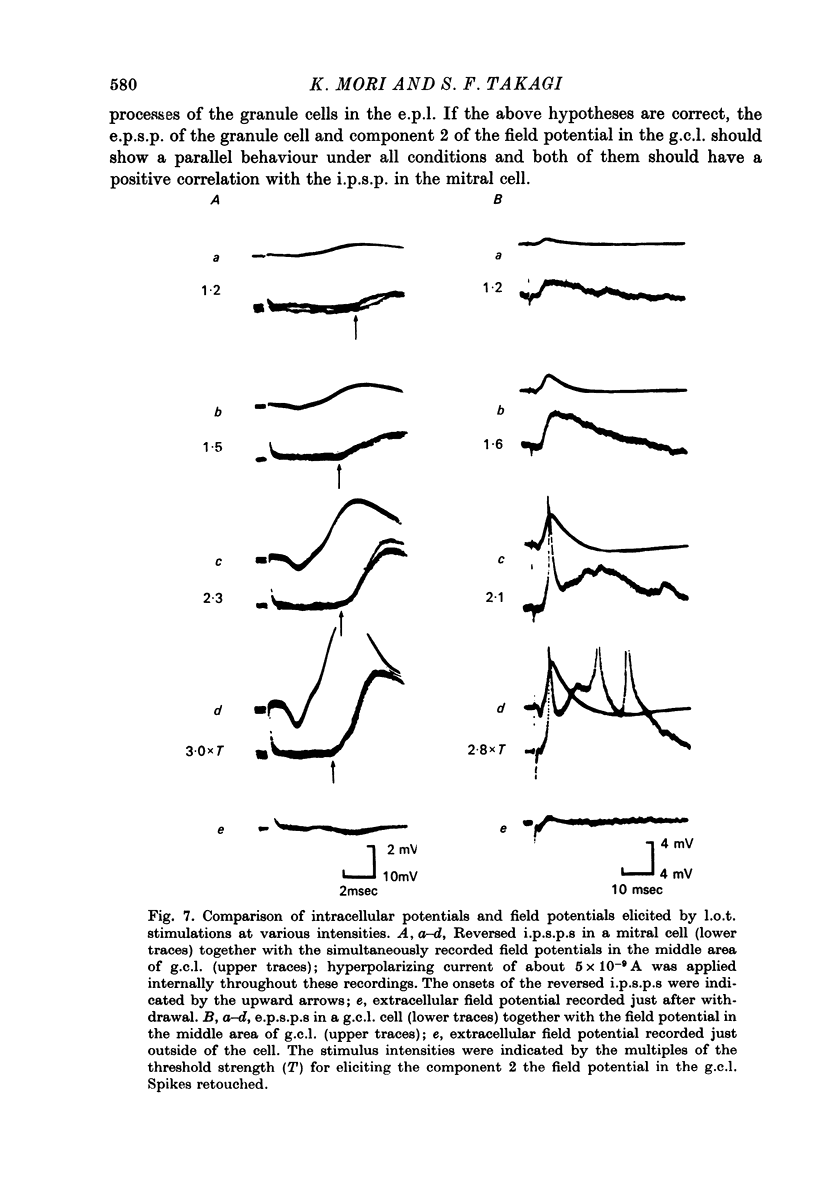
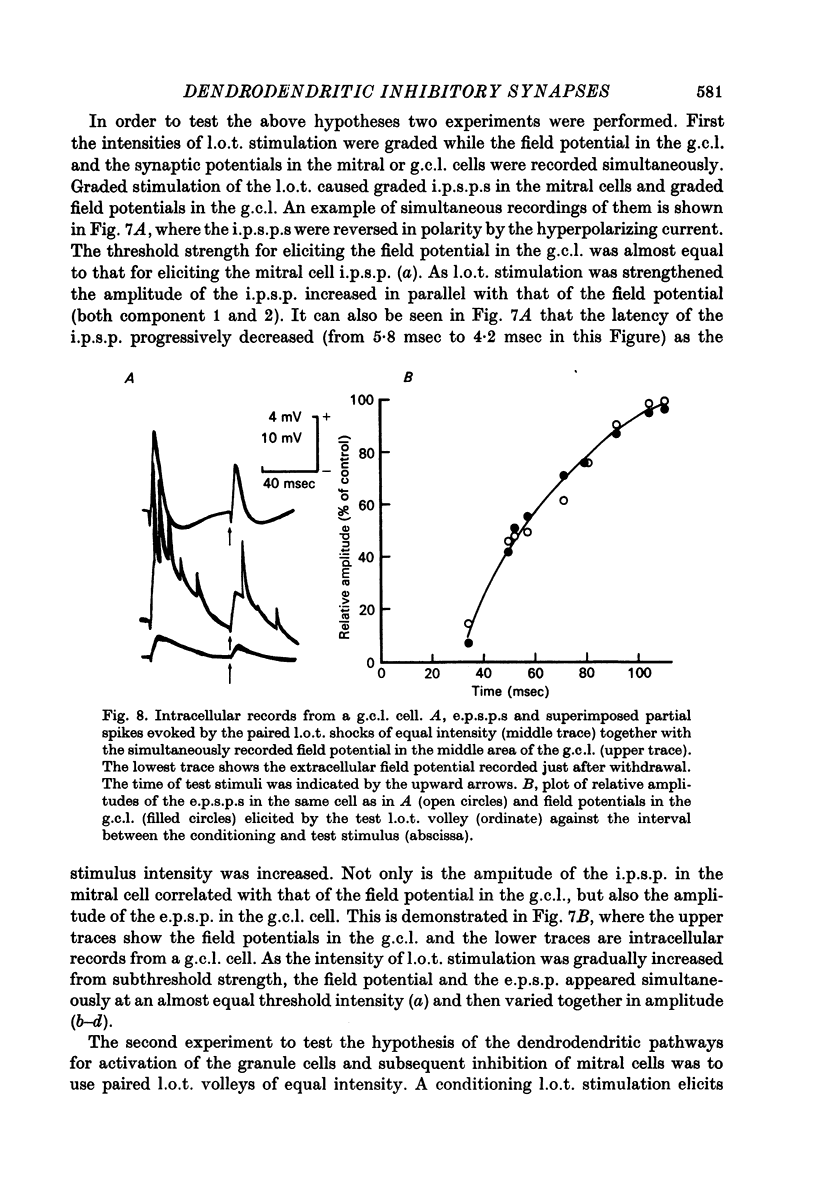
1. In the rabbit olfactory bulb, intracellular potentials were recorded from mitral cells and from neurones in the granule cell layer (g.c.l.) following lateral olfactory tract (l.o.t.) stimulation. 2. Most recordings from mitral cells showed large (5-21 mV) and prolonged (60-650 msec) i.p.s.p.s subseuqent to the antidromic spikes. These i.p.s.p.s decreased in amplitude and then reversed in polarity by progressive increase in hyperpolarizing current applied intracellularly. They were accompanied by a prominent and long lasting (up to 100 msec) conductance increase of the mitral cell membrane. 3. Reversed i.p.s.p.s of mitral cells having quite different time courses from the original hyperpolarizing i.p.s.p.s suggest that the inhibitory synapses are widely distributed on the soma and dendrites. 4. E.p.s.p.s could be recorded from g.c.l. cells whose onset latency was approximately 0.6 msec shorter than that of mitral cell i.p.s.p.s. Comparison of the behaviour of e.p.s.p.s in g.c.l. cells and that of mitral cell i.p.s.p. under various conditions of l.o.t. stimulation suggests that these g.c.l. cells are the inhibitory interneurones mediating mitral cell inhibition. 5. The results support the hypothesis of dendrodentritic pathways for activation of granule cells and subsequent inhibition of mitral cells.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADRIAN E. D. The electrical activity of the mammalian olfactory bulb. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1950 Nov;2(4):377–388. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(50)90075-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDRES K. H. DER FEINBAU DES BULBUS OFACTORIUS DER RATTE UNTER BESONDERER BERUECKSICHTIGUNG DER SYNAPTISCHEN VERBINDUNGEN. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1965 Feb 9;65:530–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS J. S., ECCLES J. C., FATT P. The specific ionic conductances and the ionic movements across the motoneuronal membrane that produce the inhibitory post-synaptic potential. J Physiol. 1955 Nov 28;130(2):326–374. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccles J. C., Llinás R., Sasaki K. Intracellularly recorded responses of the cerebellar Purkinje cells. Exp Brain Res. 1966;1(2):161–183. doi: 10.1007/BF00236869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN J. D., MANCIA M., von BAUMGARTEN Recurrent inhibition in the olfactory bulb. I. Effects of antidromic stimulation of the lateral olfactory tract. J Neurophysiol. 1962 Jul;25:467–488. doi: 10.1152/jn.1962.25.4.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRATA Y. SOME OBSERVATIONS ON THE FINE STRUCTURE OF THE SYNAPSES IN THE OLFACTORY BULB OF THE MOUSE, WITH PARTICULAR REFERENCE TO THE ATYPICAL SYNAPTIC CONFIGURATIONS. Arch Histol Jpn. 1964 Feb;24:293–302. doi: 10.1679/aohc1950.24.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANDEL E. R., SPENCER W. A., BRINLEY F. J., Jr Electrophysiology of hippocampal neurons. I. Sequential invasion and synaptic organization. J Neurophysiol. 1961 May;24:225–242. doi: 10.1152/jn.1961.24.3.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. F., Dacheux R. Dendritic and somatic spikes in mudpuppy amacrine cells: indentification and TTX sensitivity. Brain Res. 1976 Mar 5;104(1):157–162. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90657-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori K., Kogure S., Takagi S. Alternating responses of olfactory bulb neurons to repetitive lateral olfactory tract stimulation. Brain Res. 1977 Sep 9;133(1):150–155. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90056-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori K., Takagi S. F. Activation and inhibition of olfactory bulb neurones by anterior commissure volleys in the rabbit. J Physiol. 1978 Jun;279:589–604. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori K., Takagi S. F. Spike generation in the mitral cell dendrite of the rabbit olfactory bulb. Brain Res. 1975 Dec 26;100(3):685–689. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90170-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll R. A. Inhibitory mechanisms in the rabbit olfactory bulb: dendrodendritic mechanisms. Brain Res. 1969 Jun;14(1):157–172. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OCHI J. Olfactory bulb response to antidromic olfactory tract stimulation in the rabbit. Jpn J Physiol. 1963 Apr 15;13:113–128. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.13.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIPS C. G. Actions of antidromic pyramidal volleys on single Betz cells in the cat. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1959 Jan;44(1):1–25. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1959.sp001364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIPS C. G., POWELL T. P., SHEPHERD G. M. RESPONSES OF MITRAL CELLS TO STIMULATION OF THE LATERAL OLFACTORY TRACT IN THE RABBIT. J Physiol. 1963 Aug;168:65–88. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PURPURA D. P., COHEN B. Intracellular recording from thalamic neurons during recruiting responses. J Neurophysiol. 1962 Sep;25:621–635. doi: 10.1152/jn.1962.25.5.621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollen D. A., Lux H. D. Conductance changes during inhibitory postsynaptic potentials in normal and strychninized cortical neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1966 May;29(3):369–381. doi: 10.1152/jn.1966.29.3.369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price J. L., Powell T. P. The mitral and short axon cells of the olfactory bulb. J Cell Sci. 1970 Nov;7(3):631–651. doi: 10.1242/jcs.7.3.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price J. L., Powell T. P. The synaptology of the granule cells of the olfactory bulb. J Cell Sci. 1970 Jul;7(1):125–155. doi: 10.1242/jcs.7.1.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall W., Shepherd G. M., Reese T. S., Brightman M. W. Dendrodendritic synaptic pathway for inhibition in the olfactory bulb. Exp Neurol. 1966 Jan;14(1):44–56. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(66)90023-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall W., Shepherd G. M. Theoretical reconstruction of field potentials and dendrodendritic synaptic interactions in olfactory bulb. J Neurophysiol. 1968 Nov;31(6):884–915. doi: 10.1152/jn.1968.31.6.884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribak C. E., Vaughn J. E., Saito K., Barber R., Roberts E. Glutamate decarboxylase localization in neurons of the olfactory bulb. Brain Res. 1977 Apr 22;126(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90211-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEPHERD G. M. NEURONAL SYSTEMS CONTROLLING MITRAL CELL EXCITABILITY. J Physiol. 1963 Aug;168:101–117. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd G. M. Synaptic organization of the mammalian olfactory bulb. Physiol Rev. 1972 Oct;52(4):864–917. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1972.52.4.864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukahara N., Fuller D. R. Conductance changes during pyramidally induced postsynaptic potentials in red nucleus neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1969 Jan;32(1):35–42. doi: 10.1152/jn.1969.32.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willey T. J. The ultrastructure of the cat olfactory bulb. J Comp Neurol. 1973 Dec 1;152(3):211–232. doi: 10.1002/cne.901520302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMAMOTO C., YAMAMOTO T., IWAMA K. The inhibitory systems in the olfactory bulb studied by intracellular recording. J Neurophysiol. 1963 May;26:403–415. doi: 10.1152/jn.1963.26.3.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


