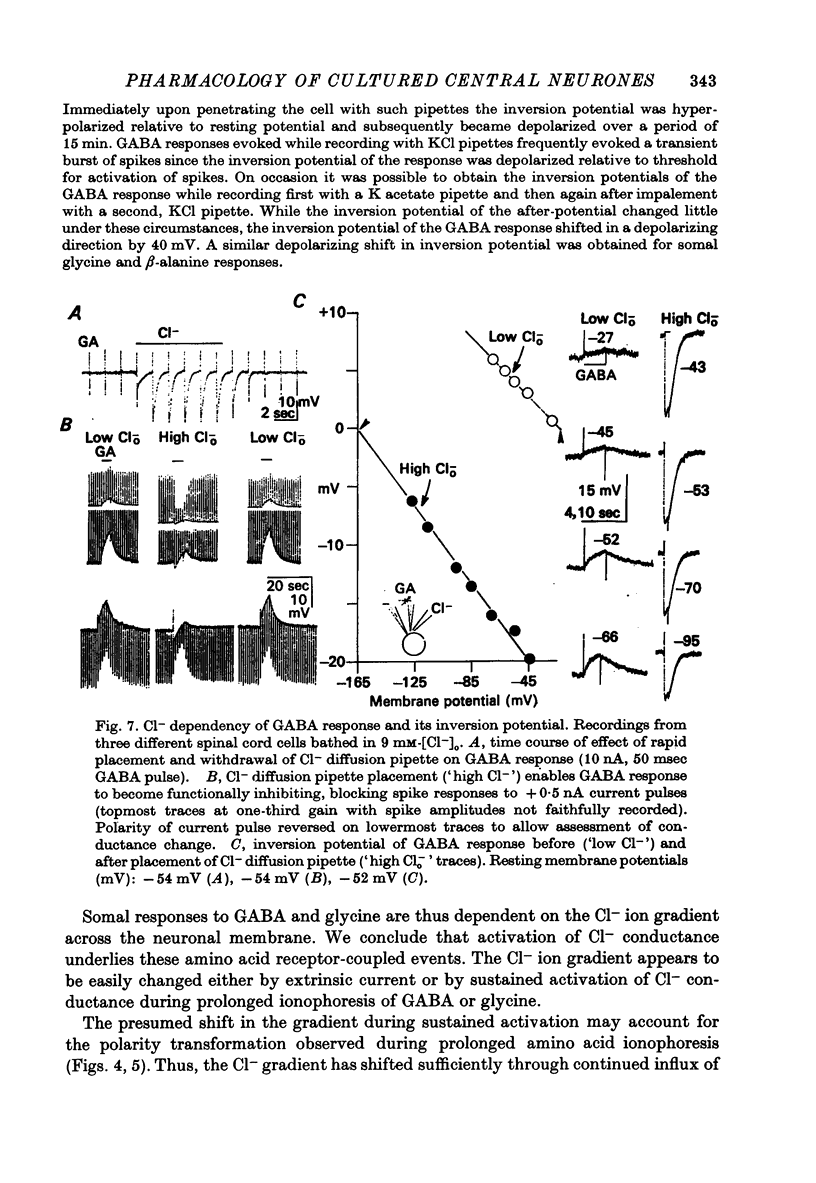
Abstract
1. Spinal and cerebellar-brainstem areas of fetal mouse were dissociated and grown in tissue culture until large enough to permit stable intracellular recording. 2. The tissue-cultured neurones, growing as a monolayer and accessible under direct vision using phase contrast optics, allowed precise placement of intracellular recording and extracellular ionophoretic pipettes. 3. Ionophoresis of GABA and glutamate revealed a non-uniform distribution of responses over the cell surface, with a lack of spatial coincidence in sensitivity between the two. GABA inhibited and glutamate excited all cells tested. 4. GABA responses evoked at the cell body and on nearby process membrane were almost uniformly hyperpolarizing, while those at some peripheral process membrane were either hyperpolarizing, depolarizing or a combination of both events. All responses were associated with an increase in membrane slope conductance. 5. Membrane polarization showed that all hyperpolarizing events extrapolated to about the same inversion potential, which averaged about 9 mV more negative than resting potential (n = 95 cells). The depolarizing phases of responses evoked at peripheral membranes extrapolated to about 0 mV (n = 5 cells). 6. The hyperpolarization and increase in membrane conductance of GABA responses at the cell body were dependent on Cl- ions and the inversion potential of the response was dependent on the Cl- ion concentration gradient. The inversion potentials of GABA, glycine and beta-alanine responses were identical. 7. When matched in magnitude for evoked conductance increase, glycine responses decayed more rapidly than GABA. Glycine and beta-alanine voltage responses both decayed faster than GABA responses of comparable size. 8. In about half the cells tested sustained or rapidly repeated application of GABA and glycine transformed hyperpolarizing responses into depolarizations which were associated with a maintained conductance increase. Results from conditioning-test experiments with pairs of GABA and glycine responses suggest that the reversal of response polarity is due to a rapid redistribution of Cl- ions. 9. The limiting slope of log-log dose-response curves for GABA-induced conductance averaged about 2, while those for glutamate-induced depolarizations averaged about 1. The results suggest that two molecules of GABA and one molecule of glutamate participate in the respective post-synaptic responses. 10. The observation indicate that mammalian C.N.S. tissue grown in culture is a suitable model to study C.N.S. membrane pharmacology with increasing precision.
Full text
PDF






















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A. Actions of gamma-aminobutyric acid on sympathetic ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1975 Aug;250(1):85–120. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams P. R., Pixner D. B. Proceedings: Exitation of frog spinal motoneurones by glycine. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(1):67P–68P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker J. L., Nicoll R. A. Gamma-aminobutyric acid: role in primary afferent depolarization. Science. 1972 Jun 2;176(4038):1043–1045. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4038.1043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker J. L., Nicoll R. A., Padjen A. Studies on convulsants in the isolated frog spinal cord. I. Antagonism of amino acid responses. J Physiol. 1975 Mar;245(3):521–536. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker J. L., Nicoll R. A. The pharmacology and ionic dependency of amino acid responses in the frog spinal cord. J Physiol. 1973 Jan;228(2):259–277. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker J. L., Ransom B. R. Pentobarbitone pharmacology of mammalian central neurones grown in tissue culture. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:355–372. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Brown D. A. Depolarizing actions of gamma-aminobutyric acid and related compounds on rat superior cervical ganglia in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Feb;50(2):205–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb08563.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brookes N., Blank M., Werman R. The kinetics of the conductance increase produced by -aminobutyric acid at the membrane of locust muscle fibers. Mol Pharmacol. 1973 Jul;9(4):580–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brookes N. Werman R:The cooperativity of -aminobutyric action on the membrane of locust muscle fibers. Mol Pharmacol. 1973 Jul;9(4):571–579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Hösli L., Johnston G. A. A pharmacological study of the depression of spinal neurones by glycine and related amino acids. Exp Brain Res. 1968;6(1):1–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00235443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Johnston G. A. Amino acid transmitters in the mammalian central nervous system. Ergeb Physiol. 1974;69(0):97–188. doi: 10.1007/3-540-06498-2_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidoff R. A., Aprison M. H., Werman R. The effects of strychnine on the inhibition of interneurons by glycine and gamma-aminobutyric acid. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1969 Mar;8(2):191–194. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(69)90013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidoff R. A. Gamma-aminobutyric acid antagonism and presynaptic inhibition in the frog spinal cord. Science. 1972 Jan 21;175(4019):331–333. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4019.331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J., Huxley A. F. The activation and distribution of GABA and L-glutamate receptors on goldfish Mauthner neurones: an analysis of dendritic remote inhibition. J Physiol. 1968 Feb;194(3):669–723. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J., Roper S. Analysis of Mauthner cell responses to iontophoretically delivered pulses of GABA, glycine and L-glutamate. J Physiol. 1973 Jul;232(1):113–128. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J., Roper S., Yasargil G. M. The membrane effects, and sensitivity to strychnine, of neural inhibition of the Mauthner cell, and its inhibition by glycine and GABA. J Physiol. 1973 Jul;232(1):87–111. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreifuss J. J., Kelly J. S., Krnjević K. Cortical inhibition and gamma-aminobutyric acid. Exp Brain Res. 1969;9(2):137–154. doi: 10.1007/BF00238327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer F., Peper K. Density and dose-response curve of acetylcholine receptors in frog neuromuscular junction. Nature. 1975 Feb 20;253(5493):641–643. doi: 10.1038/253641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudel J. Kinetics of postsynaptic action of glutamate pulses applied iontophoretically through high resistance micropipettes. Pflugers Arch. 1975;356(4):329–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00580006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feltz P., Rasminsky M. A model for the mode of action of GABA on primary afferent terminals: depolarizing effects of GABA applied iontophoretically to neurones of mammalian dorsal root ganglia. Neuropharmacology. 1974 Jun;13(6):553–563. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(74)90145-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner D., Kandel E. R. Physiological and kinetic properties of cholinergic receptors activated by multiaction interneurons in buccal ganglia of Aplysia. J Neurophysiol. 1977 Mar;40(2):333–348. doi: 10.1152/jn.1977.40.2.333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerschenfeld H. M. Chemical transmission in invertebrate central nervous systems and neuromuscular junctions. Physiol Rev. 1973 Jan;53(1):1–119. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1973.53.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. The influence of potassium and chloride ions on the membrane potential of single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:127–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. J., Kuffler S. W., Dennis M. J. Differential chemosensitivity of synaptic and extrasynaptic areas on the neuronal surface membrane in parasympathetic neurons of the frog, tested by microapplication of acetylcholine. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971 Apr 27;177(1049):541–553. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1971.0046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell H. C., Kuffler S. W., Yoshikami D. Post-synaptic potentiation: interaction between quanta of acetylcholine at the skeletal neuromuscular synapse. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(2):427–463. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard J. I. Microphysiology of vertebrate neuromuscular transmission. Physiol Rev. 1973 Jul;53(3):674–723. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1973.53.3.674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hösli L., Hösli E., Andrès P. F. Nervous tissue culture--a model to study action and uptake of putative neurotransmitters such as amino acids. Brain Res. 1973 Nov 23;62(2):597–602. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90727-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., PHILLIS J. W. Iontophoretic studies of neurones in the mammalian cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1963 Feb;165:274–304. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. S., Krnjević K. The action of glycine on cortical neurones. Exp Brain Res. 1969;9(2):155–163. doi: 10.1007/BF00238328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Puil E., Werman R. GABA and glycine actions on spinal motoneurons. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1977 Jun;55(3):658–669. doi: 10.1139/y77-090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Schwartz S. The action of gamma-aminobutyric acid on cortical neurones. Exp Brain Res. 1967;3(4):320–336. doi: 10.1007/BF00237558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitan H., Tauc L. Acetylcholine receptors: topographic distribution and pharmacological properties of two receptor types on a single molluscan neurone. J Physiol. 1972 May;222(3):537–558. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy R. A. GABA: a direct depolarizing action at the mammalian primary afferent terminal. Brain Res. 1974 Aug 9;76(1):155–160. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90522-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. G. Nerve and muscle cells in culture. Physiol Rev. 1975 Jan;55(1):1–61. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1975.55.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll R. A., Padjen A., Barker J. L. Analysis of amino acid responses on frog motoneurones. Neuropharmacology. 1976 Jan;15(1):45–53. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(76)90096-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi S., Minota S., Karczmar A. G. Primary afferent neurones: the ionic mechanism of GABA-mediated depolarization. Neuropharmacology. 1974 Mar;13(3):215–219. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(74)90110-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obata K., Takeda K., Shinozaki H. Further study on pharmacological properties of the cerebellar-induced inhibition of deiters neurones. Exp Brain Res. 1970 Nov 26;11(4):327–342. doi: 10.1007/BF00237907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock J. H., Nelson P. G., Goldstone M. W. Electrophysiologic study of cultured neurons dissociated from spinal cords and dorsal root ganglia of fetal mice. Dev Biol. 1973 Jan;30(1):137–152. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90053-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peper K., Dreyer F., Müller K. D. Analysis of cooperativity of drug-receptor interaction by quantitative iontophoresis at frog motor end plates. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:187–192. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransom B. R., Barker J. L. Pentobarbital selectively enhances GABA-mediated post-synaptic inhibition in tissue cultured mouse spinal neurons. Brain Res. 1976 Sep 24;114(3):530–535. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90977-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransom B. R., Bullock P. N., Nelson P. G. Mouse spinal cord in cell culture. III. Neuronal chemosensitivity and its relationship to synaptic activity. J Neurophysiol. 1977 Sep;40(5):1163–1177. doi: 10.1152/jn.1977.40.5.1163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransom B. R., Christian C. N., Bullock P. N., Nelson P. G. Mouse spinal cord in cell culture. II. Synaptic activity and circuit behavior. J Neurophysiol. 1977 Sep;40(5):1151–1162. doi: 10.1152/jn.1977.40.5.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransom B. R., Neale E., Henkart M., Bullock P. N., Nelson P. G. Mouse spinal cord in cell culture. I. Morphology and intrinsic neuronal electrophysiologic properties. J Neurophysiol. 1977 Sep;40(5):1132–1150. doi: 10.1152/jn.1977.40.5.1132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickholm A., Wallin B. G. Relative ion permeabilities in the crayfish giant axon determined from rapid external ion changes. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Aug;50(7):1929–1953. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.7.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tebecis A. K., Phillis J. W. The use of convulsants in studying possible functions of amino acids in the toad spinal cord. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1969 Mar;28(3):1303–1315. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(69)90568-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ten Bruggencate G., Engberg I. Analysis of glycine actions on spinal interneurones by intracellular recording. Brain Res. 1968 Nov;11(2):446–450. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(68)90037-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werman R. An electrophysiological approach to drug-receptor mechanisms. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1969 Sep 15;30(6):997–1017. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(69)91038-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werman R., Davidoff R. A., Aprison M. H. Inhibitory of glycine on spinal neurons in the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1968 Jan;31(1):81–95. doi: 10.1152/jn.1968.31.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Bruggencate G., Engberg I. Iontophoretic studies in Deiters' nucleus of the inhibitory actions of GABA and related amino acids and the interactions of strychnine and picrotoxin. Brain Res. 1971 Feb 5;25(3):431–448. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90453-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



