Abstract
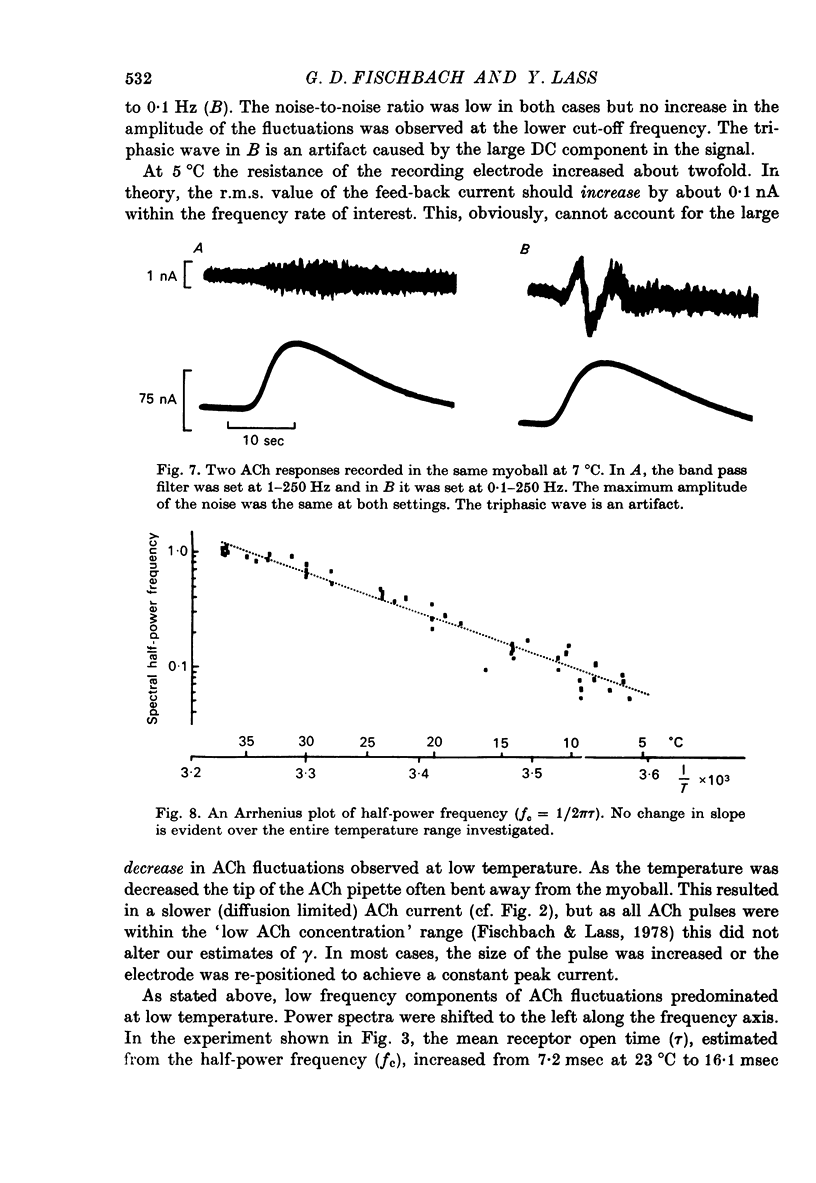
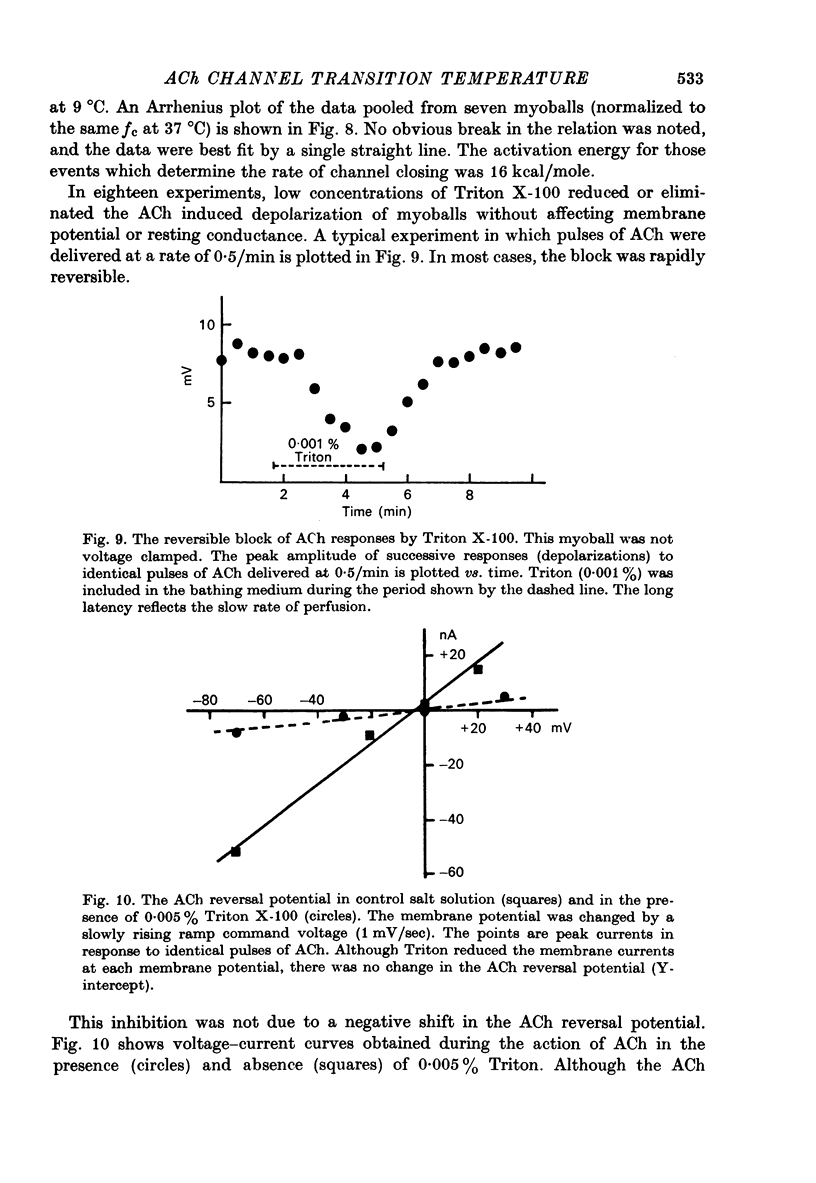
1. The temperature dependence of ACh channel conductance (gamma) and channel open time (tau) was determined by analysing ACh induced membrane current fluctuations in voltage clamped chick myoballs. 2. gamma decreased from 25-30 pmho at 37 degrees C to less than 5 phmo at 10 degrees C. An Arrhenius plot of gamma vs. temperature exhibited a clear break or 'transition temperature' at 20 degrees C. 3. tau increased from 2 msec at 37 degrees C to 16 msec at 10 degrees C. The Arrhenius plot of tau vs. temperature was linear. No transition temperature was detected. 4. Submicellar concentrations of the non-ionic detergent, Triton X-100 reversibly blocked ACh respnses. The effect was all-or-none at the molecular level. 5. These results are consistent with the possibility that the fluidity of membrane lipids in the ACh receptor micro-environment may influence the degree to which the channel can open.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. R., Cull-Candy S. G., Miledi R. Potential-dependent transition temperature of ionic channels induced by glutamate in locust muscle. Nature. 1977 Aug 18;268(5621):663–665. doi: 10.1038/268663a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. R., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp analysis of acetylcholine produced end-plate current fluctuations at frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(3):655–691. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartels E., Rosenberg P. Correlation between electrical activity and splitting of phospholipids by snake venom in the single electroplax. J Neurochem. 1972 May;19(5):1251–1265. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01451.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P., Benedetti L., Bourgeois J. P., Brisson A., Cartaud J., Devaux P., Grünhagen H., Moreau M., Popot J. L., Sobel A. Some structural properties of the cholinergic receptor protein in its membrane environmental relevant to its function as a pharmacological receptor. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:211–230. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. B., Changeux J. P. The cholinergic receptor protein in its membrane environment. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1975;15:83–103. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.15.040175.000503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Dionne V. E., Steinbach J. H., Stevens C. F. Conductance of channels opened by acetylcholine-like drugs in muscle end-plate. Nature. 1975 Jan 17;253(5488):204–206. doi: 10.1038/253204a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer F., Müller K. D., Peper K., Sterz R. The M. omohyoideus of the mouse as a convenient mammalian muscle preparation. A study of junctional and extrajunctional acetylcholine receptors by noise analysis and cooperativity. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Dec 28;367(2):115–122. doi: 10.1007/BF00585146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischbach G. D., Lass Y. Acetylcholine noise in cultured chick myoballs: a voltage clamp analysis. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:515–526. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., Hamill O. P. Effects of several inhalation anaesthetics on the kinetics of postsynaptic conductance changes in mouse diaphragm. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Jun;57(2):263–272. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1976.tb07476.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., McBurney R. N., Schneider G. T. Effects of some aliphatic alcohols on the conductance change caused by a quantum of acetylcholine at the toad end-plate. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(2):409–429. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Simons K. Solubilization of membranes by detergents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):29–79. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz A. F., Hatten M. E., Burger M. M. Membrane fatty acid replacements and their effect on growth and lectin-induced agglutinability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3115–3119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houslay M. D., Warren G. B., Birdsall N. J., Metcalfe J. C. Lipid phase transitions control beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase activity in defined-lipid protein complexes. FEBS Lett. 1975 Mar 1;51(1):146–151. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80873-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The effect of procaine on the action of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):269–284. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The statistical nature of the acetycholine potential and its molecular components. J Physiol. 1972 Aug;224(3):665–699. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimelberg H. K., Papahadjopoulos D. Effects of phospholipid acyl chain fluidity, phase transitions, and cholesterol on (Na+ + K+)-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 25;249(4):1071–1080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lass Y., Fischbach G. D. A discontinuous relationship between the acetylcholine-activated channel conductance and temperature. Nature. 1976 Sep 9;263(5573):150–151. doi: 10.1038/263150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linden C. D., Wright K. L., McConnell H. M., Fox C. F. Lateral phase separations in membrane lipids and the mechanism of sugar transport in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2271–2275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Sakmann B. Single-channel currents recorded from membrane of denervated frog muscle fibres. Nature. 1976 Apr 29;260(5554):799–802. doi: 10.1038/260799a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overath P., Träuble H. Phase transitions in cells, membranes, and lipids of Escherichia coli. Detection by fluorescent probes, light scattering, and dilatometry. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 3;12(14):2625–2634. doi: 10.1021/bi00738a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


