Abstract
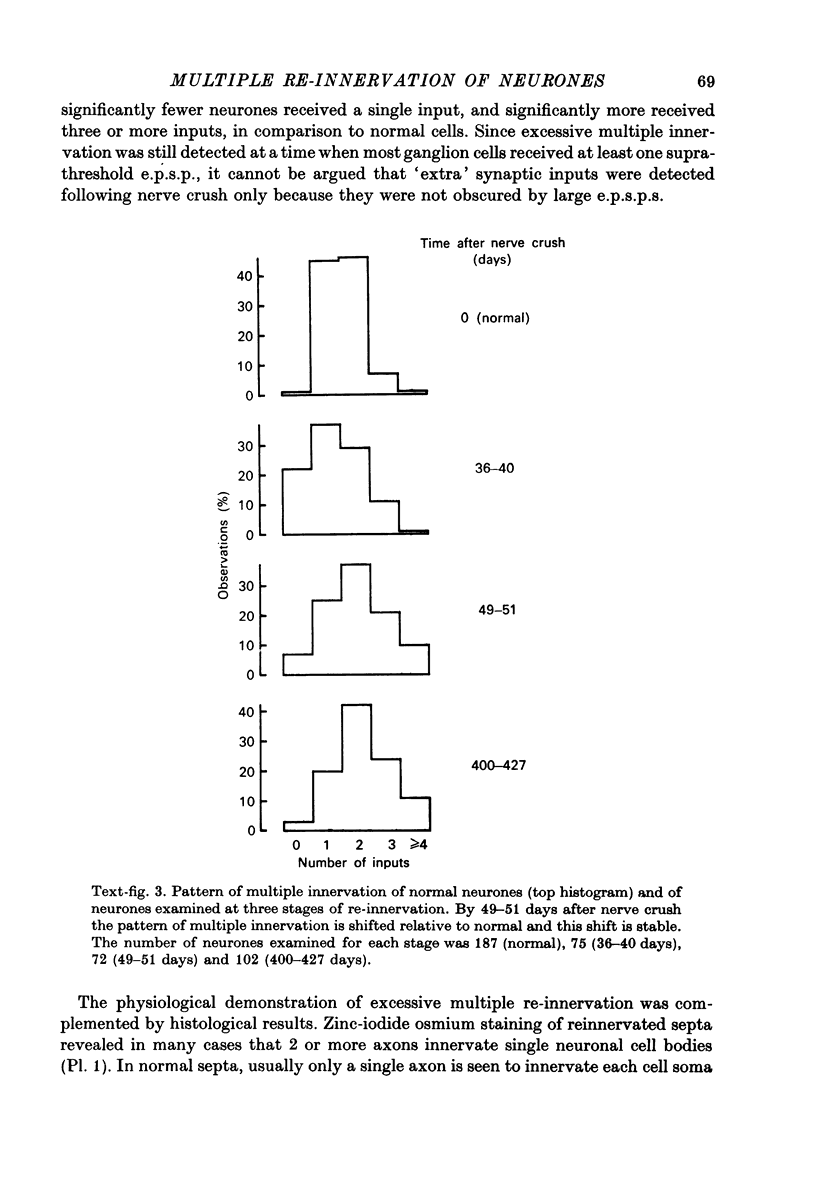
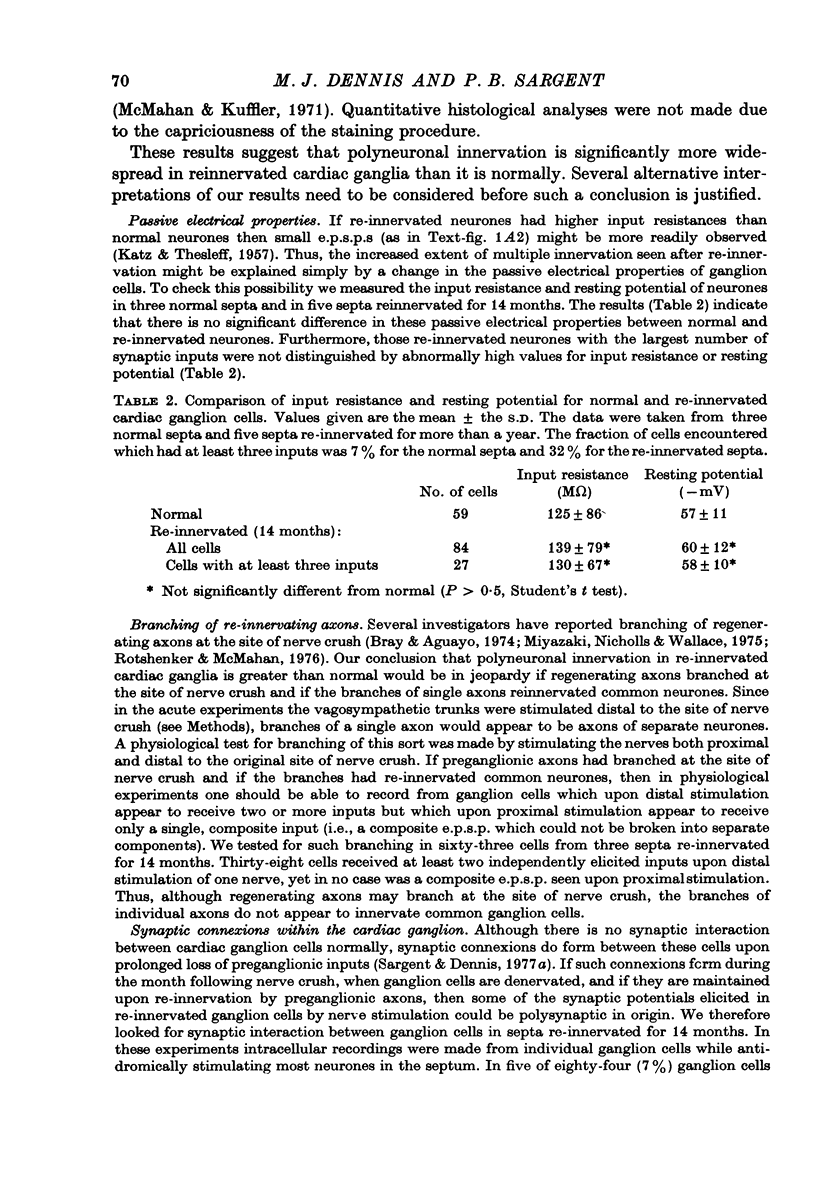
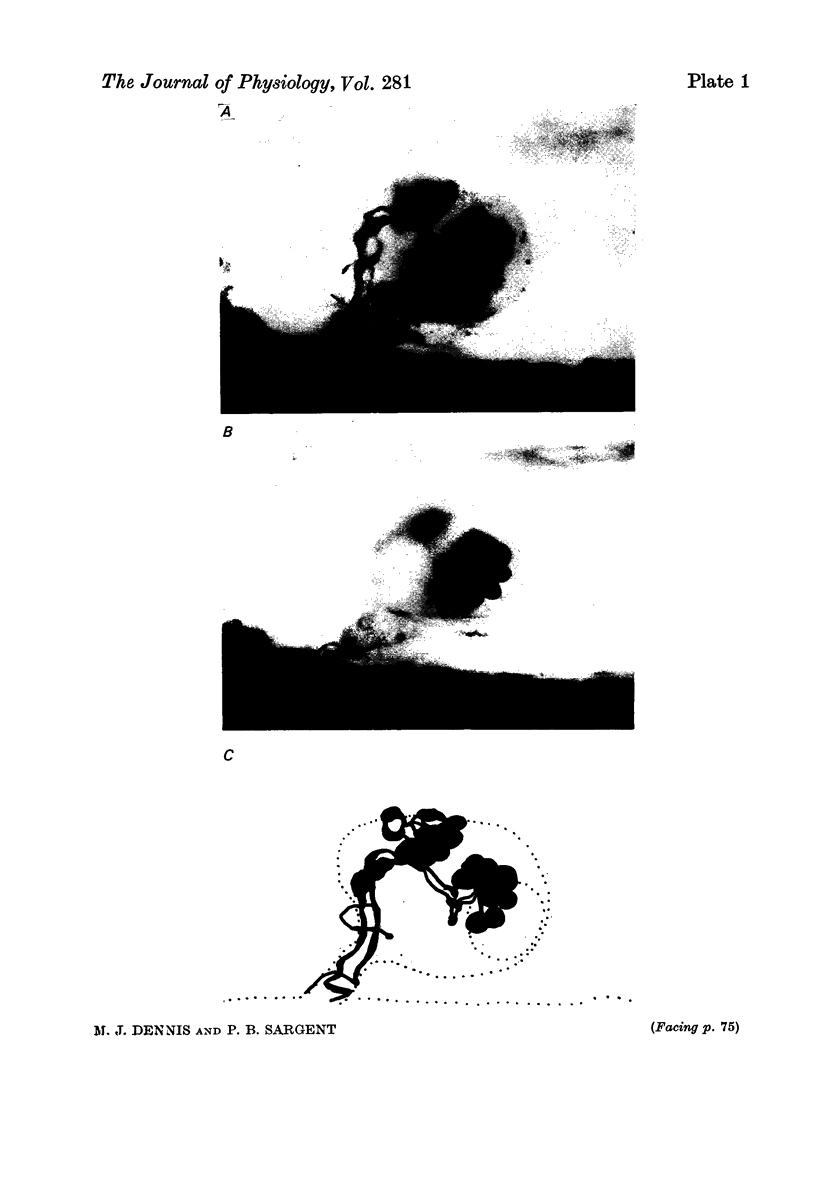
1. Multiple innervation of parasympathetic neurones was examined in normal and re-innervated frog cardiac ganglia. The number of synaptic inputs impinging upon individual ganglion cells was determined by recording intracellularly and stimulating the vagosympathetic nerves. 2. In unoperated cardiac ganglia most neurones (93%) received a large, suprathreshold synaptic input. Some ganglion cells received additional, small synaptic inputs. Roughly equal numbers of cells encountered were singly and doubly innervated, and only 8% received more than two inputs. 3. Re-innervation of cardiac ganglion cells began three weeks after bilateral crush of the vagosympathetic nerves. By 7 weeks more than 90% of the ganglion cells were re-innervated. At this stage the pattern of multiple innervation was significantly different than normal: doubly innervated neurones outnumbered singly innervated ones, and 31% of the cells encountered received more than two inputs. This pattern was stable for at least a year. 4. These results indicate that polyneuronal innervation of cardiac ganglion cells is more widespread after re-innervation than it is normally and, furthermore, that synapse elimination does not occur during re-innervation of these cells.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akert K., Sandri C. An electron-microscopic study of zinc iodide-osmium impregnation of neurons. I. Staining of synaptic vesicles at cholinergic junctions. Brain Res. 1968 Feb;7(2):286–295. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(68)90104-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagust J., Lewis D. M., Westerman R. A. Polyneuronal innervation of kitten skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1973 Feb;229(1):241–255. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., McLachlan E. M., Taylor R. S. The formation of synapses in reinnervated mammalian striated muscle. J Physiol. 1973 Sep;233(3):481–500. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Pettigrew A. G. The formation of synapses in amphibian striated muscle during development. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;252(1):203–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Pettigrew A. G. The formation of synapses in striated muscle during development. J Physiol. 1974 Sep;241(2):515–545. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray G. M., Aguayo A. J. Regeneration of peripheral unmyelinated nerves. Fate of the axonal sprouts which develop after injury. J Anat. 1974 Jul;117(Pt 3):517–529. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. C., Jansen J. K., Van Essen D. Polyneuronal innervation of skeletal muscle in new-born rats and its elimination during maturation. J Physiol. 1976 Oct;261(2):387–422. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conradi S., Ronnevi L. O. Ultrastructure and synaptology of the initial axon segment of cat spinal motoneurons during early postnatal development. J Neurocytol. 1977 Apr;6(2):195–210. doi: 10.1007/BF01261505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtney K., Roper S. Sprouting of synapses after partial denervation of frag cardic ganglion. Nature. 1976 Jan 29;259(5541):317–319. doi: 10.1038/259317a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crepel F., Mariani J., Delhaye-Bouchaud N. Evidence for a multiple innervation of Purkinje cells by climbing fibers in the immature rat cerebellum. J Neurobiol. 1976 Nov;7(6):567–578. doi: 10.1002/neu.480070609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis M. J., Harris A. J., Kuffler S. W. Synaptic transmission and its duplication by focally applied acetylcholine in parasympathetic neurons in the heart of the frog. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971 Apr 27;177(1049):509–539. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1971.0045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huizar P., Kuno M., Kudo N., Miyata Y. Reaction of intact spinal motoneurones to partial denervation of the muscle. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(1):175–191. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen J. K., Van Essen D. C. Re-innervation of rat skeleton muscle in the presence of alpha-bungarotoxin. J Physiol. 1975 Sep;250(3):651–667. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., THESLEFF S. On the factors which determine the amplitude of the miniature end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):267–278. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuffler S. W., Dennis M. J., Harris A. J. The development of chemosensitivity in extrasynaptic areas of the neuronal surface after denervation of parasympathetic ganglion cells in the heart of the frog. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971 Apr 27;177(1049):555–563. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1971.0047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis P. R., Jones P. B., Breathnach S. M., Navaratnam V. Regenerative capacity of visceral preganglionic neurones. Nat New Biol. 1972 Apr 12;236(67):181–182. doi: 10.1038/newbio236181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtman J. W. The reorganization of synaptic connexions in the rat submandibular ganglion during post-natal development. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(1):155–177. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McArdle J. J. Complex end-plate potentials at the regenerating neuromuscular junction of the rat. Exp Neurol. 1975 Dec;49(3):629–638. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(75)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahan U. J., Kuffler S. W. Visual identification of synaptic boutons on living ganglion cells and of varicosities in postganglionic axons in the heart of the frog. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971 Apr 27;177(1049):485–508. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1971.0044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendell L. M., Henneman E. Terminals of single Ia fibers: location, density, and distribution within a pool of 300 homonymous motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1971 Jan;34(1):171–187. doi: 10.1152/jn.1971.34.1.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki S., Nicholls J. G., Wallace B. G. Modification and regeneration of synaptic connections in cultured leech ganglia. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:483–493. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nja A., Purves D. Re-innervation of guinea-pig superior cervical ganglion cells by preganglionic fibres arising from different levels of the spinal cord. J Physiol. 1977 Nov;272(3):633–651. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Njå A., Purves D. Specific innervation of guinea-pig superior cervical ganglion cells by preganglionic fibres arising from different levels of the spinal cord. J Physiol. 1977 Jan;264(2):565–583. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palkovits M., Magyar P., Szentágothai J. Quantitative histological analysis of the cerebellar cortex in the cat. 3. Structural organization of the molecular layer. Brain Res. 1971 Nov;34(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90347-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves D. Competitive and non-competitive re-innervation of mammalian sympathetic neurones by native and foreign fibres. J Physiol. 1976 Oct;261(2):453–475. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves D. Functional and structural changes in mammalian sympathetic neurones following interruption of their axons. J Physiol. 1975 Nov;252(2):429–463. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfern P. A. Neuromuscular transmission in new-born rats. J Physiol. 1970 Aug;209(3):701–709. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley D. A. Multiple axon branches innervating single endplates of kitten soleus myofibers. Brain Res. 1976 Jun 25;110(1):158–161. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90216-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roper S. An electrophysiological study of chemical and electrical synapses on neurones in the parasympathetic cardiac ganglion of the mudpuppy, Necturus maculosus: evidence for intrinsic ganglionic innervation. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):427–454. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roper S. Sprouting and regeneration of synaptic terminals in the frog cardiac ganglion. Nature. 1976 May 13;261(5556):148–149. doi: 10.1038/261148a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal J. L., Taraskevich P. S. Reduction of multiaxonal innervation at the neuromuscular junction of the rat during development. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(2):299–310. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotshenker S., McMahan U. J. Altered patterns of innervation in frog muscle after denervation. J Neurocytol. 1976 Dec;5(6):719–730. doi: 10.1007/BF01181583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent P. B., Dennis M. J. Formation of synapses between parasympathetic neurones deprived of preganglionic innervation. Nature. 1977 Aug 4;268(5619):456–458. doi: 10.1038/268456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt H., Stefani E. Action potentials in slow muscle fibres of the frog during regeneration of motor nerves. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(2):507–517. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WYCKOFF R. W., YOUNG J. Z. The motorneuron surface. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1956 Mar 13;144(917):440–450. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1956.0002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitsen H. A., Weight F. F. Synaptic innervation of sympathetic ganglion cells in the bullfrog. Brain Res. 1977 Jun 10;128(2):197–211. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90988-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]