Abstract
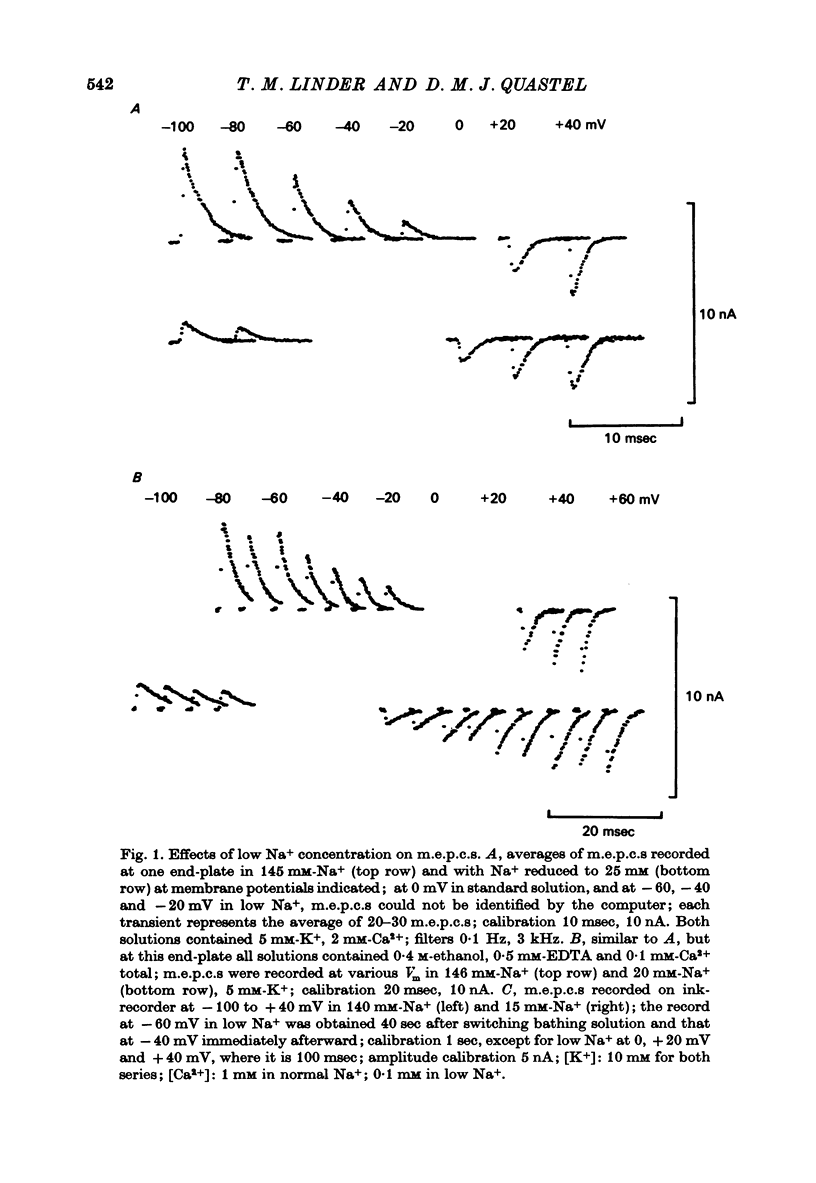
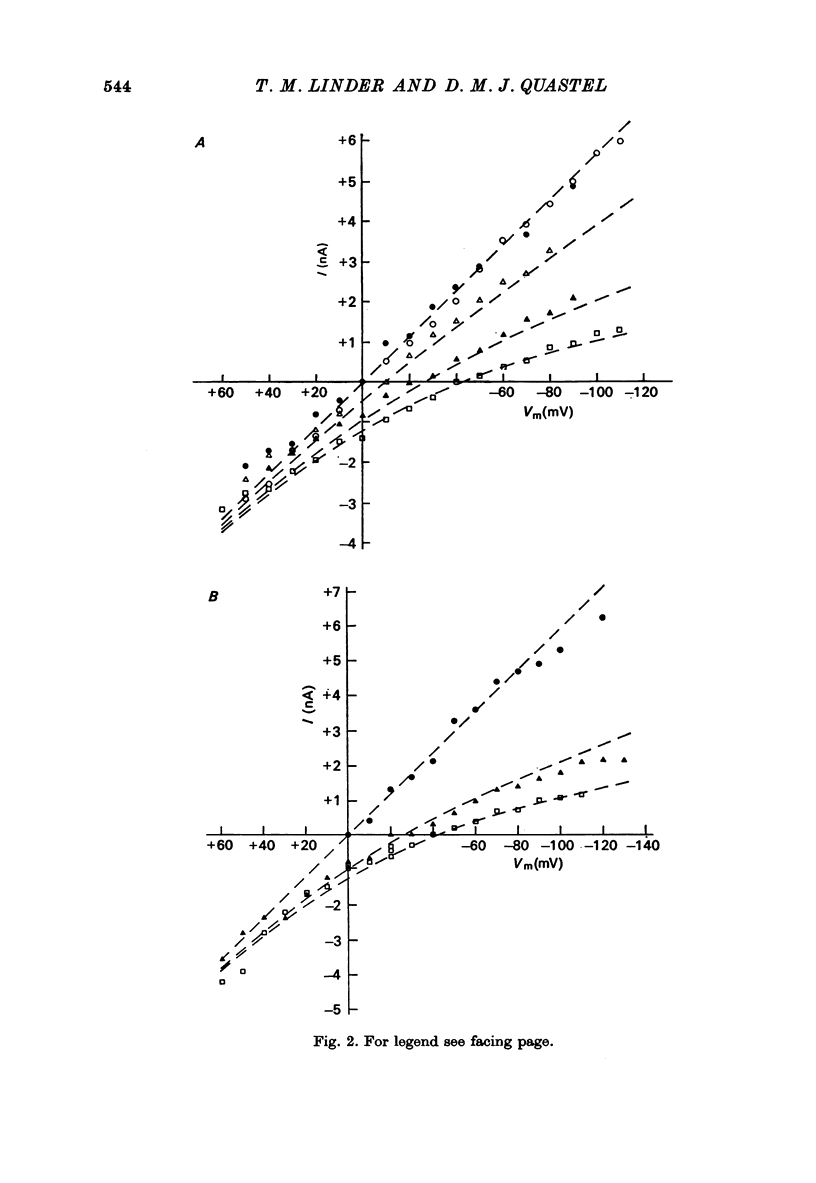
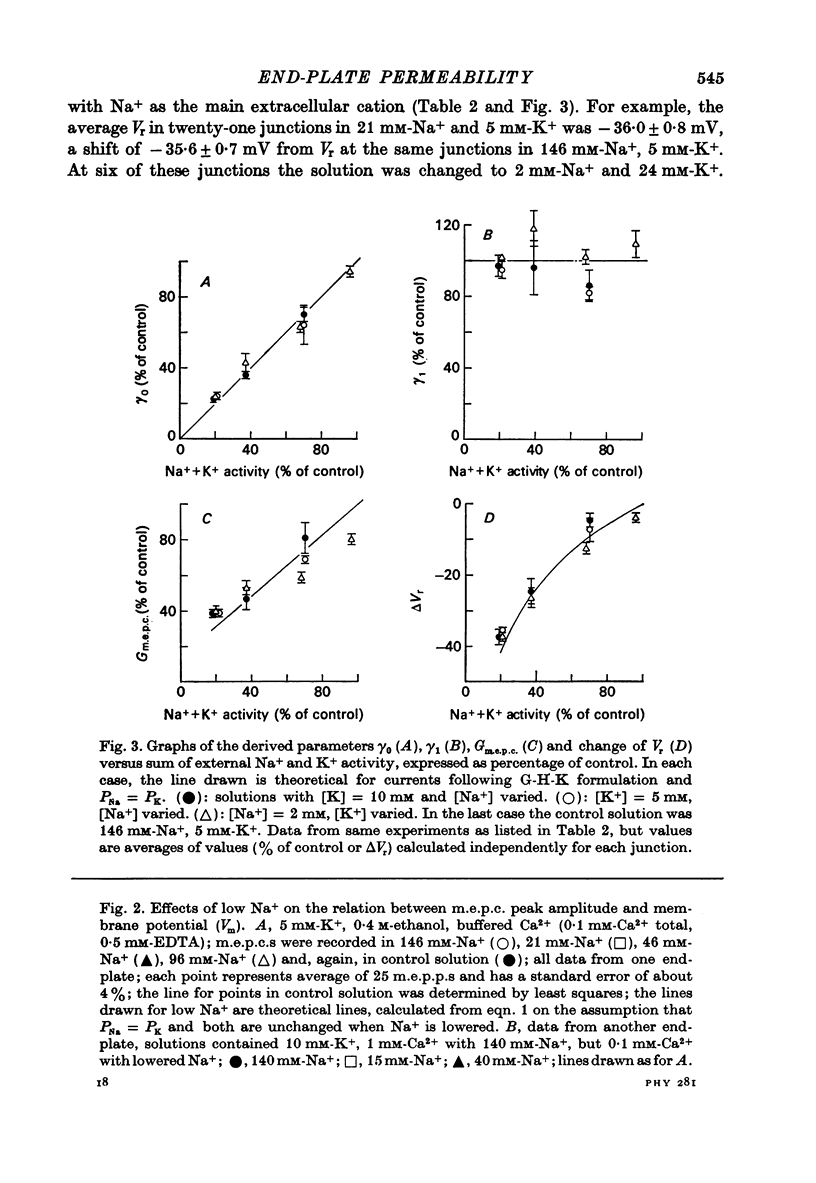
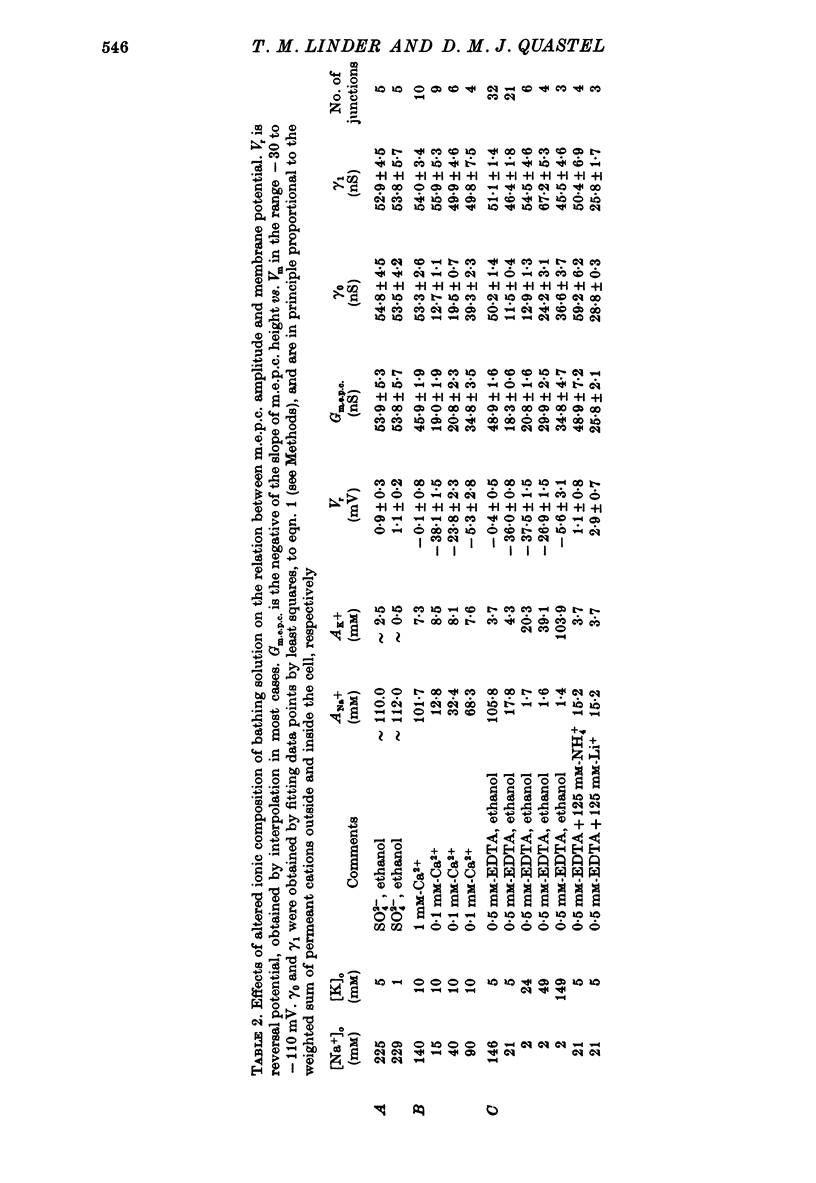
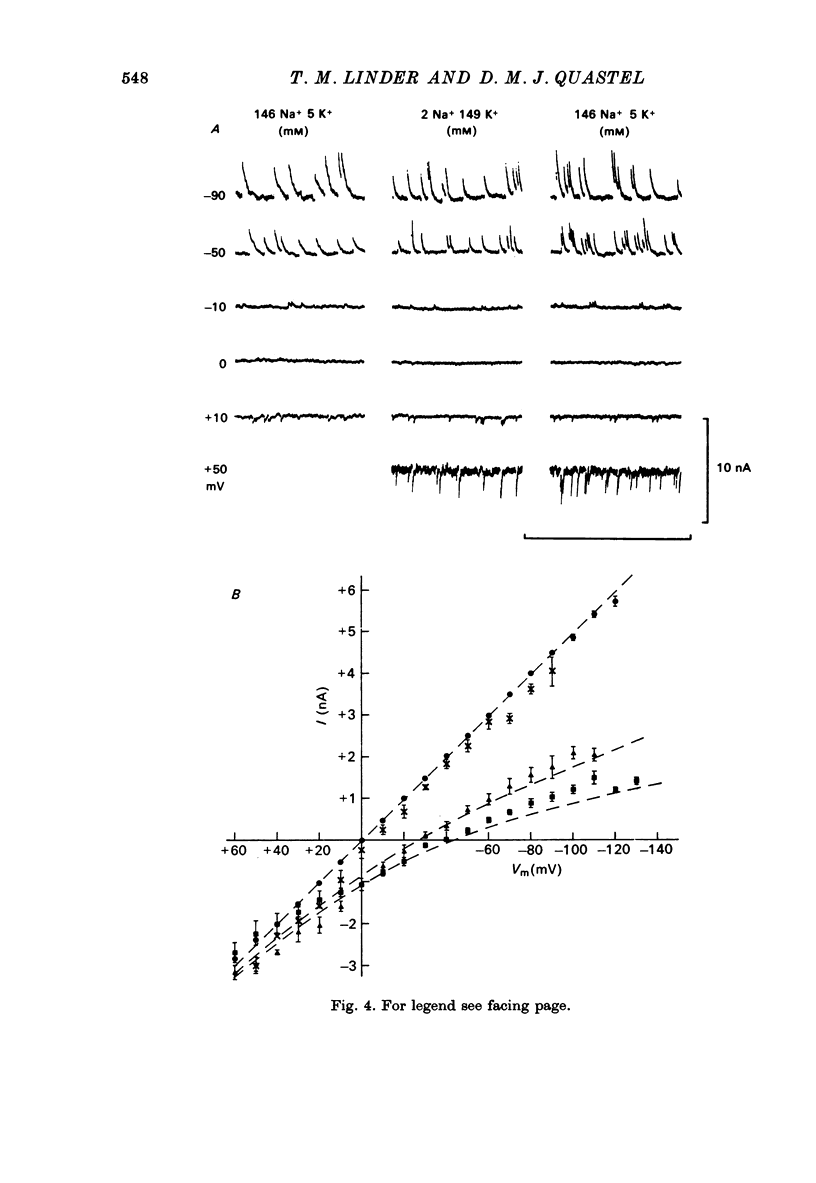
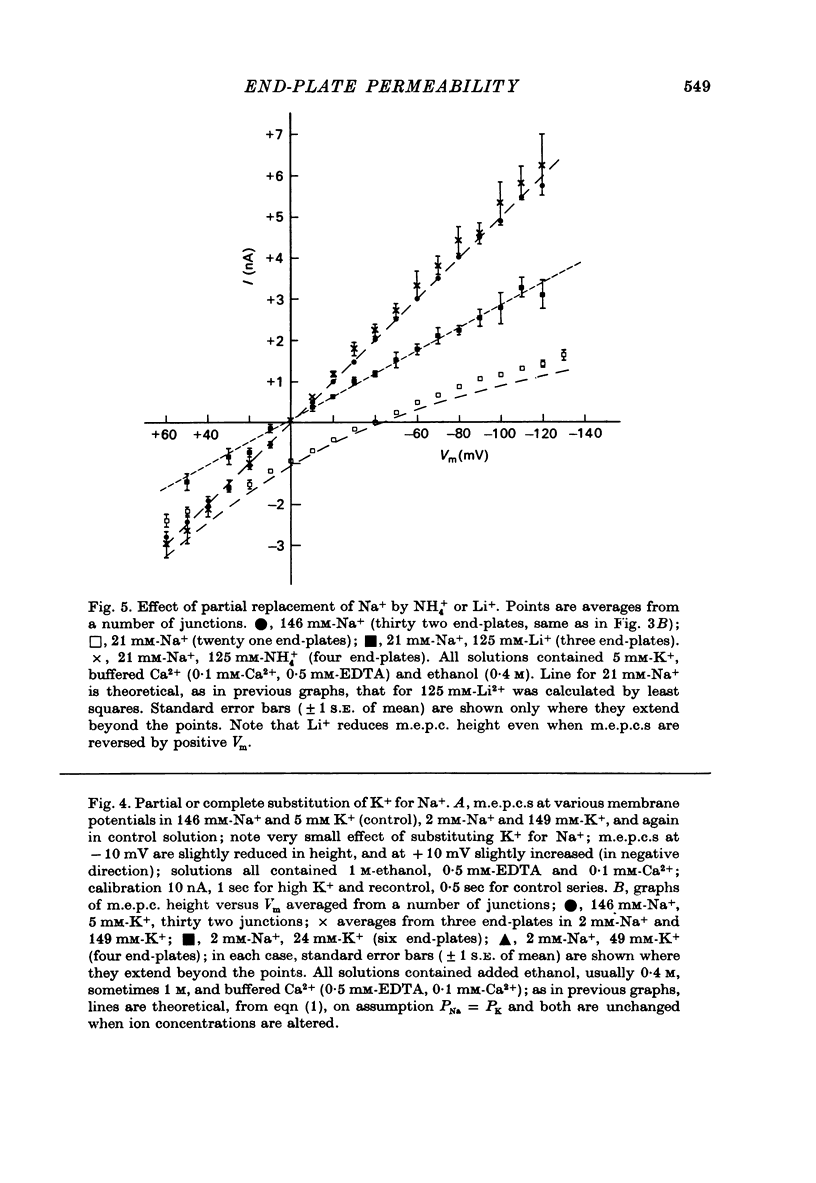
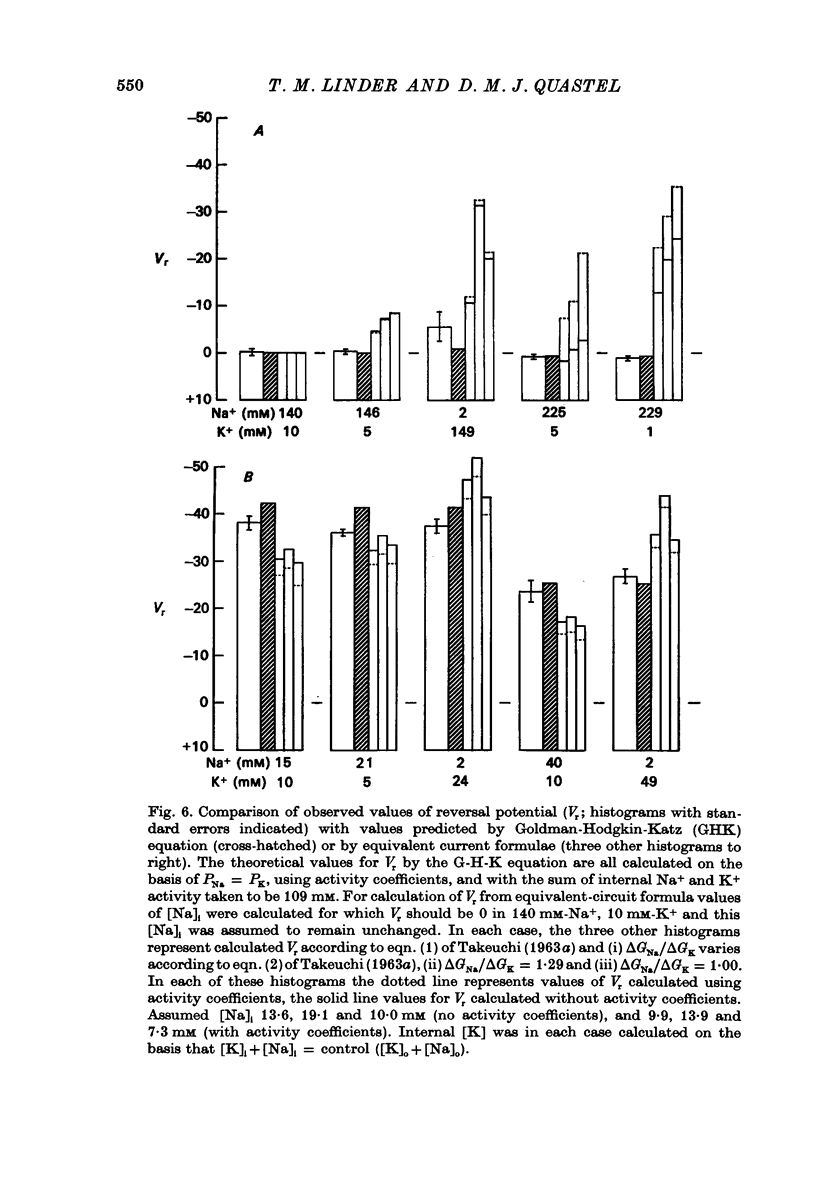
1. Miniature end-plate currents (m.e.p.c.s) were recorded from mouse diaphragm using a point voltage-clamp. The relation between m.e.p.c. amplitude and membrane potential was determined in bathing solutions of varied composition. 2. In solution containing normal sodium the relation between m.e.p.c. height and membrane potential (Im.e.p.c./Vm relation) was always linear, at least in the range +30 to -100 mV; the reversal potential (Vr) at which Im.e.p.c. was zero was close to 0. The slope of the Im.e.p.c./Vm line varied little between junctions (coefficient of variation about 20%) and was about 50 nS, or 1nA per 20 mV. The Im.e.p.c./Vm relation was not altered by withdrawal of Ca2+, addition of ethanol, or substitution of NO-3 or SO2-(4) for Cl-. 3. Alteration of K+ concentration in the bathing medium, in the range 10 to 1 mM, had no apparent effect on the Im.e.p.c./Vm relation. 4. Reduction of Na+ concentration, with isosmotic substitution of sucrose, caused rapid alteration of the Im.e.p.c./Vm relation, which became rectifying, with a slope at negative Vm less than at positive Vm. Vr was shifted in the negative direction. Quantitatively these changes were close to those predicted by the Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz formulation for permeation of monovalent ions through a membrane with constant field. 5. In solution with low Na+ (2 mM) and partial substitution of K+ for Na+, the Im.e.p.c./Vm relation was indistinguishable from that in solutions with Na" as the predominant extracellular cation. With complete substitution of K+ for Na+ the Im.e.p.c./Vm relation was a little less steep (at negative Vm) than in Na+ solution and Vr was shifted slightly in the negative direction. 6. With substitution of NH+4 for Na+, the Im.e.p.c./Vm relation was little changed (about 10% steeper at negative Vm). With substitution of Li+ for Na+, the Im.e.p.c./Vm relation remained linear, but was made less steep, at positive as well as negative Vm, and Vr was shifted slightly in the positive direction. 7. These results indicate that the permeability change associated with generation of the m.e.p.c. (i.e., evoked by a quantum of transmitter) corresponds to the opening of a single species of membrane channel that allows the free movement of K+, Na+, NH+4, AND Li+ ions along their electrochemical gradients. The channel discriminates little between these ions. The apparent order of permeability is Li+ greater than NH+4 greater than Na+ greater than or equal to K+. The apparent permeability per channel corresponds to that expected for channels of about 6.4 A diameter, 100 A length, and ionic mobility the same as in dilute solution.
Full text
PDF
















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R. Drug blockade of open end-plate channels. J Physiol. 1976 Sep;260(3):531–552. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams P. R. Voltage jump analysis of procaine action at frog end-plate. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;268(2):291–318. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. R., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp analysis of acetylcholine produced end-plate current fluctuations at frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(3):655–691. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I., Van der Kloot W. Effects of [Ca2+] and [Mg2+] on the decay of miniature endplate currents. Nature. 1978 Jan 5;271(5640):77–79. doi: 10.1038/271077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Large W. A., Rang H. P. An analysis of the action of a false transmitter at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1977 Apr;266(2):361–395. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke J. D., Okamoto K., Quastel D. M. The role of calcium in depolarization-secretion coupling at the motor nerve terminal. J Physiol. 1973 Jan;228(2):459–497. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke J. D., Quastel D. M. Transmitter release by mammalian motor nerve terminals in response to focal polarization. J Physiol. 1973 Jan;228(2):377–405. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Miledi R., Trautmann A. Acetylcholine-induced channels and transmitter release at human endplates. Nature. 1978 Jan 5;271(5640):74–75. doi: 10.1038/271074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Biophysical aspects of neuro-muscular transmission. Prog Biophys Biophys Chem. 1956;6:121–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Changes in end-plate activity produced by presynaptic polarization. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):586–604. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. The membrane change produced by the neuromuscular transmitter. J Physiol. 1954 Sep 28;125(3):546–565. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dionne V. E., Stevens C. F. Voltage dependence of agonist effectiveness at the frog neuromuscular junction: resolution of a paradox. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(2):245–270. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer F., Müller K. D., Peper K., Sterz R. The M. omohyoideus of the mouse as a convenient mammalian muscle preparation. A study of junctional and extrajunctional acetylcholine receptors by noise analysis and cooperativity. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Dec 28;367(2):115–122. doi: 10.1007/BF00585146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer F., Walther C., Peper K. Junctional and extrajunctional acetylcholine receptors in normal and denervated frog muscle fibres. Noise analysis experiments with different agonists. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Oct 15;366(1):1–9. doi: 10.1007/BF02486555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunin-Barkovskii V. L., Kovalev S. A., Magazanik L. G., Potapova T. V., Chailakhian L. M. Potentsialy ravnovesiia postsinapticheskoi membrany, aktivirovannoi razlichnymi kholinomineikami, pri izmenenii vnekletochnoi ionnoi sredy. Biofizika. 1969 May-Jun;14(3):485–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards F. R., Redman S. J., Walmsley B. The effect of polarizing currents on unitary Ia excitatory post-synaptic potentials evoked in spinal motoneurones. J Physiol. 1976 Aug;259(3):705–723. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. An analysis of the end-plate potential recorded with an intracellular electrode. J Physiol. 1951 Nov 28;115(3):320–370. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. Spontaneous subthreshold activity at motor nerve endings. J Physiol. 1952 May;117(1):109–128. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P. The electromotive action of acetylcholine at the motor end-plate. J Physiol. 1950 Oct 16;111(3-4):408–422. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1950.sp004492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURUKAWA T., FURUKAWA A., TAKAGI T. Fibrillation of muscle fibers produced by ammonium ions and its relation to the spontaneous activity at the neuromuscular junction. Jpn J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;7(3):252–263. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.7.252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feltz A., Mallart A. Ionic permeability changes induced by some cholinergic agonists on normal and denervated frog muscles. J Physiol. 1971 Oct;218(1):101–116. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein A., Mauro A. Equivalent Circuits as Related to Ionic Systems. Biophys J. 1963 May;3(3):215–237. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(63)86817-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W. Generation of end-plate potentials. Physiol Rev. 1976 Jan;56(1):177–247. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1976.56.1.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., McBurney R. N. Effects of membrane potential, temperature and neostigmine on the conductance change caused by a quantum or acetylcholine at the toad neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(2):385–407. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., McBurney R. N. Miniature end-plate currents and potentials generated by quanta of acetylcholine in glycerol-treated toad sartorius fibres. J Physiol. 1972 Oct;226(1):79–94. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., McBurney R. N., Schneider G. T. Effects of some aliphatic alcohols on the conductance change caused by a quantum of acetylcholine at the toad end-plate. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(2):409–429. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., Quastel D. M. Competition between sodium and calcium ions in transmitter release at mammalian neuromuscular junctions. J Physiol. 1966 Jul;185(1):95–123. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D. E. POTENTIAL, IMPEDANCE, AND RECTIFICATION IN MEMBRANES. J Gen Physiol. 1943 Sep 20;27(1):37–60. doi: 10.1085/jgp.27.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. The influence of potassium and chloride ions on the membrane potential of single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:127–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 1;108(1):37–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell H. C., Kuffler S. W., Yoshikami D. Post-synaptic potentiation: interaction between quanta of acetylcholine at the skeletal neuromuscular synapse. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(2):427–463. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. L-glutamate as an excitatory transmitter at the Drosophila larval neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1976 Oct;262(1):215–236. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLY J. S. ANTAGONISM BETWEEN NA+ AND CA2+ AT THE NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION. Nature. 1965 Jan 16;205:296–297. doi: 10.1038/205296a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. S. The antagonism of Ca2+ by Na+ and other monovalent ions at the frog neuromuscular junction. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1968 Jul;53(3):239–249. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1968.sp001967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriebel M. E., Gross C. E. Multimodal distribution of frog miniature endplate potentials in adult denervated and tadpole leg muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Jul;64(1):85–103. doi: 10.1085/jgp.64.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILEY A. W., NORTH K. A. An electrical investigation of effects of repetitive stimulation on mammalian neuromuscular junction. J Neurophysiol. 1953 Sep;16(5):509–527. doi: 10.1152/jn.1953.16.5.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassignal N. L., Martin A. R. Effect of acetylcholine on postjunctional membrane permeability in eel electroplaque. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Jul;70(1):23–36. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeno T., Edwards C., Anraku M. Permeability of the endplate membrane activated by acetylcholine to some organic cations. J Neurobiol. 1977 Mar;8(2):173–184. doi: 10.1002/neu.480080208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magazanik L. G., Potapova T. V. Potentsialy ravnovesiia vnesinapticheskoi membrany denervirovannoi myshtsy pri izmenenii vnekletochnoi ionnoi sredy. Biofizika. 1969 Jul-Aug;14(4):658–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Stevens C. F. The effect of voltage on the time course of end-plate currents. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):151–171. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallart A., Dreyer F., Peper K. Current-voltage relation and reversal potential at junctional and extrajunctional ACh-receptors of the frog neuromuscular junction. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Mar 11;362(1):43–47. doi: 10.1007/BF00588679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onodera K., Yamakawa K. The effects of lithium on the neuromuscular junction of the frog. Jpn J Physiol. 1966 Oct 15;16(5):541–550. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.16.541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie A. K., Fambrough D. M. Ionic properties of the acetylcholine receptor in cultured rat myotubes. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Jun;65(6):751–767. doi: 10.1085/jgp.65.6.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandblom J. P., Eisenman G. Membrane potentials at zero current. The significance of a constant ionic permeability ratio. Biophys J. 1967 May;7(3):217–242. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(67)86585-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz T. L., Kado R. T. Permeability, phase-boundary potential and conductance in a cholinergic channel without constant field. Biophys J. 1977 Jun;18(3):323–349. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85617-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI A., TAKEUCHI N. Active phase of frog's end-plate potential. J Neurophysiol. 1959 Jul;22(4):395–411. doi: 10.1152/jn.1959.22.4.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI A., TAKEUCHI N. Changes in potassium concentration around motor nerve terminals, produced by current flow, and their effects on neuromuscular transmission. J Physiol. 1961 Jan;155:46–58. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI A., TAKEUCHI N. On the permeability of end-plate membrane during the action of transmitter. J Physiol. 1960 Nov;154:52–67. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI N. Some properties of conductance changes at the end-plate membrane during the action of acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1963 Jun;167:128–140. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


