Abstract
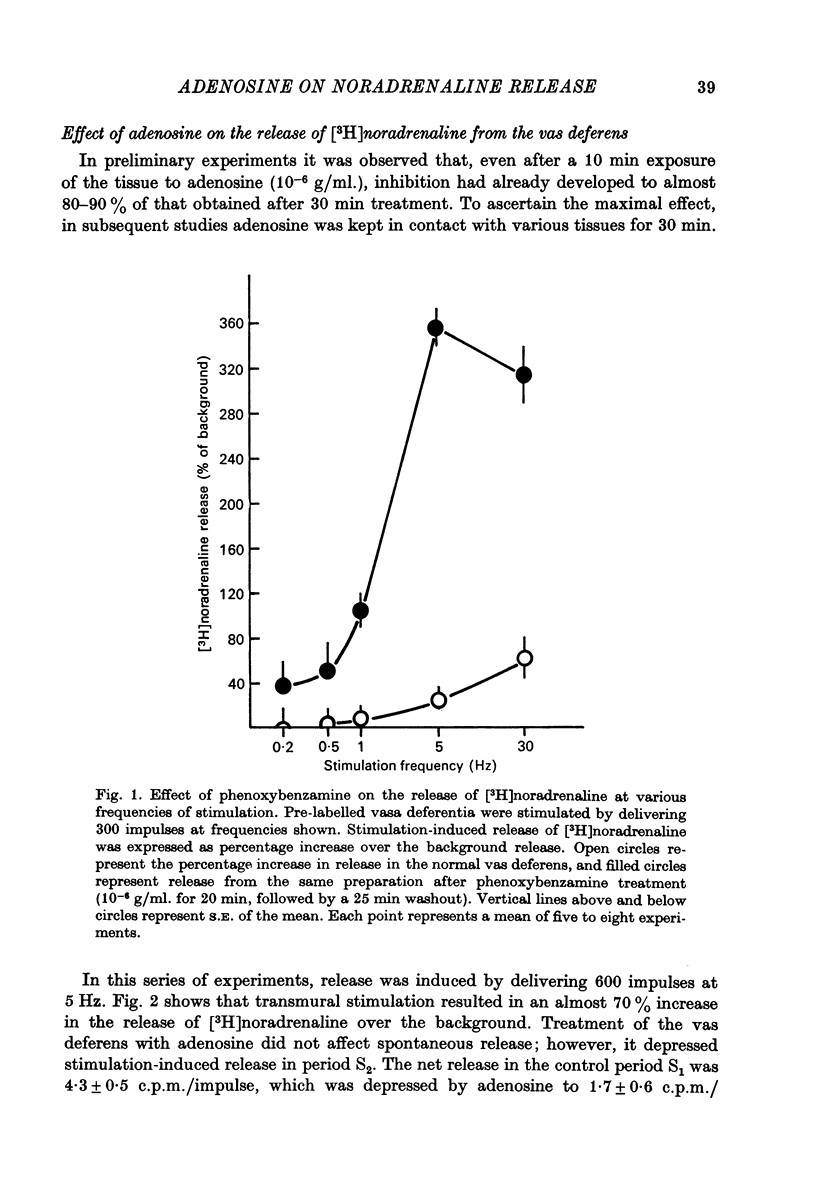
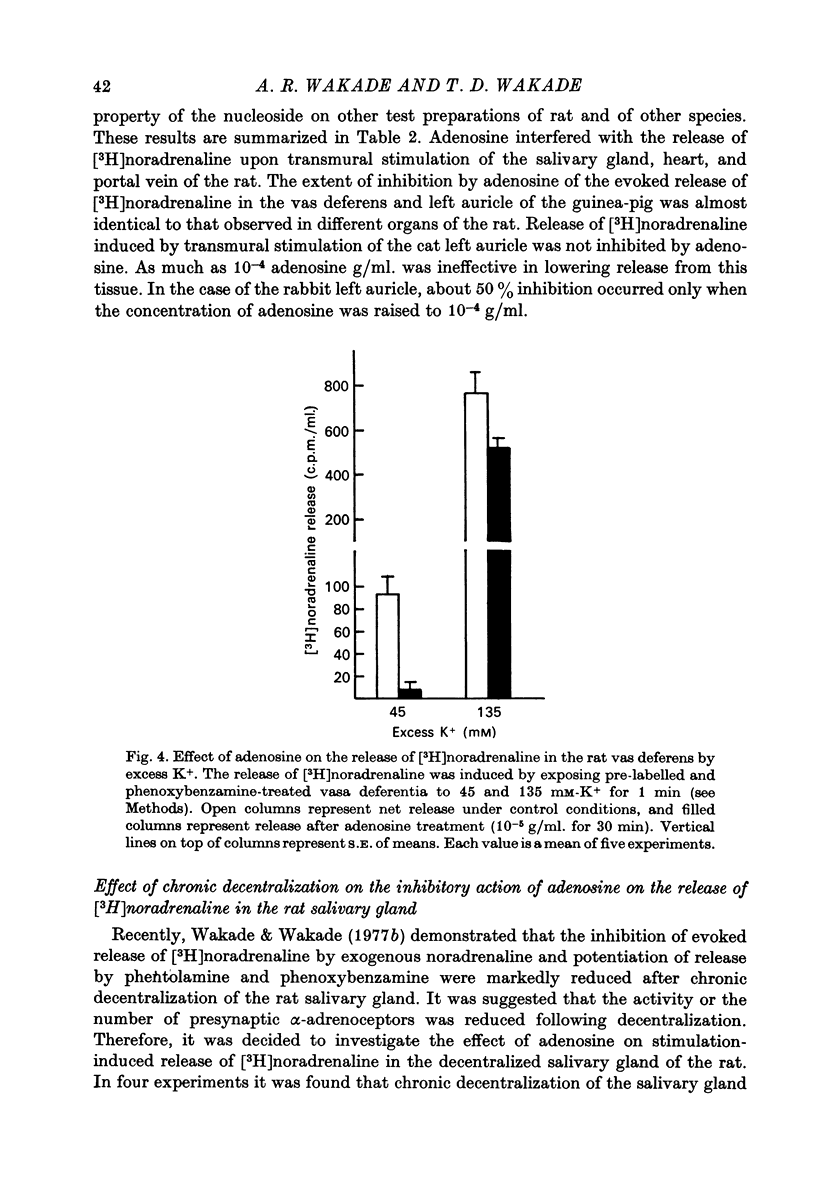
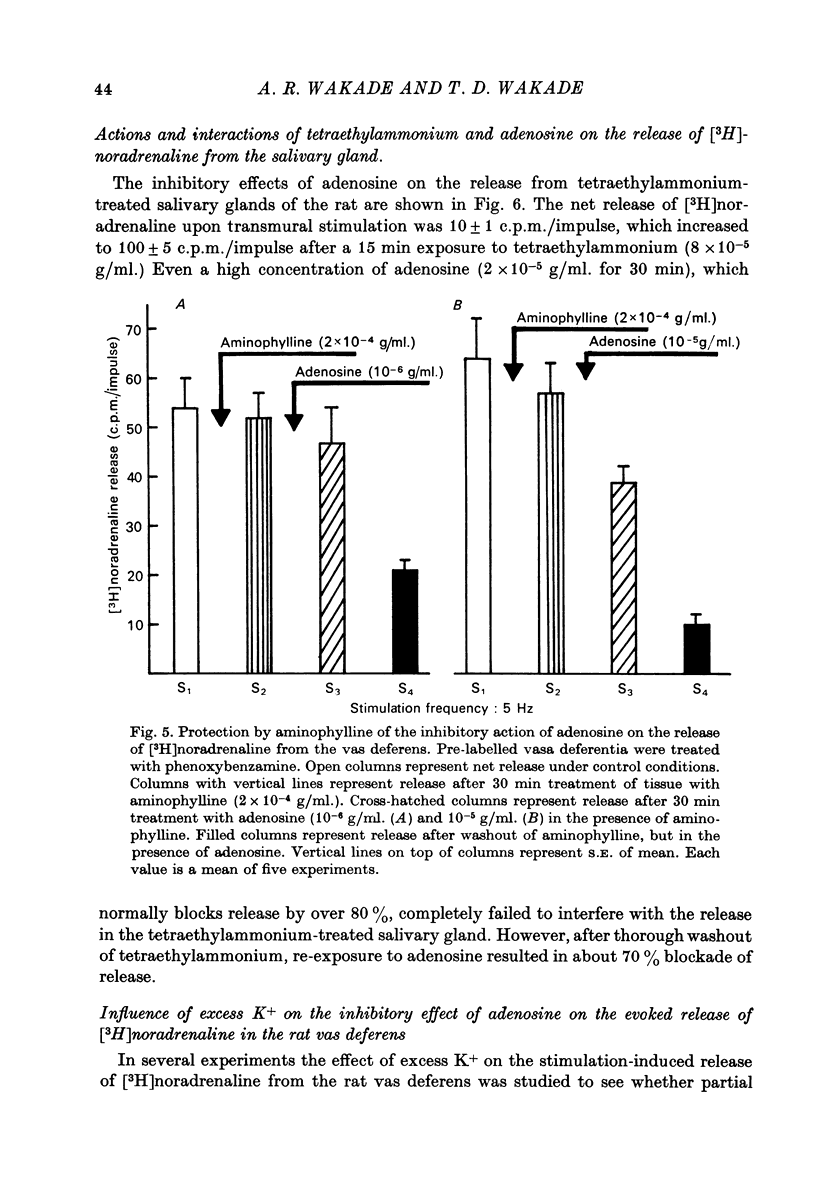
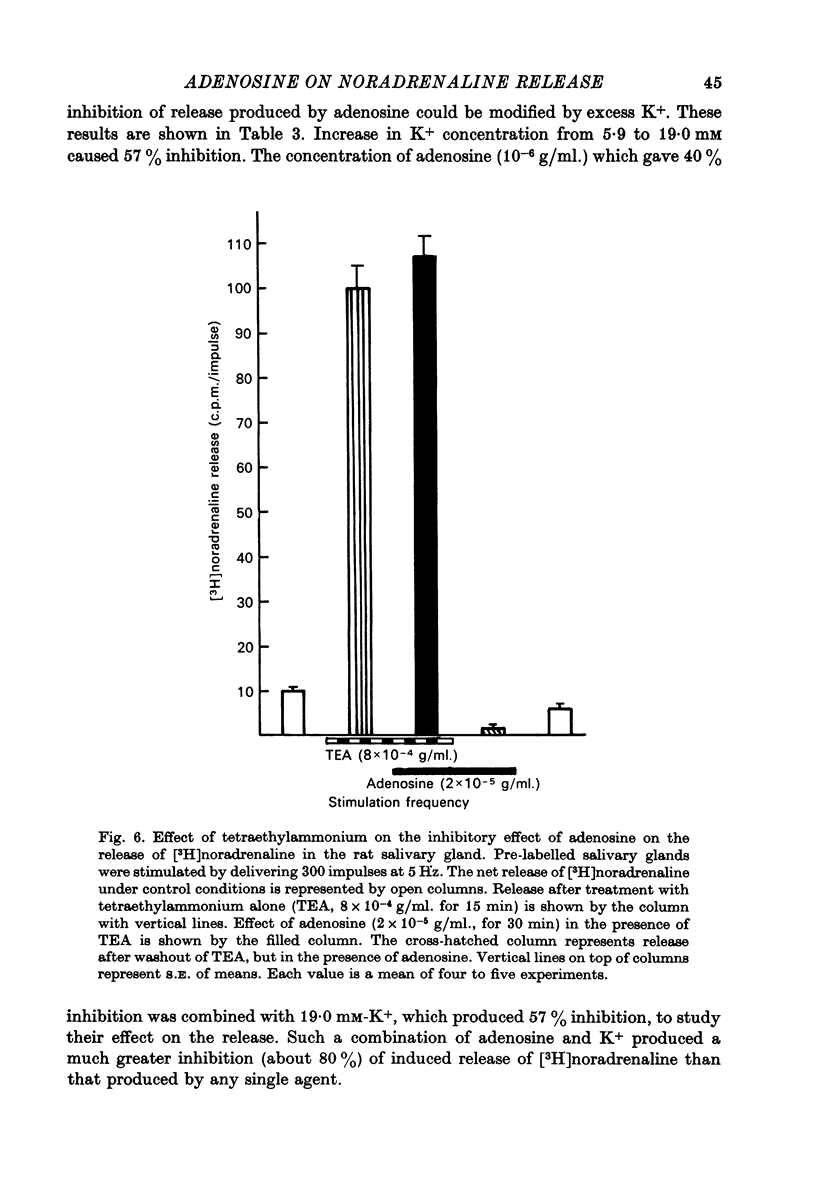
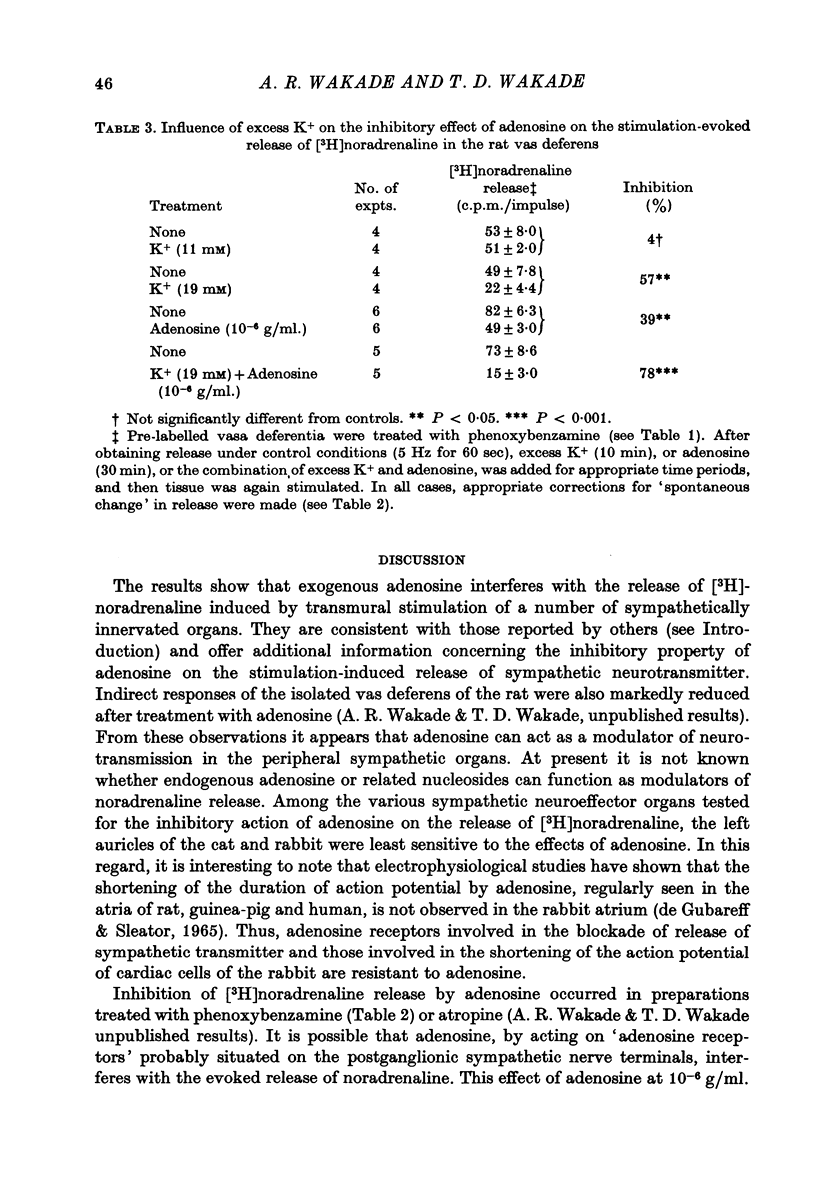
1. Release of [3H]noradrenaline evoked by stimulation (5 Hz) of the pre-labelled rat vas deferens was reduced to 50% by adenosine (10(-6) g/ml.). Inhibition of release was dependent on the concentration of adenosine and was inversely related to the frequency of stimulation. Phenoxybenzamine did not interfere with the action of adenosine on release. 2. Exposure of the pre-labelled rat vas deferens to 135 mM-K+ released almost 10 times more [3H]noradrenaline than exposure to 45 mM-K+. Release induced by 45 mM-K+ was almost abolished by adenosine (10(-6) g/ml.) but that induced by 135 mM-K+ was reduced to only 45%. 3. Inhibition of [3H]noradrenaline release was observed in salivary gland, heart and portal vein of the rat, and in the guinea-pig heart and vas deferens. A very high concentration of adenosine (10(-4) g/ml.) reduced the release (about 50%) in the rabbit heart, but the cat heart was totally insensitive to the inhibitory action of adenosine. 4. Aminophylline (2 x 10(-4) g/ml.) antagonized the inhibitory action of adenosine (10(-6) g/ml.) on the release of [3H]noradrenaline in the phenoxybenzamine-treated vas deferens. 5. Tetraethylammonium (8 x 10(-4) g/ml.) enhanced stimulation-evoked release in the rat salivary gland by almost tenfold. In the presence of tetraethylammonium, even higher concentrations (2 x 10(-5) g/ml.) of adenosine failed to interfere with release. 6. Elevation of external K+ (19 mM) blocked stimulation-evoked release in the rat vas deferens by about 55%. Combination of high K+ and adenosine (10(-6) g/ml.), which blocked release by about 40%, caused still greater inhibition (80%) of the release. 7. The possible mechanism of action of the inhibitory effect of adenosine on the stimulation-evoked release of noradrenaline is discussed in relation to the calcium hypothesis.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROWN G. L., GILLESPIE J. S. The output of sympathetic transmitter from the spleen of the cat. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 29;138(1):81–102. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROUT J. R. THE UPTAKE AND RELEASE OF H3-NOREPINEPHRINE BY THE GUINEA-PIG HEART IN VIVO. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1964 Apr 21;248:85–98. doi: 10.1007/BF00247061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEGUBAREFF T., SLEATOR W., Jr EFFECTS OF CAFFEINE ON MAMMALIAN ATRIAL MUSCLE, AND ITS INTERACTION WITH ADENOSINE AND CALCIUM. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1965 May;148:202–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enero M. A., Saidman B. Q. Possible feed-back inhibition of noradrenaline release by purine compounds. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1977 Mar;297(1):39–46. doi: 10.1007/BF00508808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnebo L. O., Hamberger B. Influence of alpha- and beta-adrenoceptors on the release of noradrenaline from field stimulated atria and cerebral cortex slices. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1974 Aug;26(8):644–646. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1974.tb10681.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsborg B. L., Hirst G. D. The effect of adenosine on the release of the transmitter from the phrenic nerve of the rat. J Physiol. 1972 Aug;224(3):629–645. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedqvist P., Fredholm B. B. Effects of adenosine on adrenergic neurotransmission; prejunctional inhibition and postjunctional enhancement. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1976 Jun;293(3):217–223. doi: 10.1007/BF00507344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. Evaluation of mechanisms controlling the release and inactivation of the adrenergic transmitter in the rabbit portal vein and vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Mar;44(3):472–491. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb07285.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katori M., Berne R. M. Release of adenosine from anoxic hearts. Relationship to coronary flow. Circ Res. 1966 Aug;19(2):420–425. doi: 10.1161/01.res.19.2.420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirpekar S. M., Furchgott R. F., Wakade A. R., Prat J. C. Inhibition by sympathomimetic amines of the release of norepinephrine evoked by nerve stimulation in the cat spleen. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Dec;187(3):529–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirpekar S. M., Misu Y. Release of noradrenaline by splenic nerve stimulation and its dependence on calcium. J Physiol. 1967 Jan;188(2):219–234. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirpekar S. M., Prat J. C., Puig M., Wakade A. R. Modification of the evoked release of noradrenaline from the perfused cat spleen by various ions and agents. J Physiol. 1972 Mar;221(3):601–615. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirpekar S. M., Prat J. C., Wakade A. R. Effect of calcium on the relationship between frequency of stimulation and release of noradrenaline from the perfused spleen of the cat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1975;287(2):205–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00510451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirpekar S. M., Wakade A. R., Prat J. C. Effect of tetraethylammonium and barium on the release of noradrenaline from the perfused cat spleen by nerve stimulation and potassium. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1976 Jul;294(1):23–29. doi: 10.1007/BF00692781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shellenberger M. K., Gordon J. H. A rapid, simplified procedure for simultaneous assay of norepinephrine, dopamine, and 5-hydroxytryptamine from discrete brain areas. Anal Biochem. 1971 Feb;39(2):356–372. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90426-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Alpha sympathomimetic inhibition of adrenergic and cholinergic transmission in the rabbit heart. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1972;274(1):18–45. doi: 10.1007/BF00501004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Regulation of noradrenaline release by presynaptic receptor systems. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1977;77:1–124. doi: 10.1007/BFb0050157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stjärne L. Alpha-adrenoceptor mediated feed-back control of sympathetic neurotransmitter secretion in guinea-pig vas deferens. Nat New Biol. 1973 Feb 7;241(110):190–191. doi: 10.1038/newbio241190a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stjärne L. Rate limiting factors in sympathetic neurotransmitter secretion. Acta Physiol Scand. 1975 Feb;93(2):220–227. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1975.tb05812.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhaeghe R. H., Vanhoutte P. M., Shepherd J. T. Inhibition of sympathetic neurotransmission in canine blood vessels by adenosine and adenine nucleotides. Circ Res. 1977 Feb;40(2):208–215. doi: 10.1161/01.res.40.2.208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


