Abstract
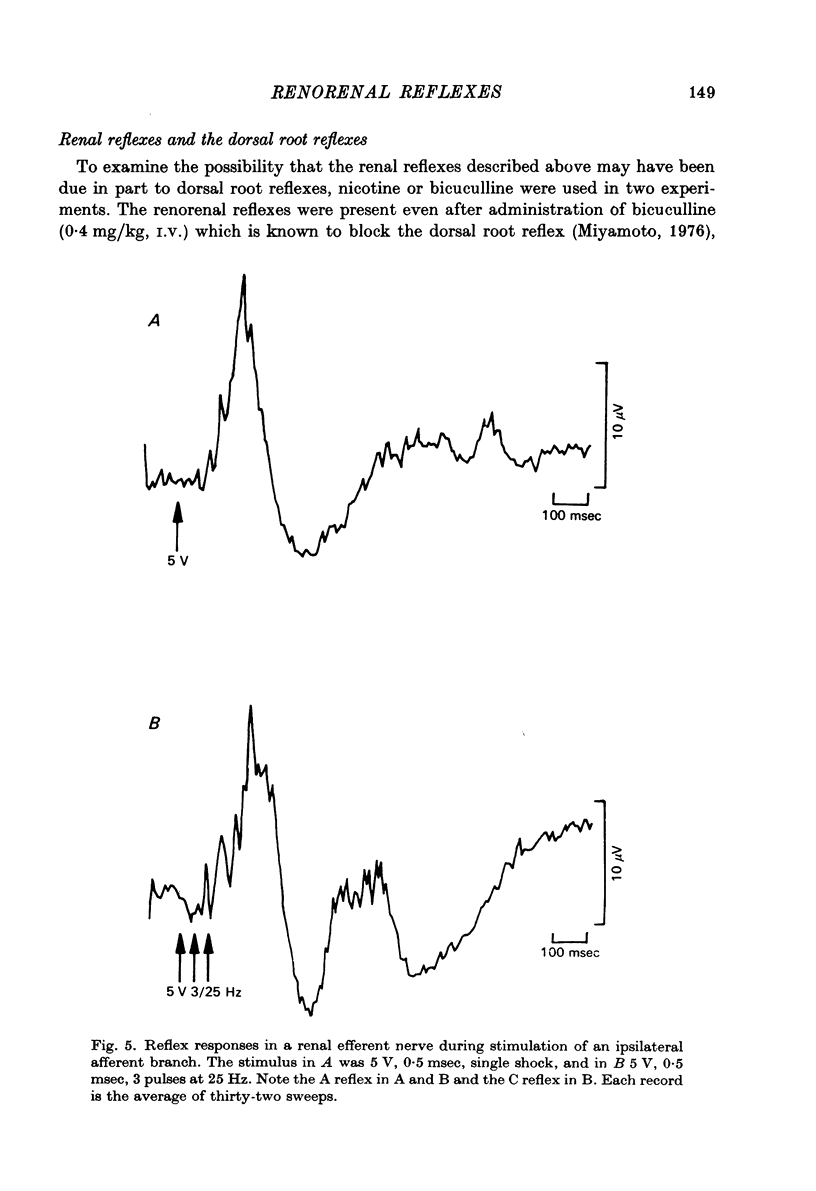
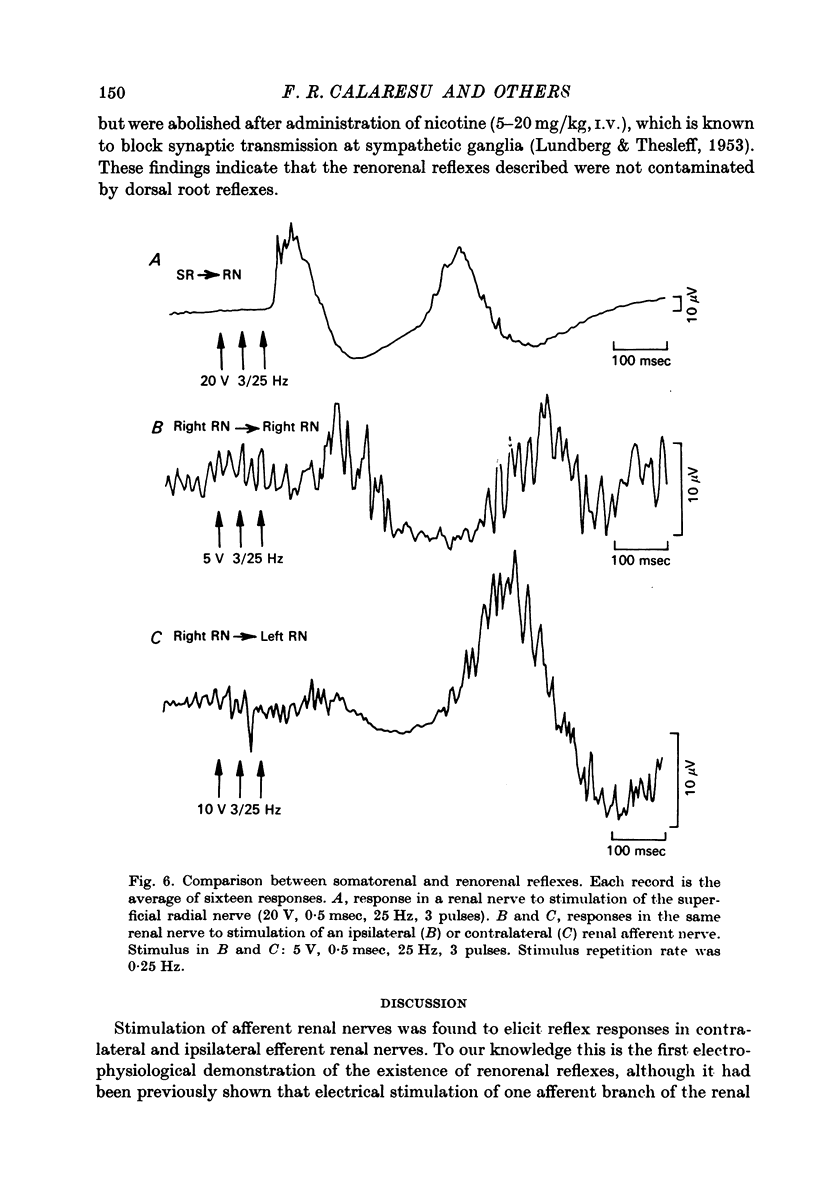
1. Experiments were done in anaesthetized, paralysed and artificially ventilated cats to determine the fibre composition of renal nerves and to study the functional characteristics of reflex responses recorded in efferent renal nerves during electrical stimulation of contralateral and ipsilateral afferent renal nerves. 2. Renal nerves were found to contain three afferent fibre groups (Abeta, Adelta and C); the majority of these fibres reach the sympathetic chain through the least splanchnic nerve. Efferent sympathetic nerves to the kidney were found to originate from the greater, lesser and least splanchnic nerves through a synapse in the coeliac ganglion. 3. Two contralateral renorenal reflex responses were demonstrated during selective stimulation of renal afferent A and C fibres. The first (A renorenal reflex) was elicited by stimulation with trains of pulses at low voltage and high frequency (200 Hz), had an onset latency of approximately 100 msec and was followed by post-excitatory depression. The second (C renorenal reflex) was demonstrated by trains of pulses at high voltage and low frequency (20--30 Hz), had an onset latency of approximately 350 msec and was also followed by post-excitatory depression. 4. Ipsilateral renorenal reflexes with characteristics similar to the contralateral reflexes were also demonstrated. 5. Renorenal reflexes were abolished by destruction of the spinal cord and administration of nicotine sulphate (5--20 mg/kg, i.v.), but were not affected by bicuculline (0.4 mg/kg, i.f.). 6. The significance and the physiological role of these renorenal reflexes as well as their pathways within the central nervous system remain to be determined.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aars H., Akre S. Reflex changes in sympathetic activity and arterial blood pressure evoked by afferent stimulation of the renal nerve. Acta Physiol Scand. 1970 Feb;78(2):184–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1970.tb04654.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aström A., Crafoord J. Afferent activity recorded in the kidney nerves of rats. Acta Physiol Scand. 1967 May;70(1):10–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1967.tb03595.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aström A., Crafoord J. Afferent and efferent activity in the renal nerves of cats. Acta Physiol Scand. 1968 Sep-Oct;74(1):69–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1968.tb04215.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barajas L., Silverman A. J., Muller J. Ultrastructural localization of acetylcholinesterase in the renal nerves. J Ultrastruct Res. 1974 Dec;49(3):297–311. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(74)90046-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beacham W. S., Kunze D. L. Renal receptors evoking a spinal vasometer reflex. J Physiol. 1969 Mar;201(1):73–85. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calaresu F. R., Stella A., Zanchetti A. Haemodynamic responses and renin release during stimulation of afferent renal nerves in the cat. J Physiol. 1976 Mar;255(3):687–700. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBona G. F. Neurogenic regulation of renal tubular sodium reabsorption. Am J Physiol. 1977 Aug;233(2):F73–F81. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.233.2.F73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi K., Brooks C. M. The integration of autonomic system reactions: a discussion of autonomic reflexes, their control and their association with somatic reactions. Ergeb Physiol. 1972;67:1–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUNDBERG A., THESLEFF S. Dual action of nicotine on the sympathetic ganglion of the cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1953;28(2-3):218–223. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1953.tb00972.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malliani A., Lombardi F., Pagani M., Recordati G., Schwartz P. J. Spinal cardiovascular reflexes. Brain Res. 1975 Apr 11;87(2-3):239–246. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90421-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto J. K. Dorsal root reflex response in sympathetic nerves. Brain Res. 1976 Jul 23;111(1):172–180. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)91059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller J., Barajas L. Electron microscopic and histochemical evidence for a tubular innervation in the renal cortex of the monkey. J Ultrastruct Res. 1972 Dec;41(5):533–549. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(72)90054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niijima A. Observation on the localization of mechanoreceptors in the kidney and afferent nerve fibres in the renal nerves in the rabbit. J Physiol. 1975 Feb;245(1):81–90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niijima A. The effect of efferent discharges in renal nerves on the activity of arterial mechanoreceptors in the kidney in rabbit. J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(2):335–343. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nijima A. Afferent discharges from arterial mechanoreceptors in the kidney of the rabbit. J Physiol. 1971 Dec;219(2):477–485. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson D., Stella A., Leonetti G., Bartorelli A., Zanchetti A. Mechanisms of renal release of renin by electrical stimulation of the brainstem in the cat. Circ Res. 1974 Apr;34(4):425–434. doi: 10.1161/01.res.34.4.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELL R., ERDELYI A., SCHAEFER H. Untersuchungen über den Einfluss peripherer Nervenreizung auf die sympathische Aktivität. Pflugers Arch. 1958;267(6):566–581. doi: 10.1007/BF00362960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato A. Spinal and medullary reflex components of the somatosympathetic reflex discharges evoked by stimulation of the group IV somatic afferents. Brain Res. 1973 Mar 15;51:307–318. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90381-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R. F., Weller E. Reflex activity in the cervical and lumbar sympathetic trunk induced by unmyelinated somatic afferents. Brain Res. 1970 Dec 1;24(2):207–218. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90101-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida Y., Kamisaka K., Ueda H. Two types of renal mechanoreceptors. Jpn Heart J. 1971 May;12(3):233–241. doi: 10.1536/ihj.12.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda H., Uchida Y., Kamisaka K. Mechanism of the reflex depressor effect by the kidney in dog. Jpn Heart J. 1967 Nov;8(6):597–606. doi: 10.1536/ihj.8.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDINGER H., FEDINA L., KEHREL H., SCHAEFER H. [On the localization of the "bulbar sympathetic center" and its modifications by respiration and blood pressure]. Z Kreislaufforsch. 1961 Mar;50:229–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


