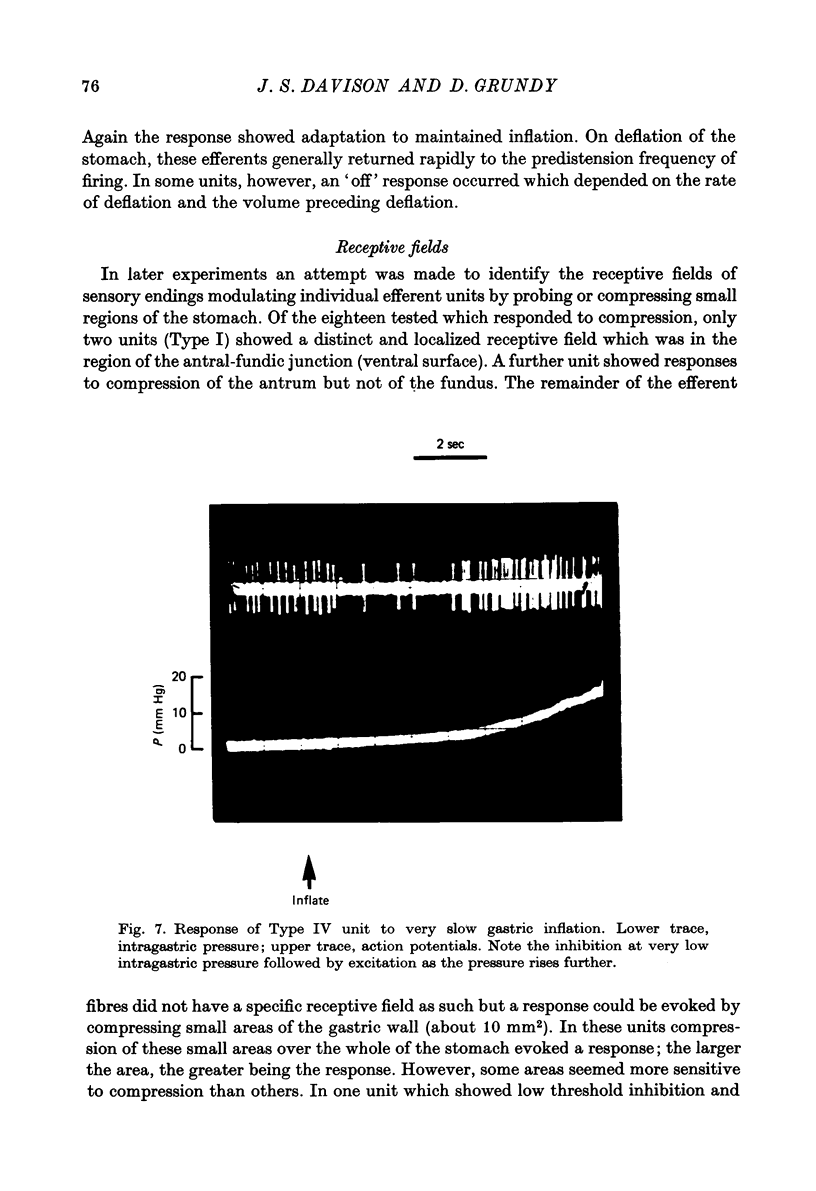
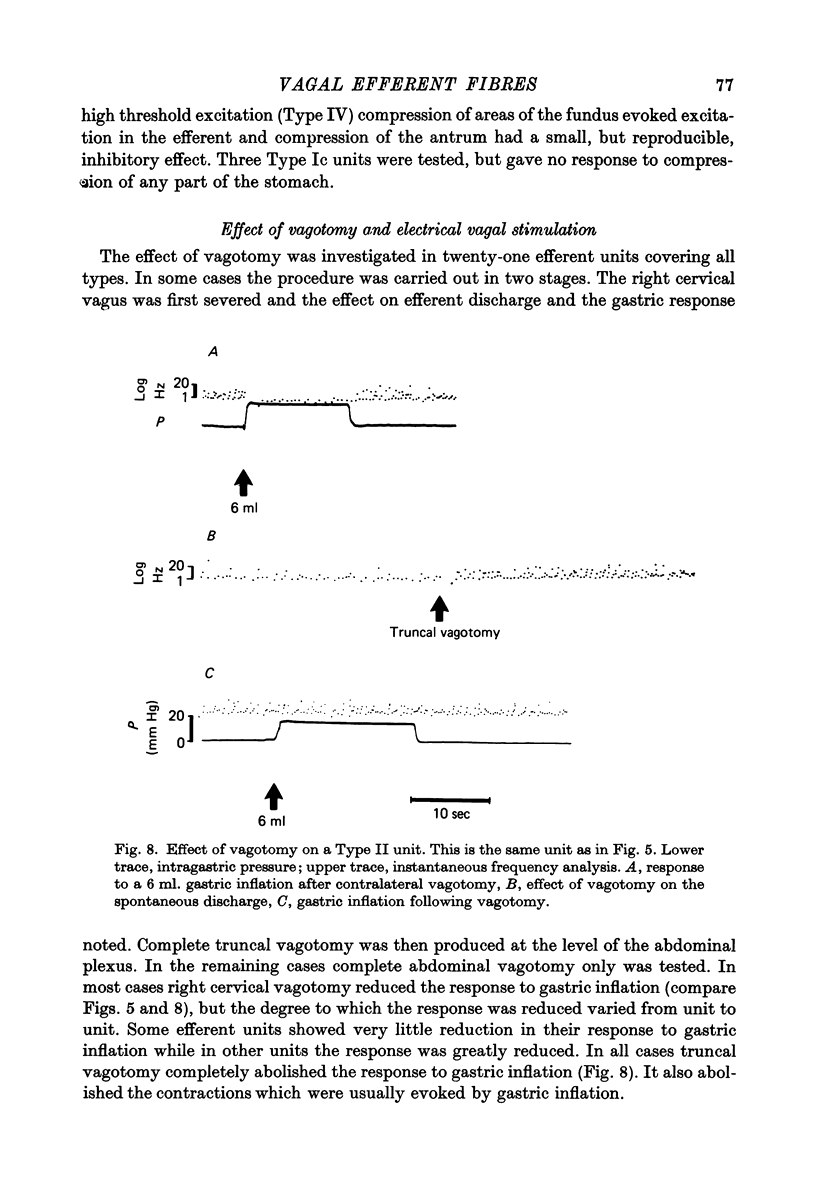
Abstract
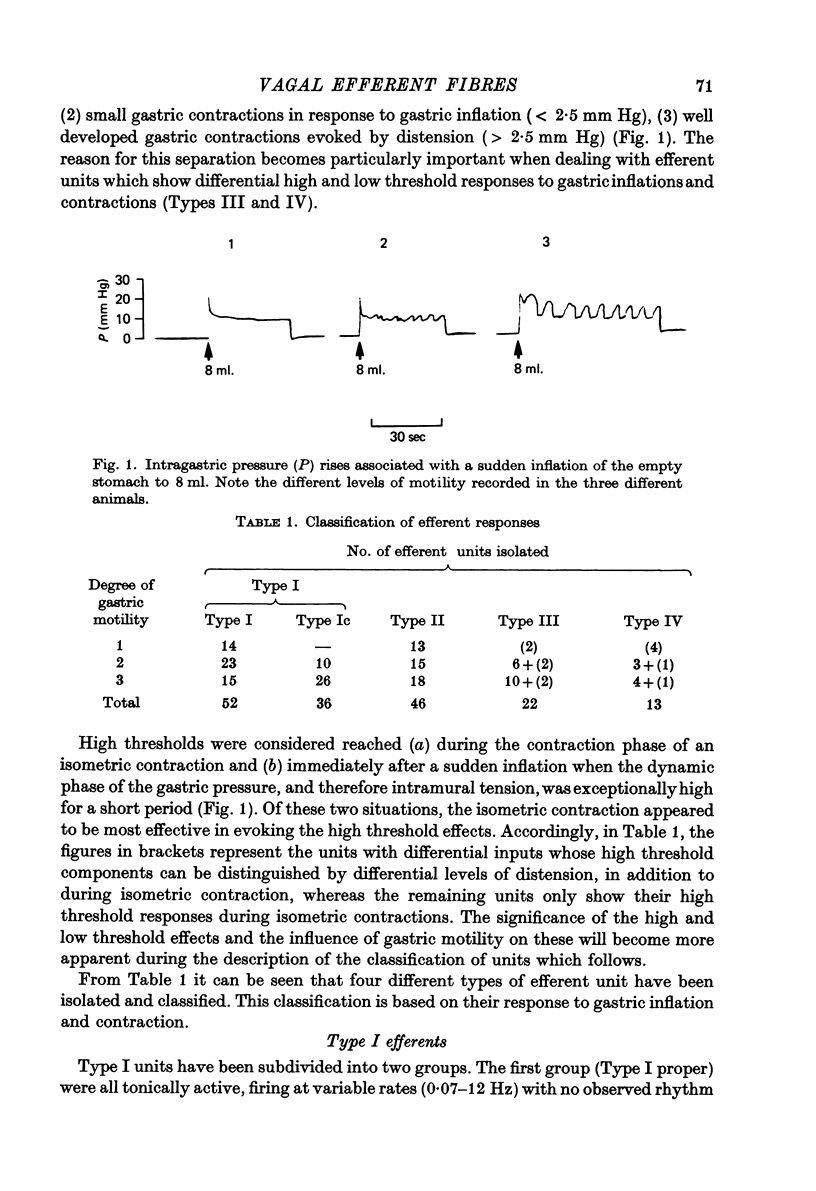
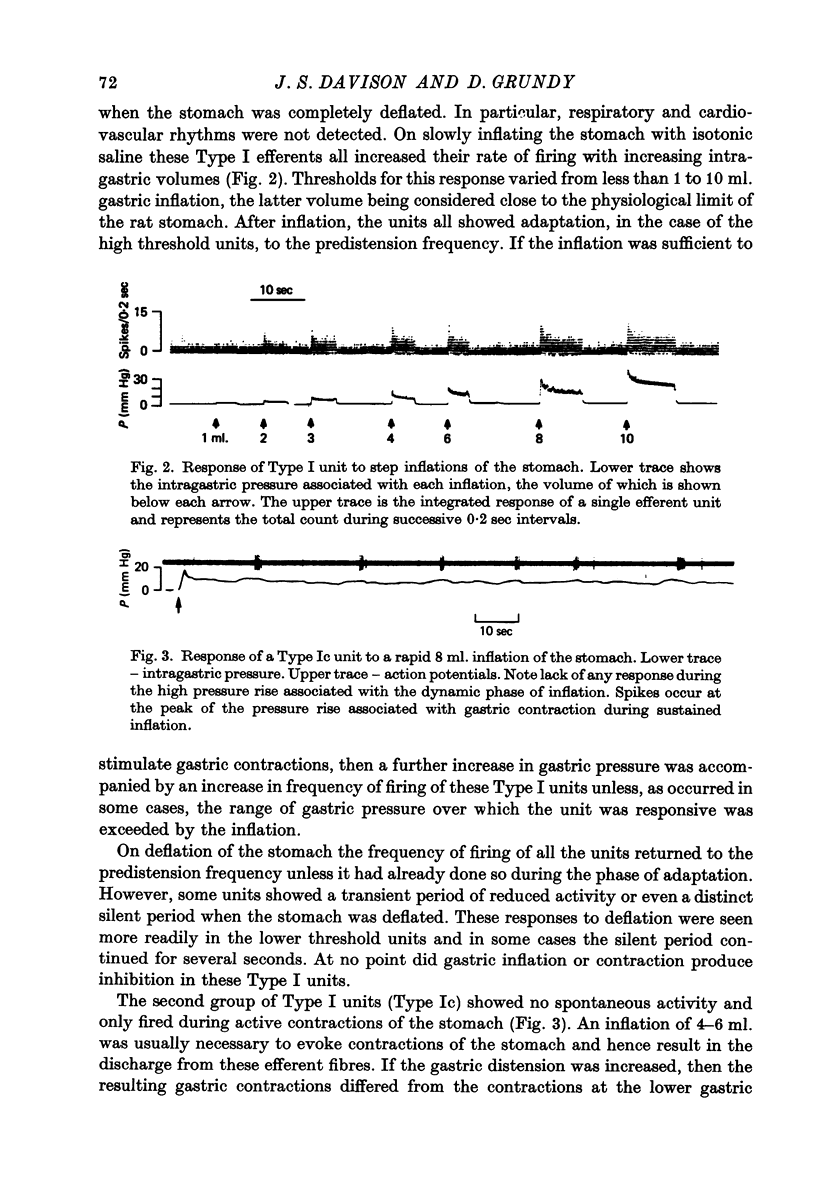
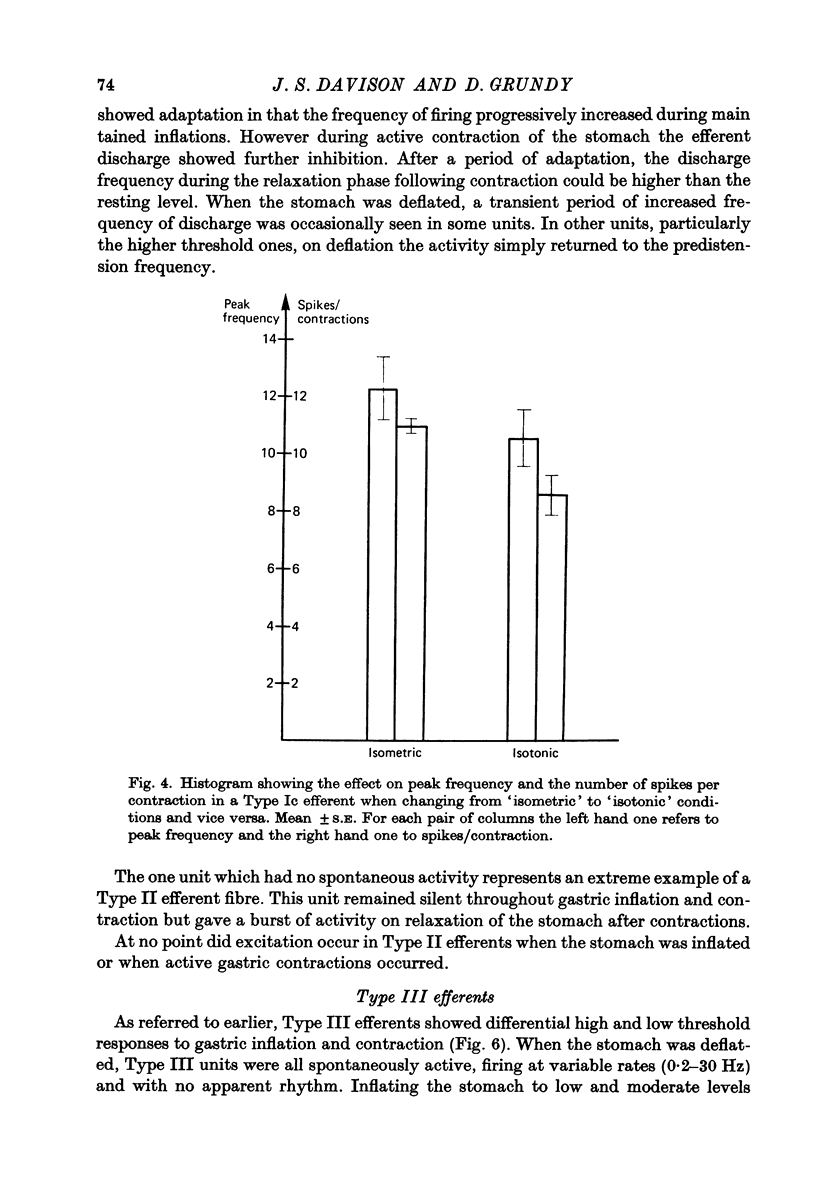
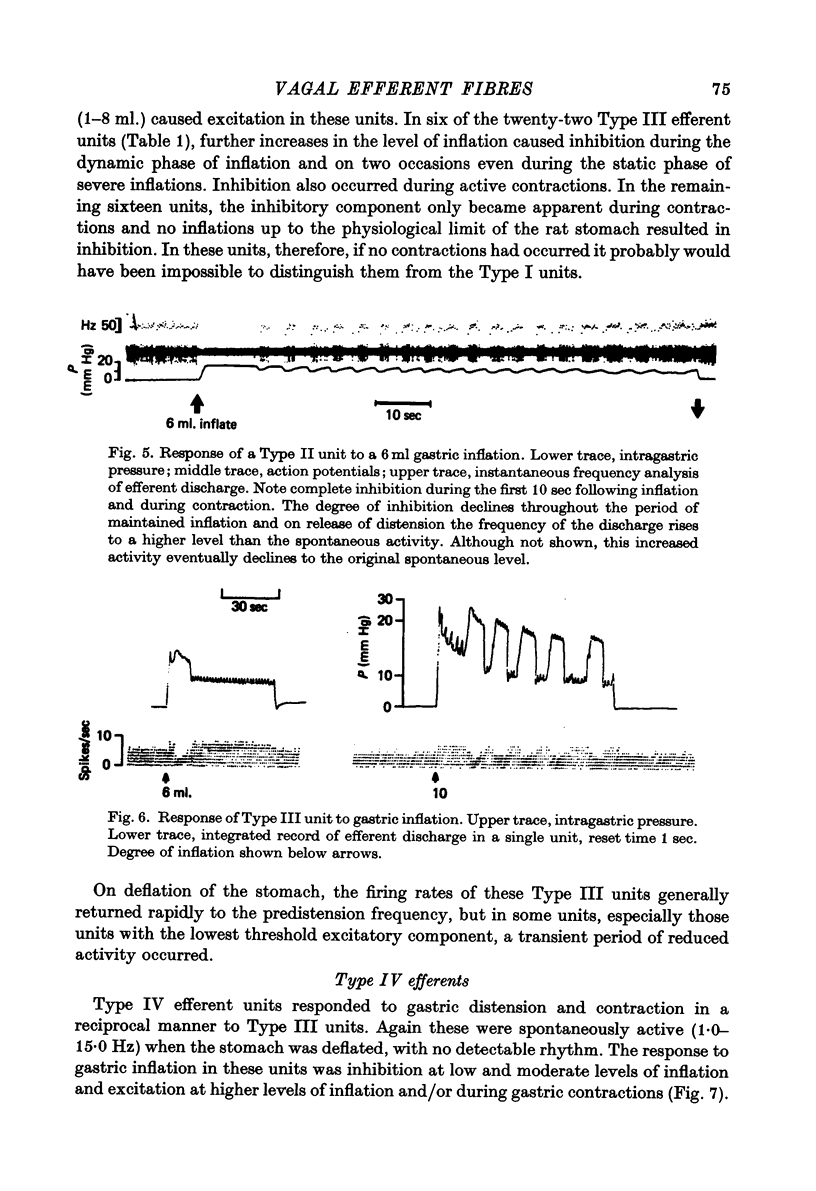
1. A single fibre dissection technique was used to record activity from efferent fibres in the left cervical vagus nerve of urethane anaesthetized rats. 2. The efferent discharge, in all units, was modulated by gastric inflation, gastric contractions or compression of the stomach wall. The receptors mediating these effects are the slowly adapting 'in-series' tension receptors in the gastric musculature with afferent fibres in the vagus nerves. 3. Efferent units were classified according to their response to passive gastric distension and active gastric contractions. 4. Four distinct types of efferent unit were isolated. Type I units were excited and Type II units were inhibited by gastric distension and contraction. Type III units were excited at low or moderate levels of inflation and inhibited at high levels of inflation or during gastric contractions. Type IV units were inhibited by low levels of inflation but excited at higher levels. 5. Since there is clearly a reciprocal organization at least of some neurones in the vagal nucleus the possibility of reciprocal control of antagonist, cholinergic and 'purinergic' vagal pathways is discussed.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. L., Duthie H. L., Fussey I. F., Mellersh A. Brainstem neurones sending efferent fibres to the abdominal viscera of the dog [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1977 Mar;266(1):90P–91P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G. Purinergic nerves. Pharmacol Rev. 1972 Sep;24(3):509–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke G. D., Davison J. S. Mucosal receptors in the gastric antrum and small intestine of the rat with afferent fibres in the cervical vagus. J Physiol. 1978 Nov;284:55–67. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke G. D., Davison J. S. Tension receptors in the oesophagus and stomach of the rat. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(1):41P–42P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison J. S. The electrophysiology of gastrointestinal chemoreceptors. Digestion. 1972;7(5):312–317. doi: 10.1159/000197289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floyd K., Morrison J. F. Splanchnic mechanoreceptors in the dog. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1974 Oct;59(4):361–366. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1974.sp002279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARPER A. A., KIDD C., SCRATCHERD T. Vago-vagal reflex effects on gastric and pancreatic secretion and gastrointestinal motility. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:417–436. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding R., Leek B. F. Central projections of gastric afferent vagal inputs. J Physiol. 1973 Jan;228(1):73–90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding R., Leek B. F. The effects of peripheral and central nervous influences on gastric centre neuronal activity in sheep. J Physiol. 1972 Sep;225(2):309–338. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding R., Leek B. F. The locations and activities of medullary neurons associated with ruminant forestomach motility. J Physiol. 1971 Dec;219(3):587–610. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IGGO A. Tension receptors in the stomach and the urinary bladder. J Physiol. 1955 Jun 28;128(3):593–607. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iggo A., Leek B. F. An electrophysiological study of single vagal efferent units associated with gastric movements in sheep. J Physiol. 1967 Jul;191(1):177–204. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iggo A., Leek B. F. An electrophysiological study of some reticulo-ruminal and abomasal reflexes in sheep. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(1):95–119. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leek B. F. Abdominal and pelvic visceral receptors. Br Med Bull. 1977 May;33(2):163–168. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miolan J. P., Roman C. Décharge unitaire des fibres vagales efférentes lors de la relaxation réceptive de l'estomac du chien. J Physiol (Paris) 1974;68(6):692–704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paintal A. S. Vagal sensory receptors and their reflex effects. Physiol Rev. 1973 Jan;53(1):159–227. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1973.53.1.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



