Abstract
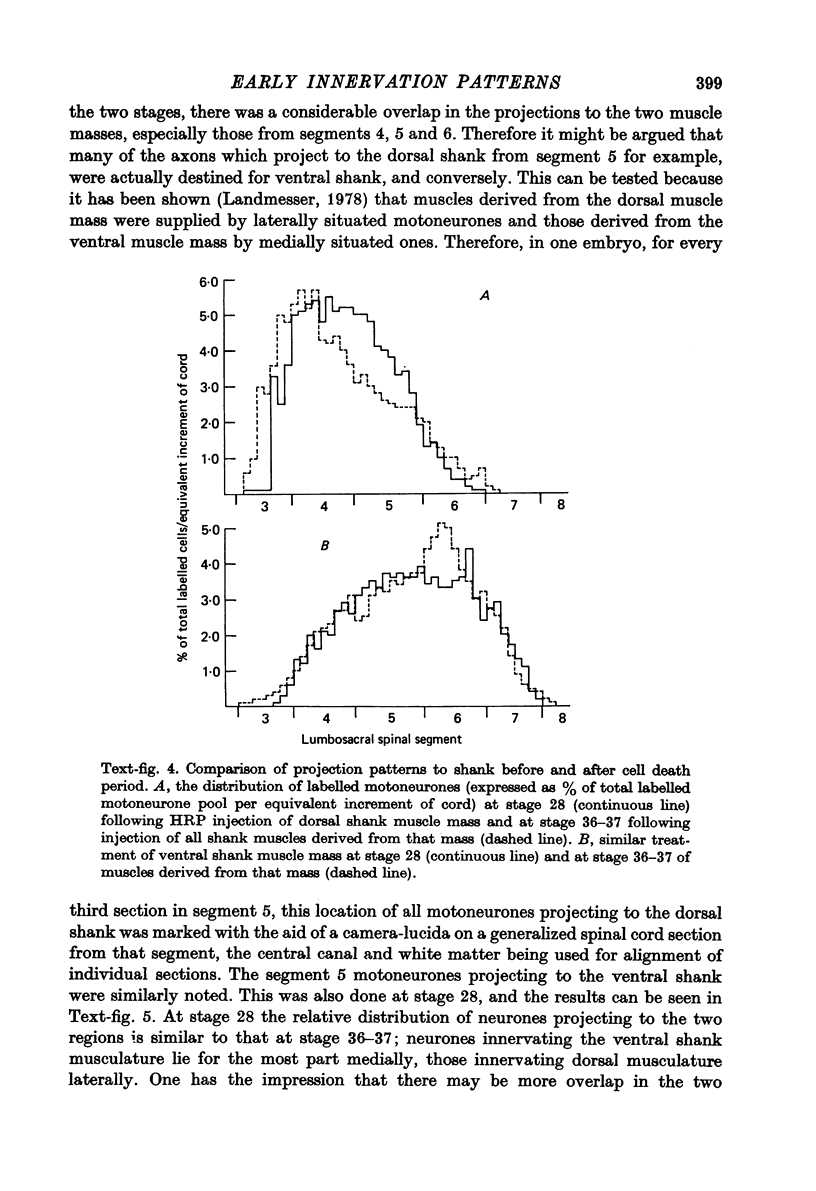
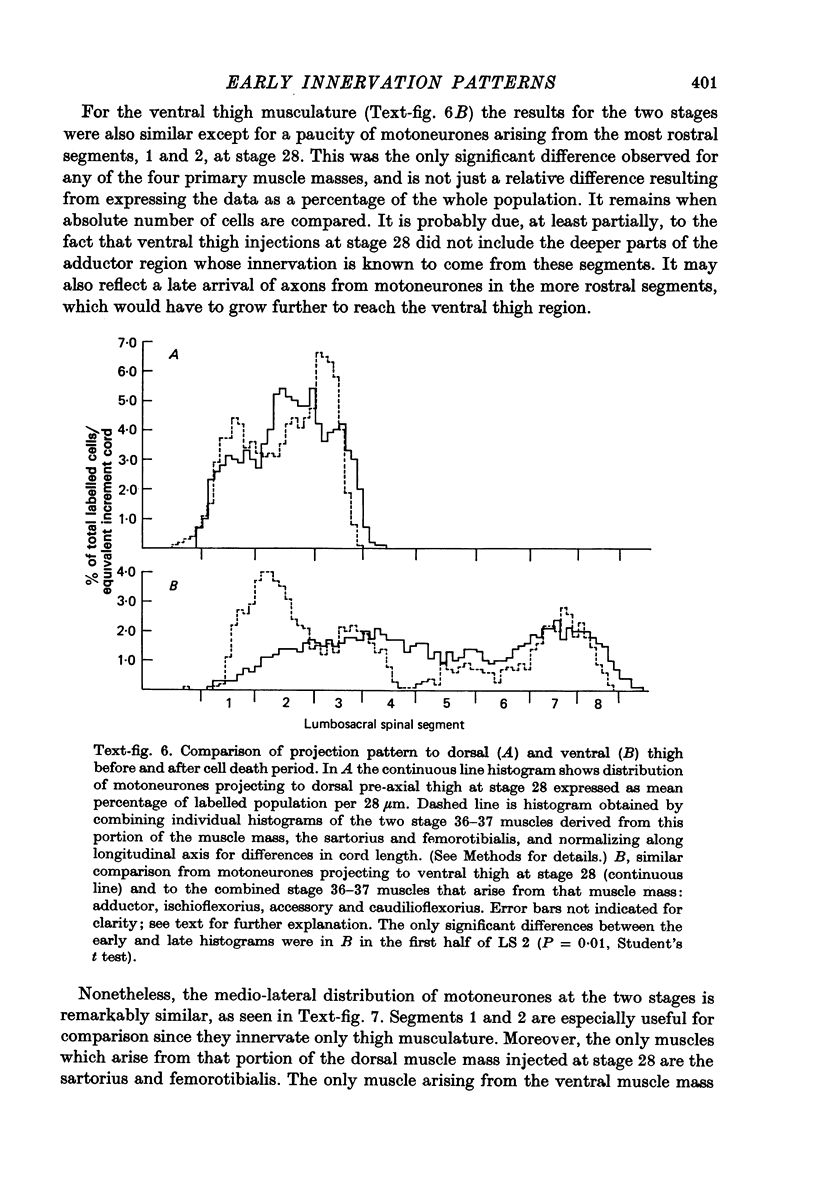
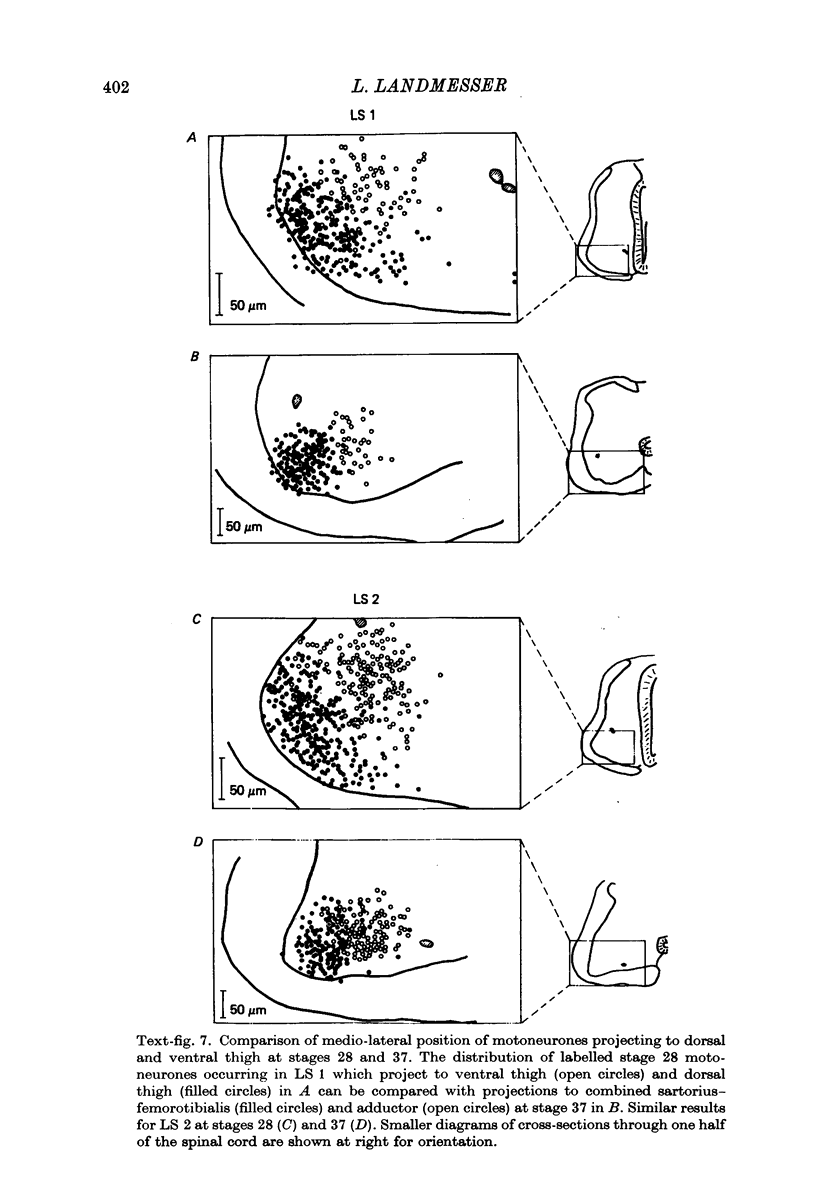
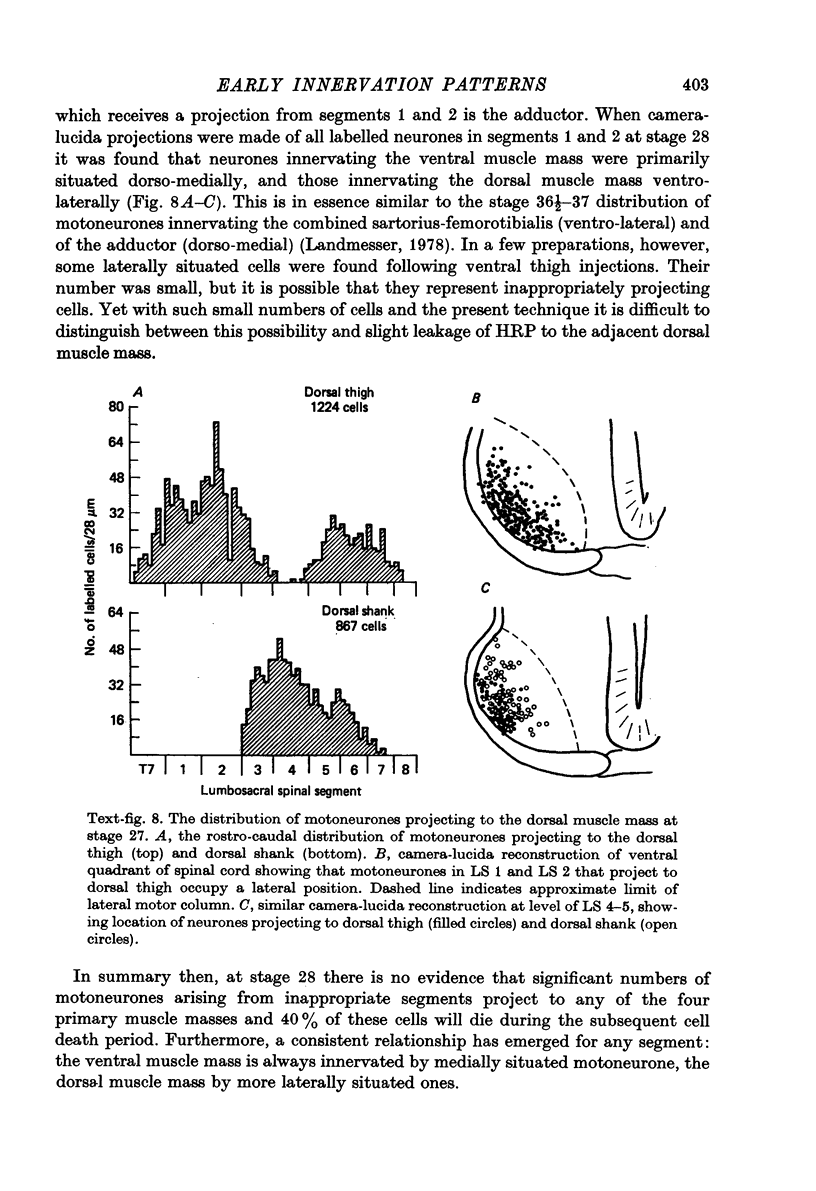
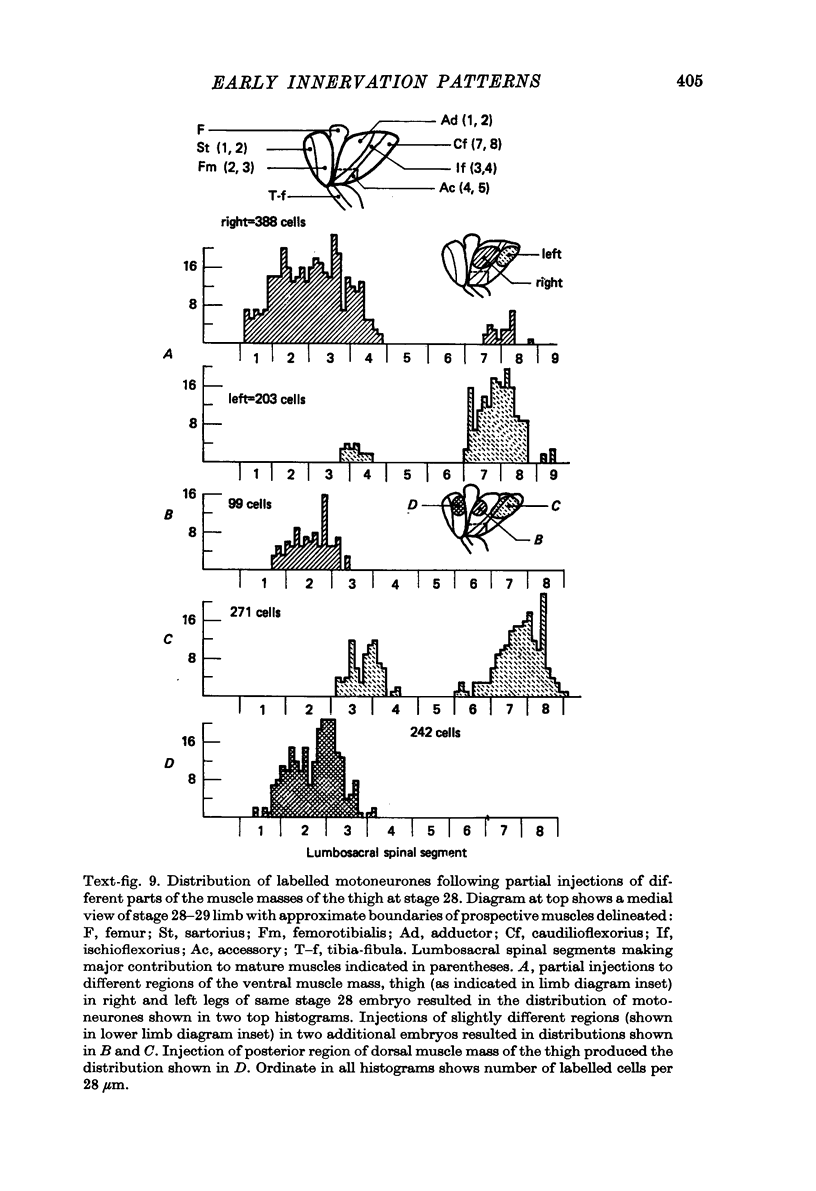
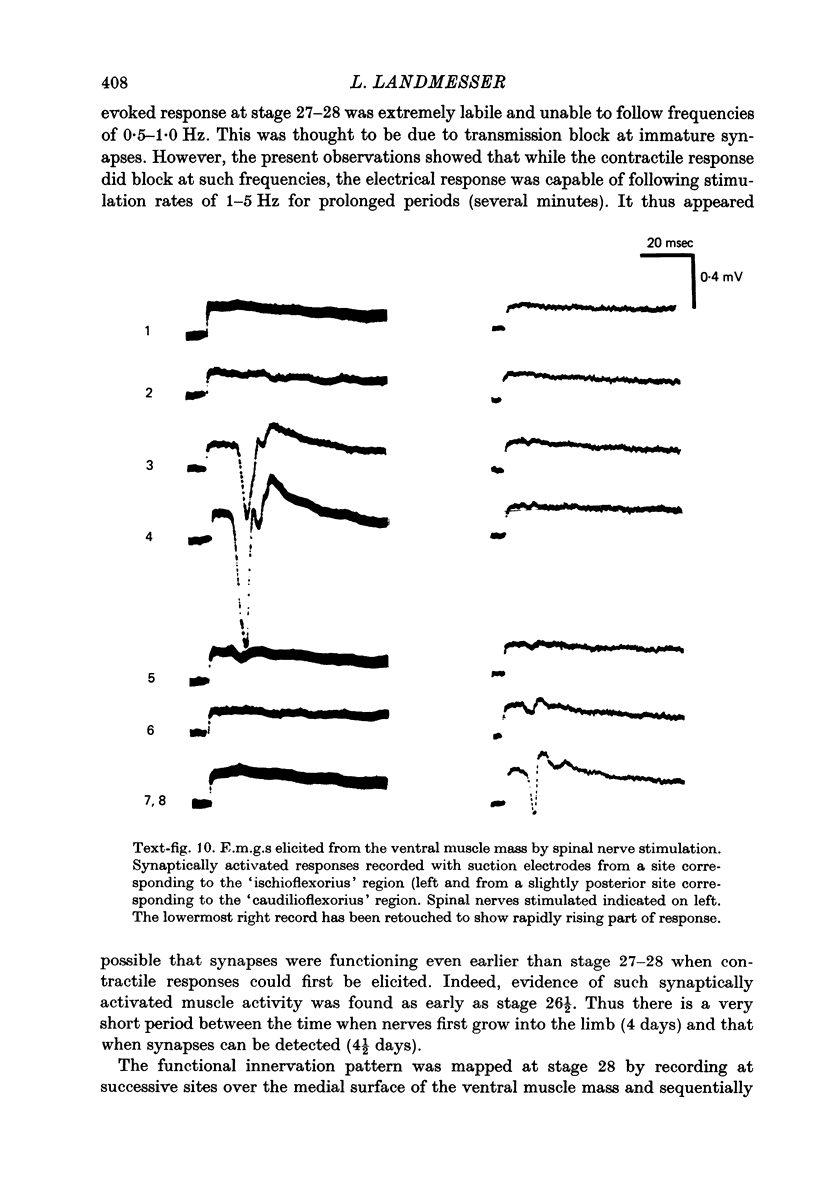
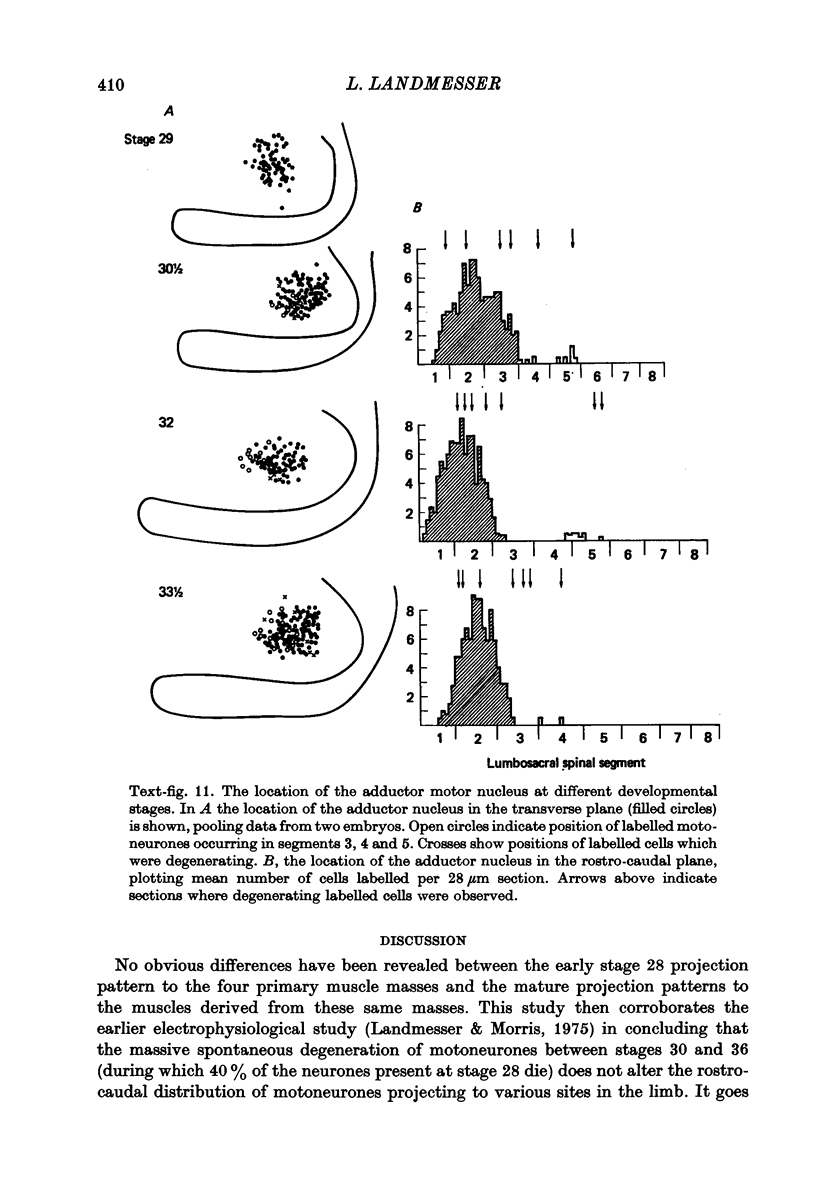
1. Retrograde transport of horseradish peroxidase was used to map the initial projection patterns of lumbosacral motoneurones to the embryonic chick hind limb. 2. The stage 28 segmental projection pattern to each of the four primary muscle masses was characteristic and indistinguishable from the stage 36 projection pattern to the sum of the muscles derived from that mass. In addition, the adductor motoneurone pool was found to be similar in position (both rostro-caudal and mediolateral) at stages 29, 30, 32, 33 1/2 and 36. 3. Therefore axons from lumbosacral motoneurones project for the most part only to appropriate regions from early times shortly after they grow into the limb bud. Furthermore, the attainment of the segmental projection pattern occurs prior to the normal time of, and therefore without the aid of, cell death. This conclusion was supported by electrophysiological recordings made from muscle nerves. 4. A regionalization of the projection patterns within a single muscle mass could be shown both anatomically and physiologically prior to the cleavage of the mass into individual muscles and the projections were in a general way appropriate for the muscles derived from those regions. 5. Therefore the process of muscle cleavage does not in itself create the specific projection patterns observed, and motoneurone axons appear to grow to and to ramify and make synapses only within regions which correspond to their adult muscles. 6. Finally, the termination site of each motoneurone axon in the early limb was found to be tightly correlated in a somatotopic fashion with the position occupied by its soma in the cord. This suggests that some feature of the motoneurone related to its position may be of importance in achieving the specific projection patterns observed.
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bekoff A. Ontogeny of leg motor output in the chick embryo: a neural analysis. Brain Res. 1976 Apr 23;106(2):271–291. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)91025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Pettigrew A. G. The formation of synapses in striated muscle during development. J Physiol. 1974 Sep;241(2):515–545. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. C., Jansen J. K., Van Essen D. Polyneuronal innervation of skeletal muscle in new-born rats and its elimination during maturation. J Physiol. 1976 Oct;261(2):387–422. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu-Wang I. W., Oppenheim R. W. Cell death of motoneurons in the chick embryo spinal cord. II. A quantitative and qualitative analysis of degeneration in the ventral root, including evidence for axon outgrowth and limb innervation prior to cell death. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Jan 1;177(1):59–85. doi: 10.1002/cne.901770106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke P. G., Rogers L. A., Cowan W. M. The time of origin and the pattern of survival of neurons in the isthmo-optic nucleus of the chick. J Comp Neurol. 1976 May 15;167(2):125–142. doi: 10.1002/cne.901670202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruce W. L. The anatomical organization of hindlimb motoneurons in the lumbar spinal cord of the frog, Rana catesbiana. J Comp Neurol. 1974 Jan 1;153(1):59–76. doi: 10.1002/cne.901530106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giacobini G. Embryonic and postnatal development of choline acetyltransferase activity in muscles and sciatic nerve of the chick. J Neurochem. 1972 May;19(5):1401–1403. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01466.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giacobini G., Filogamo G., Weber M., Boquet P., Changeux J. P. Effects of a snake alpha-neurotoxin on the development of innervated skeletal muscles in chick embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1708–1712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamburger V. Cell death in the development of the lateral motor column of the chick embryo. J Comp Neurol. 1975 Apr 15;160(4):535–546. doi: 10.1002/cne.901600408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollyday M., Hamburger V. An autoradiographic study of the formation of the lateral motor column in the chick embryo. Brain Res. 1977 Aug 26;132(2):197–208. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90416-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollyday M., Hamburger V., Farris J. M. Localization of motor neuron pools supplying identified muscles in normal and supernumerary legs of chick embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3582–3586. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope R. A., Hammond B. J., Gaze R. M. The arrow model: retinotectal specificity and map formation in the goldfish visual system. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1976 Nov 12;194(1117):447–466. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1976.0088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landmesser L., Morris D. G. The development of functional innervation in the hind limb of the chick embryo. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):301–326. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landmesser L. The distribution of motoneurones supplying chick hind limb muscles. J Physiol. 1978 Nov;284:371–389. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim R. W., Chu-wang I. Spontaneous cell death of spinal motoneurons following peripheral innervation in the chick embryo. Brain Res. 1977 Apr 8;125(1):154–160. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90367-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim R. W., Heaton M. B. The retrograde transport of horseradish peroxidase from the developing limb of the chick embryo. Brain Res. 1975 Nov 14;98(2):291–302. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prestige M. C. The control of cell number in the lumbar ventral horns during the development of Xenopus laevis tadpoles. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1967 Dec;18(3):359–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prestige M. C., Willshaw D. J. On a role for competition in the formation of patterned neural connexions. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Jun 20;190(1098):77–98. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1975.0080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROMANES G. J. THE MOTOR POOLS OF THE SPINAL CORD. Prog Brain Res. 1964;11:93–119. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)64045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROMANES G. J. The motor cell columns of the lumbo-sacral spinal cord of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1951 Apr;94(2):313–363. doi: 10.1002/cne.900940209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHARRARD W. J. The distribution of the permanent paralysis in the lower limb in poliomyelitis; a clinical and pathological study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1955 Nov;37-B(4):540–558. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.37B4.540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirling R. V., Summerbell D. The development of functional innervation in the chick wing-bud following truncations and deletions of the proximal-distal axis. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1977 Oct;41:189–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]