Abstract
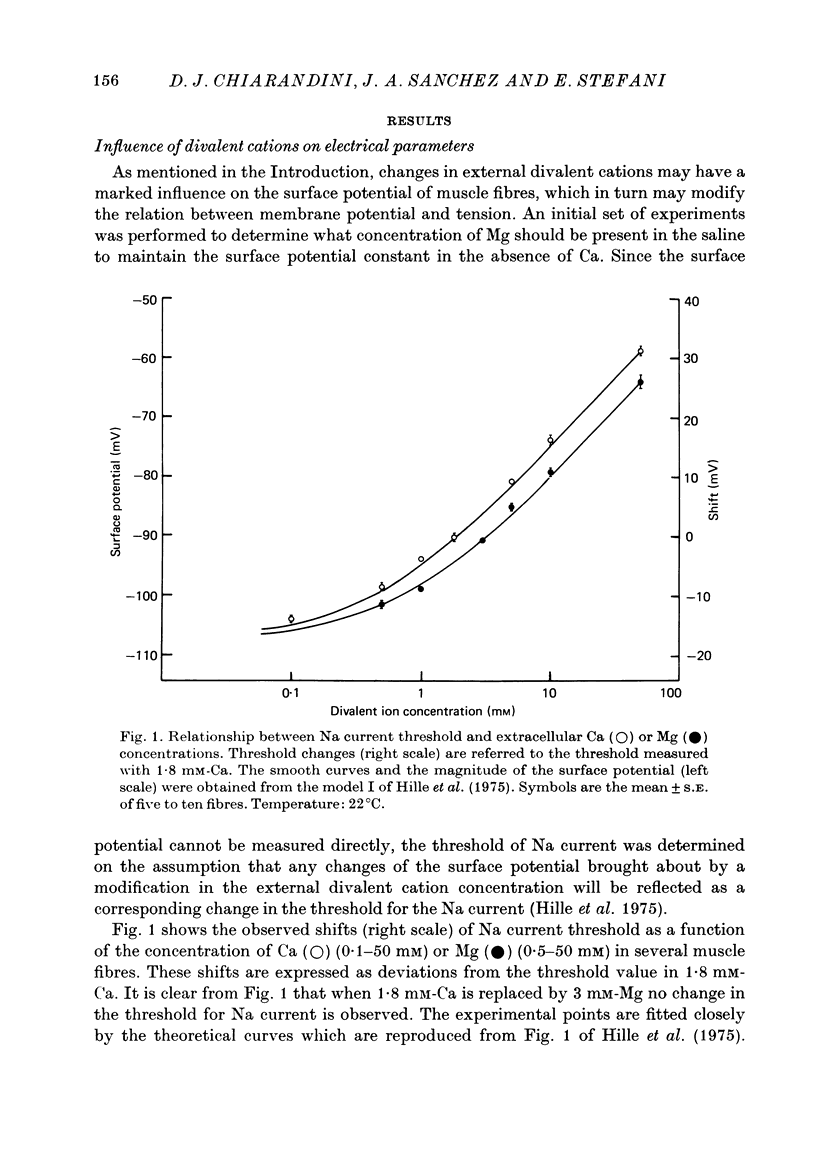
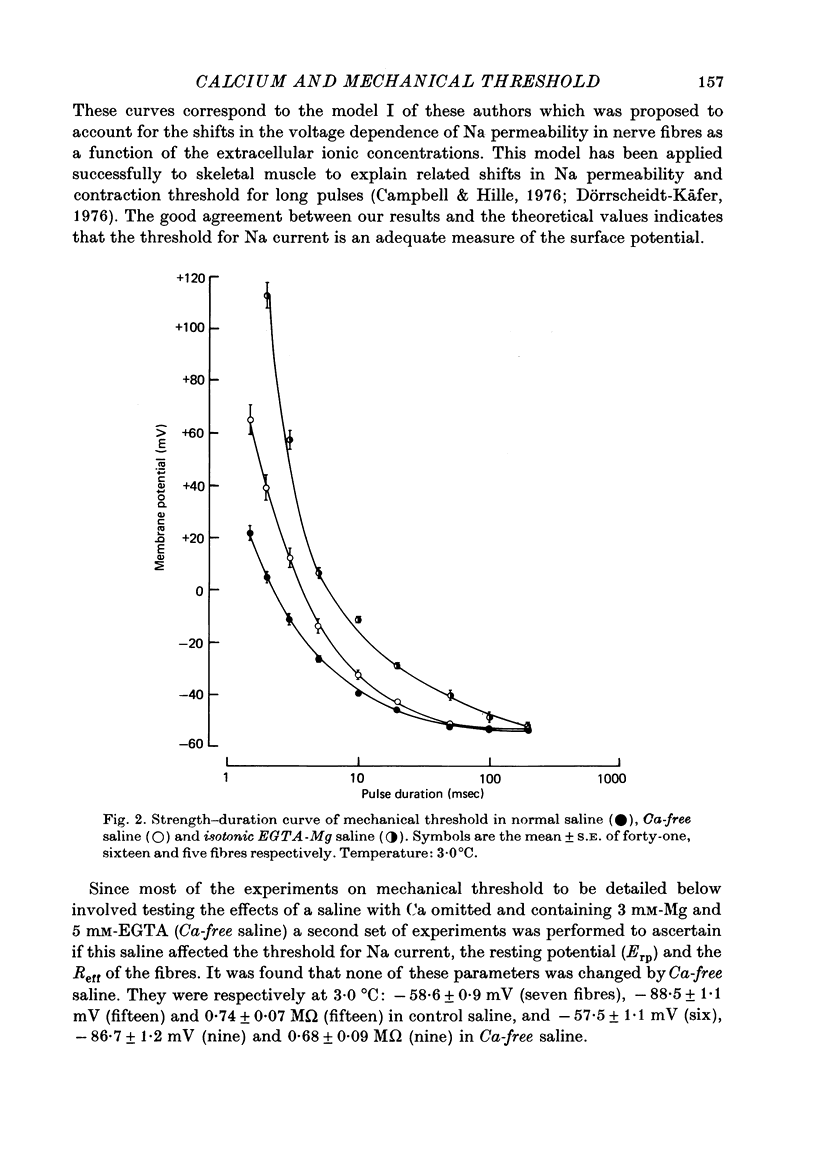
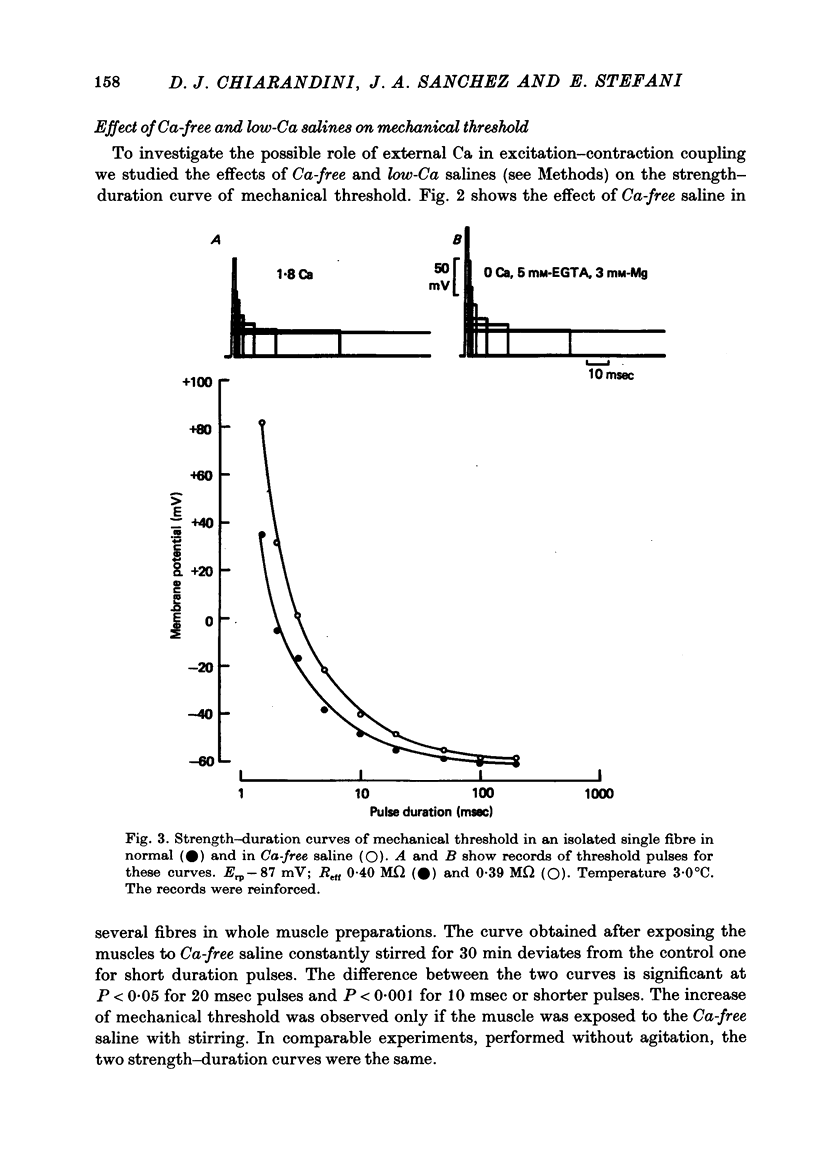
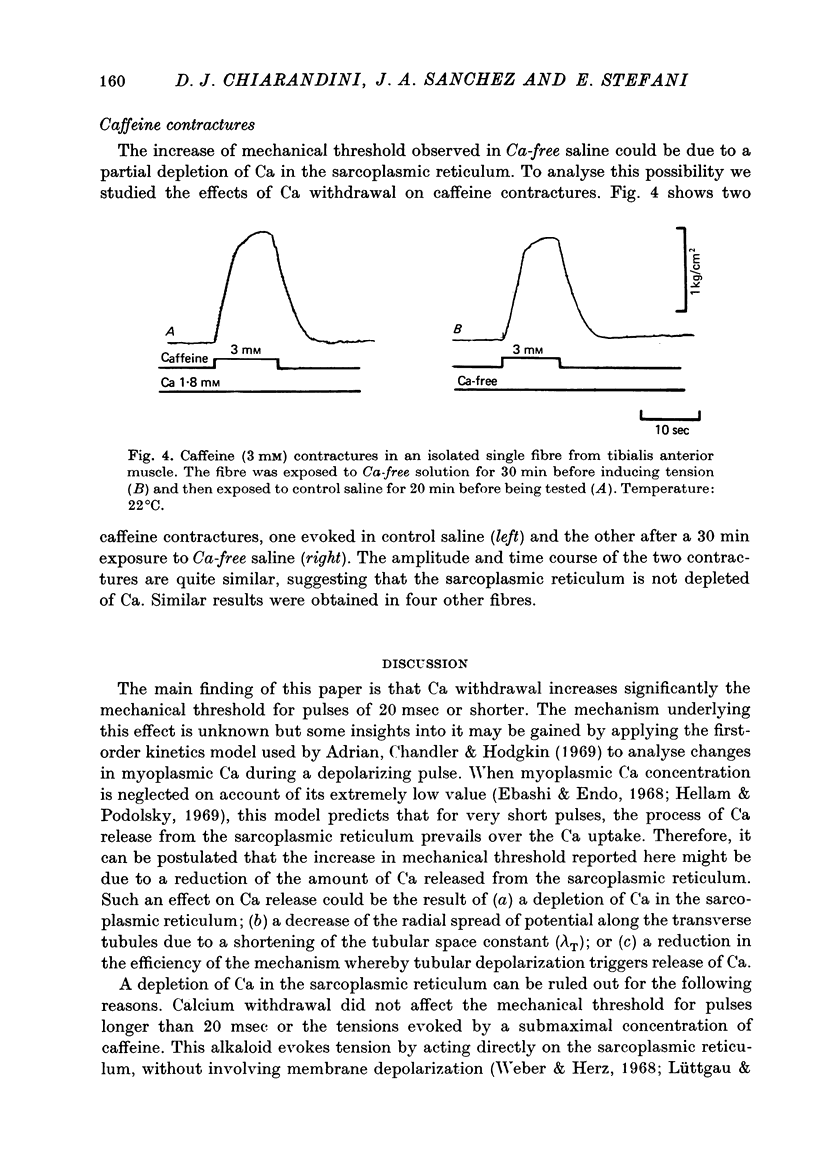
1. Voltage-clamp experiments were performed on frog skeletal muscle fibres using two intracellular micro-electrodes. The threshold for the Na current and the strength-duration curve for mechanical threshold were determined. 2. The change in threshold for the Na current was studied as a function of the external Ca and Mg concentrations which ranged from 0.1 to 50 mM. 3. The resting potential, effective resistance and threshold for the Na current were unchanged when 1.8 mM-Ca was replaced by 3 mM-Mg, indicating that the surface potential and the electrical properties of the fibres were not modified. The additon of 5 mM-EGTA did not affect these parameters. 4. In Ca-free saline (3 mM-Mg and 5 mM-EGTA) the mechanical threshold was significantly increased for short pulses (less than or equal to 20 msec.). In isolated single muscle fibres this effect was observed shortly after applying the Ca-free saline, and was rapidly reversed upon the return to control saline. 5. In isotonic EGTA (85 mM-EGTA) the muscle fibres were depolarized and were unable to contract even if they were hyperpolarized to --90 mV for 12 min prior to stimulation. If 3 mM-Mg was added, most fibres contracted locally. 6. In single muscle fibres caffeine contractures were unmodified after a 30 min exposure to Ca-free saline. 7. It can be concluded that external Ca withdrawal impairs Ca release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum and that external Ca is not essential for triggering contraction.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L. The kinetics of mechanical activation in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1969 Sep;204(1):207–230. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Costantin L. L., Peachey L. D. Radial spread of contraction in frog muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1969 Sep;204(1):231–257. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Peachey L. D. Reconstruction of the action potential of frog sartorius muscle. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;235(1):103–131. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W. Gating currents and charge movements in excitable membranes. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;82:96–190. doi: 10.1007/BFb0030498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F. M., Horowicz P. Twitches in the presence of ethylene glycol bis( -aminoethyl ether)-N,N'-tetracetic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jun 23;267(3):605–608. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90194-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett N., Barrett E. F. Excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle: blockade by high extracellular concentrations of calcium buffers. Science. 1978 Jun 16;200(4347):1270–1272. doi: 10.1126/science.96524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaty G. N., Stefani E. Calcium dependent electrical activity in twitch muscle fibres of the frog. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1976 Aug 27;194(1114):141–150. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1976.0070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi C. P., Bolton T. C. Action of local anesthetics on coupling systems in muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1967 Aug;157(2):388–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinks J. R., Rüdel R., Taylor S. R. Calcium transients in isolated amphibian skeletal muscle fibres: detection with aequorin. J Physiol. 1978 Apr;277:291–323. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. T., Hille B. Kinetic and pharmacological properties of the sodium channel of frog skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Mar;67(3):309–323. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.3.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caputo C., Gimenez M. Effects of external calcium deprivation on single muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Oct;50(9):2177–2195. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.9.2177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiarandini D. J., Stefani E. Effects of manganese on the electrical and mechanical properties of frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1973 Jul;232(1):129–147. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costantin L. L. The effect o f calcium on contraction and conductance thresholds in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(1):119–132. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis B. A. Calcium efflux from frog twitch muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Feb;55(2):243–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S., Endo M. Calcium ion and muscle contraction. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1968;18:123–183. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(68)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S. Excitation-contraction coupling. Annu Rev Physiol. 1976;38:293–313. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.38.030176.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo M. Calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Physiol Rev. 1977 Jan;57(1):71–108. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):218–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford L. E., Podolsky R. J. Regenerative calcium release within muscle cells. Science. 1970 Jan 2;167(3914):58–59. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3914.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankenhaeuser B., Lännergren J. The effect of calcium on the mechanical response of single twitch muscle fibres of Xenopus laevis. Acta Physiol Scand. 1967 Mar;69(3):242–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1967.tb03518.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellam D. C., Podolsky R. J. Force measurements in skinned muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(3):807–819. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Woodhull A. M., Shapiro B. I. Negative surface charge near sodium channels of nerve: divalent ions, monovalent ions, and pH. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Jun 10;270(908):301–318. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin A. L., Nakajima S. Analysis of the membrane capacity in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1972 Feb;221(1):121–136. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUETTGAU H. C. THE ACTION OF CALCIUM IONS ON POTASSIUM CONTRACTURES OF SINGLE MUSCLE FIBRES. J Physiol. 1963 Oct;168:679–697. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüttgau H. C., Glitsch H. G. Membrane physiology of nerve and muscle fibres. Fortschr Zool. 1976;24(1):1–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüttgau H. C., Melzer W., Spiecker W. The effects of Ca2+ removal on excitation-contraction coupling [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1977 Oct;271(2):45P–45P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüttgau H. C., Oetliker H. The action of caffeine on the activation of the contractile mechanism in straited muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1968 Jan;194(1):51–74. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüttgau H. C., Spiecker W. The effects of calcium deprivation upon mechanical and electrophysiological parameters in skeletal muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:411–429. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I., Schalow G. Measurement of calcium transients in frog muscle by the use of arsenazo III. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Aug 22;198(1131):201–210. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez J. A., Stefani E. Inward calcium current in twitch muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1978 Oct;283:197–209. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandow A., Krishna M., Pagala D., Sphicas E. C. Excitation-contraction coupling: effects of "zero"-Ca2+ medium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 8;404(1):157–163. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90157-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. F., Chandler W. K. Voltage dependent charge movement of skeletal muscle: a possible step in excitation-contraction coupling. Nature. 1973 Mar 23;242(5395):244–246. doi: 10.1038/242244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefani E., Chiarandini D. J. Skeletal muscle: dependence of potassium contractures on extracellular calcium. Pflugers Arch. 1973 Oct 17;343(2):143–150. doi: 10.1007/BF00585709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber A., Herz R. The relationship between caffeine contracture of intact muscle and the effect of caffeine on reticulum. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Nov;52(5):750–759. doi: 10.1085/jgp.52.5.750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



