Abstract
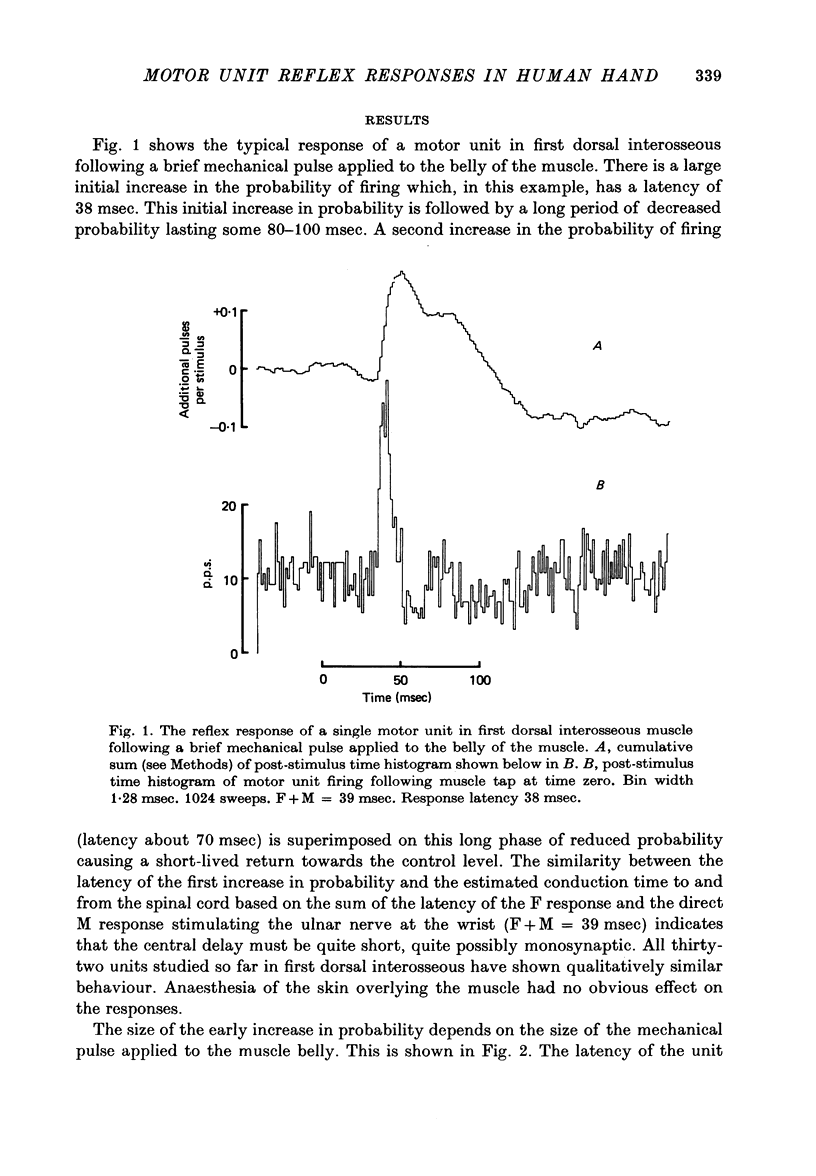
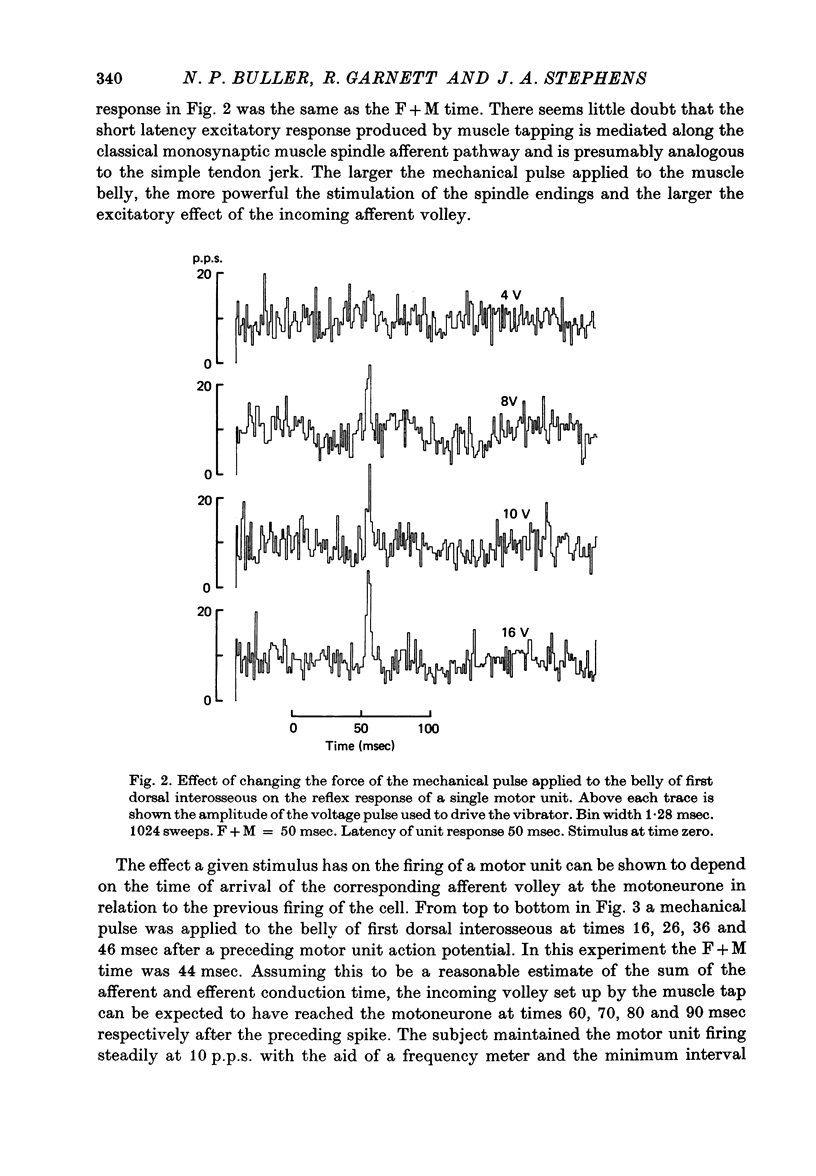
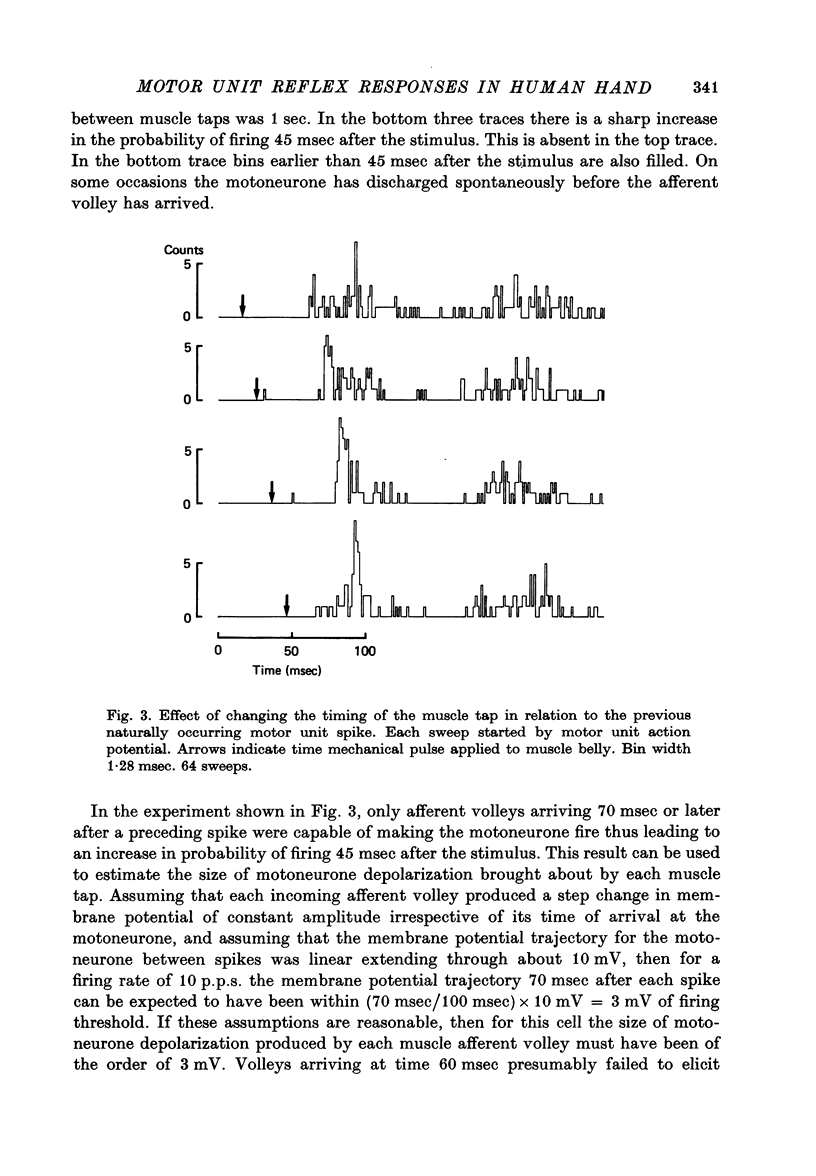
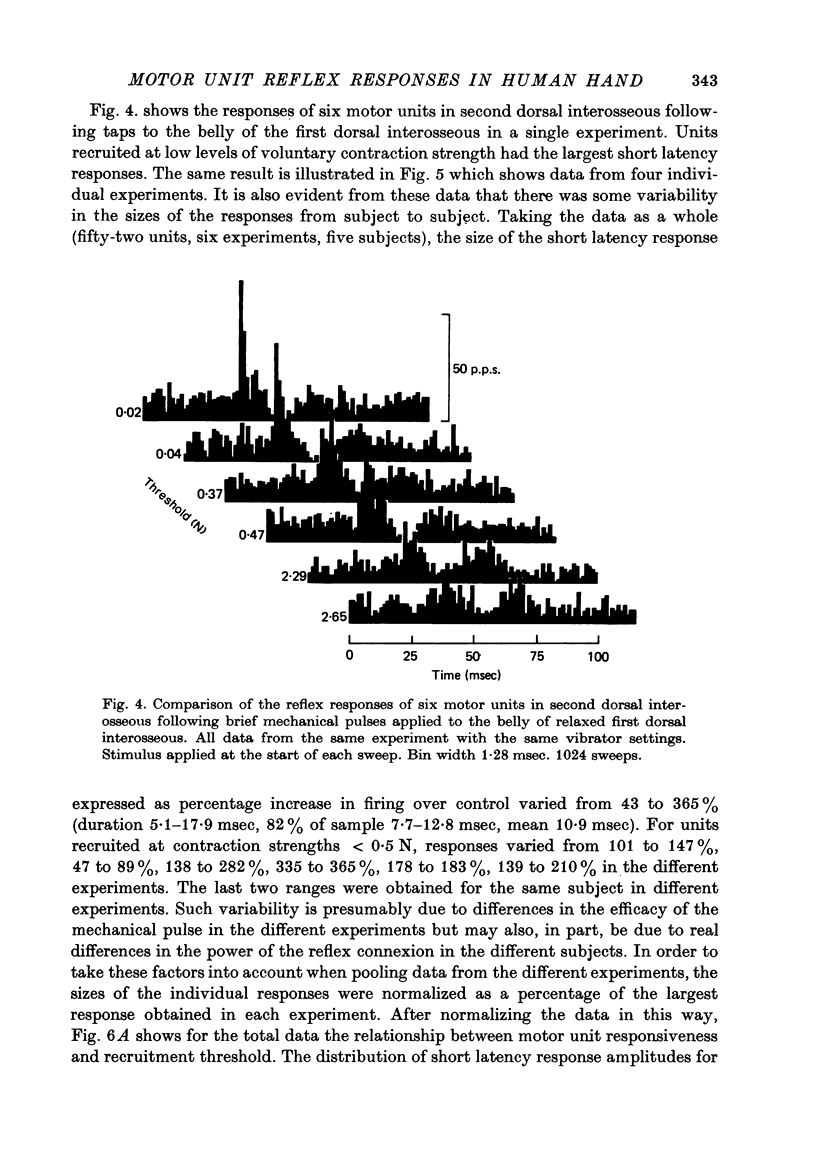
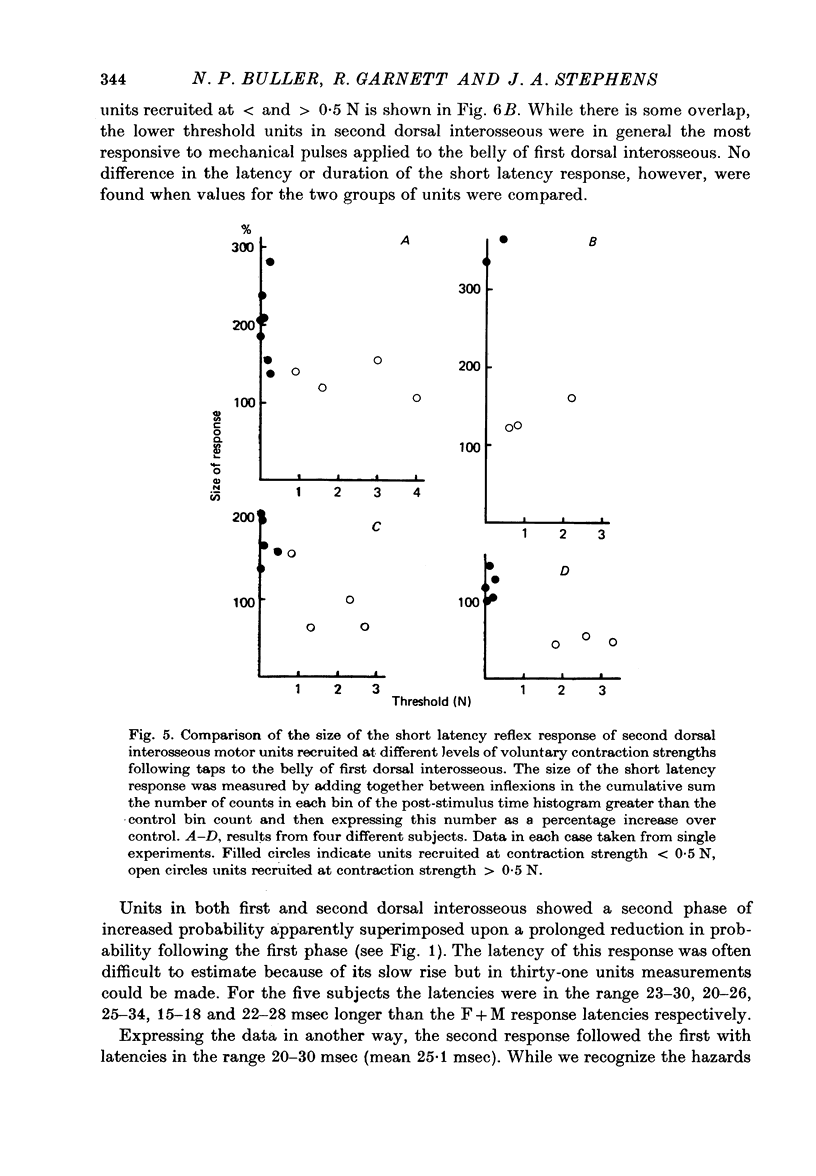
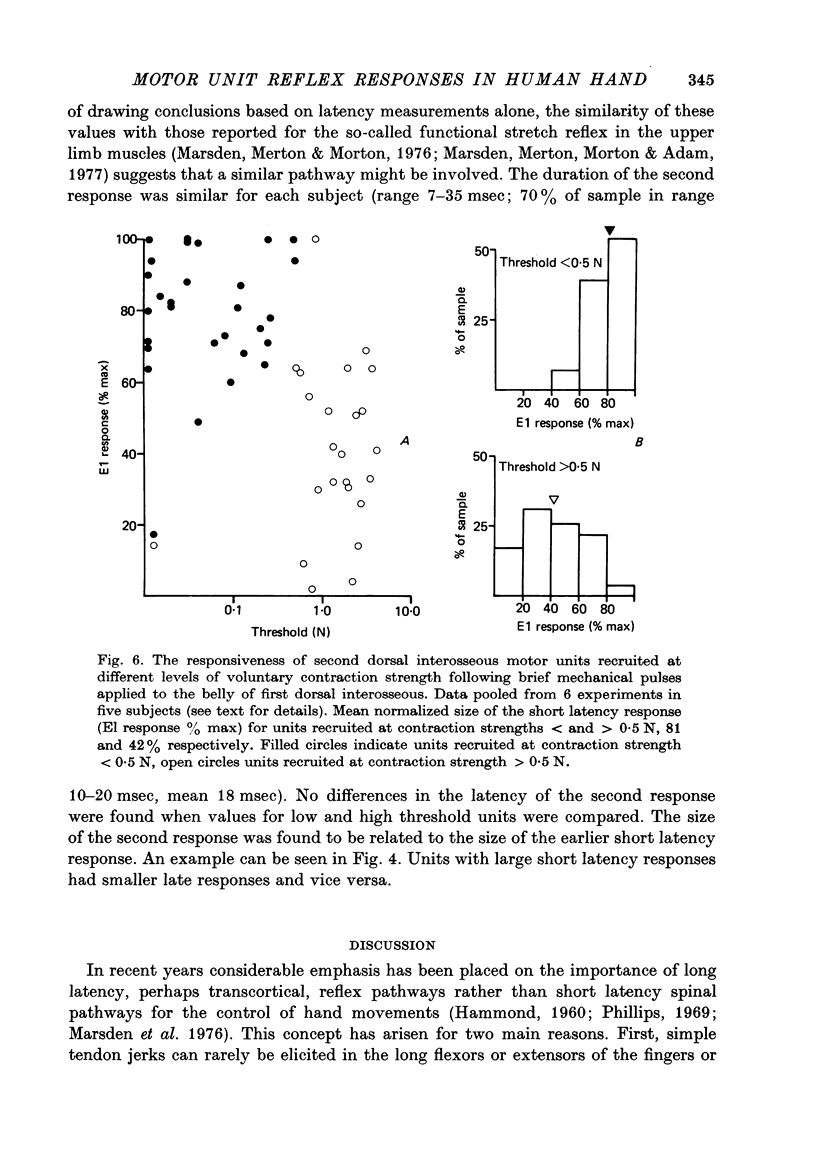
1. Changes in the probability of firing of motor units active during voluntary muscle contraction have been studied in human first and second dorsal interosseous muscles in response to muscle afferent stimulation. 2. Short latency, possibly monosynaptic, excitatory responses were found in both first and second dorsal interosseous muscles following brief mechanical pulses applied to the belly of first dorsal interosseous. A second longer latency excitatory response followed the first with a mean latency of 25 msec. 3. All units in both muscles showed qualitatively the same responses but units recruited at low levels of voluntary contraction strength were more responsive to muscle afferent input than units recruited at high contraction strengths. The excitatory effect of muscle afferent input within the two motoneurone pools appears to be weighted in the same way as the more complicated input associated with a gradually increasing voluntary contraction. 4. These findings are discussed in relation to the relative importance of short and long latency reflex effects of muscle afferent input in the control of hand movements.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashby P., Labelle K. Effects of extensor and flexor group I afferent volleys on the excitability of individual soleus motoneurones in man. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1977 Sep;40(9):910–919. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.40.9.910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betts R. P., Johnston D. M., Brown B. H. Nerve fibre velocity and refractory period distributions in nerve trunks. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1976 Jul;39(7):694–700. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.39.7.694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buller N. P., Stephens J. A. Changes in the probability of firing of human motor units following stimulation of muscle receptors [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1977 Oct;271(2):1P–2P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E. Group Ia synaptic input to fast and slow twitch motor units of cat triceps surae. J Physiol. 1968 Jun;196(3):605–630. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E., Rymer W. Z. Relative strength of synaptic input from short-latency pathways to motor units of defined type in cat medial gastrocnemius. J Neurophysiol. 1976 May;39(3):447–458. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.3.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clamann H. P., Gillies J. D., Henneman E. Effects of inhibitory inputs on critical firing level and rank order of motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1974 Nov;37(6):1350–1360. doi: 10.1152/jn.1974.37.6.1350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellaway P. H. An application of cumulative sum technique (cusums) to neurophysiology [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(1):1P–2P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellaway P. H. Cumulative sum technique and its application to the analysis of peristimulus time histograms. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1978 Aug;45(2):302–304. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(78)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henneman E., Clamann H. P., Gillies J. D., Skinner R. D. Rank order of motoneurons within a pool: law of combination. J Neurophysiol. 1974 Nov;37(6):1338–1349. doi: 10.1152/jn.1974.37.6.1338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henneman E., Somjen G., Carpenter D. O. Excitability and inhibitability of motoneurons of different sizes. J Neurophysiol. 1965 May;28(3):599–620. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.3.599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanda K., Burke R. E., Walmsley B. Differential control of fast and slow twitch motor units in the decerebrate cat. Exp Brain Res. 1977 Aug 8;29(1):57–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00236875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox C. K., Kubota S., Poppele R. E. A determination of excitability changes in dorsal spinocerebellar tract neurons from spike-train analysis. J Neurophysiol. 1977 May;40(3):626–646. doi: 10.1152/jn.1977.40.3.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox C. K., Poppele R. E. Correlation analysis of stimulus-evoked changes in excitability of spontaneously firing neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1977 May;40(3):616–625. doi: 10.1152/jn.1977.40.3.616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kranz H., Adorjani C., Baumgartner G. The effect of nociceptive cutaneous stimuli on human motoneurons. Brain. 1973 Sep;96(3):571–590. doi: 10.1093/brain/96.3.571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kranz H., Corti V. Laboratory note. Reflex responses of single human motoneurones. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1973 Oct;35(4):395–397. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(73)90197-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D., Merton P. A., Morton H. B., Adam J. The effect of lesions of the sensorimotor cortex and the capsular pathways on servo responses from the human long thumb flexor. Brain. 1977 Sep;100(3):503–526. doi: 10.1093/brain/100.3.503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D., Merton P. A., Morton H. B. Stretch reflex and servo action in a variety of human muscles. J Physiol. 1976 Jul;259(2):531–560. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner-Brown H. S., Stein R. B., Yemm R. The contractile properties of human motor units during voluntary isometric contractions. J Physiol. 1973 Jan;228(2):285–306. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner-Brown H. S., Stein R. B., Yemm R. The orderly recruitment of human motor units during voluntary isometric contractions. J Physiol. 1973 Apr;230(2):359–370. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. P., Segundo J. P., Perkel D. H., Levitan H. Statistical signs of synaptic interaction in neurons. Biophys J. 1970 Sep;10(9):876–900. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(70)86341-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips C. G. The Ferrier lecture, 1968. Motor apparatus of the baboon's hand. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1969 May 20;173(1031):141–174. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1969.0044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens J. A., Usherwood T. P., Garnett R. Technique for studying synaptic connections of single motoneurones in man. Nature. 1976 Sep 23;263(5575):343–344. doi: 10.1038/263343a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens J. A., Usherwood T. P. Proceedings: Changes in the probability of firing of human motor units following cutaneous nerve stimulation. J Physiol. 1976 Jun;258(2):49P–51P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens J. A., Usherwood T. P. The mechanical properties of human motor units with special reference to their fatiguability and recruitment threshold. Brain Res. 1977 Apr 8;125(1):91–97. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90361-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


