Abstract
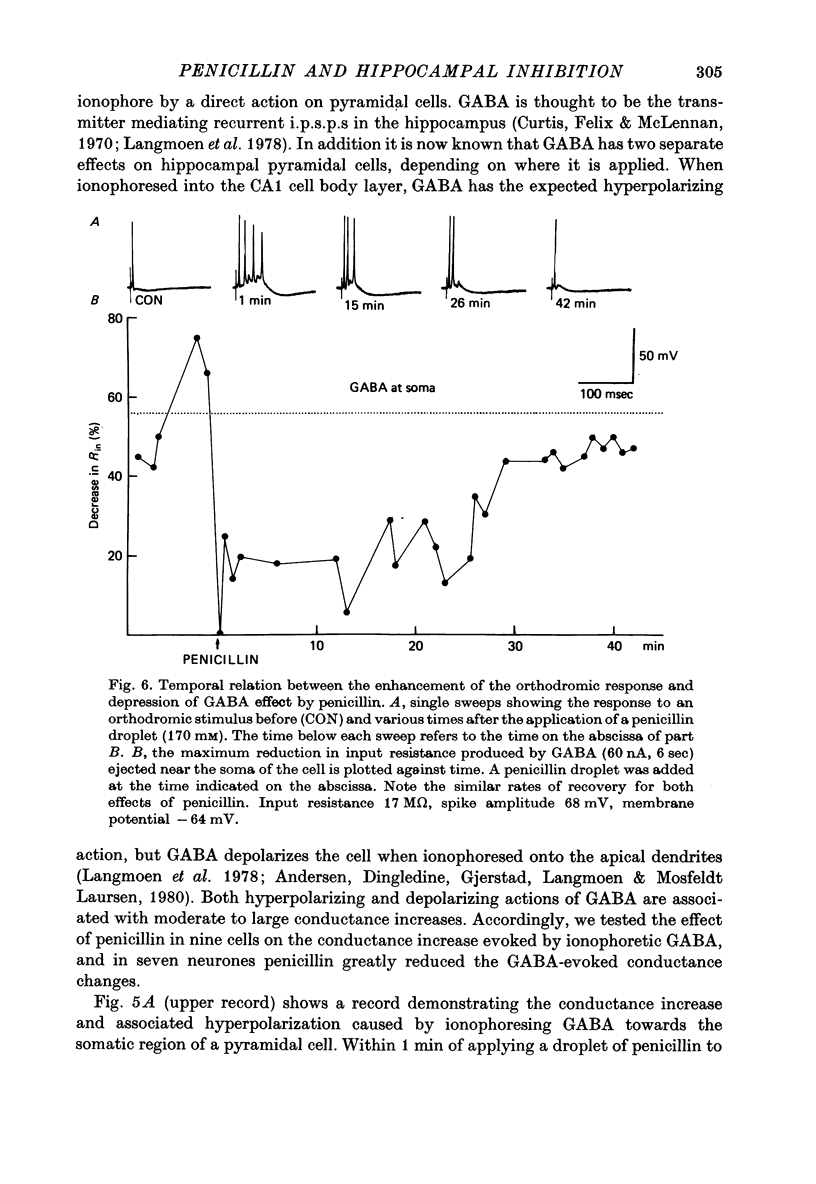
1. Intracellular recordings were made from CA1 pyramidal cells in the hippocampal slice in vitro. The responses to orthodromic and antidromic activation and to ionophoretically applied GABA were studied. 2. The epileptogenic agent sodium benzyl penicillin reduced the recurrent i.p.s.p. evoked by subthreshold antidromic stimulation. Reversal potential studies of the i.p.s.p. and resistance measurements showed that this reduction was mainly due to a decrease in i.p.s.p. conductance. 3. Penicillin also reduced the conductance and associated membrane potential changes induced by ejecting GABA near the soma or into the apical dendritic region. 4. The mixed e.p.s.p.-i.p.s.p. evoked by orthodromic stimulation was converted to a pure depolarizing potential as the i.p.s.p. was blocked. Concurrently the probability of discharge to a constant orthodromic stimulus was increased. Similar changes were seen in a low chloride solution. 5. The time course of the reduction of inhibition was similar to that of the enhanced orthodromic response seen after penicillin treatment. 6. We conclude that reduction of postsynaptic inhibition is partly responsible for the increased probability of orthodromic discharge caused by penicillin. The longer latency all-or-nothing burst seen in some cells, however, seems to require an additional mechanism, although reduced inhibition may facilitate the triggering of this burst.
Full text
PDF















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSEN P., ECCLES J. C., LOYNING Y. PATHWAY OF POSTSYNAPTIC INHIBITION IN THE HIPPOCAMPUS. J Neurophysiol. 1964 Jul;27:608–619. doi: 10.1152/jn.1964.27.4.608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen G. I., Eccles J., Nicoll R. A., Oshima T., Rubia F. J. The ionic mechanisms concerned in generating the i.p.s.ps of hippocampal pyramidal cells. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Sep 19;198(1133):363–384. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Dingledine R., Gjerstad L., Langmoen I. A., Laursen A. M. Two different responses of hippocampal pyramidal cells to application of gamma-amino butyric acid. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:279–296. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayala G. F., Johnston D., Lin S., Dichter H. N. The mechanism of action of diphenylhydantoin on invertebrate neurons. II. Effects on synaptic mechanisms. Brain Res. 1977 Feb;121(2):259–270. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90151-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvin W. H. Dendritic synapses and reversal potentials: theoretical implications of the view from the soma. Exp Neurol. 1969 Jun;24(2):248–264. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(69)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi D. W., Farb D. H., Fischbach G. D. Chlordiazepoxide selectively augments GABA action in spinal cord cell cultures. Nature. 1977 Sep 22;269(5626):342–344. doi: 10.1038/269342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke G., Hill R. G. Effects of a focal penicillin lesion on responses of rabbit cortical neurones to putative neurotransmitters. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Mar;44(3):435–441. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb07281.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Felix D., McLellan H. GABA and hippocampal inhibition. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Dec;40(4):881–883. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb10663.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Game C. J., Johnston G. A., McCulloch R. M., MacLachlan R. M. Convulsive action of penicillin. Brain Res. 1972 Aug 11;43(1):242–245. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90288-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Lodge D., Johnston G. A., Brand S. J. Central actions of benzodiazepines. Brain Res. 1976 Dec 17;118(2):344–347. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90723-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davenport J., Schwindt P. C., Crill W. E. Penicillin-induced spinal seizures: selective effects on synaptic transmission. Exp Neurol. 1977 Jul;56(1):132–150. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(77)90144-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davenport J., Schwindt P. C., Crill W. E. Presynaptic and long-lasting postsynaptic inhibition during penicillin-induced spinal seizures. Neurology. 1978 Jun;28(6):592–597. doi: 10.1212/wnl.28.6.592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidoff R. A. Penicillin and inhibition in the cat spinal cord. Brain Res. 1972 Oct 27;45(2):638–642. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90498-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidoff R. A. Penicillin and presynaptic inhibition in the amphibian spinal cord. Brain Res. 1972 Jan 14;36(1):218–222. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90778-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dichter M., Spencer W. A. Penicillin-induced interictal discharges from the cat hippocampus. I. Characteristics and topographical features. J Neurophysiol. 1969 Sep;32(5):649–662. doi: 10.1152/jn.1969.32.5.649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingledine R., Gjerstad L. Penicillin blocks hippocampal IPSPs, unmasking prolonged EPSPs. Brain Res. 1979 May 18;168(1):205–209. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90141-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreifuss J. J., Kelly J. S., Krnjević K. Cortical inhibition and gamma-aminobutyric acid. Exp Brain Res. 1969;9(2):137–154. doi: 10.1007/BF00238327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccles J., Nicoll R. A., Oshima T., Rubia F. J. The anionic permeability of the inhibitory postsynaptic membrane of hippocampal pyramidal cells. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Sep 19;198(1133):345–361. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. G., Simmonds M. A., Straughan D. W. Antagonism of gamma-aminobutyric acid and glycine by convulsants in the cuneate nucleus of cat. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Jan;56(1):9–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1976.tb06952.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochner B., Spira M. E., Werman R. Penicillin decreases chloride conductance in crustacean muscle: a model for the epileptic neuron. Brain Res. 1976 Apr 30;107(1):85–103. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90097-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANDEL E. R., SPENCER W. A., BRINLEY F. J., Jr Electrophysiology of hippocampal neurons. I. Sequential invasion and synaptic organization. J Neurophysiol. 1961 May;24:225–242. doi: 10.1152/jn.1961.24.3.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Schwartz S. The action of gamma-aminobutyric acid on cortical neurones. Exp Brain Res. 1967;3(4):320–336. doi: 10.1007/BF00237558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LI C. L. Cortical intracellular potentials and their responses to strychnine. J Neurophysiol. 1959 Jul;22(4):436–450. doi: 10.1152/jn.1959.22.4.436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lothman E. W., Somjen G. G. Reflex effects and postsynaptic membrane potential changes during epileptiform activity induced by penicillin in decapitate spinal cords. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1976 Oct;41(4):337–347. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(76)90096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux H. D. Ammonium and chloride extrusion: hyperpolarizing synaptic inhibition in spinal motoneurons. Science. 1971 Aug 6;173(3996):555–557. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3996.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux H. D., Loracher C., Neher E. The action of ammonium on postsynaptic inhibition of cat spinal motoneurons. Exp Brain Res. 1970;11(5):431–447. doi: 10.1007/BF00233967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATSUMOTO H., MARSAN C. A. CORTICAL CELLULAR PHENOMENA IN EXPERIMENTAL EPILEPSY: INTERICTAL MANIFESTATIONS. Exp Neurol. 1964 Apr;9:286–304. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(64)90025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald R. L., Barker J. L. Pentylenetetrazol and penicillin are selective antagonists of GABA-mediated post-synaptic inhibition in cultured mammalian neurones. Nature. 1977 Jun 23;267(5613):720–721. doi: 10.1038/267720a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald R., Barker J. L. Benzodiazepines specifically modulate GABA-mediated postsynaptic inhibition in cultured mammalian neurones. Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):563–564. doi: 10.1038/271563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto H., Ayala G. F., Gumnit R. J. Neuronal behavior and triggering mechanism in cortical epileptic focus. J Neurophysiol. 1969 Sep;32(5):688–703. doi: 10.1152/jn.1969.32.5.688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer H., Prince D. Convulsant actions of penicillin: effects on inhibitory mechanisms. Brain Res. 1973 Apr 27;53(2):477–482. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90237-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll R. A., Eccles J. C., Oshima T., Rubia F. Prolongation of hippocampal inhibitory postsynaptic potentials by barbiturates. Nature. 1975 Dec 18;258(5536):625–627. doi: 10.1038/258625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll R. A. Pentobarbital: action on frog motoneurons. Brain Res. 1975 Oct 10;96(1):119–123. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90582-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll R. A. The effects of anaesthetics on synaptic excitation and inhibition in the olfactory bulb. J Physiol. 1972 Jun;223(3):803–814. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLLEN D. A., MARSAN C. A. CORTICAL INHIBITORY POSTSYNAPTIC POTENTIALS AND STRYCHNINIZATION. J Neurophysiol. 1965 Mar;28:342–358. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.2.342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellmar T. C., Wilson W. A. Penicillin effects on iontophoretic responses in Aplysia californica. Brain Res. 1977 Nov 4;136(1):89–101. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90134-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polc P., Haefely W. Effects of two benzodiazepines, phenobarbitone, and baclofen on synaptic transmission in the cat cuneate nucleus. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1976 Aug;294(2):121–131. doi: 10.1007/BF00507844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollen D. A., Lux H. D. Conductance changes during inhibitory postsynaptic potentials in normal and strychninized cortical neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1966 May;29(3):369–381. doi: 10.1152/jn.1966.29.3.369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince D. A. The depolarization shift in "epileptic" neurons. Exp Neurol. 1968 Aug;21(4):467–485. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(68)90066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raabe W., Ayala G. F. Diphenylhydantoin increases cortical postsynaptic inhibition. Brain Res. 1976 Apr 9;105(3):597–601. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90611-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransom B. R., Barker J. L. Pentobarbital modulates transmitter effects on mouse spinal neurones grown in tissue culture. Nature. 1975 Apr 24;254(5502):703–705. doi: 10.1038/254703a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R. F., Vogel M. E., Zimmermann M. Die Wirkung von Diazepam auf die präsynaptische Hemmung und andere Rückenmarksreflexe. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1967;258(1):69–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholfield C. N. A barbiturate induced intensification of the inhibitory potential in slices of guinea-pig olfactory cortex. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:559–566. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzkroin P. A. Characteristics of CA1 neurons recorded intracellularly in the hippocampal in vitro slice preparation. Brain Res. 1975 Mar 7;85(3):423–436. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90817-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzkroin P. A. Further characteristics of hippocampal CA1 cells in vitro. Brain Res. 1977 Jun 3;128(1):53–68. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90235-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzkroin P. A., Prince D. A. Penicillin-induced epileptiform activity in the hippocampal in vitro prepatation. Ann Neurol. 1977 May;1(5):463–469. doi: 10.1002/ana.410010510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skrede K. K., Westgaard R. H. The transverse hippocampal slice: a well-defined cortical structure maintained in vitro. Brain Res. 1971 Dec 24;35(2):589–593. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90508-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Duijn H., Schwartzkroin P. A., Prince D. A. Action of penicillin on inhibitory processes in the cat's cortex. Brain Res. 1973 Apr 27;53(2):470–476. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90236-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh G. O. Penicillin iontophoresis in neocortex of cat: effects on the spontaneous and induced activity of single neurons. Epilepsia. 1971 Mar;12(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1971.tb03911.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson W. A., Escueta A. V. Common synaptic effects of pentylenetetrazol and penicillin. Brain Res. 1974 May 31;72(1):168–171. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90662-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto C. Intracellular study of seizure-like afterdischarges elicited in thin hippocampal sections in vitro. Exp Neurol. 1972 Apr;35(1):154–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(72)90066-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



