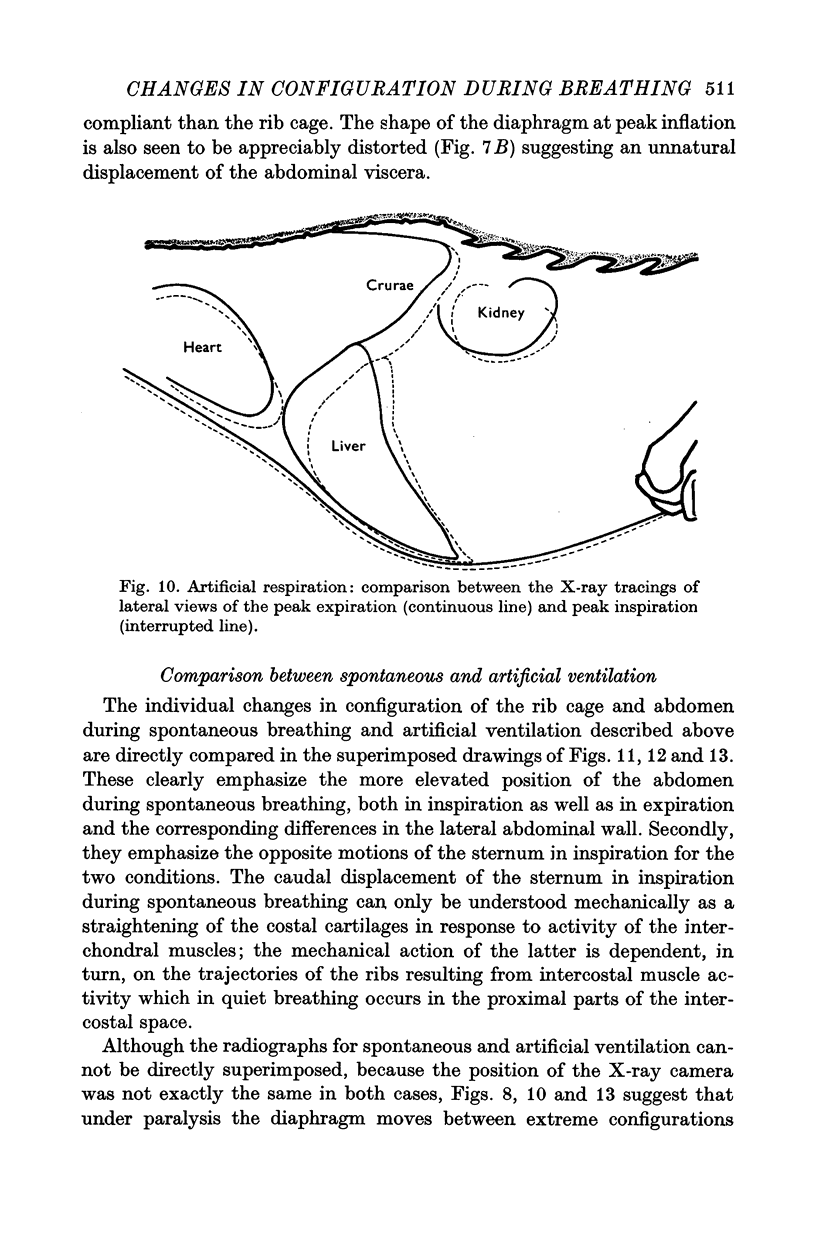
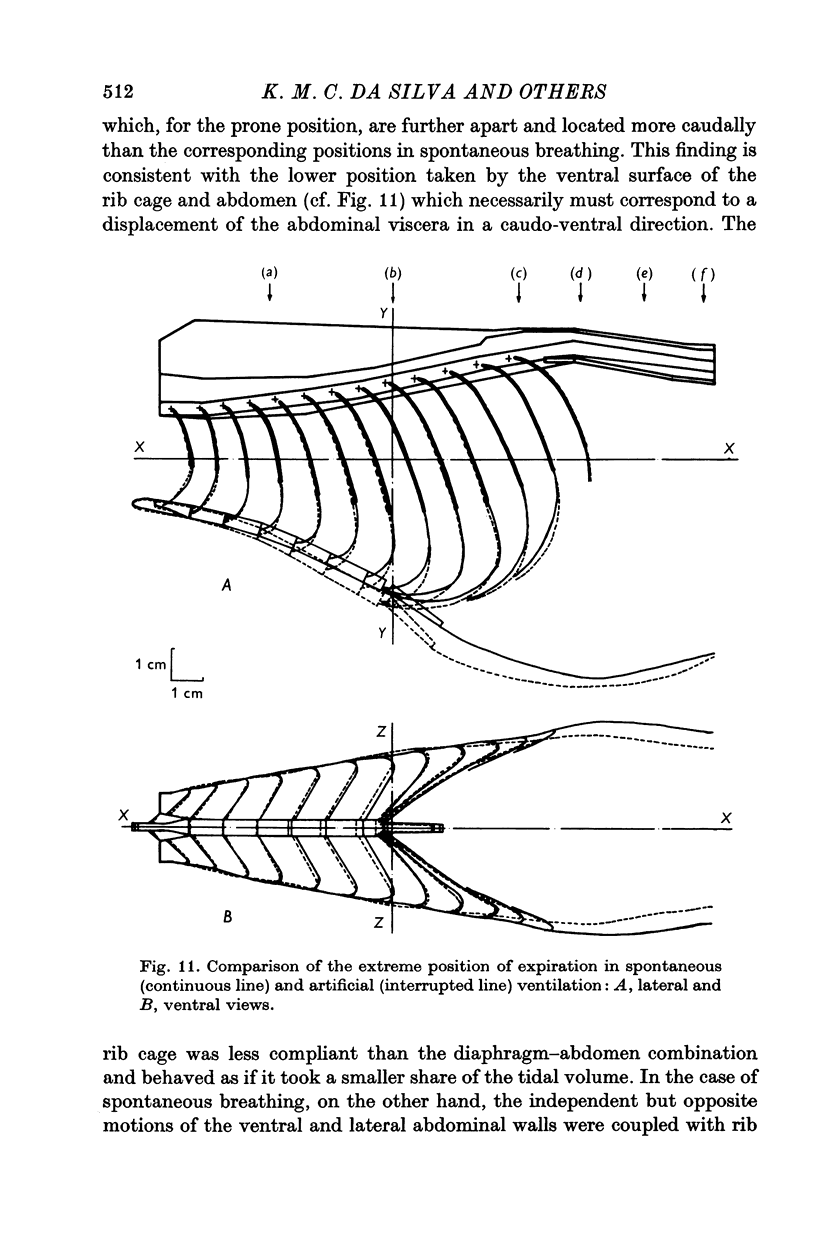
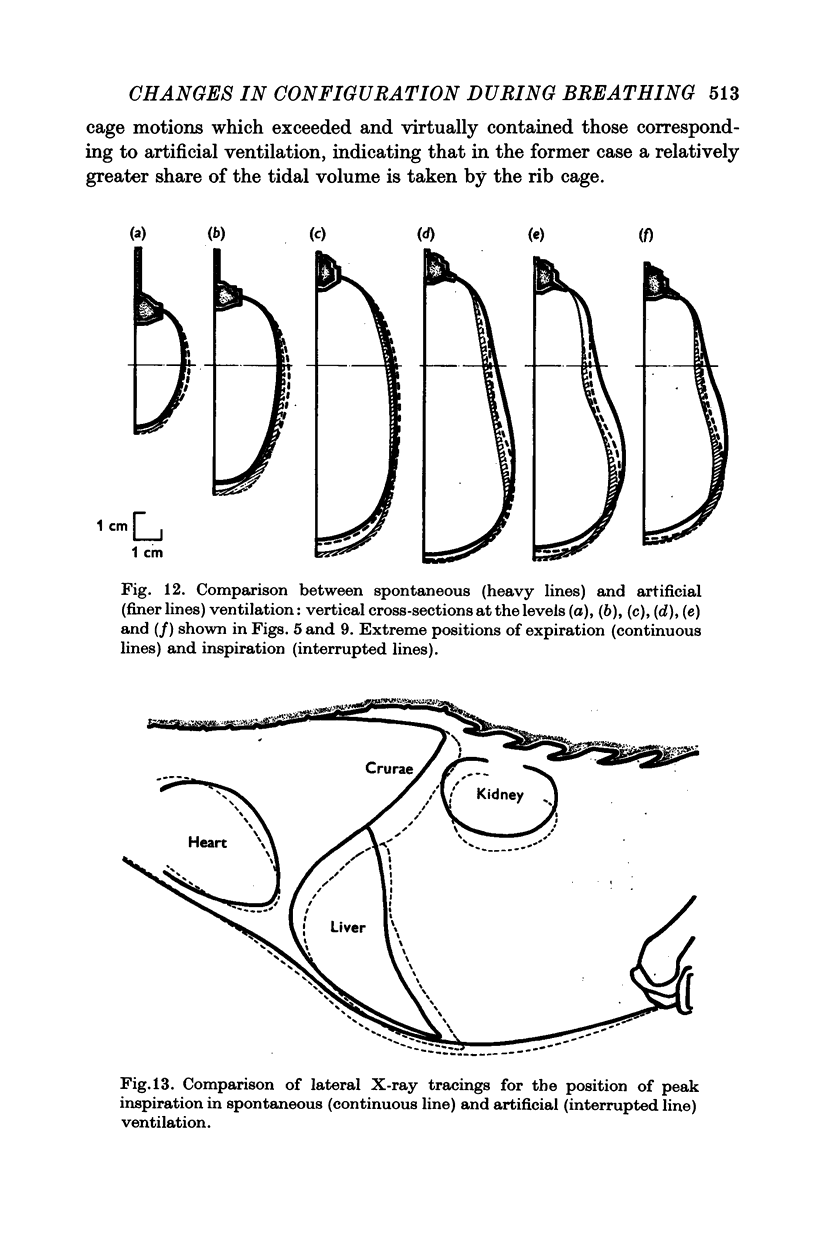
Abstract
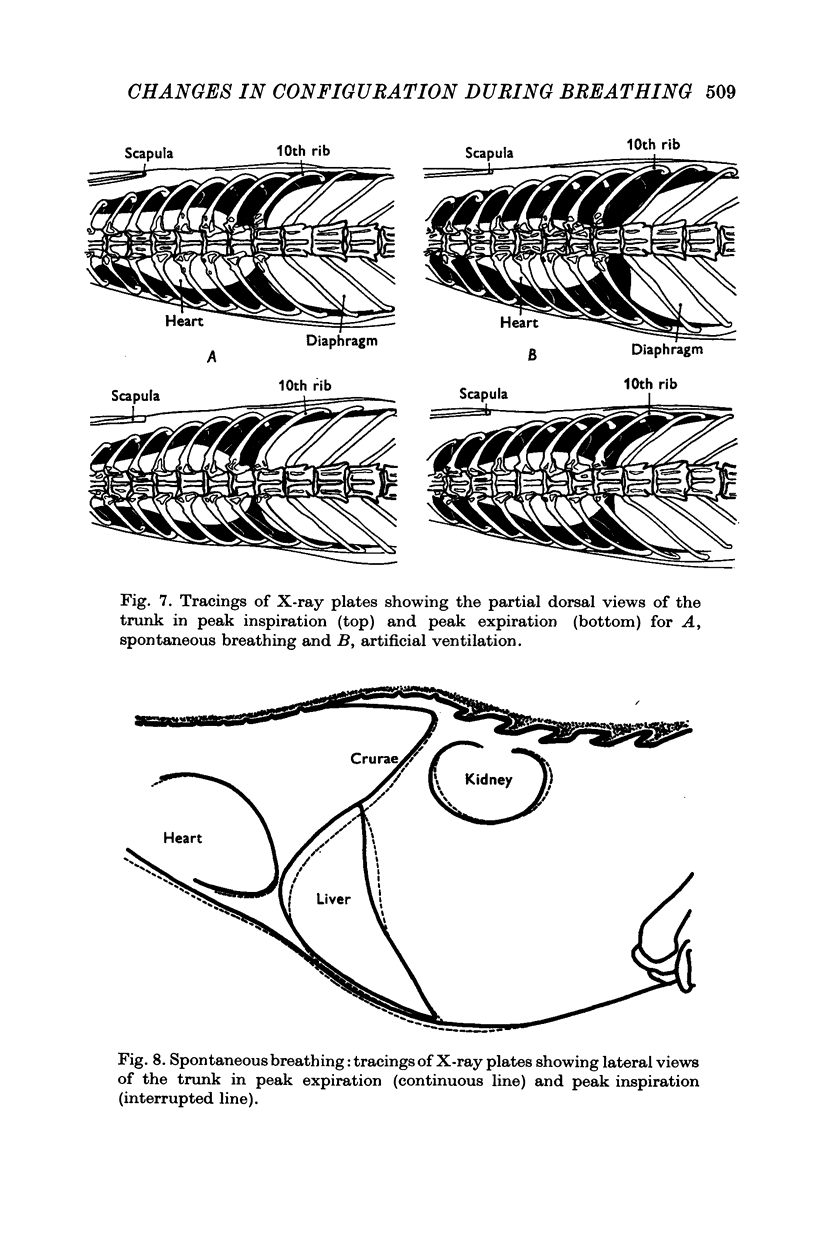
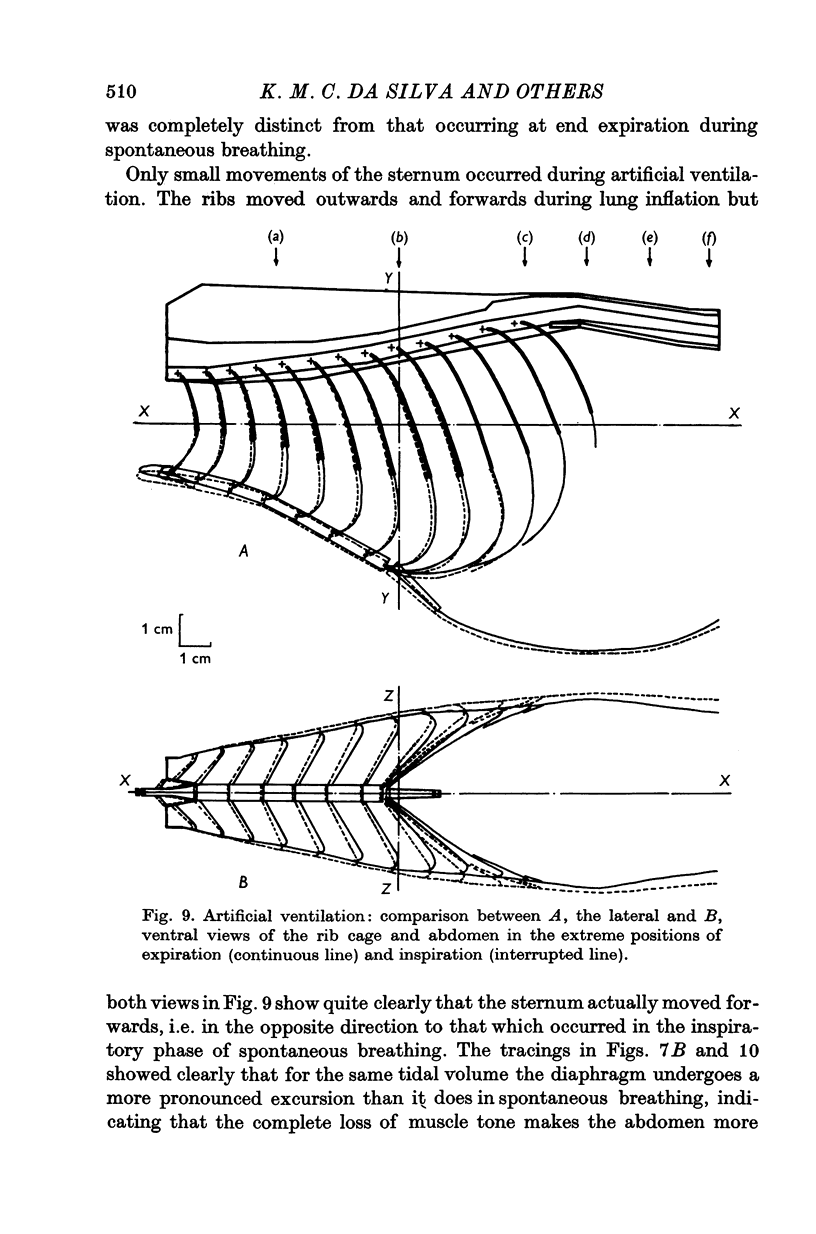
1. The external surface of the rib cage and abdominal wall in anaesthetized cats was surgically exposed in order to record their movements cinematographically in spontaneous breathing and in paralysed cats, during artificial positive pressure ventilation. 2. Cine-stereophotography was used to allow the recording of the movements of a set of markers placed on the external surface of the trunk wall and the corresponding stereometric data were numerically and graphically processed into three-dimensional drawings. The cine-film frames corresponding to the phases of maximum inflation and deflation of the lungs were analysed to reveal the changes in configuration associated with the respiratory movements of the trunk wall. 3. The changes in shape of the diaphragm and the diaphragm and the displacements of the abdominal viscera between extreme inflation and deflation were recorded by X-ray photography. 4. During spontaneous inspiratory movements, the ribs rotated outwards and rostrally about the costovertebral joints, bringing about an increase in the transverse dimensions of the cage all along its length; these movements were accompanied by a clear-cut caudad displacement of the sternum, caused by the straightening of the costal cartilages and by the widening of the angles defined at sternochondral joints between the sternum and each of the costal cartilages. 5. Neuromuscular blockade abolished muscle tone in the trunk wall, allowing the weight of the viscera markedly to deform its configuration. 6. The inspiratory rib movements of the paralysed animal during artificial inspiration were similar to those during spontaneous breathing but the movements of the sternum were inverted and showed small cranial displacements. 7. The loss of muscular tone under neuromuscular blockade made the abdominal wall more compliant than the rib cage to the positive lung pressure and allowed greater mobility of the viscera with consequent distortion of the shape of the diaphragm. 8. The role of rib cage muscle tone in meeting requirements of purely configurational character in such a shell-like structure is discussed in relation to the optimal mechanical performance of the diaphragm.
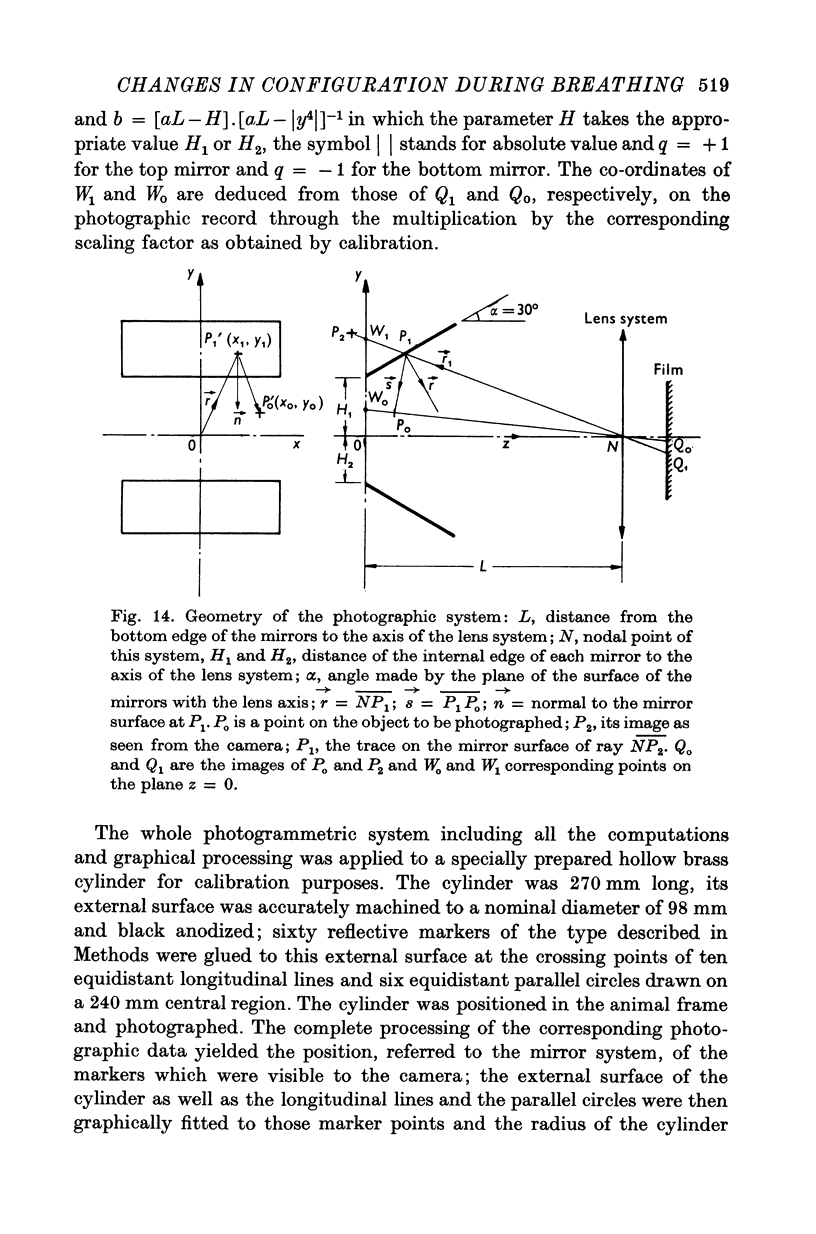
Full text
PDF


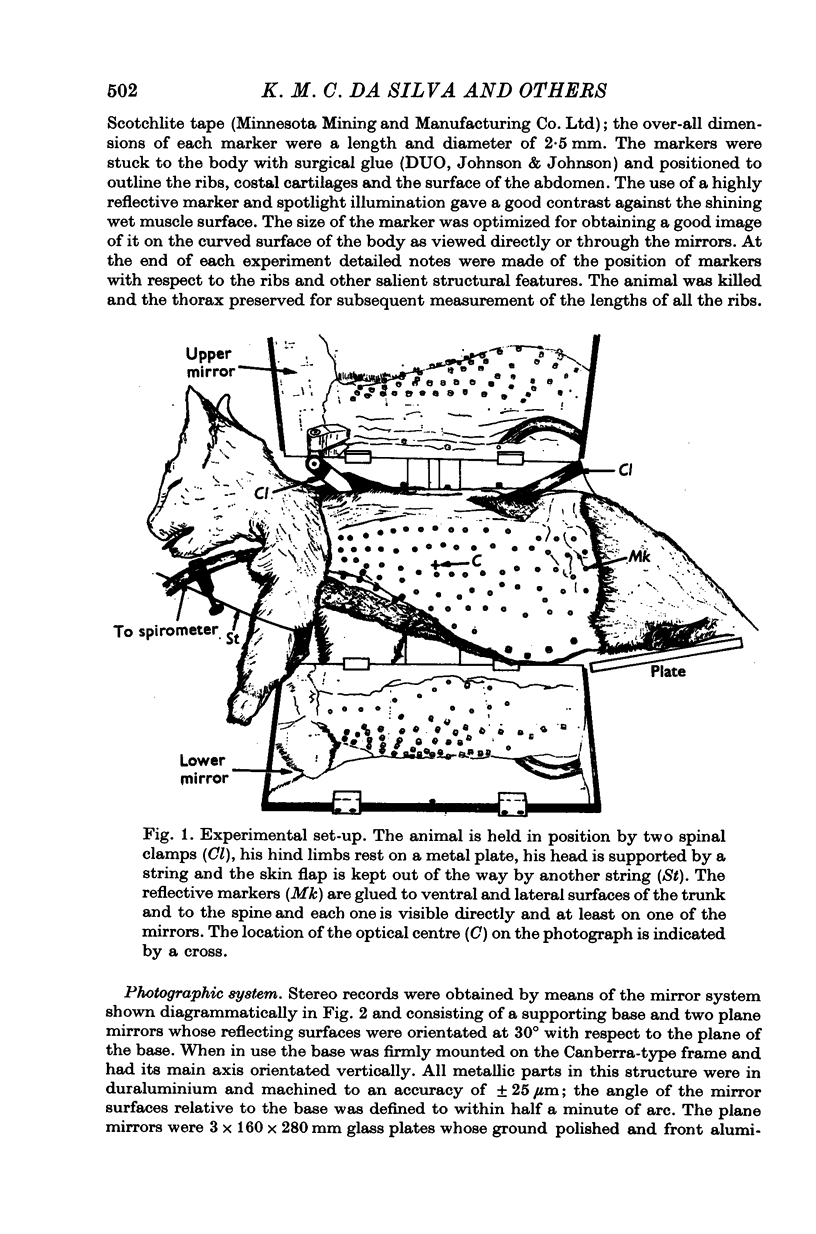
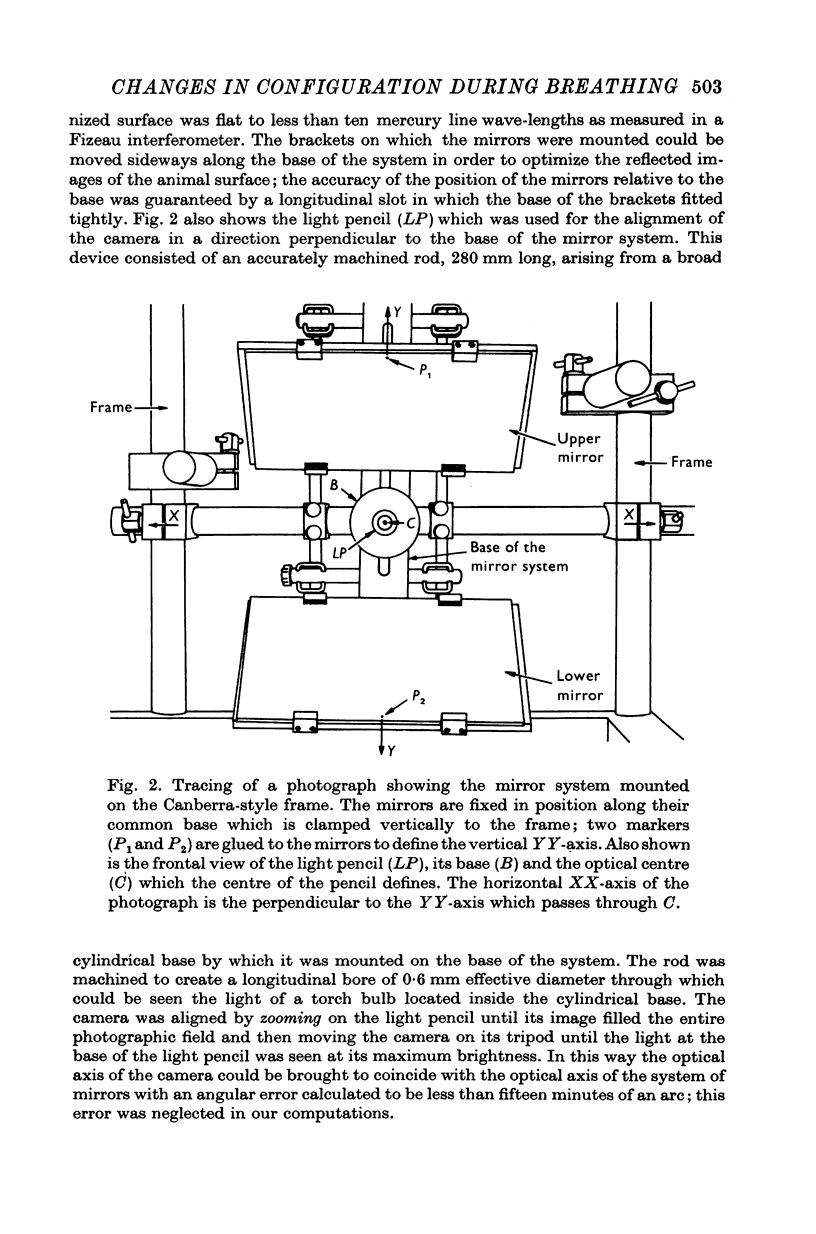
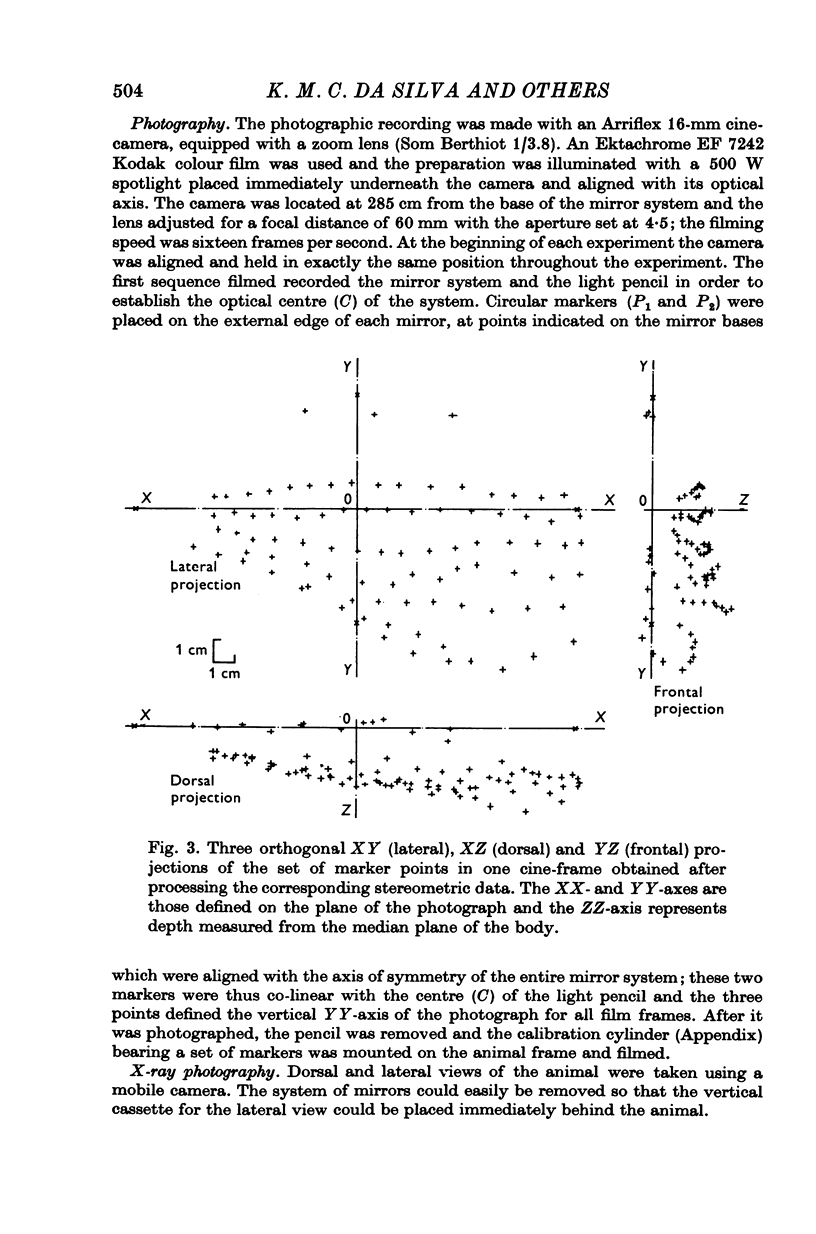
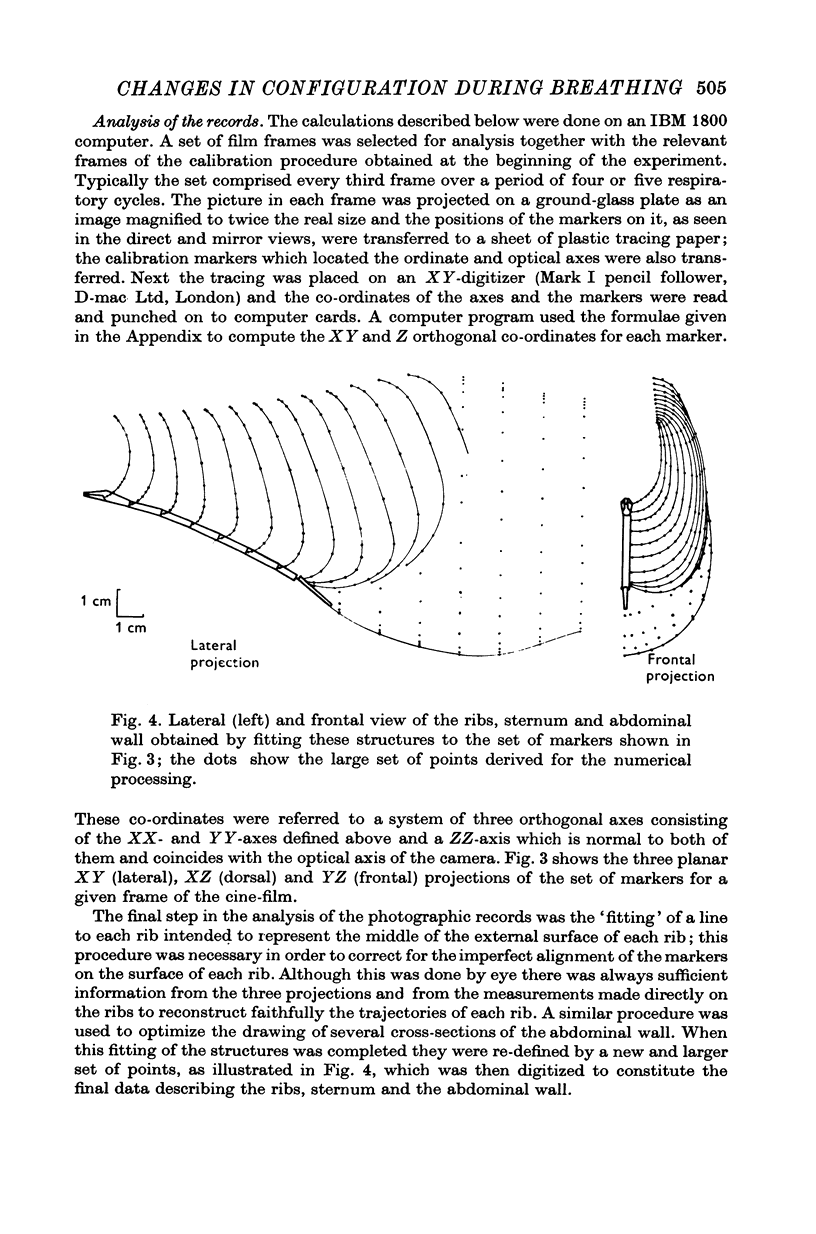
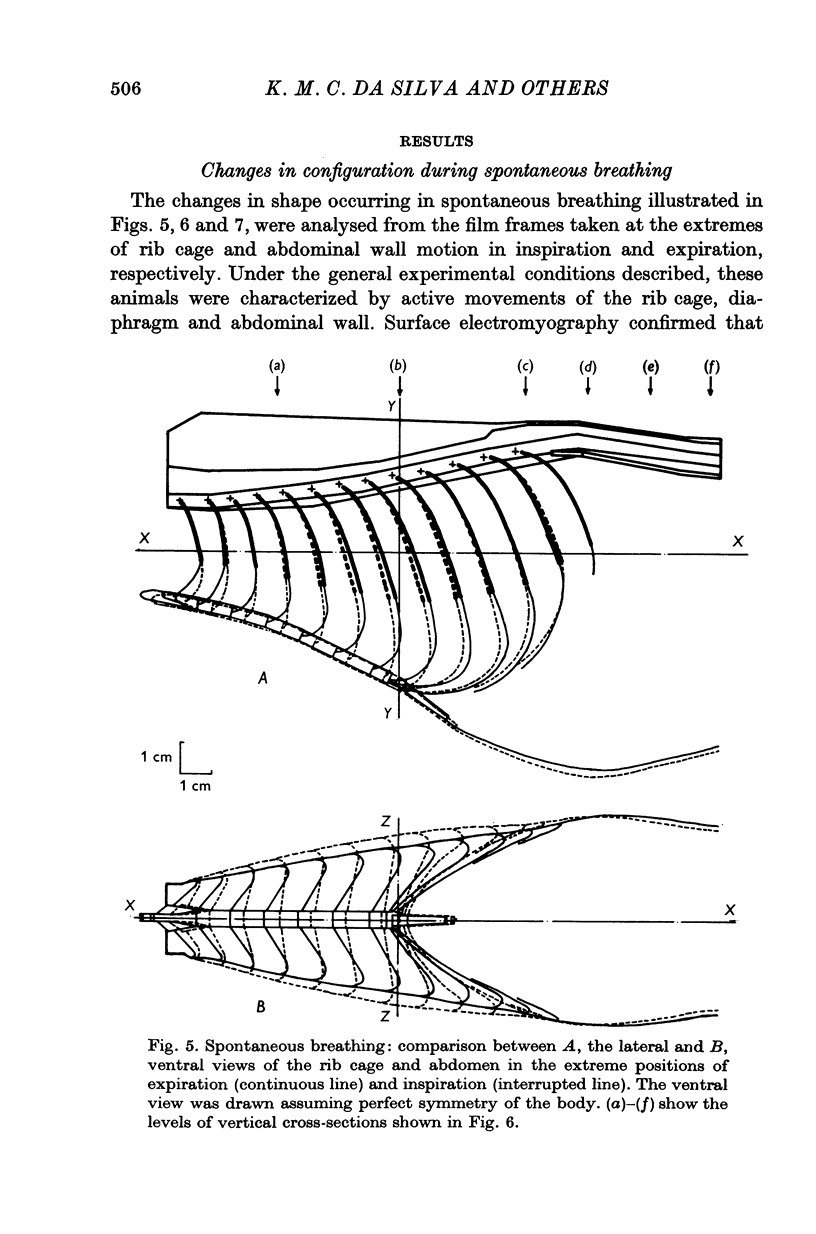
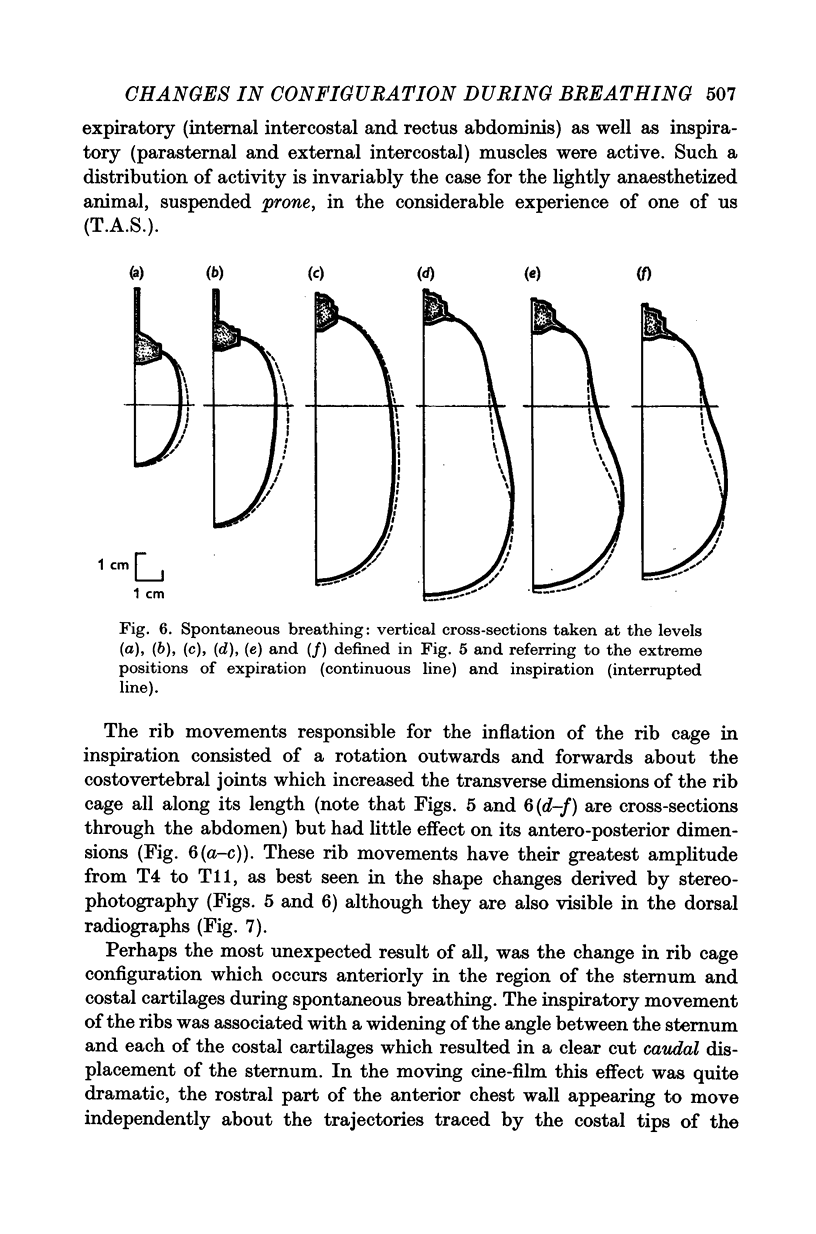








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agostoni E., D'Angelo E., Bonanni M. V. The effect of the abdomen on the vertical gradient of pleural surface pressure. Respir Physiol. 1970 Mar;8(3):332–346. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(70)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agostoni E., D'Angelo E. Topography of pleural surface pressure during simulation of gravity effect on abdomen. Respir Physiol. 1971 Apr;12(1):102–109. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(71)90105-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard L. F., Burke P. H. Evolution of a system of stereophotogrammetry for the study of facial morphology. Med Biol Illus. 1967 Jan;17(1):20–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Angelo E., Sant'Ambrogio G. Direct action of contracting diaphragm on the rib cage in rabbits and dogs. J Appl Physiol. 1974 Jun;36(6):715–719. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1974.36.6.715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J., Goldman M., Loh L., Casson M. Diaphragm function and alveolar hypoventilation. Q J Med. 1976 Jan;45(177):87–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konno K., Mead J. Measurement of the separate volume changes of rib cage and abdomen during breathing. J Appl Physiol. 1967 Mar;22(3):407–422. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1967.22.3.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konno K., Mead J. Static volume-pressure characteristics of the rib cage and abdomen. J Appl Physiol. 1968 Apr;24(4):544–548. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1968.24.4.544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASSION J., MEULDERS M., COLLE J. [Postural function of the respiratory muscles]. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1960 Mar;68:314–326. doi: 10.3109/13813456009083552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pengelly L. D., Alderson A. M., Milic-Emili J. Mechanics of the diaphragm. J Appl Physiol. 1971 Jun;30(6):797–805. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1971.30.6.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Euler C. The role of proprioceptive afferents in the control of respiratory muscles. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 1973;33(1):329–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


