Abstract
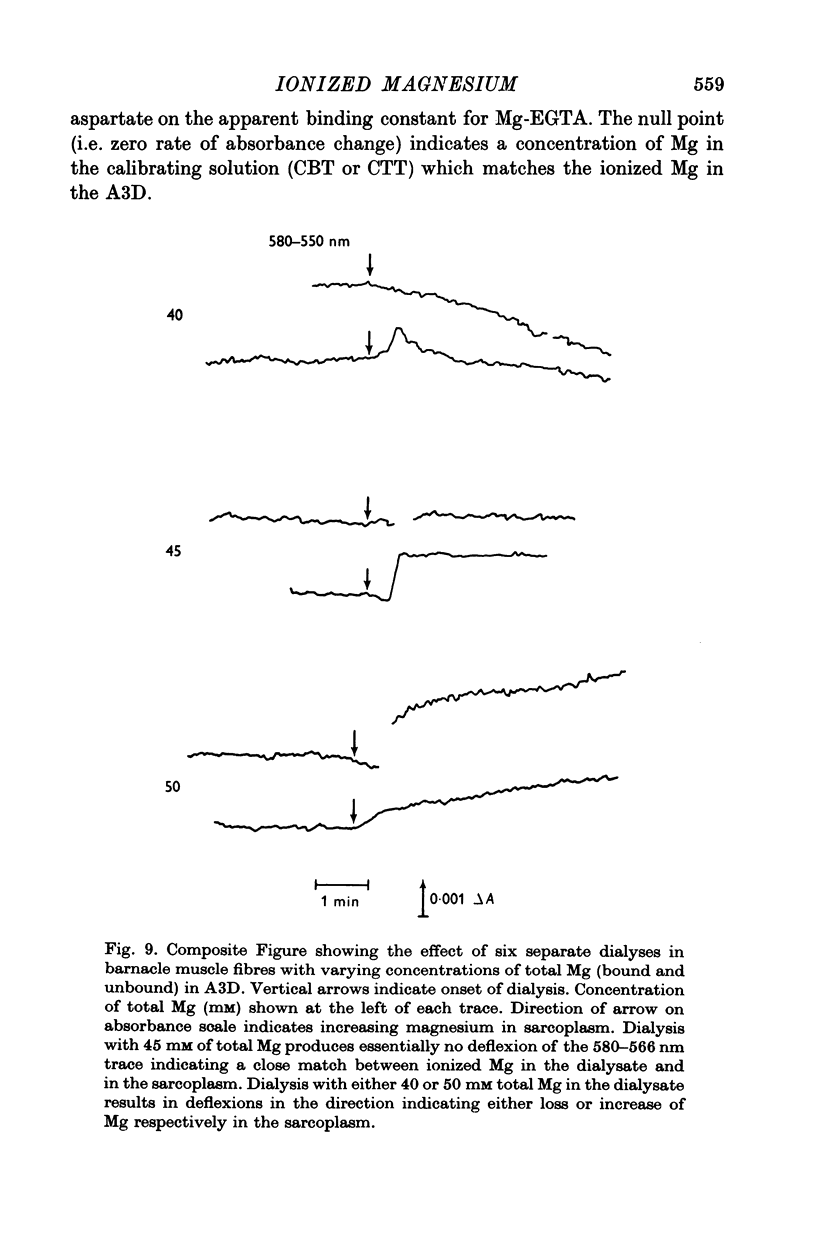
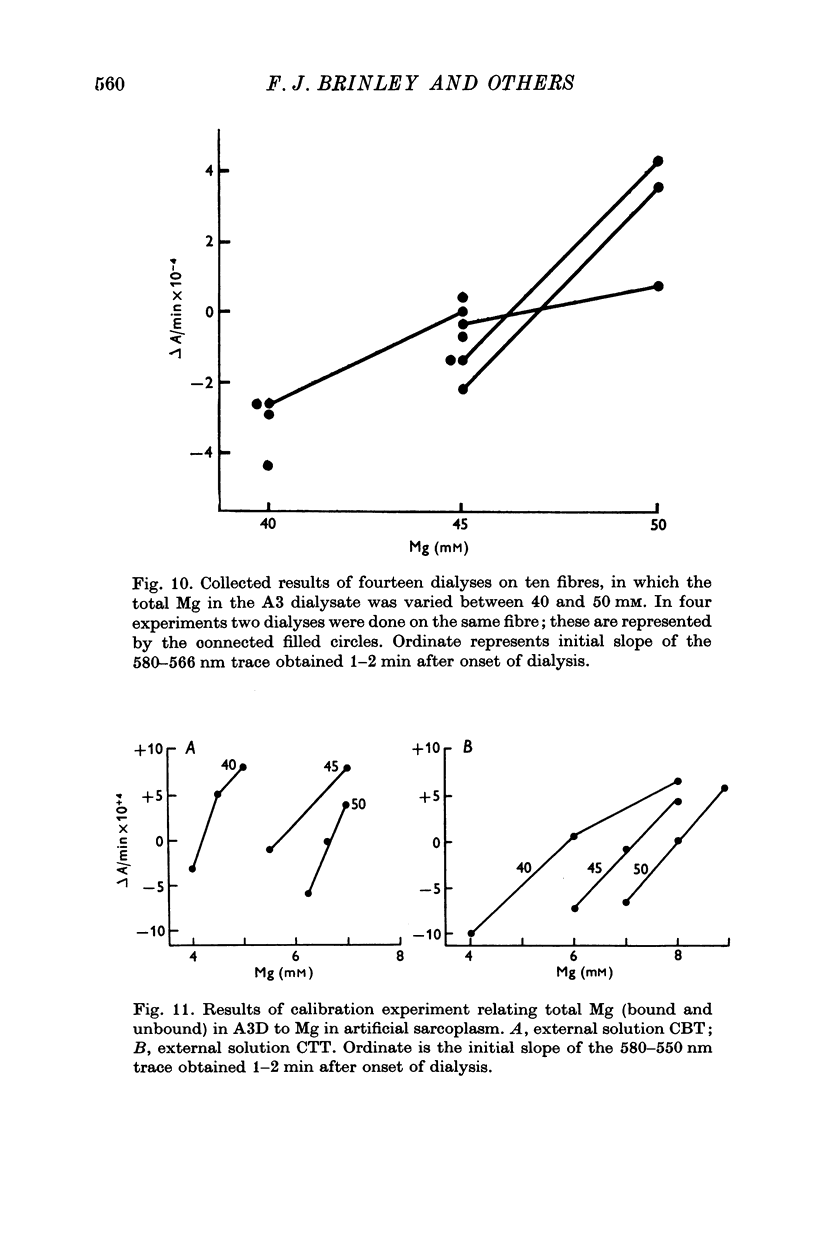
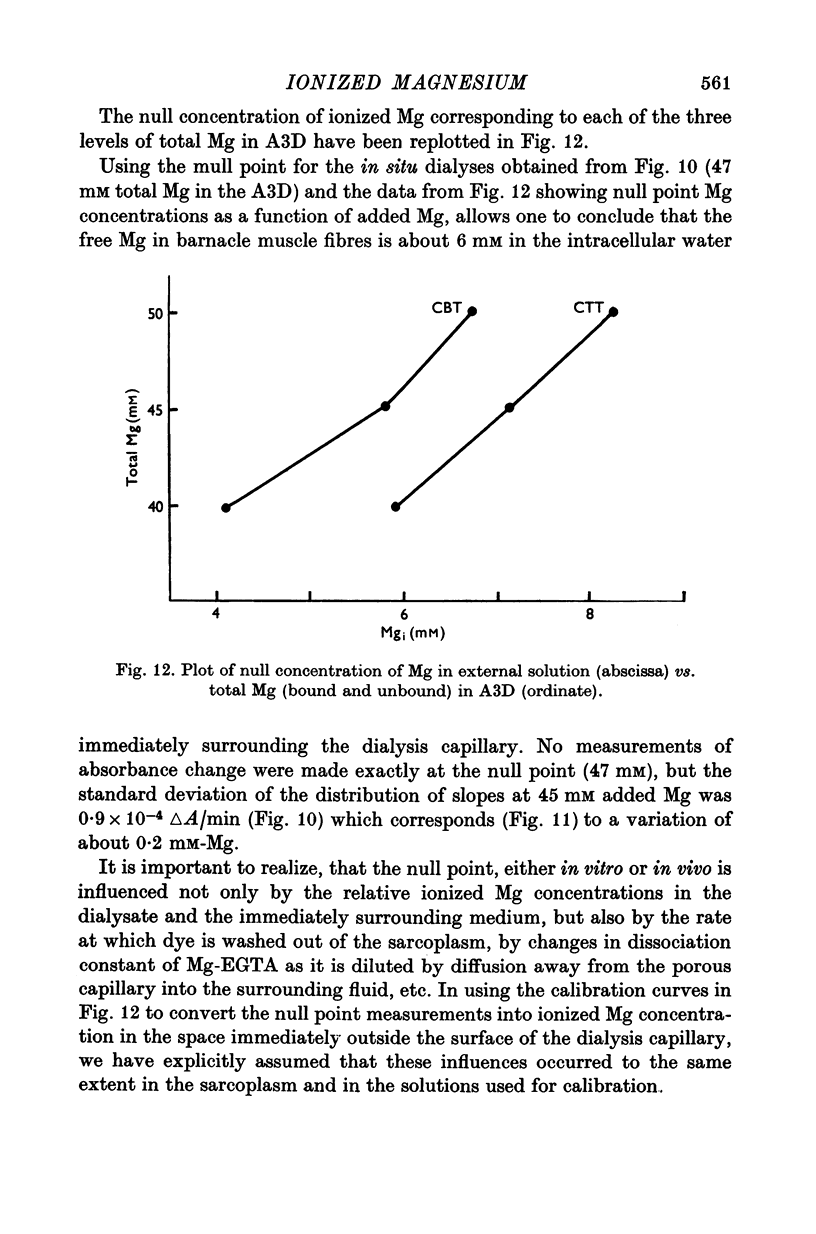
1. The total Mg in isolated fibres of Balanus aquila was 10-5 m-mole/kg wet wt. 2. The intracellular free Mg was measured by a null point method using Eriochrome Blue as an indicator of free Mg, and internal dialysis with solutions of varying ionized Mg concentrations. The results indicated a free Mg of 6 mM or 4-2 m-mole/kg wet wt. in the intracellular water immediately surrounding the dialysis capillary. 3. The ATP concentration was estimated to be 4-9 m-mole/kg wet wt. 4. A tentative partitioning of Mg among various intracellular constitutents based on present data combined with published work by others is (m-mole/kg wet wt): free, 4-2; MgATP, 4-2; myofibrillar bound, 1; residual (presumably bound to arginine phosphate and phosphate) ca. 1.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashley C. C., Ellory J. C. The efflux of magnesium from single crustacean muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1972 Nov;226(3):653–674. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachelard H. S., Goldfarb P. S. Adenine nucleotides and magnesium ions in relation to control of mammalian cerebral-cortex hexokinase. Biochem J. 1969 May;112(5):579–586. doi: 10.1042/bj1120579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Crawford A. C. Mobility and transport of magnesium in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(3):855–874. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boron W. F., Roos A. Comparison of microelectrode, DMO, and methylamine methods for measuring intracellular pH. Am J Physiol. 1976 Sep;231(3):799–809. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.3.799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinley F. J., Jr, Mullins L. J. Effects of membrane potential on sodium and potassium fluxes in squid axons. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974;242(0):406–433. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb19106.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinley F. J., Jr, Scarpa A. Ionized magnesium concentration in axoplasm of dialyzed squid axons. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jan 15;50(1):82–85. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)81046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CALDWELL P. C. The phosphorus metabolism of squid axons and its relationship to the active transport of sodium. J Physiol. 1960 Jul;152:545–560. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dipolo R., Requena J., Brinley F. J., Jr, Mullins L. J., Scarpa A., Tiffert T. Ionized calcium concentrations in squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Apr;67(4):433–467. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.4.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günther T. Die intrazelluläre Mg-Ionenkonzentration. Z Naturforsch B. 1967 Feb;22(2):149–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keynes R. D., Rojas E., Taylor R. E., Vergara J. Calcium and potassium systems of a giant barnacle muscle fibre under membrane potential control. J Physiol. 1973 Mar;229(2):409–455. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins L. J., Brinley F. J., Jr Some factors influencing sodium extrusion by internally dialyzed squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Nov;50(10):2333–2355. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.10.2333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NANNINGA L. B. Calculation of free magnesium, calcium and potassium in muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Dec 9;54:338–344. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90374-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page E., Mobley B. A., Johnson M., Upshaw J. E. Magnesium in single skeletal muscle cells of Balanus. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Feb;57(2):188–201. doi: 10.1085/jgp.57.2.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. M., Blaustein M. P. Calcium efflux from barnacle muscle fibers. Dependence on external cations. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Feb;63(2):144–167. doi: 10.1085/jgp.63.2.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpa A. Indicators of free magnesium in biological systems. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 2;13(14):2789–2794. doi: 10.1021/bi00711a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veloso D., Guynn R. W., Oskarsson M., Veech R. L. The concentrations of free and bound magnesium in rat tissues. Relative constancy of free Mg 2+ concentrations. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 10;248(13):4811–4819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharová D., Zachar J. The effect of external calcium ions on the excitation-contraction coupling in single muscle fibres of the crayfish. Physiol Bohemoslov. 1967;16(3):191–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


