Abstract
1. The distribution of α-bungarotoxin binding sites on embryonic and neonatal rat skeletal muscle fibres was determined by autoradiography. Most of the bungarotoxin binding could be inhibited by curare. This observation, together with the spatial distribution of toxin-binding sites, indicates that the distribution of bound toxin reflects that of acetylcholine (ACh) receptors on these developing muscle cells.
2. At 15 days of embryogenesis, muscle fibres showed an essentially uniform distribution of receptors. By 16 days, many fibres showed an accumulation of receptors in their mid-region. This accumulation was at the same location as histochemically demonstrated cholinesterase activity.
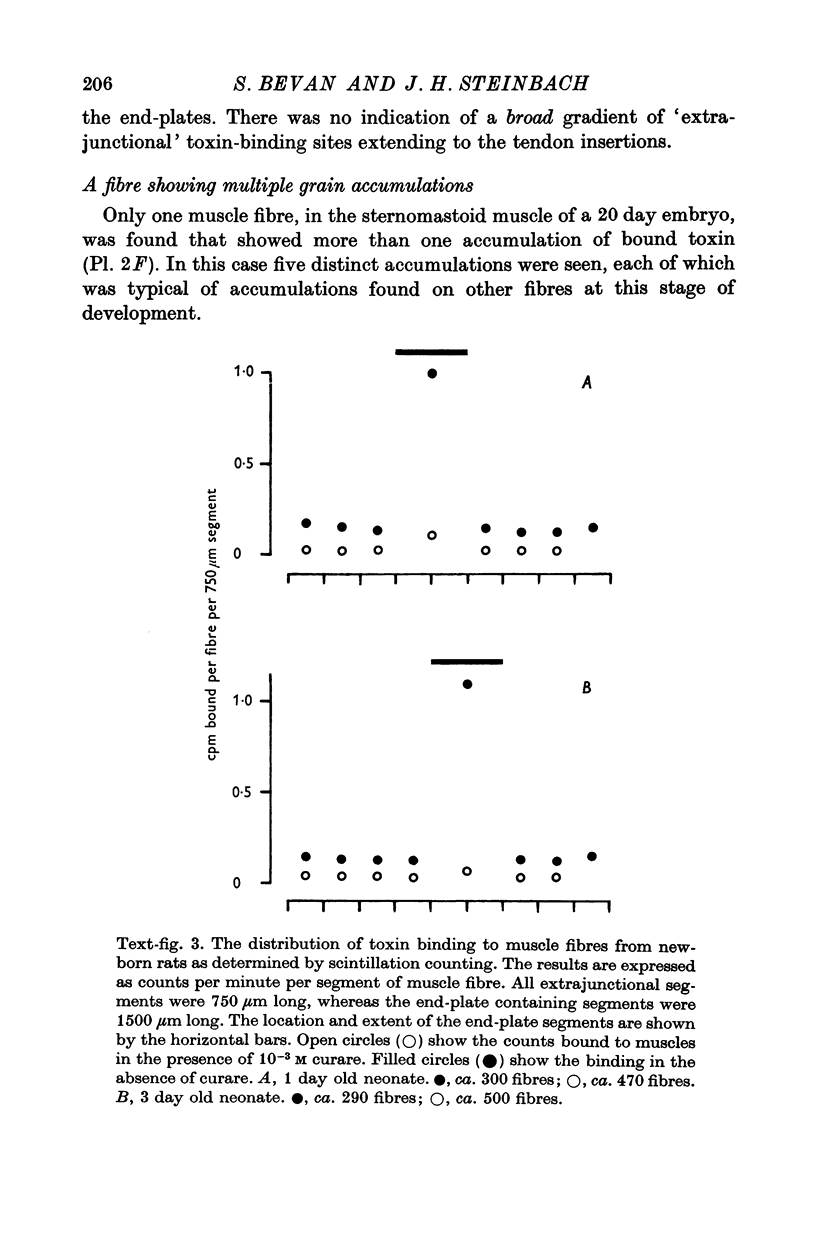
3. At 16 days ACh receptors were distributed over the entire length of the fibres, with a gradient of increasing density as the accumulation was appoached. The density of toxin binding sites in the accumulation was greater than the general level on 15 day cells, suggesting that the high junctional density does not develop solely by the loss of extrajunctional receptors.
4. The accumulations of ACh receptors became more pronounced and circumscribed with embryonic development, and after birth the extent of the localizations appeared to follow the size of the neuromuscular junction. The extrajunctional receptor density decreased with development, and by 1 week after birth was undetectable by the methods used.
5. The results suggest that the high junctional receptor density found on adult, innervated skeletal muscle fibres develops after the formation of the neuromuscular junction.
Full text
PDF



















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ada G. L., Humphrey J. H., Askonas B. A., McDevitt H. O., Nossal G. J. Correlation of grain counts with radioactivity (125I and tritium) in autoradiography. Exp Cell Res. 1966 Mar;41(3):557–572. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(66)80106-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg D. K., Kelly R. B., Sargent P. B., Williamson P., Hall Z. W. Binding of -bungarotoxin to acetylcholine receptors in mammalian muscle (snake venom-denervated muscle-neonatal muscle-rat diaphragm-SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):147–151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COERS C. Les variations structurelles normales et pathologiques de la jonction neuromusculaire. Acta Neurol Psychiatr Belg. 1955 Oct;55(10):741–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. A., Fischbach G. D. Regulation of muscle acetylcholine sensitivity by muscle activity in cell culture. Science. 1973 Jul 6;181(4094):76–78. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4094.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Rang H. P., Ritchie J. M. The binding of tetrodotoxin and alpha-bungarotoxin to normal and denervated mammalian muscle. J Physiol. 1974 Jul;240(1):199–226. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devreotes P. N., Fambrough D. M. Acetylcholine receptor turnover in membranes of developing muscle fibers. J Cell Biol. 1975 May;65(2):335–358. doi: 10.1083/jcb.65.2.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ertl H. H., Feinendegen L. E., Heiniger H. J. Iodine-125, a tracer in cell biology: physical properties and biological aspects. Phys Med Biol. 1970 Jul;15(3):447–456. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/15/3/005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fambrough D. M. Acetylcholine receptors. Revised estimates of extrajunctional receptor density in denervated rat diaphragm. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Oct;64(4):468–472. doi: 10.1085/jgp.64.4.468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fambrough D. M., Hartzell H. C. Acetylcholine receptors: number and distribution at neuromuscular junctions in rat diaphragm. Science. 1972 Apr 14;176(4031):189–191. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4031.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fertuck H. C., Salpeter M. M. Sensitivity in electron microscope autoradiography for 125I. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Feb;22(2):80–87. doi: 10.1177/22.2.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filogamo G., Gabella G. The development of neuro-muscular correlations, in vertebrates. Arch Biol (Liege) 1967;78(1):9–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischbach G. D., Cohen S. A. The distribution of acetylcholine sensitivity over uninnervated and innervated muscle fibers grown in cell culture. Dev Biol. 1973 Mar;31(1):147–162. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90326-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guth L. "Trophic" influences of nerve on muscle. Physiol Rev. 1968 Oct;48(4):645–687. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1968.48.4.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. J. Inductive functions of the nervous system. Annu Rev Physiol. 1974;36:251–305. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.36.030174.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell H. C., Fambrough D. M. Acetylcholine receptors. Distribution and extrajunctional density in rat diaphragm after denervation correlated with acetylcholine sensitivity. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Sep;60(3):248–262. doi: 10.1085/jgp.60.3.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARNOVSKY M. J., ROOTS L. A "DIRECT-COLORING" THIOCHOLINE METHOD FOR CHOLINESTERASES. J Histochem Cytochem. 1964 Mar;12:219–221. doi: 10.1177/12.3.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly A. M., Zacks S. I. The fine structure of motor endplate morphogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jul;42(1):154–169. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.1.154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landon D. N. The fine structure of the equatorial regions of developing muscle spindles in the rat. J Neurocytol. 1972 Sep;1(2):189–210. doi: 10.1007/BF01099184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomo T., Rosenthal J. Control of ACh sensitivity by muscle activity in the rat. J Physiol. 1972 Mar;221(2):493–513. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomo T., Westgaard R. H. Further studies on the control of ACh sensitivity by muscle activity in the rat. J Physiol. 1975 Nov;252(3):603–626. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILEDI R. Junctional and extra-junctional acetylcholine receptors in skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1960 Apr;151:24–30. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milburn A. The early development of muscle spindles in the rat. J Cell Sci. 1973 Jan;12(1):175–195. doi: 10.1242/jcs.12.1.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Potter L. T. Acetylcholine receptors in muscle fibres. Nature. 1971 Oct 29;233(5322):599–603. doi: 10.1038/233599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyström B. Postnatal development of motor nerve terminals in "slow-red" and "fast-white" cat muscles. Acta Neurol Scand. 1968;44(3):363–383. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1968.tb05578.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick J., Heinemann S. F., Lindstrom J., Schubert D., Steinbach J. H. Appearance of acetylcholine receptors during differentiation of a myogenic cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2762–2766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter C. W., Barnard E. A., Chiu T. H. The ultrastructural localization and quantitation of cholinergic receptors at the mouse motor endplate. J Membr Biol. 1973;14(4):383–402. doi: 10.1007/BF01868086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter C. W., Chiu T. H., Wieckowski J., Barnard E. A. Types and locations of cholinergic receptor-like molecules in muscle fibres. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jan 3;241(105):3–7. doi: 10.1038/newbio241003a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfern P. A. Neuromuscular transmission in new-born rats. J Physiol. 1970 Aug;209(3):701–709. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salpeter M. M., Elderfrawi M. E. Sizes of end plate compartments, densities of acetylcholine receptor and other quantitative aspects of neuromuscular transmission. J Histochem Cytochem. 1973 Sep;21(9):769–778. doi: 10.1177/21.9.769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salpeter M. M., Plattner H., Rogers A. W. Quantitative assay of esterases in end plates of mouse diaphragm by electron microscope autoradiography. J Histochem Cytochem. 1972 Dec;20(12):1059–1068. doi: 10.1177/20.12.1059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ter3AV3AINEN H. Carboxylic esterases in developing myoneural junctions of rat striated muscle. Histochemie. 1968;12(4):307–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGT M., DULBECCO R. Steps in the neoplastic transformation of hamster embryo cells by polyoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Feb 15;49:171–179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.2.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel Z., Sytkowski A. J., Nirenberg M. W. Acetylcholine receptors of muscle grown in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3180–3184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZELENA J., SZENTAGOTHAI J. Verlagerung der Lokalisation spezifischer Cholinesterase während der Entwicklung der Muskelinnervation. Acta Histochem. 1957 Mar 30;3(7/8):284–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]