Abstract
1. The objective was to find out what kind of informatioon regarding systemic blood pressure is transduced by baroreceptors in vivo and how this information is coded in the receptor discharge. 2. Carotid sinus pressure, e.c.g., and receptor action potentials were recorded for fifty-two single fibre carotid sinus receptors found in twenty decerebrated unanaesthetized cats. 3. The inflation and gradual deflation of an intraaortic catheter tip balloon manipulated the blood pressure in the carotid sinus in a way as to define the full in vivo stimulus-response curve for each receptor. 4. Correlation coefficients were computed between stimulus and response variables for several points on the response curve of each receptor and for every possible combination of stimulus and response variables defined. 5. Stimulus variables were (a) systolic, (b) diastolic,, (c) mean, (d) pulse pressures and (e) peak positive dP/dt. Response variables were (a) average discharge rat, (b) peak instantaneous frequency, and (c) average burst frequency. 6. For every fibre in the sample only the correlations between systolic, diastolic and mean pressures vs. average discharge rate were consistently high and positive. All other correlations were numerically low and/or negative. 7. It was concluded that in vivo baroreceptors signal mainly pressure level (systolic, diastolic or mean) as opposed to pulse pressure or dP/dt, and that the average discharge rate is their best index of information content.
Full text
PDF















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
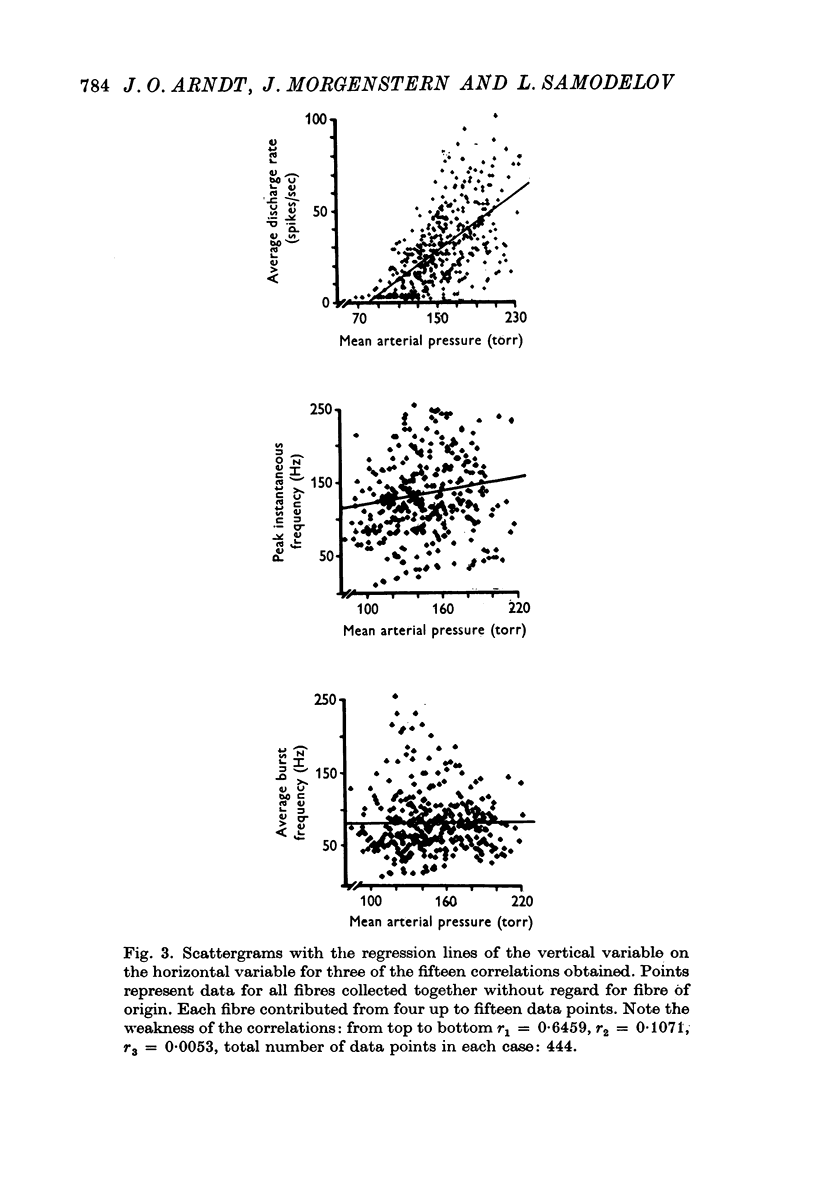
- Angell James J. E. The effects of altering mean pressure, pulse pressure and pulse frequency on the impulse activity in baroreceptor fibres from the aortic arch and right subclavian artery in the rabbit. J Physiol. 1971 Apr;214(1):65–88. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arndt J. O., Dörrenhaus A., Wiecken H. The aortic arch baroreceptor response to static and dynamic stretches in an isolated aorta-depressor nerve preparation of cats in vitro. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;252(1):59–78. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BISCOE T. J., MILLAR R. A. THE EFFECT OF HALOTHANE ON CAROTID SINUS BARORECEPTOR ACTIVITY. J Physiol. 1964 Sep;173:24–37. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOOR C. M. AORTIC BARORECEPTOR THRESHOLD AND SENSITIVITY IN RABBITS AT DIFFERENT AGES. J Physiol. 1964 Nov;174:163–171. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS W. W., RITCHIE J. M., SCHAUMANN W. A study of the effect of the pattern of electrical stimulation of the aortic nerve on the reflex depressor responses. J Physiol. 1956 Jul 27;133(1):232–242. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franz G. N., Scher A. M., Ito C. S. Small signal characteristics of carotid sinus baroreceptors of rabbits. J Appl Physiol. 1971 Apr;30(4):527–535. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1971.30.4.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta P. D., Henry J. P., Sinclair R., Von Baumgarten R. Responses of atrial and aortic baroreceptors to nonhypotensive hemorrhage and to tranfusion. Am J Physiol. 1966 Dec;211(6):1429–1437. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.6.1429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenau W., Pietsch D., Arndt J. O. Der Effekt von Halothan und Enflurane sowie von Propanidid und Ketamin auf die Aktivität der Barorezeptoren des Aortenbogens decerebrierter Katzen. Anaesthesist. 1976 Jul;25(7):331–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James J. E., Daly M. de B. Comparison of the reflex vasomotor responses to separate and combined stimulation of the carotid sinus and aortic arch baroreceptors by pulsatile and non-pulsatile pressures in the dog. J Physiol. 1970 Aug;209(2):257–293. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katona P. G., Poitras J. W., Pantelakis N., Jensen E. W., Barnett G. O. Deterministic nature of baroreceptor firing. Am J Physiol. 1968 Jul;215(1):1–7. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenner T., Baertschi A. J., Allison J. L., Ono K. Amplitude dependence of the carotid sinus reflex. Pflugers Arch. 1974 Jan 16;346(1):49–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00592650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koushanpour E., McGee J. P. Effect of mean pressure on carotid sinus baroceptor response to pulsatile pressure. Am J Physiol. 1969 Mar;216(3):599–603. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.3.599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDGREN S. On the excitation mechanism of the carotid baroceptors. Acta Physiol Scand. 1952 Jul 17;26(1):1–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1952.tb00889.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langrehr D. Zur Bedeutung der "paradoxen" Entladung und verwandter Phänomene arterieller Mechanoreceptoren für den Kreislaufschock. Klin Wochenschr. 1967 Jun 15;45(12):638–643. doi: 10.1007/BF01745638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKean T. A., Poppele R. E., Rosenthal N. P., Terzuolo C. A. The biologically relevant parameter in nerve impulse trains. Kybernetik. 1970 Jan;6(5):168–170. doi: 10.1007/BF00273961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAINTAL A. S. A study of right and left atrial receptors. J Physiol. 1953 Jun 29;120(4):596–610. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTSON J. D., SWAN A. A., WHITTERIDGE D. Effect of anaesthetics on systemic baroreceptors. J Physiol. 1956 Feb 28;131(2):463–472. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHER A. M., YOUNG A. C. Servoanalysis of carotid sinus reflex effects on peripheral resistance. Circ Res. 1963 Feb;12:152–162. doi: 10.1161/01.res.12.2.152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAMPFLI R. Bau und Funktion isolierter markhaltiger Nervenfasern. Ergeb Physiol. 1952;47:70–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stegemann J., Tibes U. Sinusoidal stimulation of carotid sinus baroreceptors and peripheral blood pressure in dogs. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Apr 21;156(2):787–795. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb14014.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


