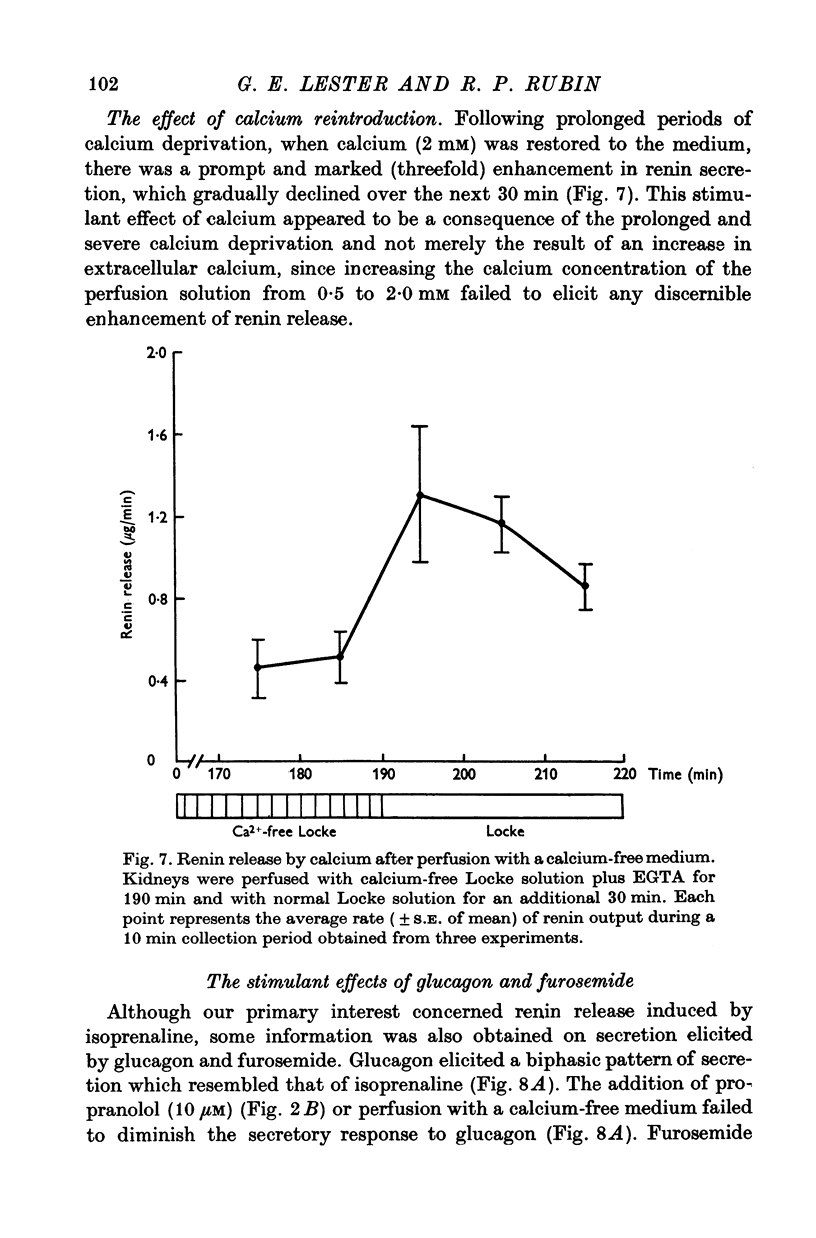
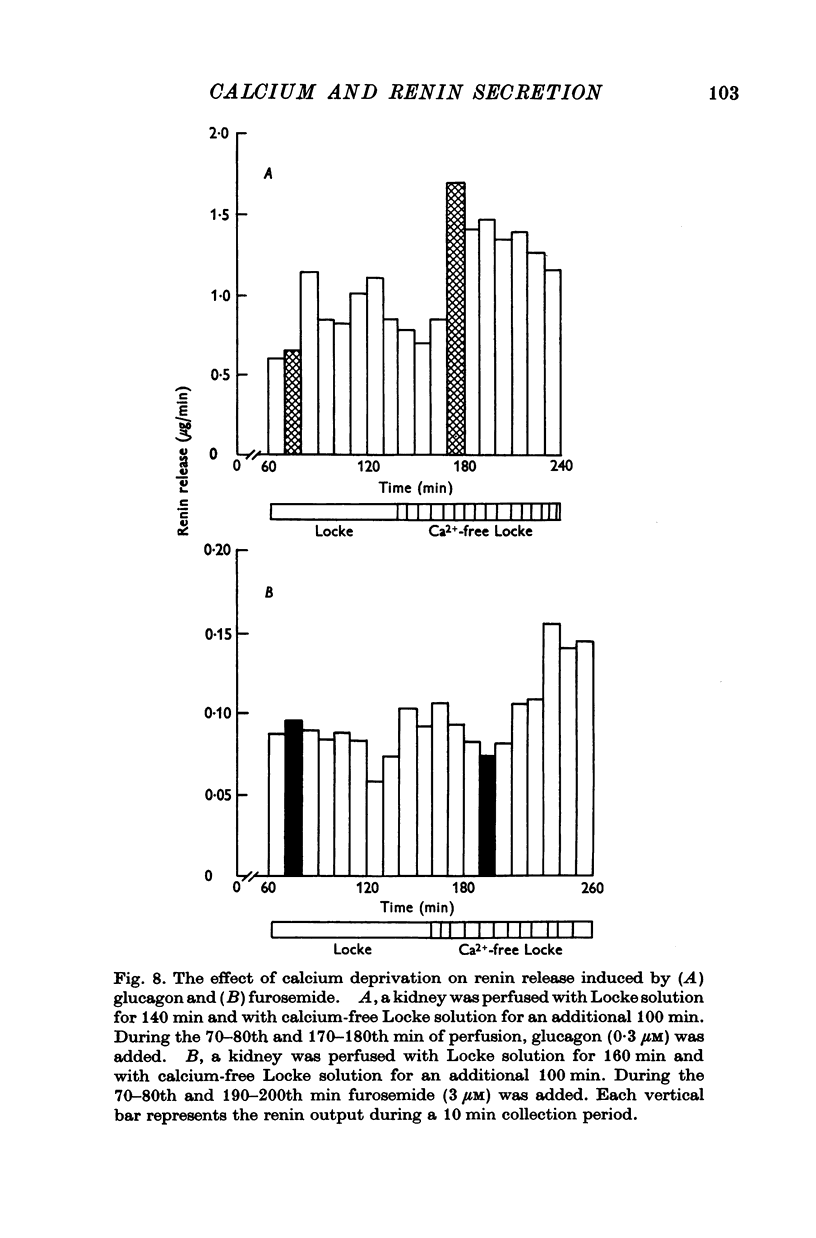
Abstract
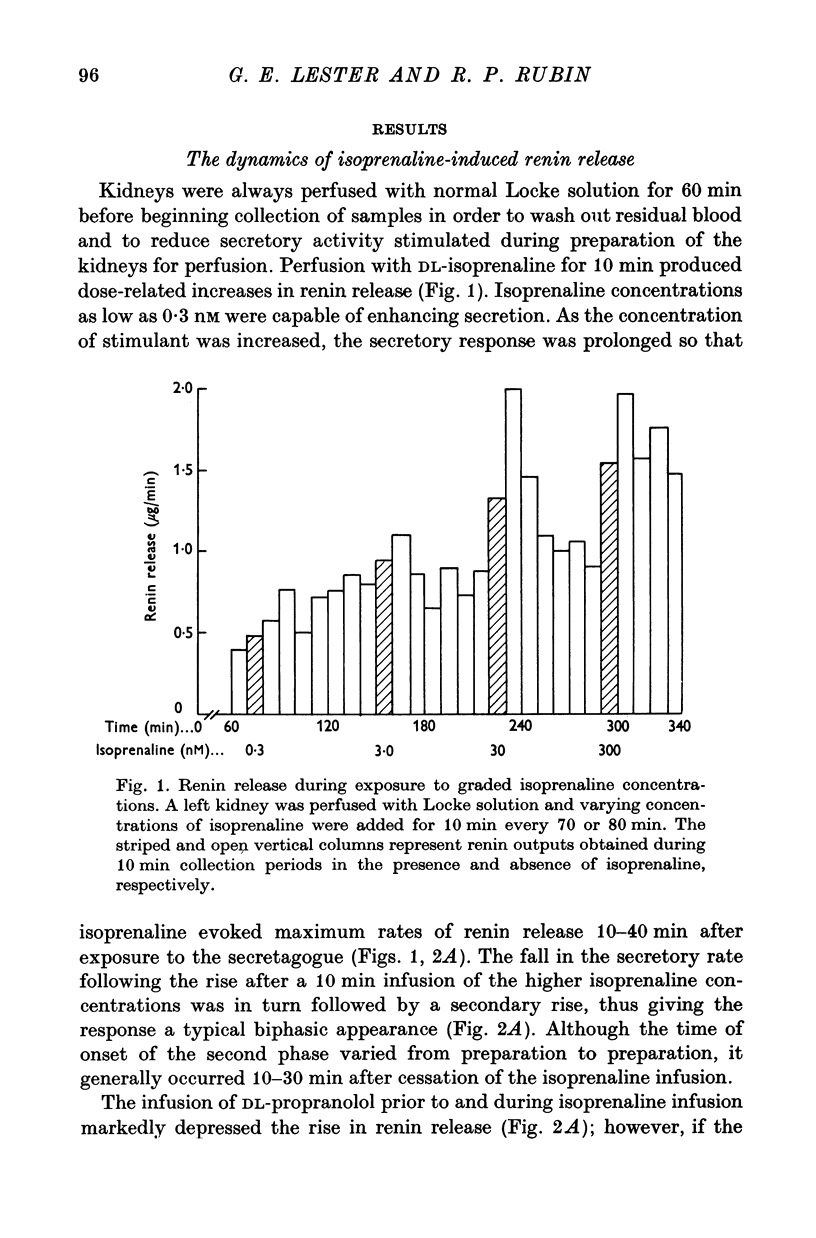
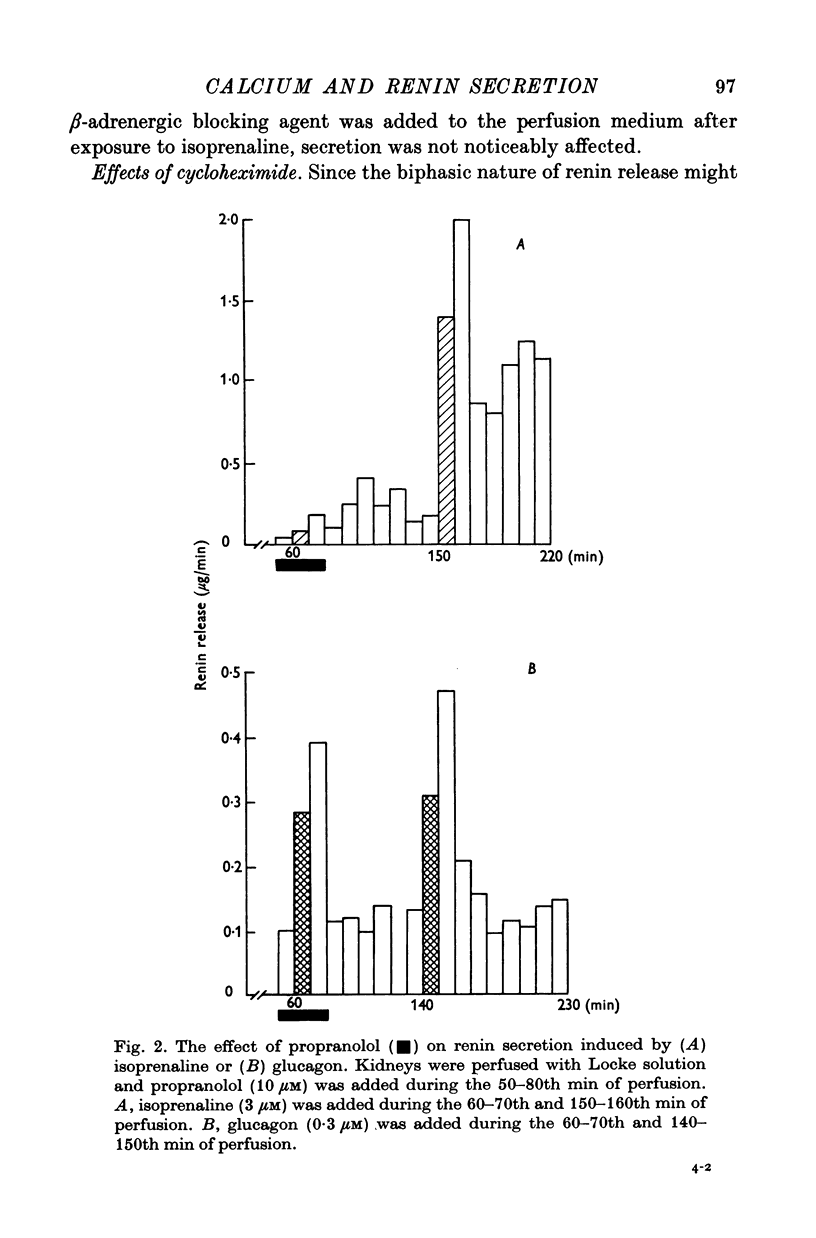
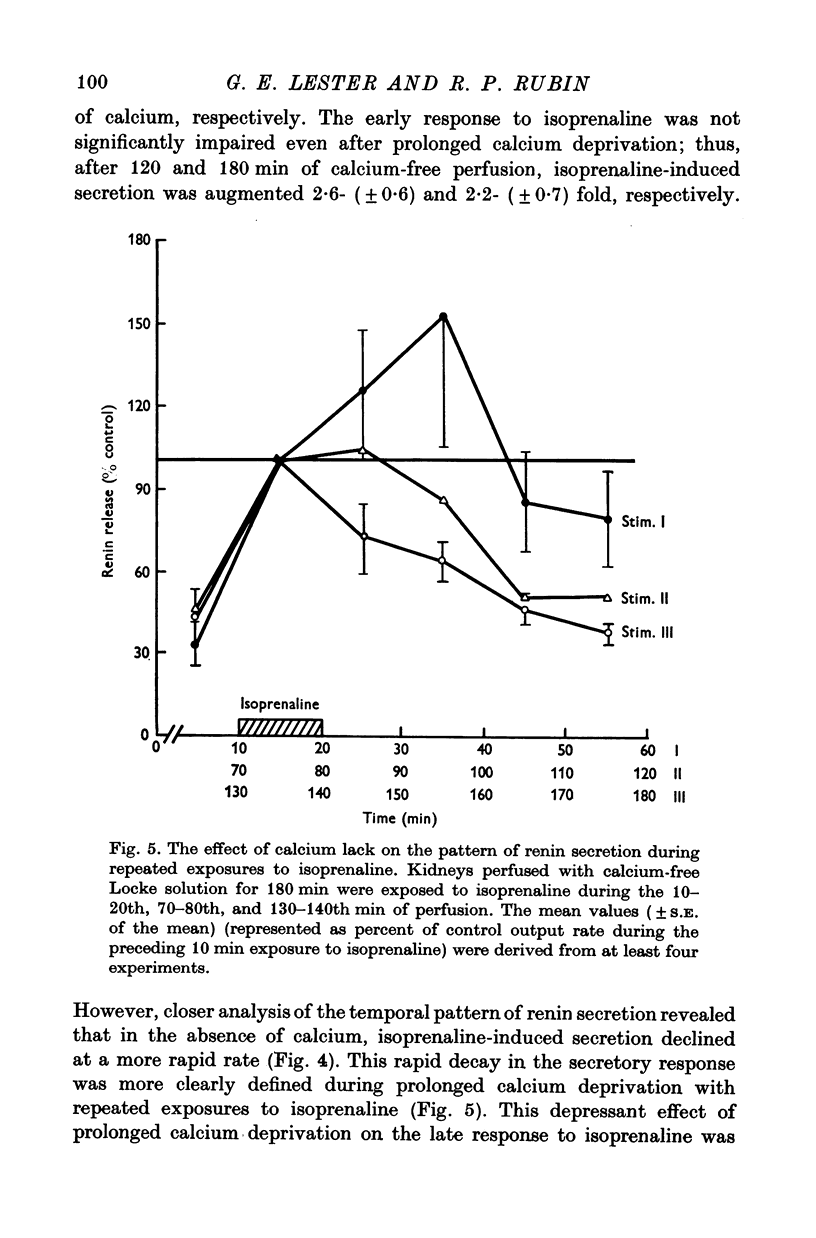
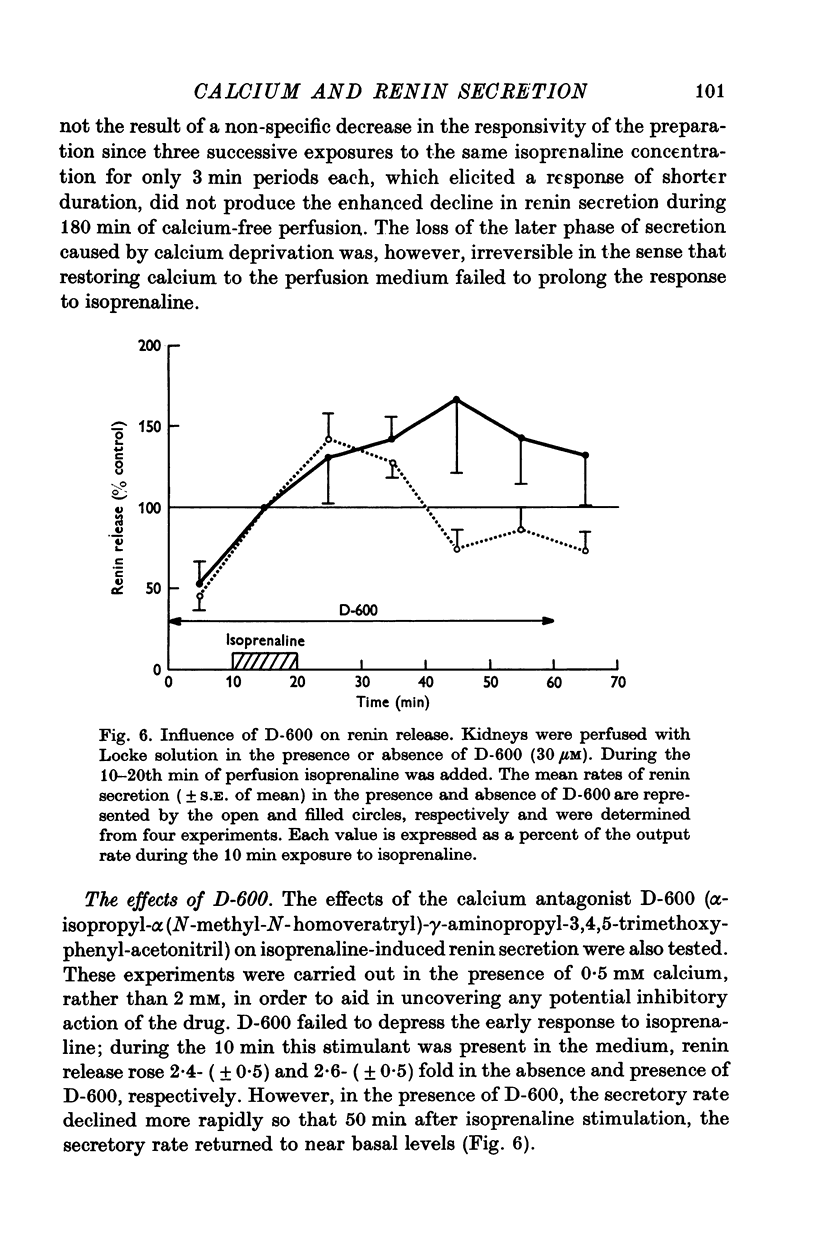
1. Isolated cat kidneys were perfused in situ with Locke solution and renin release in response to isoprenaline was studied. 2. Perfusion with isoprenaline produced a concentration-dependent enhancement of renin secretion. Increasing the concentration of stimulant also prolonged the duration of the secretory response. 3. After a 10 min exposure to isoprenaline (0-3 micrometer), there was a rapid facilitation of renin release which diminished after 10-30 min, followed by a second transient increase which declined over the next 40-60 min. Cycloheximide did not prevent augmented release when added together with the isoprenaline but did produce a reversible inhibition of the late phase when added 10 min after the isoprenaline. 4. Omission of calcium from the perfusion medium failed to depress the renin release induced by isoprenaline, glucagon, or furosemide. However, during prolonged calcium deprivation, the cycloheximide-sensitive phase of isoprenaline-evoked release was depressed. 5. The calcium antagonist D-600 failed to block the early phase of isoprenaline-induced renin secretion but inhibited the late phase of secretion. 6. Calcium alone elicited an explosive discharge of renin when added after a prolonged period of calcium-free perfusion. 7. These results support the view that extracellular calcium does not play an essential role in the mechanism of renin secretion from the renal juxtaglomerular cells, but that an increased influx of this cation is needed for synthesis and/or mobilization of the enzyme. It is tentatively proposed that the release of calcium from intracellular storage sites may be the signal which triggers renin secretion.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barajas L. The development and ultrastructure of the juxtaglomerular cell granule. J Ultrastruct Res. 1966 Jun;15(3):400–413. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(66)80116-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell B. V., Burstein S., Brock W. A., Speroff L. Radioimmunoassay of the F prostaglandins. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Aug;33(2):171–175. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-2-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen D. S., Poisner A. M. Direct stimulation of renin release by calcium. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1976 Sep;152(4):565–567. doi: 10.3181/00379727-152-39441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry D. L., Bennett L. L., Grodsky G. M. Dynamics of insulin secretion by the perfused rat pancreas. Endocrinology. 1968 Sep;83(3):572–584. doi: 10.1210/endo-83-3-572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry D. L. The effect of cycloheximide and 2-deoxyglucose on the diphasic pattern of insulin secretion. Acta Diabetol Lat. 1971 Jan-Feb;8(1):48–65. doi: 10.1007/BF01550857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS W. W., RUBIN R. P. The role of calcium in the secretory response of the adrenal medulla to acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1961 Nov;159:40–57. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. O., Freeman R. H. Mechanisms regulating renin release. Physiol Rev. 1976 Jan;56(1):1–56. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1976.56.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W., Rubin R. P. The mechanism of catecholamine release from the adrenal medulla and the role of calcium in stimulus-secretion coupling. J Physiol. 1963 Jul;167(2):288–310. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganong W. F. Biogenic amines, sympathetic nerves, and renin secretion. Fed Proc. 1973 Jul;32(7):1782–1784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodsky G. M. A threshold distribution hypothesis for packet storage of insulin. II. Effect of calcium. Diabetes. 1972;21(2 Suppl):584–593. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.2.s584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber E., Koerner T., Page L. B., Kliman B., Purnode A. Application of a radioimmunoassay for angiotensin I to the physiologic measurements of plasma renin activity in normal human subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Oct;29(10):1349–1355. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-10-1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwao H., Abe Y., Yamamoto K. Effect of intrarenal arterial infusion of calcium on renin release in dogs. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1974 Jun;24(3):482–484. doi: 10.1254/jjp.24.482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns E. J., Richards H. K., Singer B. Effects of adrenaline, noradrenaline, isoprenaline and salbutamol on the production and release of renin by isolated renal cortical cells of the cat. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Jan;53(1):67–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07331.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns E. J., Singer B. Effect of propranolol and theophylline on renin release caused by furosemide in the cat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1973 Jul;23(1):67–73. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(73)90245-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohlhardt M., Bauer B., Krause H., Fleckenstein A. Differentiation of the transmembrane Na and Ca channels in mammalian cardiac fibres by the use of specific inhibitors. Pflugers Arch. 1972;335(4):309–322. doi: 10.1007/BF00586221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotchen T. A., Mauli K. I., Luke R., Rees D., Flamenbaum W. Effect of acute and chronic calcium administration on plasma renin. J Clin Invest. 1974 Dec;54(6):1279–1286. doi: 10.1172/JCI107873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons H. J., Chruchhill P. C. Renin secretion from rat renal cortical cell suspensions. Am J Physiol. 1975 Jun;228(6):1835–1839. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.6.1835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelakis A. M., Caudle J., Liddle G. W. In vitro stimulation of renin production by epinephrine, norepinephrine, and cyclic AMP. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Mar;130(3):748–753. doi: 10.3181/00379727-130-33647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelakis A. M. The effect of sodium and calcium on renin release in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Jul;137(3):833–836. doi: 10.3181/00379727-137-35677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto S., Yamamoto K., Horiuchi K., Tanaka H., Ueda J. A release of renin from dog kidney cortex slices. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1970 Dec;20(4):536–545. doi: 10.1254/jjp.20.536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris B. J., Johnston C. I. Isolation of renin granules from rat kidney cortex and evidence for an inactive form of renin (prorenin) in granules and plasma. Endocrinology. 1976 Jun;98(6):1466–1474. doi: 10.1210/endo-98-6-1466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto J. E., Trifaró J. M. The different effects of D-600 (methoxyverapamil) on the release of adrenal catecholamines induced by acetylcholine, high potassium or sodium deprivation. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 May;57(1):127–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1976.tb07662.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. P. The role of calcium in the release of neurotransmitter substances and hormones. Pharmacol Rev. 1970 Sep;22(3):389–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. T., Thorn N. A. Calcium and stimulus-secretion coupling in the neurohypophysis. II. Effects of lanthanum, a verapamil analogue (D600) and prenylamine on 45-calcium transport and vasopressin release in isolated rat neurohypophyses. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1974 Jul;76(3):471–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sando H., Grodsky G. M. Dynamic synthesis and release of insulin and proinsulin from perifused islets. Diabetes. 1973 May;22(5):354–360. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.5.354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander A. J. Control of renin release. Physiol Rev. 1967 Jul;47(3):359–382. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1967.47.3.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander A. J. Direct effects of potassium on renin secretion and renal function. Am J Physiol. 1970 Aug;219(2):455–459. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.2.455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandongen R., Peart W. S., Boyd G. W. Andrenergic stimulation of renin secretion in the isolated perfused rat kidney. Circ Res. 1973 Feb;32(2):290–296. doi: 10.1161/01.res.32.2.290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winer N., Chokshi D. S., Walkenhorst W. G. Effects of cyclic AMP, sympathomimetic amines, and adrenergic receptor antagonists on renin secretion. Circ Res. 1971 Sep;29(3):239–248. doi: 10.1161/01.res.29.3.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


