Abstract
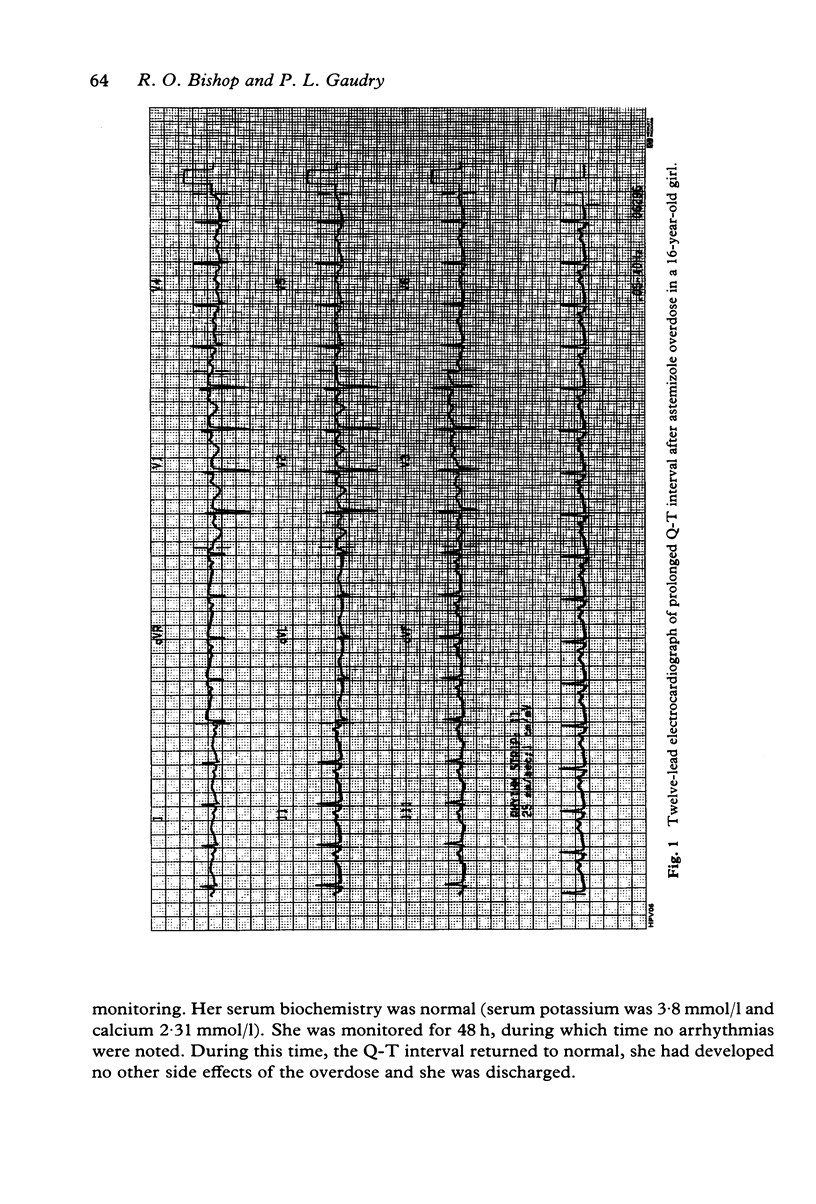
Astemizole overdose has been reported to cause torsades-de-pointes and in the present case it caused prolongation of the Q-T interval. Astemizole overdoses should be managed in a similar way to overdose with other cardiotoxic drugs.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Craft T. M. Torsade de pointes after astemizole overdose. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Mar 8;292(6521):660–660. doi: 10.1136/bmj.292.6521.660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craft T. M., Vanden Bussche G., De Cree J., Griffiths J. V. ECG studies with astemizole. Hum Toxicol. 1987 Nov;6(6):527–528. doi: 10.1177/096032718700600614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingswood J. C., Routledge P. A., Lazarus J. H. A report of overdose with astemizole. Hum Toxicol. 1986 Jan;5(1):43–44. doi: 10.1177/096032718600500108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratmann H. G., Kennedy H. L. Torsades de pointes associated with drugs and toxins: recognition and management. Am Heart J. 1987 Jun;113(6):1470–1482. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(87)90664-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


