Abstract
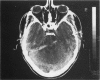
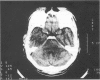
Because injury to the brain stem is usually associated with diffuse brain damage, recovery is rare and mortality high. A non-fatal penetrating injury involving the brain stem is described from a crossbow bolt. The diagnosis and management of such injuries are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crompton M. R. Brainstem lesions due to closed head injury. Lancet. 1971 Apr 3;1(7701):669–673. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92680-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jooma R., Bradshaw J. R., Coakham H. B. Computed tomography in penetrating cranial injury by a wooden foreign body. Surg Neurol. 1984 Mar;21(3):236–238. doi: 10.1016/0090-3019(84)90193-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. F., Brodkey J. S., Colombi B. J. The danger of intracranial wood. Surg Neurol. 1977 Feb;7(2):95–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shakir R. A., Khan R. A. Traumatic brain stem haematoma without prolonged loss of consciousness. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Feb 11;288(6415):446–447. doi: 10.1136/bmj.288.6415.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suddaby L., Weir B., Forsyth C. The management of .22 caliber gunshot wounds of the brain: a review of 49 cases. Can J Neurol Sci. 1987 Aug;14(3):268–272. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100026597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M. D., Siu K. An unusual cranial injury caused by an industrial nail-gun. Med J Aust. 1987 Dec 7;147(11-12):602–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]