Abstract
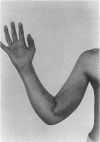
Five cases of adder bites are presented. The clinical effects and current recommendations for the treatment of adder bites are described based on a review of previously published literature. All adder bites, or snake bites of unknown species, should be observed for a minimum of 2 h. Those with no local swelling may be allowed home with appropriate antitetanus prophylaxis. Patients with local reaction or signs of systemic envenoming should be admitted for 48 h with ECG monitoring, and antivenom obtained. Indications and precautions for administration of antivenom are reviewed. Early antivenom treatment may reduce mortality and morbidity from adder bites.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cederholm I., Lennmarken C. Vipera berus bites in children--experience of early antivenom treatment. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1987 Jul;76(4):682–684. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1987.tb10547.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. S. Second-degree heart block associated with envenomation by Vipera berus. Arch Emerg Med. 1988 Jun;5(2):116–118. doi: 10.1136/emj.5.2.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Irestedt B. A study of 136 cases of adder bite treated in Swedish hospitals during one year. Acta Med Scand. 1981;210(6):433–439. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1981.tb09845.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid H. A. Adder bites in Britain. Br Med J. 1976 Jul 17;2(6028):153–156. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6028.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theakston R. D., Reid H. A. Effectiveness of Zagreb antivenom against envenoming by the adder, Vipera berus. Lancet. 1976 Jul 17;2(7977):121–123. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92846-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]