Abstract
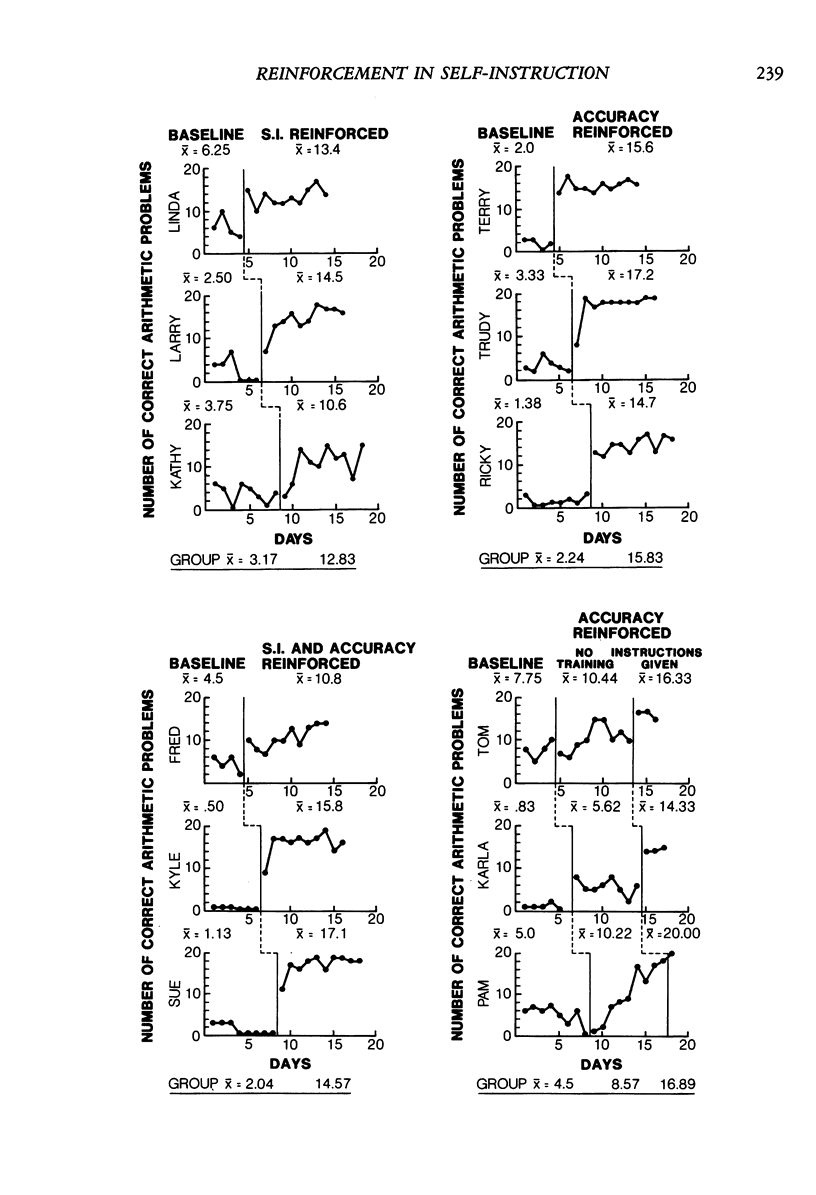
This study investigated the impact of training 9 first- and second-grade children to use a full self-instructional regimen, and then differentially reinforced the use of self-instruction only, accuracy only, or both self-instruction and accuracy. Three comparison children received no training in self-instruction and were reinforced for accuracy only. Children improved dramatically in academic accuracy subsequent to self-instructional training, independent of the use of self-instruction and of the specific behavior consequated. Children who were reinforced for using self-instruction did use self-instruction, and those who were not, did not. Comparison group children showed little improvement until training in problem-solving strategies was given after 9 days of reinforcement for accuracy. Self-instructional training is discussed as one type of event that increases the likelihood of accurate performance. Its effectiveness may be explained in terms of a teaching strategy rather than in terms of modifying cognitive processes.
Keywords: self-instruction, academic behavior, reinforcement
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bornstein P. H., Quevillon R. P. The effects of a self-instructional package on overactive preschool boys. J Appl Behav Anal. 1976 Summer;9(2):179–188. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1976.9-179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas V. I., Parry P., Marton P., Garson C. Assessment of a cognitive training program for hyperactive children. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 1976;4(4):389–410. doi: 10.1007/BF00922535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedling C., O'Leary S. G. Effects of self-instructional training on second- and third-grade hyperactive children: a failure to replicate. J Appl Behav Anal. 1979 Summer;12(2):211–219. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1979.12-211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall P. C., Braswell L. Cognitive-behavioral self-control therapy for children: a components analysis. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1982 Oct;50(5):672–689. doi: 10.1037//0022-006x.50.5.672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meichenbaum D. H., Goodman J. Training impulsive children to talk to themselves: a means of developing self-control. J Abnorm Psychol. 1971 Apr;77(2):115–126. doi: 10.1037/h0030773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahler R. G., Fox J. J. Setting events in applied behavior analysis: Toward a conceptual and methodological expansion. J Appl Behav Anal. 1981 Fall;14(3):327–338. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1981.14-327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


