Abstract
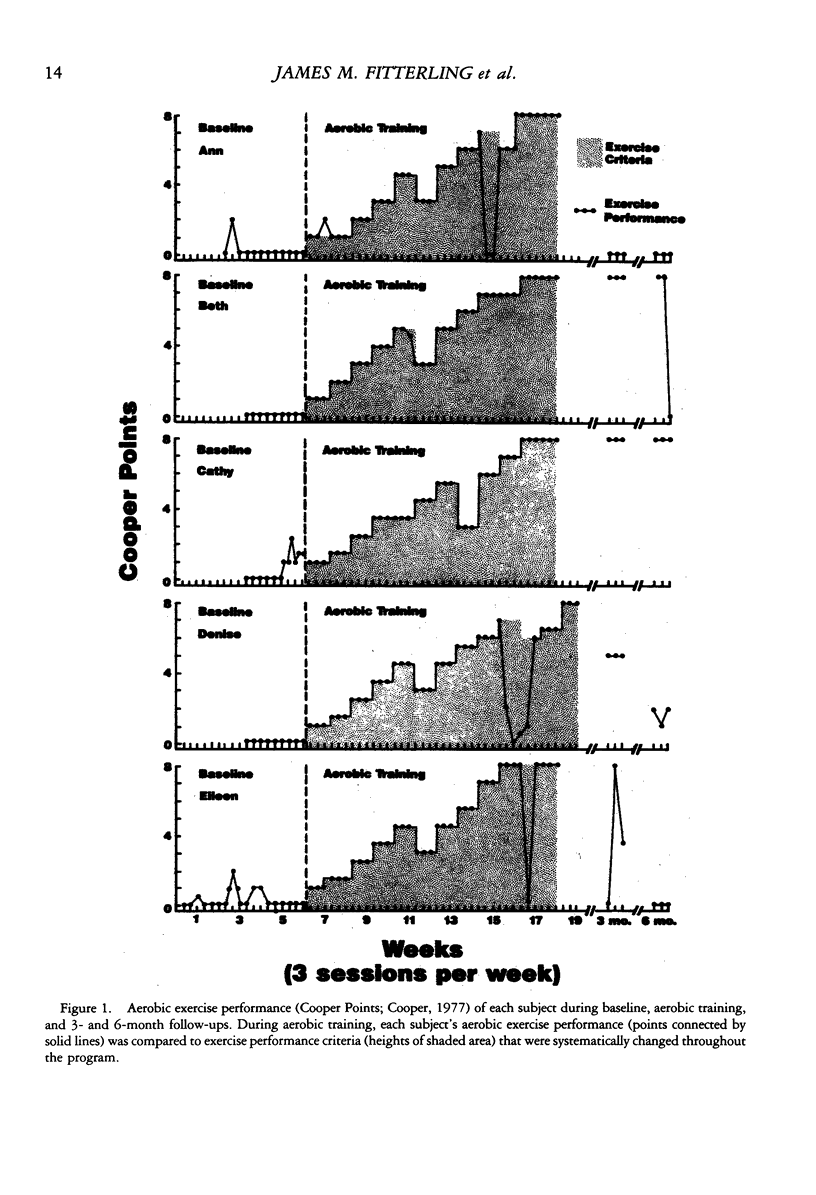
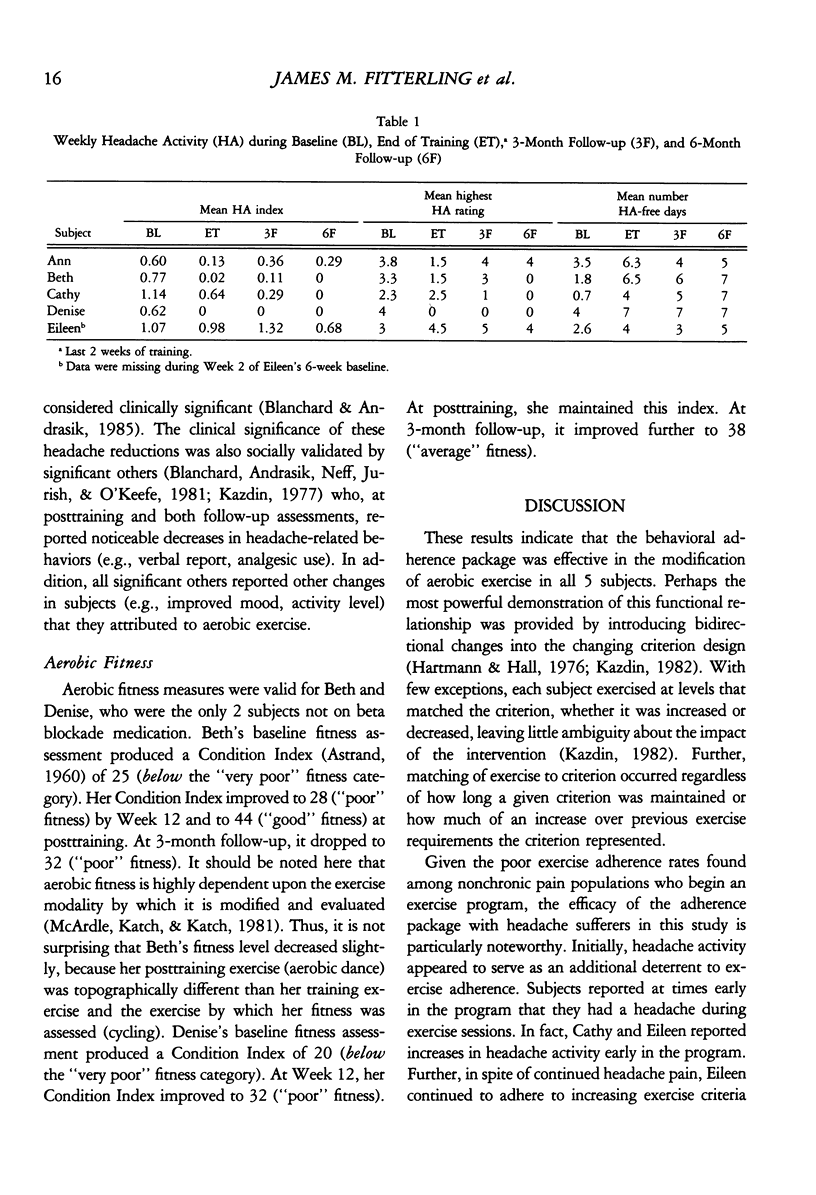
A behavioral package was used to shape and maintain the adherence of 5 subjects with vascular headache to a program of aerobic exercise training. Repeated measures of exercise behavior were examined through the use of a bidirectional changing criterion design. Repeated measures of headache activity were also collected. Results demonstrated a functional relationship between the behavioral package and exercise adherence, because all 5 subjects showed exercise behavior that matched bidirectional changing exercise criteria. The results also indicated clinically significant collateral reductions in vascular headache activity in 4 subjects. Subjects whose aerobic fitness levels were not masked by vasoactive medication also showed measurable increases in aerobic fitness. The results are discussed in terms of the methodology used to demonstrate a functional relationship between the adherence package and exercise behavior and the possible mechanism(s) by which aerobic exercise activity might affect vascular headache activity.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clausen J. P. Circulatory adjustments to dynamic exercise and effect of physical training in normal subjects and in patients with coronary artery disease. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1976 May-Jun;18(6):459–495. doi: 10.1016/0033-0620(76)90012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. H. The direct effects of compliance on health outcome. Health Psychol. 1984;3(4):385–393. doi: 10.1037//0278-6133.3.4.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. H., Wing R. R. Aerobic exercise and weight. Addict Behav. 1980;5(4):371–388. doi: 10.1016/0306-4603(80)90011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. P. Migraine. Med Clin North Am. 1978 May;62(3):481–494. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31787-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldwater B. C., Collis M. L. Psychologic effects of cardiovascular conditioning: a controlled experiment. Psychosom Med. 1985 Mar-Apr;47(2):174–181. doi: 10.1097/00006842-198503000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann D. P., Hall R. V. The changing criterion design. J Appl Behav Anal. 1976 WINTER;9(4):527–532. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1976.9-527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. E., Dubbert P. M. Adherence to exercise. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 1985;13:137–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. E., Dubbert P. M. Exercise applications and promotion in behavioral medicine: current status and future directions. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1982 Dec;50(6):1004–1017. doi: 10.1037//0022-006x.50.6.1004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. E., Dubbert P. M., Katell A. D., Thompson J. K., Raczynski J. R., Lake M., Smith P. O., Webster J. S., Sikora T., Cohen R. E. Behavioral control of exercise in sedentary adults: studies 1 through 6. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1984 Oct;52(5):795–811. doi: 10.1037//0022-006x.52.5.795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz M. A. The neurobiology of vascular head pain. Ann Neurol. 1984 Aug;16(2):157–168. doi: 10.1002/ana.410160202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saper J. R., Jones J. M. Ergotamine tartrate dependency: features and possible mechanisms. Clin Neuropharmacol. 1986;9(3):244–256. doi: 10.1097/00002826-198606000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinyor D., Schwartz S. G., Peronnet F., Brisson G., Seraganian P. Aerobic fitness level and reactivity to psychosocial stress: physiological, biochemical, and subjective measures. Psychosom Med. 1983 Jun;45(3):205–217. doi: 10.1097/00006842-198306000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysocki T., Hall G., Iwata B., Riordan M. Behavioral management of exercise: contracting for aerobic points. J Appl Behav Anal. 1979 Spring;12(1):55–64. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1979.12-55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


