Abstract
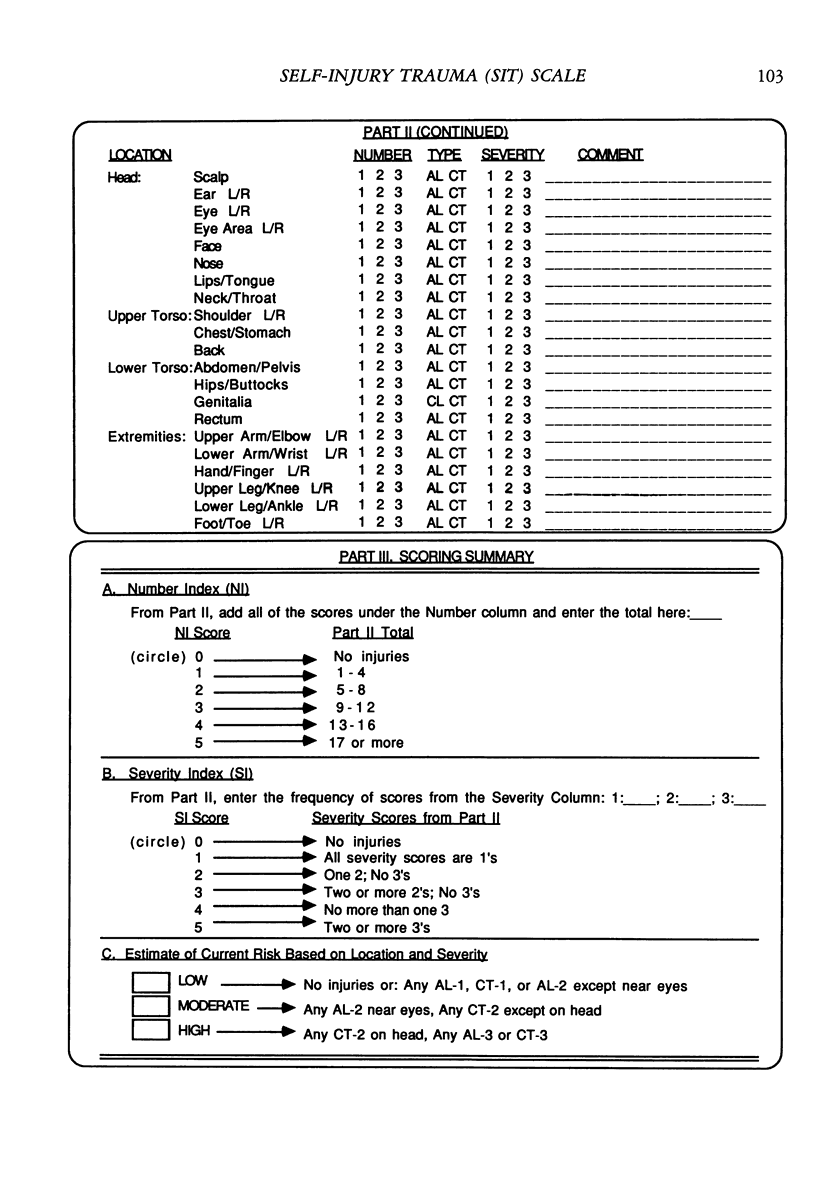
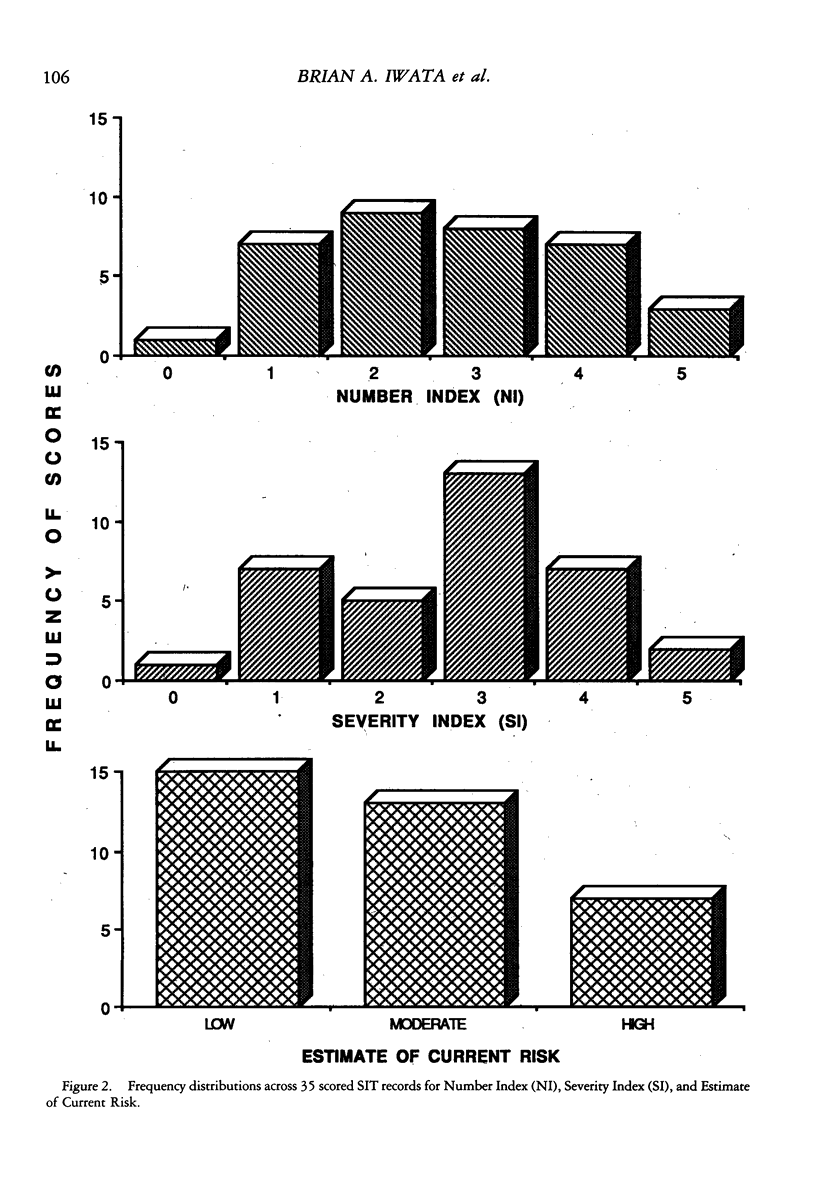
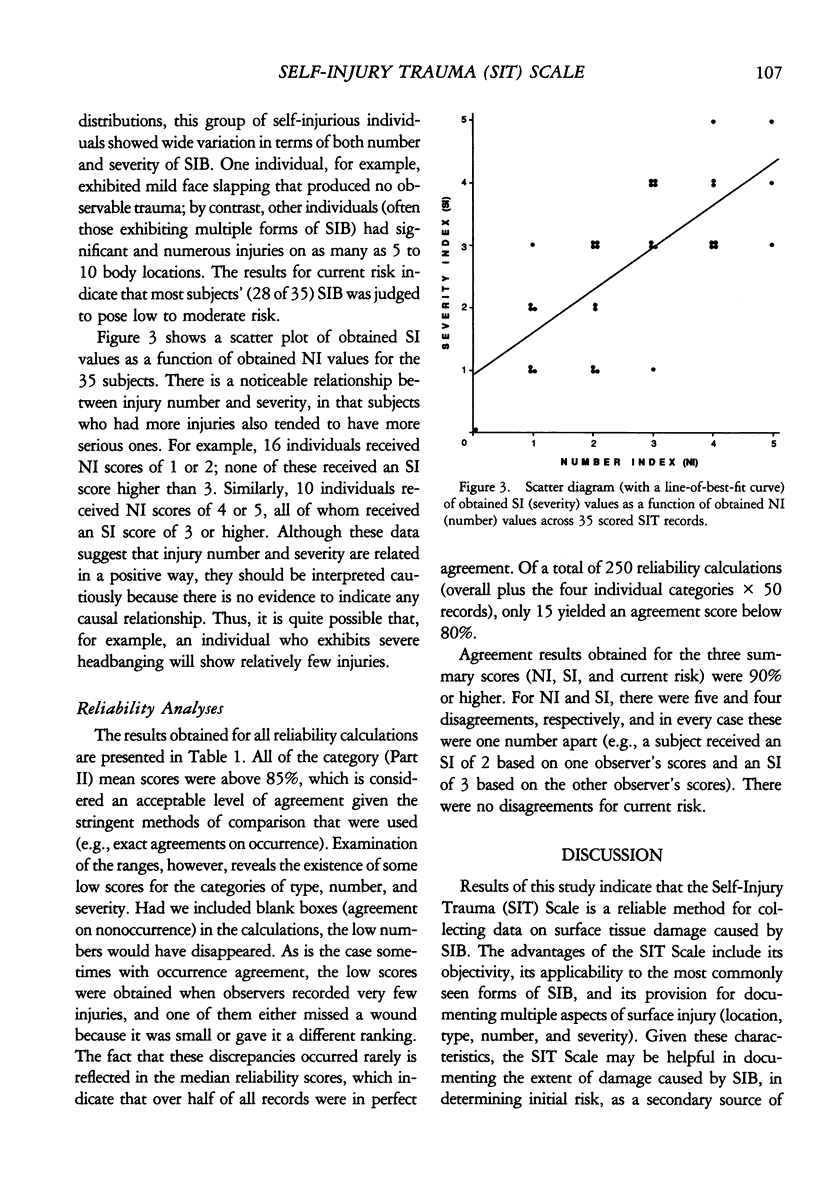
A method is described for classifying and quantifying surface tissue damage caused by self-injurious behavior. The Self-Injury Trauma Scale permits differentiation of self-injurious behavior according to topography, location of the injury on the body, type of injury, number of injuries, and estimate of severity. Fifty pairs of independently scored records were subjected to interrater reliability analyses, and the following mean (median) percentage agreement scores were obtained: overall agreement, 97% (98%); location of injury, 99% (100%); type of injury, 96% (100%); number of injuries, 89% (100%); and severity of injury, 94% (100%). Percentage agreement also was calculated for three summary scores: Number Index, 90%; Severity Index, 92%; and Estimate of Current Risk, 100%. Potential applications and limitations of the scale are discussed.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker S. P., O'Neill B., Haddon W., Jr, Long W. B. The injury severity score: a method for describing patients with multiple injuries and evaluating emergency care. J Trauma. 1974 Mar;14(3):187–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barancik J. I., Chatterjee B. F. Methodological considerations in the use of the abbreviated injury scale in trauma epidemiology. J Trauma. 1981 Aug;21(8):627–631. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198108000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champion H. R., Sacco W. J., Lepper R. L., Atzinger E. M., Copes W. S., Prall R. H. An anatomic index of injury severity. J Trauma. 1980 Mar;20(3):197–202. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198003000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan L., McLellan B. A., Greig H. Abbreviated Injury Scale and Injury Severity Score: a scoring chart. J Trauma. 1985 Jan;25(1):60–64. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198501000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer T., Matlak M. E., Johnson D. G., Walker M. L. The modified injury severity scale in pediatric multiple trauma patients. J Pediatr Surg. 1980 Dec;15(6):719–726. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(80)80271-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milholland A. V., Cowley R. A. Anatomical injury code. Am Surg. 1979 Feb;45(2):93–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repp A. C., Deitz D. E., Boles S. M., Deitz S. M., Repp C. F. Differences among common methods for calculating interobserver agreement. J Appl Behav Anal. 1976 Spring;9(1):109–113. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1976.9-109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Lawrence J. S., Drabman R. S. Interruption of self-excoriation in a pediatric burn victim. J Pediatr Psychol. 1983 Jun;8(2):155–159. doi: 10.1093/jpepsy/8.2.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate B. G., Baroff G. S. Aversive control of self-injurious behavior in a psychotic boy. Behav Res Ther. 1966 Nov;4(4):281–287. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(66)90024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf M. M. Social validity: the case for subjective measurement or how applied behavior analysis is finding its heart. J Appl Behav Anal. 1978 Summer;11(2):203–214. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1978.11-203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


