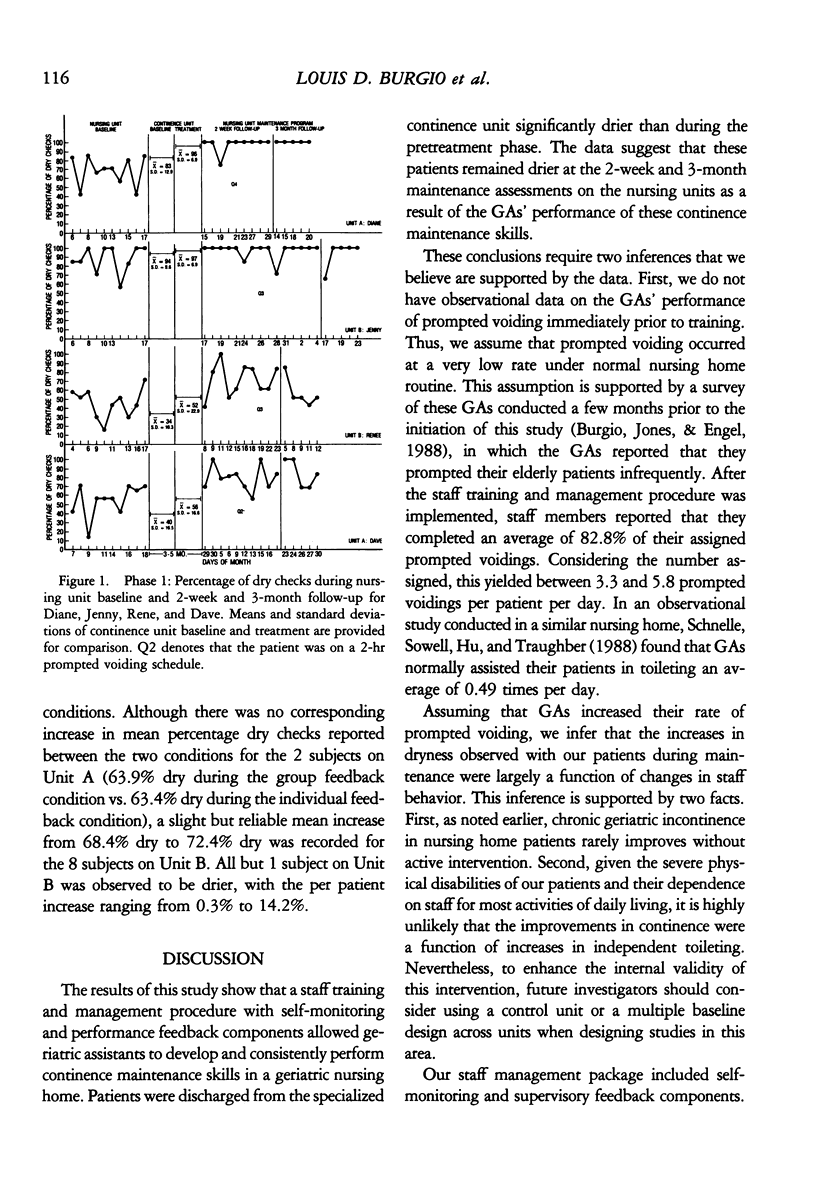
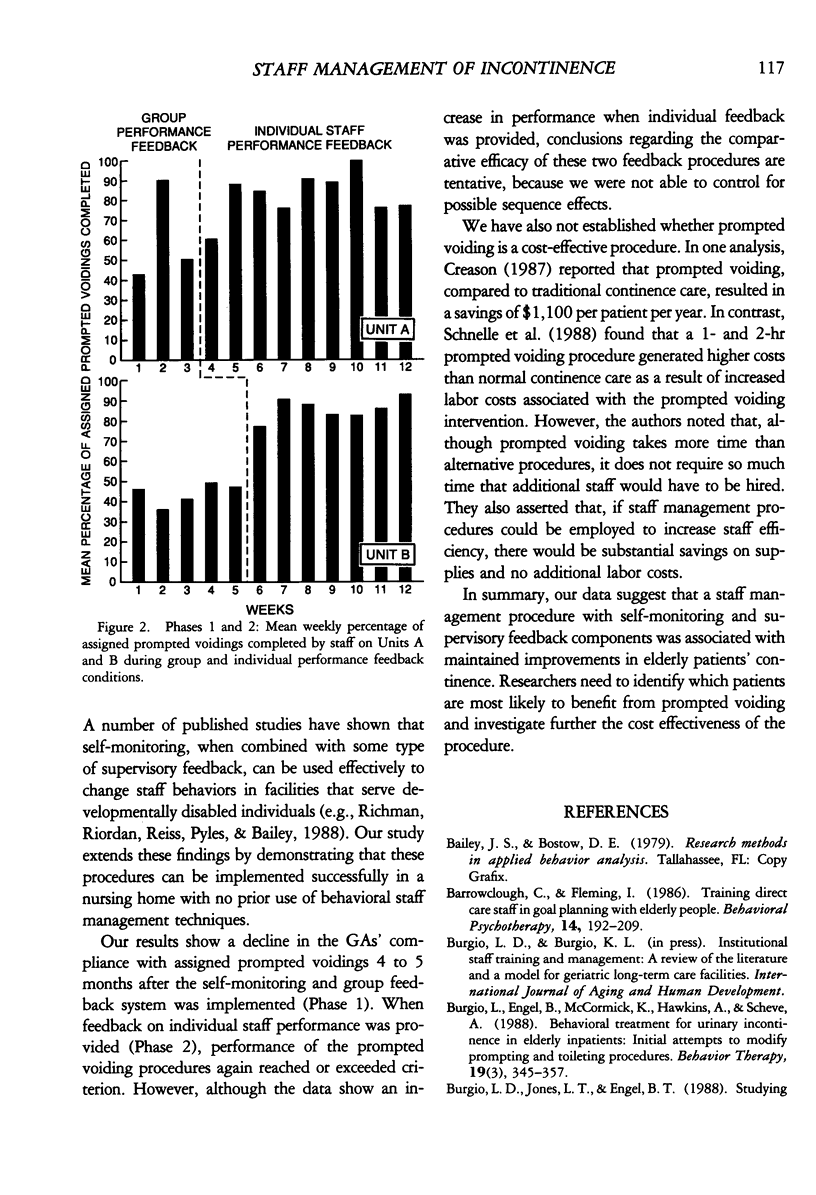
Abstract
We developed a staff management system for maintaining treatment gains achieved on a specialized continence unit located in a geriatric nursing home. Geriatric assistants learned to use a prompted voiding procedure to maintain improved dryness for 4 elderly residents. The staff management system included self-monitoring and recording of prompted voiding activities and supervisory monitoring and feedback based on group performance of these activities. Results show that the system was effective in maintaining prompted voiding activities with corresponding maintenance of improved patient continence. However, a gradual decline in staff performance was noted 4 to 5 months after the initiation of the system. During a subsequent phase of the study, provision of individual feedback restored staff performance to previous levels. Results are discussed in relation to the practicality of prompted voiding interventions in nursing home environments and the applicability of staff management systems in this setting.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burgio L. D., Jones L. T., Engel B. T. Studying incontinence in an urban nursing home. J Gerontol Nurs. 1988 Apr;14(4):40–45. doi: 10.3928/0098-9134-19880401-10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creason N. S. Costing urinary incontinence in nursing homes. Contemp Longterm Care. 1987 Jun;10(6):84–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folstein M. F., Folstein S. E., McHugh P. R. "Mini-mental state". A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975 Nov;12(3):189–198. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(75)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishara B. L., Kastenbaum R. Wine in the treatment of long-term geriatric patients in mental institutions. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1974 Feb;22(2):88–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1974.tb06276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigl A. J., Jackson B. A behavior management program to increase social responses in psychogeriatric patients. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1981 Feb;29(2):92–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1981.tb01236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouslander J. G., Kane R. L. The costs of urinary incontinence in nursing homes. Med Care. 1984 Jan;22(1):69–79. doi: 10.1097/00005650-198401000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman G. S., Riordan M. R., Reiss M. L., Pyles D. A., Bailey J. S. The effects of self-monitoring and supervisor feedback on staff performance in a residential setting. J Appl Behav Anal. 1988 Winter;21(4):401–409. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1988.21-401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnelle J. F., Sowell V. A., Hu T. W., Traughber B. Reduction of urinary incontinence in nursing homes: does it reduce or increase costs? J Am Geriatr Soc. 1988 Jan;36(1):34–39. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1988.tb03431.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnelle J. F., Traughber B., Morgan D. B., Embry J. E., Binion A. F., Coleman A. Management of geriatric incontinence in nursing homes. J Appl Behav Anal. 1983 Summer;16(2):235–241. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1983.16-235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperbeck D. J., Whitbourne S. K. Dependency in the institutional setting: a behavioral training program for geriatric staff. Gerontologist. 1981 Jun;21(3):268–275. doi: 10.1093/geront/21.3.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson P. N., Ascione F. R. Behavioral treatment of the elderly. Implications for theory and therapy. Behav Modif. 1983 Oct;7(4):583–610. doi: 10.1177/01454455830074008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


