Abstract
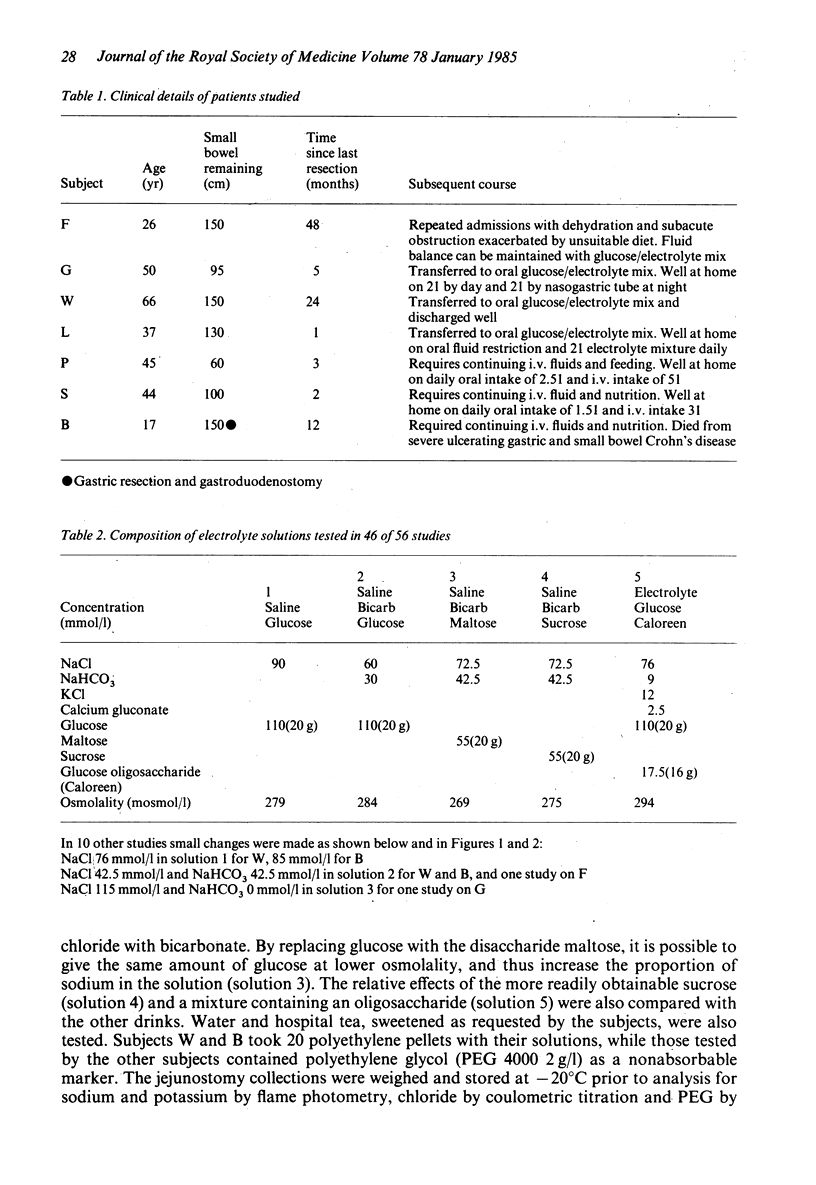
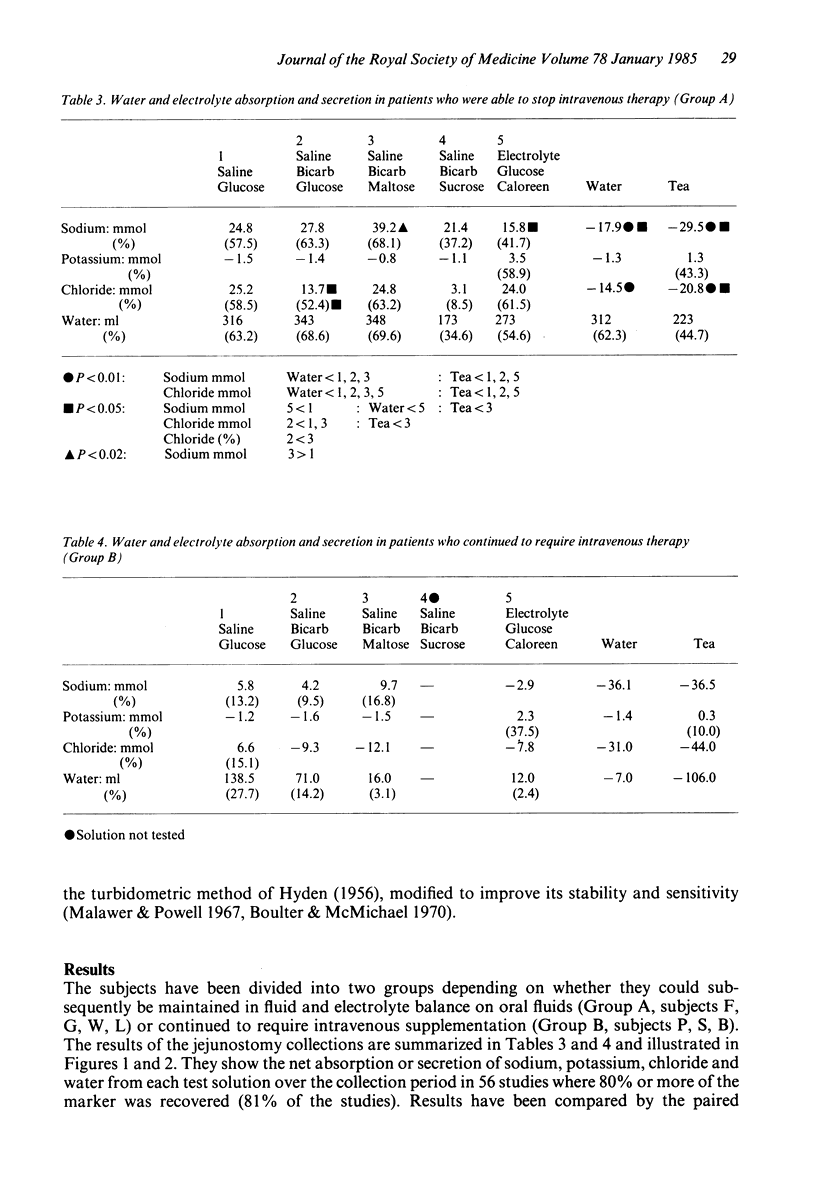
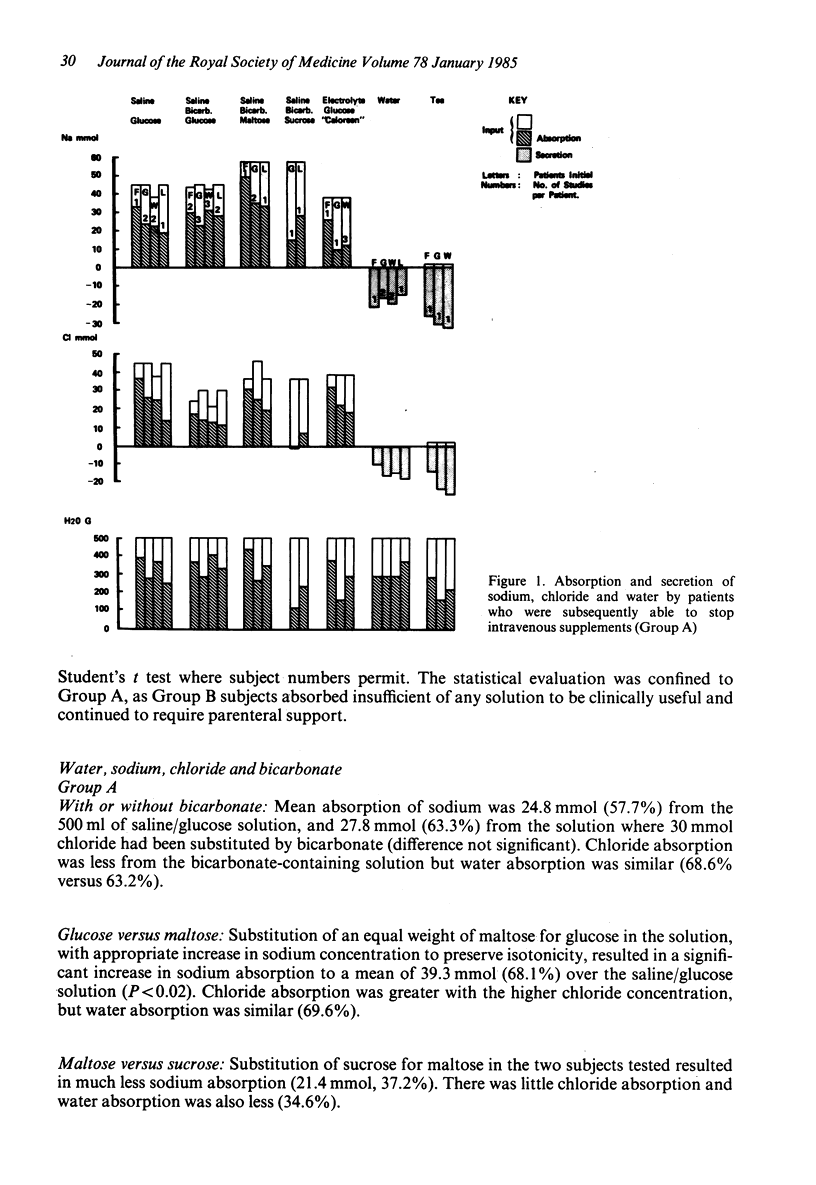
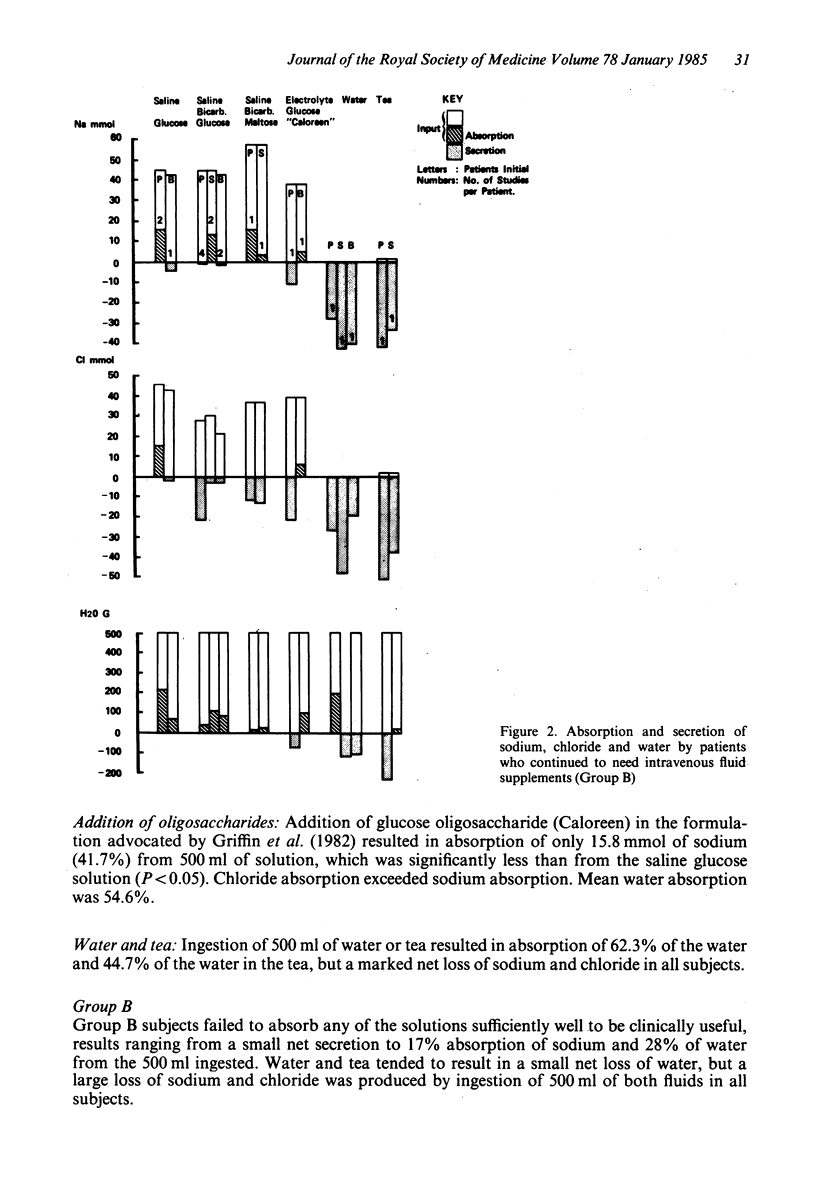
The effectiveness of 5 different solutions on the absorption of fluid and electrolytes was tested in 7 patients with a proximal intestinal stoma and large fluid losses, all of whom previously needed intravenous infusions to maintain balance. In 4 patients it proved possible to replace the intravenous infusions with an enteral supplement. The WHO glucose/electrolyte solution without added potassium (NaCl 3.5 g, NaHCO3 2.5 g, glucose 20 g/l) gave satisfactory results, though was slightly less effective than a solution containing more sodium in which maltose was substituted for glucose. Neither sucrose nor an oligosaccharide (Caloreen) gave an advantage over glucose in the formulations used. In 3 patients losses were so great, and absorption of sodium from oral solutions so small, that intravenous supplements had to be continued. These 3 patients could be distinguished from the other 4 by the fact that more than 250 ml emerged from the stoma during the 3 hours after a drink of 500 ml of glucose/electrolyte solution. In all patients a drink of water or tea led to a loss of sodium from the stoma; water should be restricted in such patients and replaced by a glucose/electrolyte solution.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boulter J. M., McMichael H. B. Modification of polyethylene glycol estimation suitable for use with small mammals. Gut. 1970 Mar;11(3):268–270. doi: 10.1136/gut.11.3.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogel M. R., Gray G. M. Starch hydrolysis in man: an intraluminal process not requiring membrane digestion. J Appl Physiol. 1973 Aug;35(2):263–267. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1973.35.2.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S., Locklear T. W. Ionic constituents and osmolality of gastric and small-intestinal fluids after eating. Am J Dig Dis. 1966 Jul;11(7):503–521. doi: 10.1007/BF02233563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S., Rector F. C., Jr, Carter N. W. The mechanisms of sodium absorption in the human small intestine. J Clin Invest. 1968 Apr;47(4):884–900. doi: 10.1172/JCI105781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S. Stimulation of active and passive sodium absorption by sugars in the human jejunum. J Clin Invest. 1975 Apr;55(4):728–737. doi: 10.1172/JCI107983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin G. E., Fagan E. F., Hodgson H. J., Chadwick V. S. Enteral therapy in the management of massive gut resection complicated by chronic fluid and electrolyte depletion. Dig Dis Sci. 1982 Oct;27(10):902–908. doi: 10.1007/BF01316574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn N., Kinzie J. L., Sachar D. B., Northrup R. S., Taylor J. O., Ahmad S. Z., Phillips R. A. Decrease in net stool output in cholera during intestinal perfusion with glucose-containing solutions. N Engl J Med. 1968 Jul 25;279(4):176–181. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196807252790402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael H. B., Webb J., Dawson A. M. The absorption of maltose and lactose in man. Clin Sci. 1967 Aug;33(1):135–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moenginah P. A., Suprapto S. J., Bachtin M., Sutrisno D., Sutaryo Rohde J. E. Letter: Oral sucrose therapy for diarroea. Lancet. 1975 Aug 16;2(7929):323–323. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92756-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molla A. M., Sarker S. A., Hossain M., Molla A., Greenough W. B., 3rd Rice-powder electrolyte solution as oral-therapy in diarrhoea due to Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Lancet. 1982 Jun 12;1(8285):1317–1319. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92396-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalin D. R., Levine M. M., Mata L., de Cespedes C., Vargas W., Lizano C., Loria A. R., Simhon A., Mohs E. Comparison of sucrose with glucose in oral therapy of infant diarrhoea. Lancet. 1978 Aug 5;2(8084):277–279. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)91686-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer D. L., Koster F. T., Islam A. F., Rahman A. S., Sack R. B. Comparison of sucrose and glucose in the oral electrolyte therapy of cholera and other severe diarrheas. N Engl J Med. 1977 Nov 17;297(20):1107–1110. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197711172972007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips S. F., Summerskill W. H. Water and electrolyte transport during maintenance of isotonicity in human jejunum and ileum. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Oct;70(4):686–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Banwell J. G., Rupak D. M., Mitra R. C., Caranasos G. J., Keimowitz R. I., Mondal A., Manji P. M. Effect of intragastric glucose-electrolyte infusion upon water and electrolyte balance in Asiatic cholera. Gastroenterology. 1968 Sep;55(3):333–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Sack R. B., Mitra R. C., Banwell J. G., Brigham K. L., Fedson D. S., Mondal A. Replacement of water and electrolyte losses in cholera by an oral glucose-electrolyte solution. Ann Intern Med. 1969 Jun;70(6):1173–1181. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-70-6-1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEDL H. P., CLIFTON J. A. SOLUTE AND WATER ABSORPTION BY THE HUMAN SMALL INTESTINE. Nature. 1963 Sep 28;199:1264–1267. doi: 10.1038/1991264a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladen G. E., Dawson A. M. Interrelationships between the absorptions of glucose, sodium and water by the normal human jejunum. Clin Sci. 1969 Feb;36(1):119–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnberg L. A., Bieberdorf F. A., Morawski S. G., Fordtran J. S. Interrelationships of chloride, bicarbonate, sodium, and hydrogen transport in the human ileum. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):557–567. doi: 10.1172/JCI106266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnberg L. A., Fordtran J. S., Carter N. W., Rector F. C., Jr Mechanism of bicarbonate absorption and its relationship to sodium transport in the human jejunum. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):548–556. doi: 10.1172/JCI106265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



