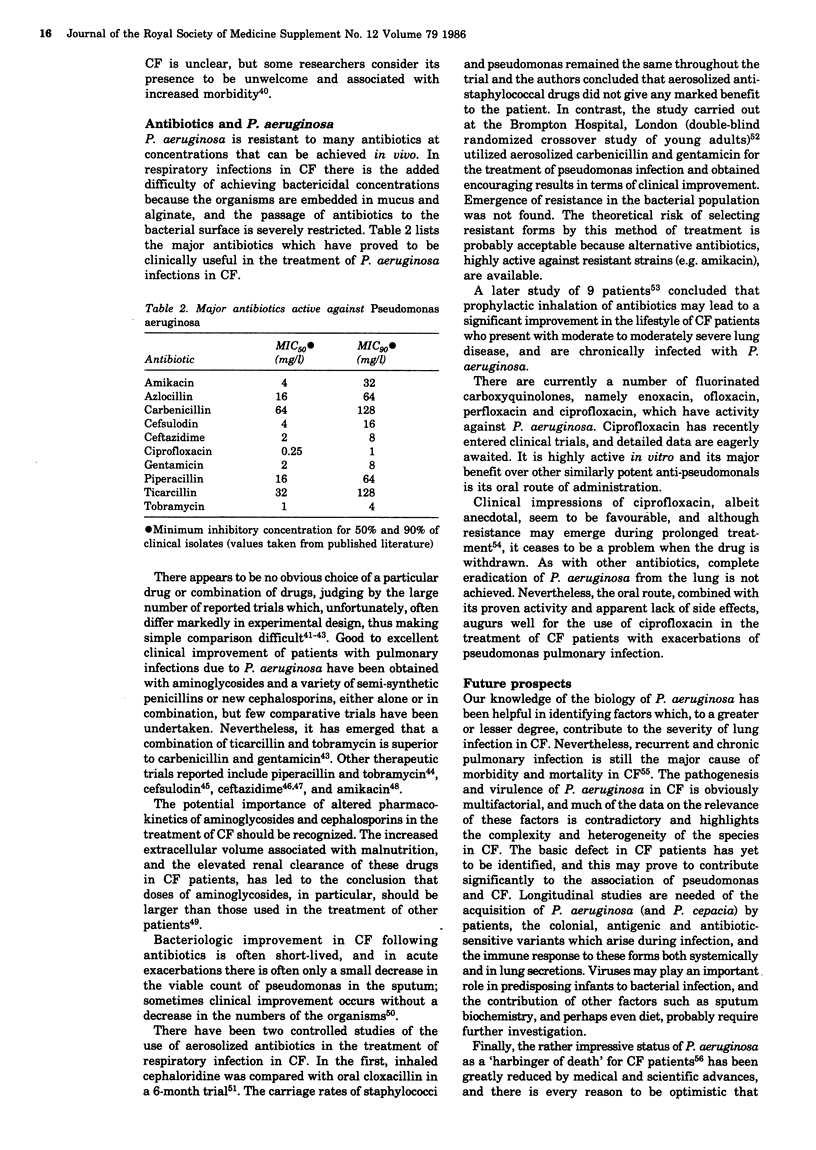
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaudry P. H., Marks M. I., McDougall D., Desmond K., Rangel R. Is anti-Pseudomonas therapy warranted in acute respiratory exacerbations in children with cystic fibrosis? J Pediatr. 1980 Jul;97(1):144–147. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80155-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berka R. M., Gray G. L., Vasil M. L. Studies of phospholipase C (heat-labile hemolysin) in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):1071–1074. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.1071-1074.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Pitt T. L., Fürer E., Germanier R. Role of lipopolysaccharide in virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):508–513. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.508-513.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fick R. B., Jr, Baltimore R. S., Squier S. U., Reynolds H. Y. IgG proteolytic activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis. J Infect Dis. 1985 Apr;151(4):589–598. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.4.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca K., MacDougall J., Pitt T. L. Inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from cystic fibrosis by selective media. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Feb;39(2):220–222. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.2.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govan J. R., Fyfe J. A., Baker N. R. Heterogeneity and reduction in pulmonary clearance of mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Nov-Dec;5 (Suppl 5):S874–S879. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_5.s874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govan J. R., Fyfe J. A. Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa and cystic fibrosis: resistance of the mucoid from to carbenicillin, flucloxacillin and tobramycin and the isolation of mucoid variants in vitro. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 May;4(3):233–240. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.3.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Mutharia L. M., Chan L., Darveau R. P., Speert D. P., Pier G. B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from patients with cystic fibrosis: a class of serum-sensitive, nontypable strains deficient in lipopolysaccharide O side chains. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):170–177. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.170-177.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodson M. E., Penketh A. R., Batten J. C. Aerosol carbenicillin and gentamicin treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in patients with cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 1981 Nov 21;2(8256):1137–1139. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90588-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoogkamp-Korstanje J. A., van der Laag J. Piperacillin and tobramycin in the treatment of Pseudomonas lung infections in cystic fibrosis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Aug;12(2):175–183. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.2.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvin R. T., Govan J. W., Fyfe J. A., Costerton J. W. Heterogeneity of antibiotic resistance in mucoid isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa obtained from cystic fibrosis patients: role of outer membrane proteins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jun;19(6):1056–1063. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.6.1056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isles A., Maclusky I., Corey M., Gold R., Prober C., Fleming P., Levison H. Pseudomonas cepacia infection in cystic fibrosis: an emerging problem. J Pediatr. 1984 Feb;104(2):206–210. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80993-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagger K. S., Bahner D. R., Warren R. L. Protease phenotypes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jan;17(1):55–59. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.1.55-59.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinger J. D., Straus D. C., Hilton C. B., Bass J. A. Antibodies to proteases and exotoxin A of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with cystic fibrosis: Demonstration by radioimmunoassay. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jul;138(1):49–48. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford D. T., Hiller J. Prospective, controlled study of a polyvalent pseudomonas vaccine in cystic fibrosis--three year results. Arch Dis Child. 1984 Dec;59(12):1131–1134. doi: 10.1136/adc.59.12.1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau W. K., Young L. S., Osher A. B., Dooley R. R. Amikacin therapy of exacerbations of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections in patients with cystic fibrosis. Pediatrics. 1977 Sep;60(3):372–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg U., Hanson L. A., Jodal U., Lidin-Janson G., Lincoln K., Olling S. Asymptomatic bacteriuria in schoolgirls. II. Differences in escherichia coli causing asymptomatic bacteriuria. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1975 May;64(3):432–436. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1975.tb03860.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORIHARA K. PRODUCTION OF ELASTASE AND PROTEINASE BY PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA. J Bacteriol. 1964 Sep;88:745–757. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.3.745-757.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin A. J., Smalley C. A., George R. H., Healing D. E., Anderson C. M. Gentamicin and tobramycin compared in the treatment of mucoid pseudomonas lung infections in cystic fibrosis. Arch Dis Child. 1980 Aug;55(8):604–607. doi: 10.1136/adc.55.8.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. R. Mucoid variation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa induced by the action of phage. J Med Microbiol. 1973 Feb;6(1):111–118. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-1-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCrae W. M., Raeburn J. A., Hanson E. J. Tobramycin therapy of infections due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with cystic fibrosis: effect of dosage and concentration of antibiotic in sputum. J Infect Dis. 1976 Aug;134 (Suppl):S191–S193. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.supplement_1.s191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. V., Rubero V. J. Mucoid conversion by phages of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 May;19(5):717–719. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.5.717-719.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Møller N. E., Koch C., Vesterhauge S., Jensen K. Treatment of pulmonary Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis with cefsulodin. Scand J Infect Dis. 1982;14(3):207–211. doi: 10.3109/inf.1982.14.issue-3.09. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan G., Moivor P., Levison H., Fleming P. C., Corey M., Gold R. Antibiotic prophylaxis in cystic fibrosis: inhaled cephaloridine as an adjunct to oral cloxacillin. J Pediatr. 1982 Oct;101(4):626–630. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80726-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry M. F., Neu H. C., Merlino M., Gaerlan P. F., Ores C. N., Denning C. R. Treatment of pulmonary infections in patients with cystic fibrosis: a comparative study of ticarcillin and gentamicin. J Pediatr. 1977 Jan;90(1):144–148. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80790-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penketh A. R., Pitt T. L., Hodson M. E., Batten J. C. Bactericidal activity of serum from cystic fibrosis patients for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Med Microbiol. 1983 Nov;16(4):401–408. doi: 10.1099/00222615-16-4-401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penketh A., Pitt T., Roberts D., Hodson M. E., Batten J. C. The relationship of phenotype changes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa to the clinical condition of patients with cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 May;127(5):605–608. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.5.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Permin H., Koch C., Høiby N., Christensen H. O., Møller A. F., Møller S. Ceftazidime treatment of chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa respiratory tract infection in cystic fibrosis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Jul;12 (Suppl A):313–323. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.suppl_a.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B., Matthews W. J., Jr, Eardley D. D. Immunochemical characterization of the mucoid exopolysaccharide of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1983 Mar;147(3):494–503. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.3.494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B. Pulmonary disease associated with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis: current status of the host-bacterium interaction. J Infect Dis. 1985 Apr;151(4):575–580. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.4.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt T. L. State of the art: typing Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Hosp Infect. 1980 Sep;1(3):193–199. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(80)90056-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt T. L., Todd H. C., Mackintosh C. A., Im S. W. Evaluation of three serological tests for detection of antibody to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in human sera. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;4(2):190–196. doi: 10.1007/BF02013596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M., Anderson S. E., Jr Toxicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A for human macrophages. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):1092–1096. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.1092-1096.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M. The role of exotoxin A in pseudomonas disease and immunity. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Nov-Dec;5 (Suppl 5):S979–S984. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_5.s979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scully B. E., Neu H. C. Clinical efficacy of ceftazidime. Treatment of serious infection due to multiresistant Pseudomonas and other gram-negative bacteria. Arch Intern Med. 1984 Jan;144(1):57–62. doi: 10.1001/archinte.144.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack M. P., Nichols W. W. The penetration of antibiotics through sodium alginate and through the exopolysaccharide of a mucoid strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Lancet. 1981 Sep 5;2(8245):502–503. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90885-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel J. D., Hashman N., Reinherz G., Merzbach D. Nosocomial Pseudomonas cepacia infection associated with chlorhexidine contamination. Am J Med. 1982 Aug;73(2):183–186. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90176-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suter S., Schaad U. B., Roux L., Nydegger U. E., Waldvogel F. A. Granulocyte neutral proteases and Pseudomonas elastase as possible causes of airway damage in patients with cystic fibrosis. J Infect Dis. 1984 Apr;149(4):523–531. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.4.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tejedor C., Foulds J., Zasloff M. Bacteriophages in sputum of patients with bronchopulmonary Pseudomonas infections. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):440–441. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.440-441.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomassen M. J., Demko C. A., Boxerbaum B., Stern R. C., Kuchenbrod P. J. Multiple of isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa with differing antimicrobial susceptibility patterns from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Infect Dis. 1979 Dec;140(6):873–880. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.6.873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vishwanath S., Ramphal R. Adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to human tracheobronchial mucin. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):197–202. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.197-202.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall M. A., Terry A. B., Eisenberg J., McNamara M., Cohen R. Inhaled antibiotics in cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 1983 Jun 11;1(8337):1325–1325. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92428-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Straus D. C., Johanson W. G., Jr, Bass J. A. Role of salivary protease activity in adherence of gram-negative bacilli to mammalian buccal epithelial cells in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;68(6):1435–1440. doi: 10.1172/JCI110395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Straus D. C., Johanson W. G., Jr, Berry V. K., Bass J. A. Role of pili in adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to mammalian buccal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):1146–1151. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.1146-1151.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



