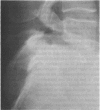
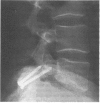
Abstract
The results of posterolateral screw fixation using the Buck technique performed on 24 patients with painful isthmic spondylolysis and up to grade I spondylolisthesis in the lumbar spine are reported. The average age at operation was 29 years and average follow-up was 5 years with a range of 13 months to 12 years. Operations were performed for persistent disabling low back pain. At review 21 patients were either free of pain or complained of only occasional backache and discomfort. All but two patients were satisfied with the operation and rated the result as excellent or good. It is concluded that Buck screw fixation is a safe and reliable method of treatment for painful Grade I spondylolisthesis due to isthmic spondylolysis in the young active adult with a low complication rate.
Full text
PDF
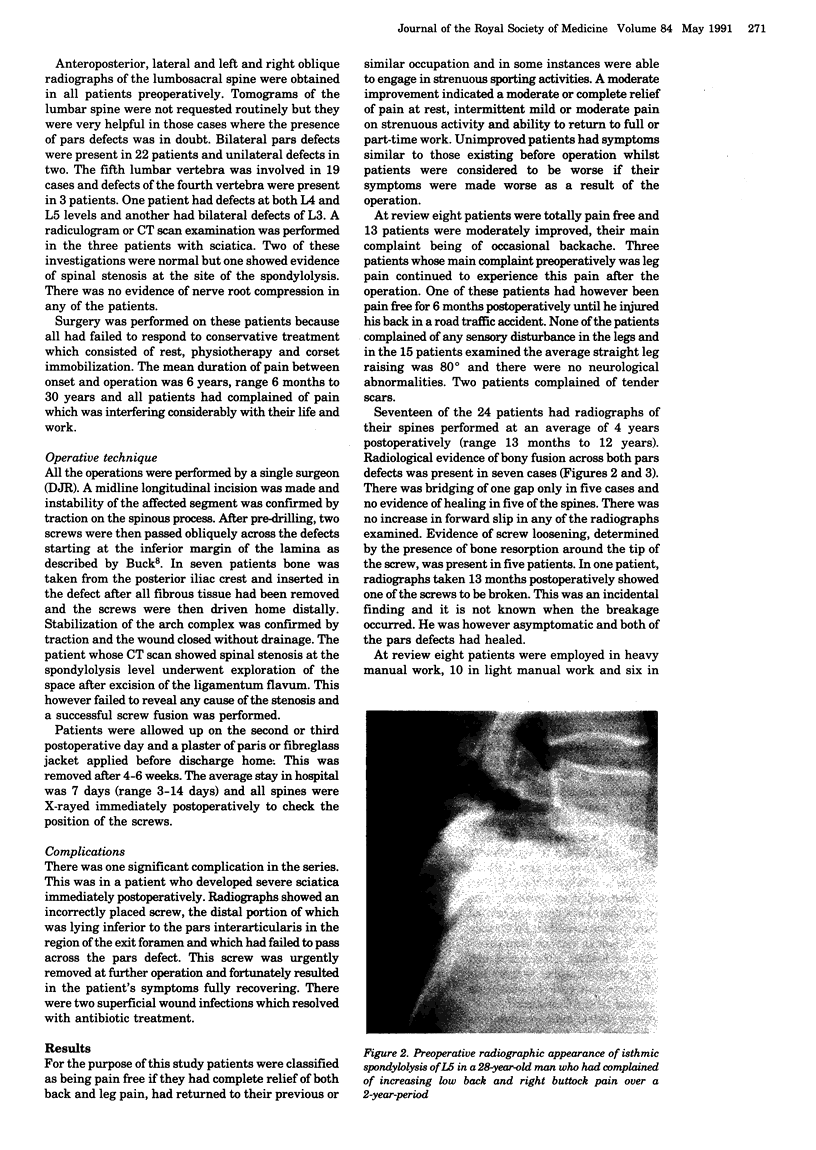


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buck J. E. Direct repair of the defect in spondylolisthesis. Preliminary report. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1970 Aug;52(3):432–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelson J. G., Nathan H. Nerve root compression in spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1986 Aug;68(4):596–599. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.68B4.3733837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freebody D., Bendall R., Taylor R. D. Anterior transperitoneal lumbar fusion. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1971 Nov;53(4):617–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson E. D. Results of the surgical treatment of spondylolisthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1966 Jun;48(4):619–642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterman K., Lindholm T. S., Laurent L. E. Late results of removal of the loose posterior element (Gill's operation) in the treatment of lytic lumbar spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976 Jun;(117):121–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPLITHOFF C. A. Lumbosacral junction; roentgenographic comparison of patients with and without backaches. J Am Med Assoc. 1953 Aug 22;152(17):1610–1613. doi: 10.1001/jama.1953.03690170024008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILTSE L. L. The etiology of spondylolisthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1962 Apr;44-A:539–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]