Abstract
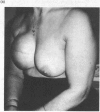
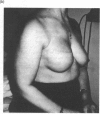
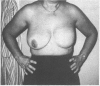
Breast reconstruction is normally carried out by plastic surgeons, but the advent of permanent tissue expanders places post-mastectomy reconstruction within easy reach of the general surgeon. Nineteen patients underwent breast reconstruction between 1989 and 1991 using a subpectoral silicone-based, double lumen tissue expander. Assessment of results was by: (a) patient completed questionnaire; and (b) third party evaluation of standardized photographs. The mean operating time was 58 min (40-80 min) and mean hospital stay 3 days (2-7 days). Complications included one flap necrosis and one leaking injection port. Outpatient tissue expansion required an average of seven visits (4-11) and was completed in an average of 12 months (7-19). The injection port was subsequently removed under local anaesthetic as a day case. The fully dressed appearance following reconstruction was graded good or excellent by 100% of patients and in over 80% of third-party assessments. Equivalent figures for the appearance when wearing a bra were 93% and 60% and undressed 57% and 47%, respectively. All patients recommended the procedure but 25% found inflation uncomfortable. Subpectoral tissue expansion is a safe, cosmetically acceptable method of breast reconstruction which is associated with a high level of patient satisfaction.
Full text
PDF
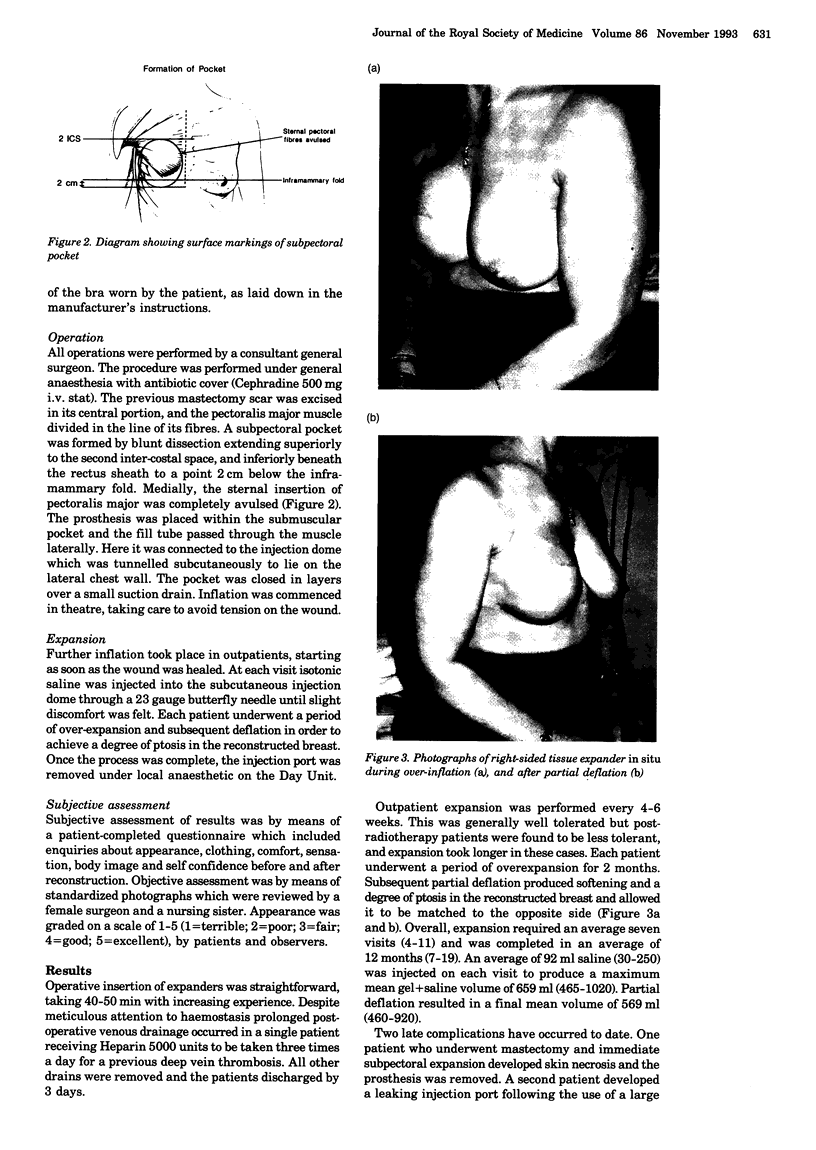


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker H. Breast reconstruction using an inflatable breast implant with detachable reservoir. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1984 Apr;73(4):678–683. doi: 10.1097/00006534-198404000-00031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker H., Maraist F. Immediate breast reconstruction after mastectomy using a permanent tissue expander. South Med J. 1987 Feb;80(2):154–160. doi: 10.1097/00007611-198702000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott L. F., Hartrampf C. R., Jr Breast reconstruction: progress in the past decade. World J Surg. 1990 Nov-Dec;14(6):763–775. doi: 10.1007/BF01670523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fallowfield L. J., Baum M., Maguire G. P. Addressing the psychological needs of the conservatively treated breast cancer patient: discussion paper. J R Soc Med. 1987 Nov;80(11):696–700. doi: 10.1177/014107688708001113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruber R. P., Kahn R. A., Lash H., Maser M. R., Apfelberg D. B., Laub D. R. Breast reconstruction following mastectomy: a comparison of submuscular and subcutaneous techniques. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1981 Mar;67(3):312–317. doi: 10.1097/00006534-198103000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath M. H., Burkhardt B. R. The safety and efficacy of breast implants for augmentation mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1984 Oct;74(4):550–560. doi: 10.1097/00006534-198410000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RENNEKER R., CUTLER M. Psychological problems of adjustment to cancer of the breast. J Am Med Assoc. 1952 Mar 8;148(10):833–838. doi: 10.1001/jama.1952.02930100051011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radovan C. Breast reconstruction after mastectomy using the temporary expander. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1982 Feb;69(2):195–208. doi: 10.1097/00006534-198202000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schain W. S., Wellisch D. K., Pasnau R. O., Landsverk J. The sooner the better: a study of psychological factors in women undergoing immediate versus delayed breast reconstruction. Am J Psychiatry. 1985 Jan;142(1):40–46. doi: 10.1176/ajp.142.9.A40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J., Cohen I. K., Knaysi G. A., Brown P. W. Immediate breast reconstruction with tissue expansion. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1987 Oct;80(4):559–566. doi: 10.1097/00006534-198710000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]