Abstract
Eighteen patients with generalized tetanus seen during an 8-year period in three regional hospitals in Hong Kong are reviewed. Eighty-nine per cent of the patients were intravenous heroin addicts who developed a severe type of generalized tetanus with autonomic dysfunction. Pain or stiffness of the neck or back was the commonest presenting symptom, followed by trismus and dysphagia. Most of the patients developed muscle spasms within 24 h of the onset of presenting symptoms. Early ventilatory support and tracheostomy, together with intensive nursing care, were the mainstay of the treatment. Pulmonary and gastrointestinal complications were common during the course of illness and treatment of autonomic dysfunction was often unsatisfactory. The case fatality rate was 25% among the heroin addicts, but full recovery was the usual outcome for those who survived. The simultaneous administration of intrathecal tetanus immunoglobulin tends to reduce mortality.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrutyn E., Berlin J. A. Intrathecal therapy in tetanus. A meta-analysis. JAMA. 1991 Oct 23;266(16):2262–2267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett J. L., Spalding J. M., Harris P. J. Hypotension in tetanus. Br Med J. 1973 Aug 25;3(5877):423–428. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5877.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta P. S., Kapoor R., Goyal S., Batra V. K., Jain B. K. Intrathecal human tetanus immunoglobulin in early tetanus. Lancet. 1980 Aug 30;2(8192):439–440. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91883-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollow V. M., Clarke G. M. Autonomic manifestations of tetanus. Anaesth Intensive Care. 1975 May;3(2):142–147. doi: 10.1177/0310057X7500300211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINSON A., MARSKE R. L., SHEIN M. K. Tetanus in heroin addicts. J Am Med Assoc. 1955 Feb 19;157(8):658–660. doi: 10.1001/jama.1955.02950250032009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powles A. B., Ganta R. Use of vecuronium in the management of tetanus. Anaesthesia. 1985 Sep;40(9):879–881. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1985.tb11050.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert R., Rouffineau J., Cremault A., Bauple J. L., Pourrat O., Gil R., Patte D. Paraplégie réversible après injection intrathécale de fortes doses de gammaglobulines humaines lors du traitement de tétanos de faible gravité. Quatre observations. Presse Med. 1984 Sep 22;13(32):1947–1949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose A. G. Catecholamine-induced myocardial dammage associated with phaeochromocytomas and tetanus. S Afr Med J. 1974 Jun 22;48(30):1285–1289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsueda K., Jean-Francois J., Richter R. W. Cardiac standstill in tetanus: review of seven consecutive cases. Int Surg. 1973 Sep;58(9):599–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsueda K., Oliver P. B., Richter R. W. Cardiovascular manifestations of tetanus. Anesthesiology. 1974 Jun;40(6):588–592. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197406000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udwadia F. E., Lall A., Udwadia Z. F., Sekhar M., Vora A. Tetanus and its complications: intensive care and management experience in 150 Indian patients. Epidemiol Infect. 1987 Dec;99(3):675–684. doi: 10.1017/s095026880006653x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
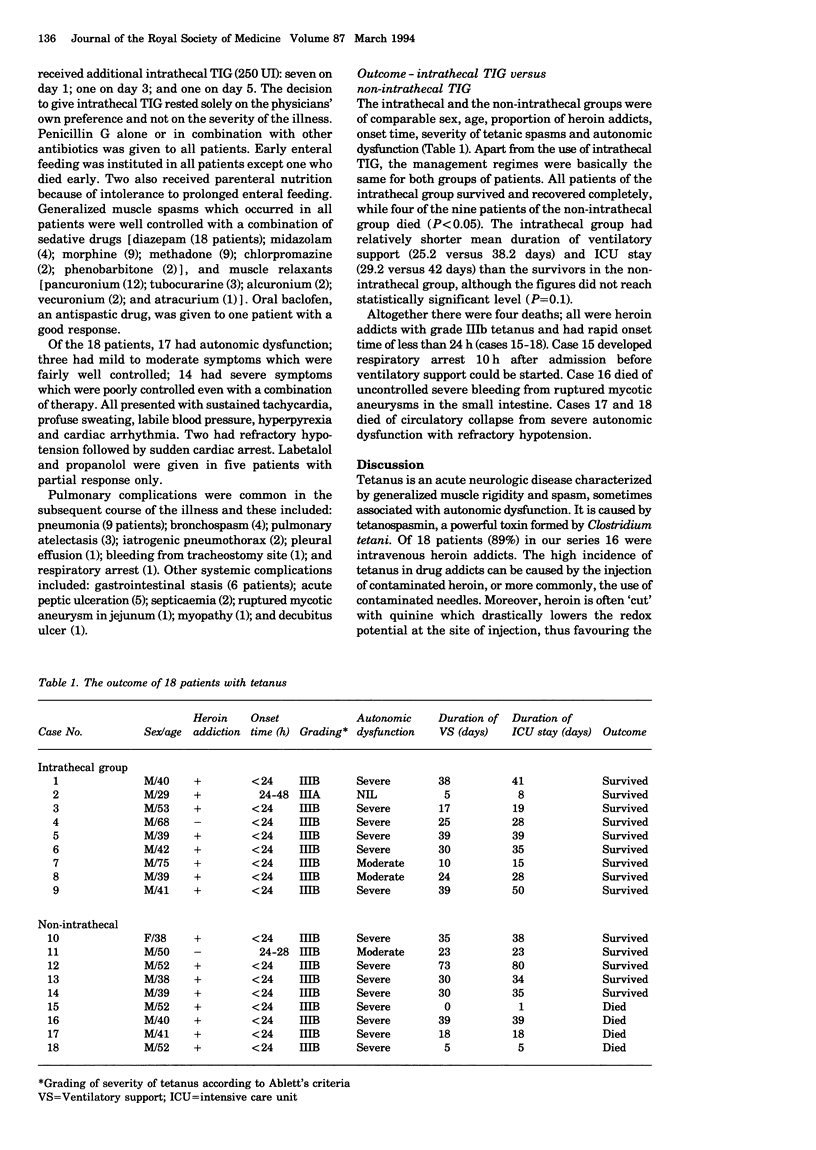
- Wright D. K., Lalloo U. G., Nayiager S., Govender P. Autonomic nervous system dysfunction in severe tetanus: current perspectives. Crit Care Med. 1989 Apr;17(4):371–375. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198904000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


