Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abernathy-Carver K. J., Sampson H. A., Picker L. J., Leung D. Y. Milk-induced eczema is associated with the expansion of T cells expressing cutaneous lymphocyte antigen. J Clin Invest. 1995 Feb;95(2):913–918. doi: 10.1172/JCI117743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker J. N., MacDonald D. M. Epidermal class II human lymphocyte antigen expression in atopic dermatitis: a comparison with experimental allergic contact dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1987 Jun;16(6):1175–1179. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(87)70153-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhisel-Broadbent J., Sampson H. A. Cross-allergenicity in the legume botanical family in children with food hypersensitivity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1989 Feb;83(2 Pt 1):435–440. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(89)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhisel-Broadbent J., Strause D., Sampson H. A. Fish hypersensitivity. II: Clinical relevance of altered fish allergenicity caused by various preparation methods. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1992 Oct;90(4 Pt 1):622–629. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(92)90135-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochner B. S., Klunk D. A., Sterbinsky S. A., Coffman R. L., Schleimer R. P. IL-13 selectively induces vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression in human endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1995 Jan 15;154(2):799–803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos J. D., Hagenaars C., Das P. K., Krieg S. R., Voorn W. J., Kapsenberg M. L. Predominance of "memory" T cells (CD4+, CDw29+) over "naive" T cells (CD4+, CD45R+) in both normal and diseased human skin. Arch Dermatol Res. 1989;281(1):24–30. doi: 10.1007/BF00424268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruynzeel-Koomen C., van Wichen D. F., Toonstra J., Berrens L., Bruynzeel P. L. The presence of IgE molecules on epidermal Langerhans cells in patients with atopic dermatitis. Arch Dermatol Res. 1986;278(3):199–205. doi: 10.1007/BF00412924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burks A. W., Mallory S. B., Williams L. W., Shirrell M. A. Atopic dermatitis: clinical relevance of food hypersensitivity reactions. J Pediatr. 1988 Sep;113(3):447–451. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80626-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandra R. K., Puri S., Hamed A. Influence of maternal diet during lactation and use of formula feeds on development of atopic eczema in high risk infants. BMJ. 1989 Jul 22;299(6693):228–230. doi: 10.1136/bmj.299.6693.228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Charlesworth E. N., Kagey-Sobotka A., Norman P. S., Lichtenstein L. M., Sampson H. A. Cutaneous late-phase response in food-allergic children and adolescents with atopic dermatitis. Clin Exp Allergy. 1993 May;23(5):391–397. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1993.tb00344.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fergusson D. M., Horwood L. J., Shannon F. T. Asthma and infant diet. Arch Dis Child. 1983 Jan;58(1):48–51. doi: 10.1136/adc.58.1.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fergusson D. M., Horwood L. J., Shannon F. T. Early solid feeding and recurrent childhood eczema: a 10-year longitudinal study. Pediatrics. 1990 Oct;86(4):541–546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillet G., Guillet M. H. Natural history of sensitizations in atopic dermatitis. A 3-year follow-up in 250 children: food allergy and high risk of respiratory symptoms. Arch Dermatol. 1992 Feb;128(2):187–192. doi: 10.1001/archderm.128.2.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamid Q., Boguniewicz M., Leung D. Y. Differential in situ cytokine gene expression in acute versus chronic atopic dermatitis. J Clin Invest. 1994 Aug;94(2):870–876. doi: 10.1172/JCI117408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamid Q., Naseer T., Minshall E. M., Song Y. L., Boguniewicz M., Leung D. Y. In vivo expression of IL-12 and IL-13 in atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996 Jul;98(1):225–231. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(96)70246-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanifin J. M. Epidemiology of atopic dermatitis. Monogr Allergy. 1987;21:116–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattevig G., Kjellman B., Sigurs N., Björkstén B., Kjellman N. I. Effect of maternal avoidance of eggs, cow's milk and fish during lactation upon allergic manifestations in infants. Clin Exp Allergy. 1989 Jan;19(1):27–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1989.tb02339.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Høst A., Husby S., Osterballe O. A prospective study of cow's milk allergy in exclusively breast-fed infants. Incidence, pathogenetic role of early inadvertent exposure to cow's milk formula, and characterization of bovine milk protein in human milk. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1988 Sep;77(5):663–670. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1988.tb10727.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irani A. M., Sampson H. A., Schwartz L. B. Mast cells in atopic dermatitis. Allergy. 1989;44 (Suppl 9):31–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
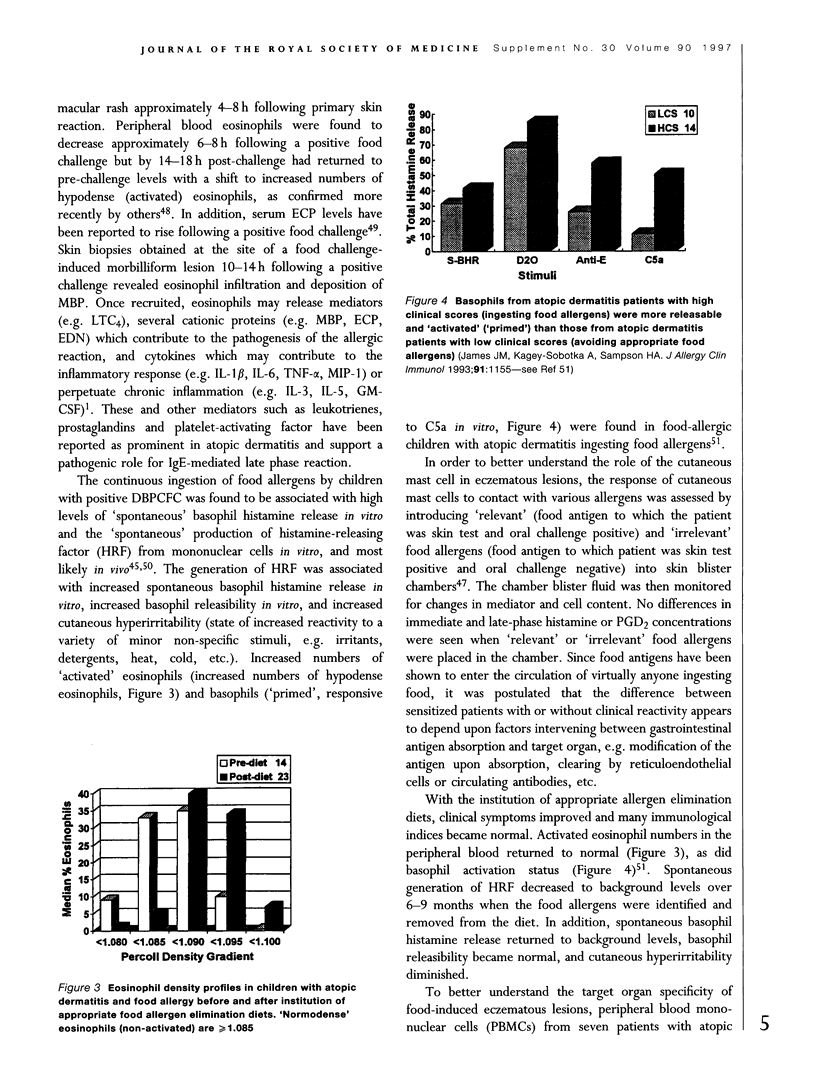
- James J. M., Kagey-Sobotka A., Sampson H. A. Patients with severe atopic dermatitis have activated circulating basophils. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1993 Jun;91(6):1155–1162. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(93)90318-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. M., Magnolfi C. F., Cooke S. K., Sampson H. A. Immunologic cross-reactivity among cereal grains and grasses in children with food hypersensitivity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995 Sep;96(3):341–351. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(95)70053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajosaari M. Atopy prophylaxis in high-risk infants. Prospective 5-year follow-up study of children with six months exclusive breastfeeding and solid food elimination. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1991;310:453–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. B., Ying S., Varney V., Gaga M., Durham S. R., Moqbel R., Wardlaw A. J., Hamid Q. Messenger RNA expression of the cytokine gene cluster, interleukin 3 (IL-3), IL-4, IL-5, and granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor, in allergen-induced late-phase cutaneous reactions in atopic subjects. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):775–778. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kägi M. K., Joller-Jemelka H., Wüthrich B. Correlation of eosinophils, eosinophil cationic protein and soluble interleukin-2 receptor with the clinical activity of atopic dermatitis. Dermatology. 1992;185(2):88–92. doi: 10.1159/000247419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiferman K. M., Ackerman S. J., Sampson H. A., Haugen H. S., Venencie P. Y., Gleich G. J. Dermal deposition of eosinophil-granule major basic protein in atopic dermatitis. Comparison with onchocerciasis. N Engl J Med. 1985 Aug 1;313(5):282–285. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198508013130502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
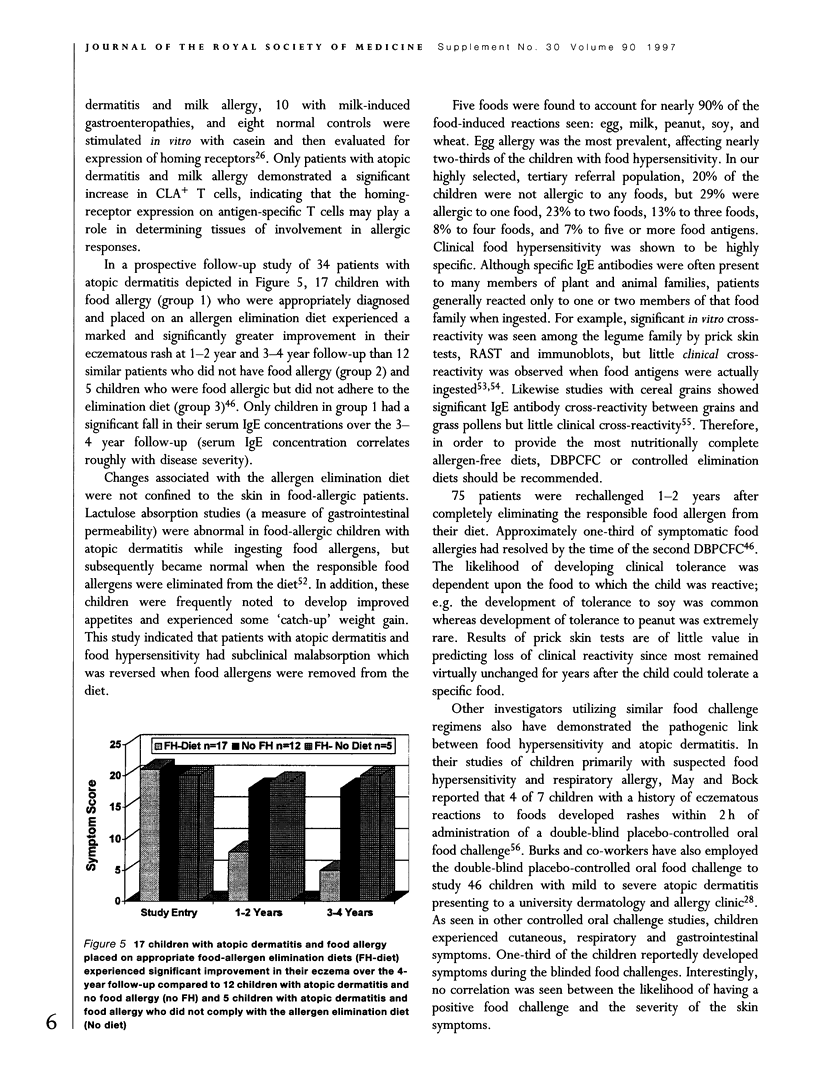
- Leung D. Y., Bhan A. K., Schneeberger E. E., Geha R. S. Characterization of the mononuclear cell infiltrate in atopic dermatitis using monoclonal antibodies. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1983 Jan;71(1 Pt 1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(83)90546-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas A., Brooke O. G., Morley R., Cole T. J., Bamford M. F. Early diet of preterm infants and development of allergic or atopic disease: randomised prospective study. BMJ. 1990 Mar 31;300(6728):837–840. doi: 10.1136/bmj.300.6728.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarin M., Knowles A., Ventura A., Vita F., Fanti L., Zabucchi G. A role for eosinophils in the pathogenesis of skin lesions in patients with food-sensitive atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995 Aug;96(2):200–208. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(95)70009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudde G. C., Bheekha R., Bruijnzeel-Koomen C. A. Consequences of IgE/CD23-mediated antigen presentation in allergy. Immunol Today. 1995 Aug;16(8):380–383. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(95)80005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picker L. J., Martin R. J., Trumble A., Newman L. S., Collins P. A., Bergstresser P. R., Leung D. Y. Differential expression of lymphocyte homing receptors by human memory/effector T cells in pulmonary versus cutaneous immune effector sites. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Jun;24(6):1269–1277. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossiter H., van Reijsen F., Mudde G. C., Kalthoff F., Bruijnzeel-Koomen C. A., Picker L. J., Kupper T. S. Skin disease-related T cells bind to endothelial selectins: expression of cutaneous lymphocyte antigen (CLA) predicts E-selectin but not P-selectin binding. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Jan;24(1):205–210. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson H. A. Atopic dermatitis. Ann Allergy. 1992 Dec;69(6):469–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson H. A., Broadbent K. R., Bernhisel-Broadbent J. Spontaneous release of histamine from basophils and histamine-releasing factor in patients with atopic dermatitis and food hypersensitivity. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jul 27;321(4):228–232. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198907273210405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson H. A., MacDonald S. M. IgE-dependent histamine-releasing factors. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1993;15(1):89–98. doi: 10.1007/BF00204628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson H. A., McCaskill C. C. Food hypersensitivity and atopic dermatitis: evaluation of 113 patients. J Pediatr. 1985 Nov;107(5):669–675. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(85)80390-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigurs N., Hattevig G., Kjellman B. Maternal avoidance of eggs, cow's milk, and fish during lactation: effect on allergic manifestations, skin-prick tests, and specific IgE antibodies in children at age 4 years. Pediatrics. 1992 Apr;89(4 Pt 2):735–739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer K. H., Tuck D. T., Sampson H. A., Hall R. P. Epidermal keratinocytes express the adhesion molecule intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in inflammatory dermatoses. J Invest Dermatol. 1989 May;92(5):746–750. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12722441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suomalainen H., Soppi E., Isolauri E. Evidence for eosinophil activation in cow's milk allergy. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 1994 Feb;5(1):27–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3038.1994.tb00215.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong A. K., Mihm M. C., Jr The pathology of atopic dermatitis. Clin Rev Allergy. 1986 Feb;4(1):27–42. doi: 10.1007/BF02991186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsicopoulos A., Hamid Q., Varney V., Ying S., Moqbel R., Durham S. R., Kay A. B. Preferential messenger RNA expression of Th1-type cells (IFN-gamma+, IL-2+) in classical delayed-type (tuberculin) hypersensitivity reactions in human skin. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 1;148(7):2058–2061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakita H., Sakamoto T., Tokura Y., Takigawa M. E-selectin and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 as critical adhesion molecules for infiltration of T lymphocytes and eosinophils in atopic dermatitis. J Cutan Pathol. 1994 Feb;21(1):33–39. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.1994.tb00688.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiger R. S., Heller S., Mellon M. H., Forsythe A. B., O'Connor R. D., Hamburger R. N., Schatz M. Effect of combined maternal and infant food-allergen avoidance on development of atopy in early infancy: a randomized study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1989 Jul;84(1):72–89. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(89)90181-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiger R. S., Heller S. The development and prediction of atopy in high-risk children: follow-up at age seven years in a prospective randomized study of combined maternal and infant food allergen avoidance. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995 Jun;95(6):1179–1190. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(95)70074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiger R. S. Prevention of food allergy in infancy. Ann Allergy. 1990 Dec;65(6):430–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Reijsen F. C., Bruijnzeel-Koomen C. A., Kalthoff F. S., Maggi E., Romagnani S., Westland J. K., Mudde G. C. Skin-derived aeroallergen-specific T-cell clones of Th2 phenotype in patients with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1992 Aug;90(2):184–193. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(92)90070-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heijden F. L., Wierenga E. A., Bos J. D., Kapsenberg M. L. High frequency of IL-4-producing CD4+ allergen-specific T lymphocytes in atopic dermatitis lesional skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Sep;97(3):389–394. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12480966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


