Abstract
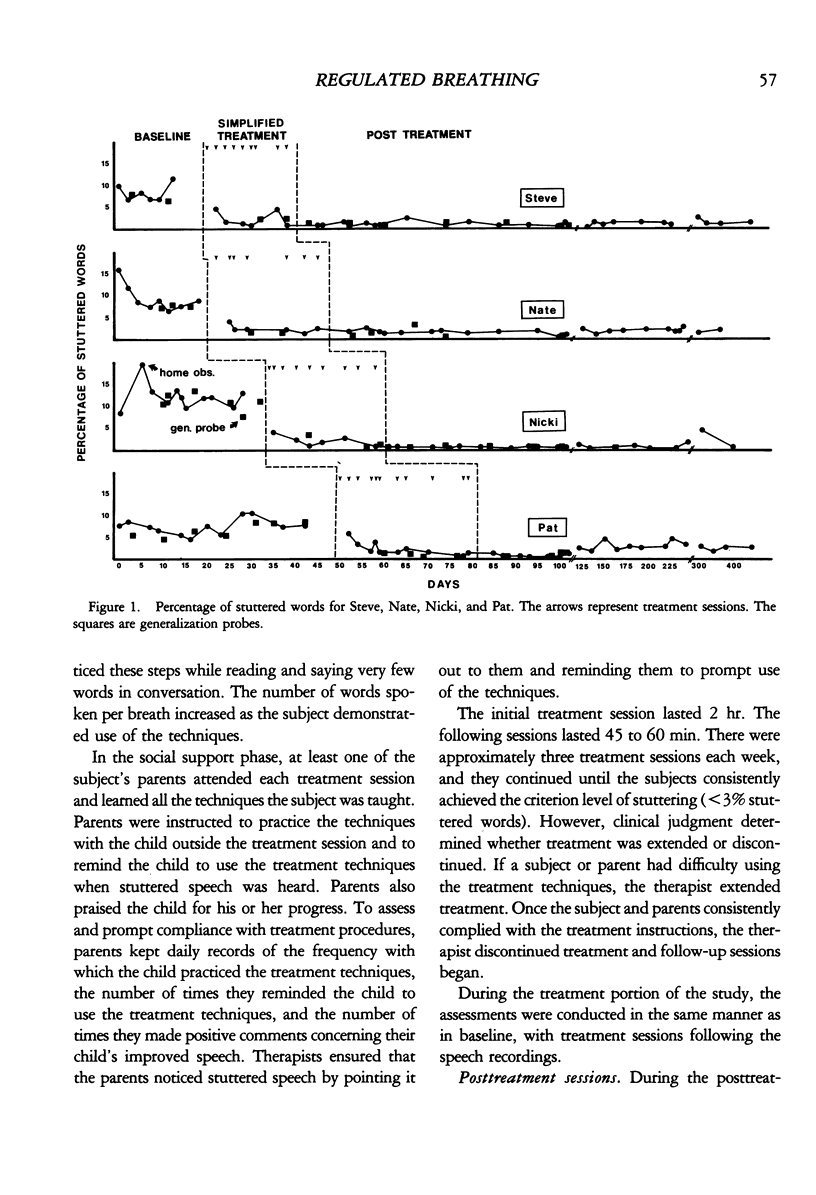
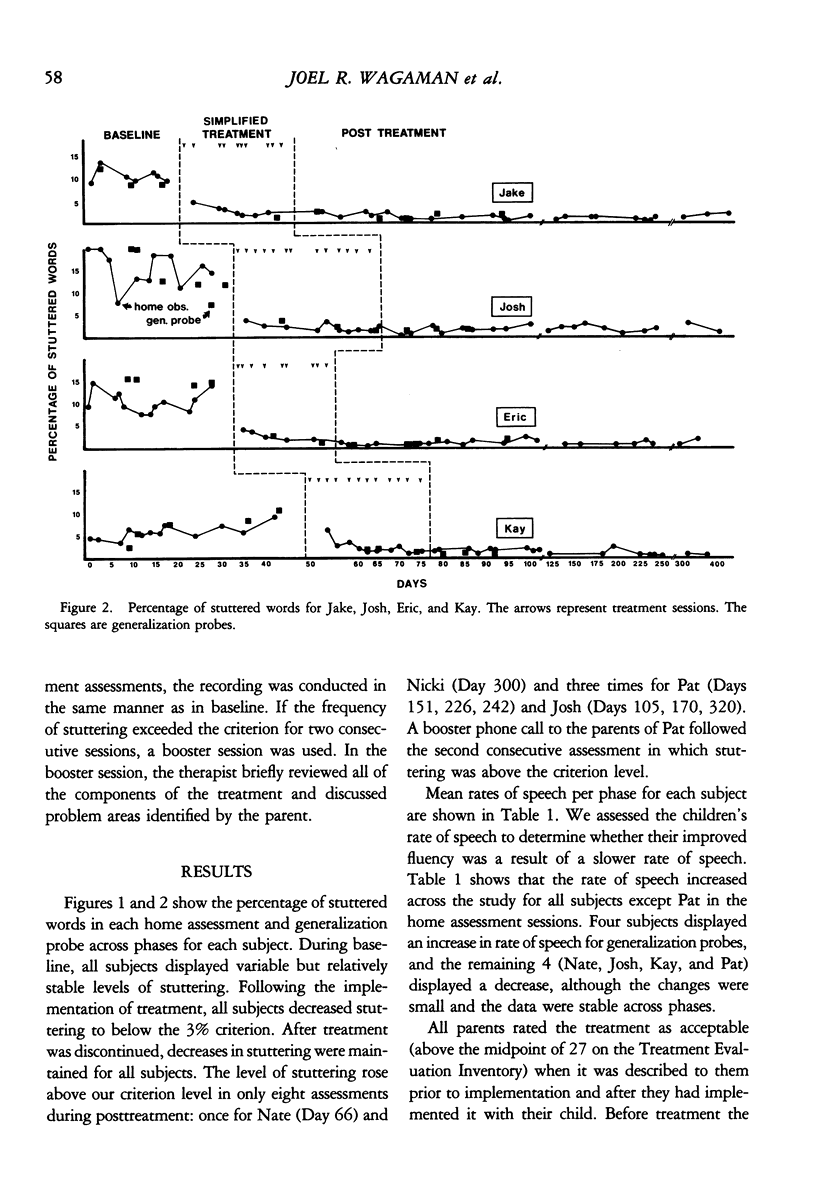
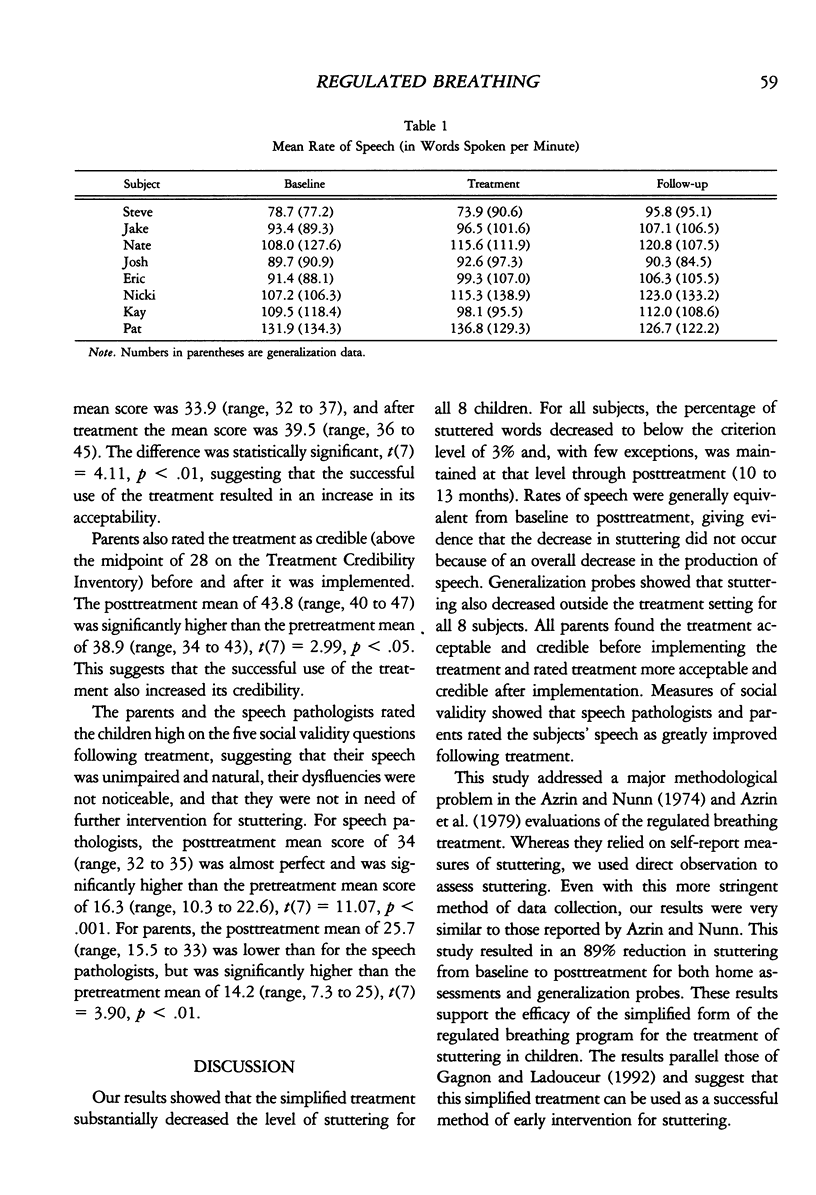
We investigated the effectiveness of a simplified program for the treatment of stuttering in children. The simplified treatment included awareness training, in which the subjects learned to detect every occurrence of stuttering; training a response incompatible with stuttering, which involved relaxation and regulation of air flow over the larynx when speaking; and social support, which involved parent-delivered prompts and praise of children's use of the techniques in everyday environments. Eight children were treated in their homes with the simplified treatment, in a multiple baseline across subjects design, and all reached the criterion level of less than 3% words stuttered. In addition, the reduction in stuttering generalized to the school setting and was maintained at posttreatment (10 to 13 months). The subjects' rates of speech remained stable throughout baseline and treatment. Pretreatment and posttreatment ratings by the parents showed that they found treatment to be both acceptable and credible. Finally, social validity measures revealed a noticeable improvement in the subjects' speech to parents and speech pathologists.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews G., Tanner S. Stuttering treatment: an attempt to replicate the regulated-breathing method. J Speech Hear Disord. 1982 May;47(2):138–140. doi: 10.1044/jshd.4702.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews G., Tanner S. Stuttering: the results of 5 days treatment with an airflow technique. J Speech Hear Disord. 1982 Nov;47(4):427–429. doi: 10.1044/jshd.4704.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azrin N. H., Nunn R. G. A rapid method of eliminating stuttering by a regulated breathing approach. Behav Res Ther. 1974 Nov;12(4):279–286. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(74)90002-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azrin N. H., Nunn R. G., Frantz S. E. Comparison of regulated-breathing verses abbreviated desensitization on reported stuttering episodes. J Speech Hear Disord. 1979 Aug;44(3):331–339. doi: 10.1044/jshd.4403.331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azrin N. H., Nunn R. G. Habit-reversal: a method of eliminating nervous habits and tics. Behav Res Ther. 1973 Nov;11(4):619–628. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(73)90119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caron C., Ladouceur R. Multidimensional behavioral treatment for child stutterers. Behav Modif. 1989 Apr;13(2):206–215. doi: 10.1177/01454455890132004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howie P. M., Tanner S., Andrews G. Short- and long-term outcome in an intensive treatment program for adult stutterers. J Speech Hear Disord. 1981 Feb;46(1):104–109. doi: 10.1044/jshd.4601.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladouceur R., Boudreau L., Théberge S. Awareness training and regulated-breathing method in modification of stuttering. Percept Mot Skills. 1981 Aug;53(1):187–194. doi: 10.2466/pms.1981.53.1.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladouceur R., Côté C., Leblond G., Bouchard L. Evaluation of regulated-breathing method and awareness training in the treatment of stuttering. J Speech Hear Disord. 1982 Nov;47(4):422–426. doi: 10.1044/jshd.4704.422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladouceur R., Martineau G. Evaluation of regulated-breathing method with and without parental assistance in the treatment of child stutterers. J Behav Ther Exp Psychiatry. 1982 Dec;13(4):301–306. doi: 10.1016/0005-7916(82)90074-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. Letter: Application of Martin Schwartz's airflow technique in the treatment of stuttering. J Speech Hear Disord. 1976 Feb;41(1):133–134. doi: 10.1044/jshd.4101.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterloo K. K., Götestam K. G. The regulated-breathing method for stuttering: an experimental evaluation. J Behav Ther Exp Psychiatry. 1988 Mar;19(1):11–19. doi: 10.1016/0005-7916(88)90005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


