Abstract
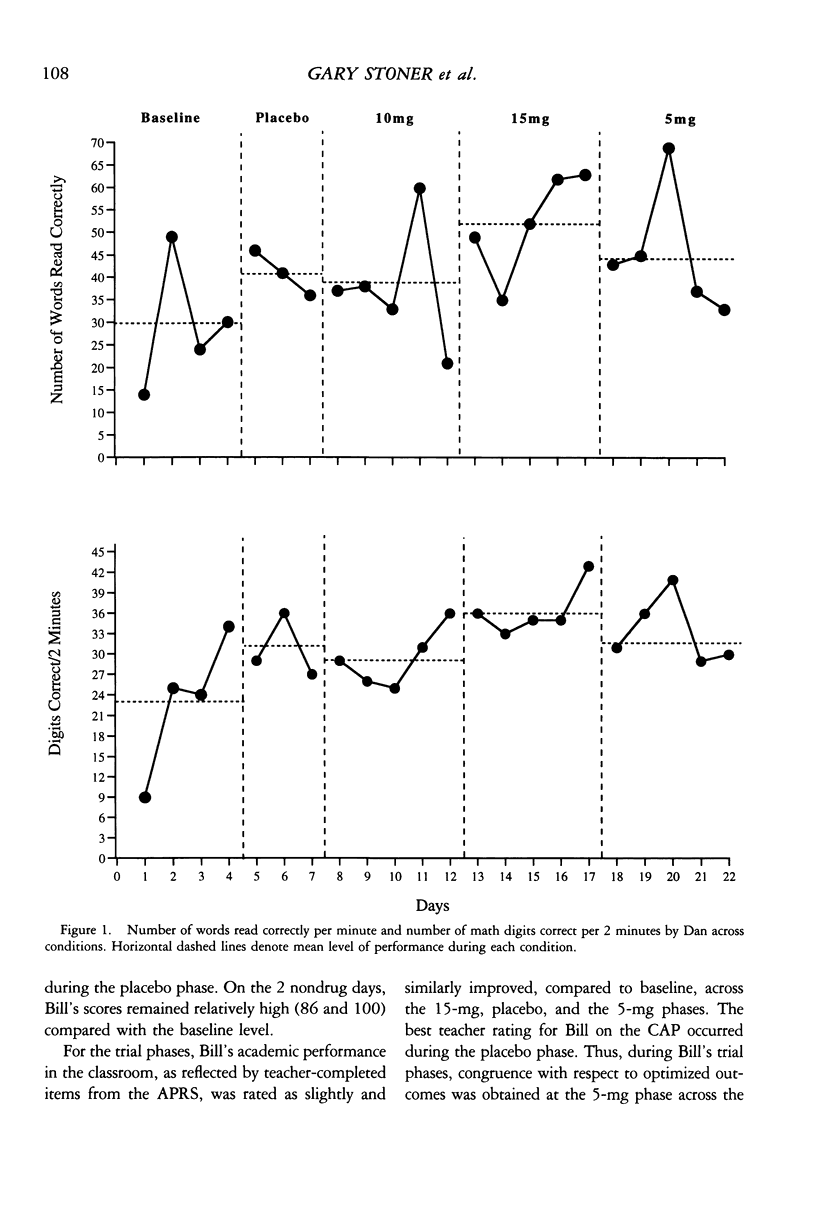
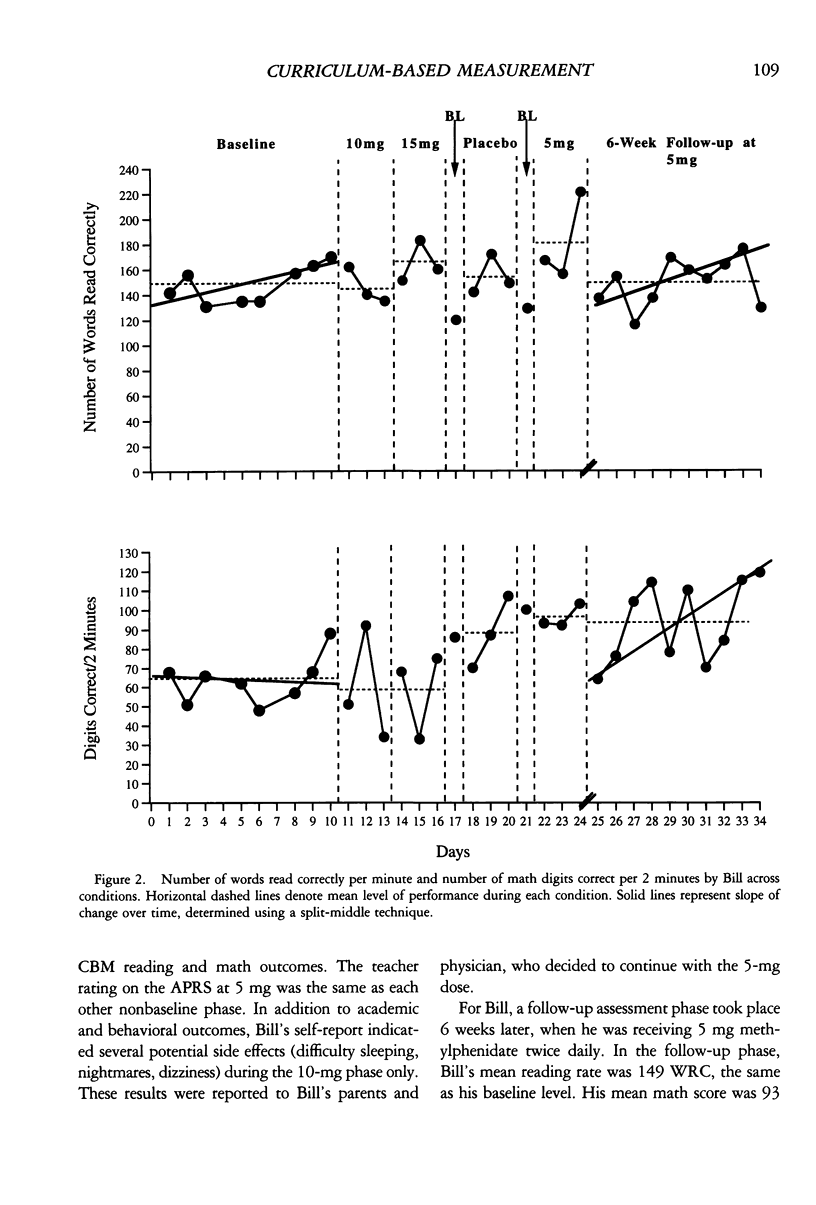
Two case studies were conducted to investigate the utility of curriculum-based measurement of math and reading for evaluating the effects of methylphenidate on the academic performance of 2 students diagnosed with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Following baseline measurement, double-blind placebo-controlled procedures were employed to evaluate each student's response to three levels (5 mg, 10 mg, and 15 mg) of the medication. Results of the first study suggest that the curriculum-based measures were sensitive indicators of the student's response to medication. This finding was replicated in the second study. In the second study, when the student's follow-up dose of medication was based on trial-phase data, follow-up performance was improved compared to baseline performance. These case studies suggest that further research is warranted on the utility of curriculum-based measurements for monitoring and evaluating stimulant medication interventions with children with this disorder.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- August G. J., Garfinkel B. D. Behavioral and cognitive subtypes of ADHD. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1989 Sep;28(5):739–748. doi: 10.1097/00004583-198909000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkley R. A., McMurray M. B., Edelbrock C. S., Robbins K. The response of aggressive and nonaggressive ADHD children to two doses of methylphenidate. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1989 Nov;28(6):873–881. doi: 10.1097/00004583-198911000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. T., Sleator E. K. Methylphenidate in hyperkinetic children: differences in dose effects on impulsive behavior. Pediatrics. 1979 Oct;64(4):408–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland L., Wolraich M., Lindgren S., Milich R., Woolson R. Pediatricians' reported practices in the assessment and treatment of attention deficit disorders. J Dev Behav Pediatr. 1987 Aug;8(4):191–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deno S. L., Mirkin P. K., Chiang B. Identifying valid measures of reading. Except Child. 1982 Sep;49(1):36–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapport M. D., DuPaul G. J., Kelly K. L. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and methylphenidate: the relationship between gross body weight and drug response in children. Psychopharmacol Bull. 1989;25(2):285–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapport M. D., DuPaul G. J., Stoner G., Jones T. J. Comparing classroom and clinic measures of attention deficit disorder: differential, idiosyncratic, and dose-response effects of methylphenidate. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1986 Jun;54(3):334–341. doi: 10.1037//0022-006x.54.3.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapport M. D., Stoner G., DuPaul G. J., Birmingham B. K., Tucker S. Methylphenidate in hyperactive children: differential effects of dose on academic, learning, and social behavior. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 1985 Jun;13(2):227–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00910644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapport M. D., Stoner G., DuPaul G. J., Kelly K. L., Tucker S. B., Schoeler T. Attention deficit disorder and methylphenidate: a multilevel analysis of dose-response effects on children's impulsivity across settings. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1988 Jan;27(1):60–69. doi: 10.1097/00004583-198801000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer D. J., Krager J. M. A survey of medication treatment for hyperactive/inattentive students. JAMA. 1988 Oct 21;260(15):2256–2258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague R. L., Sleator E. K. Methylphenidate in hyperkinetic children: differences in dose effects on learning and social behavior. Science. 1977 Dec 23;198(4323):1274–1276. doi: 10.1126/science.337493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. M., Kinsbourne M. Stimulant-related state-dependent learning in hyperactive children. Science. 1976 Jun 25;192(4246):1354–1357. doi: 10.1126/science.1273596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



