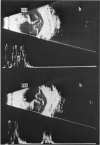
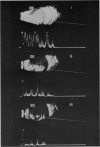
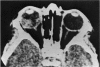
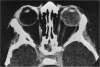
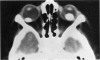
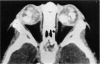
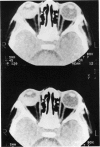
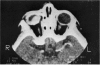
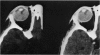
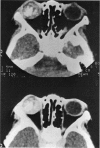
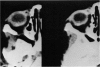
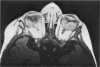
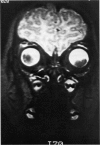
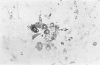
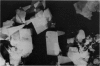
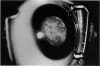
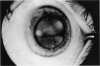
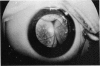
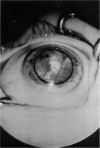
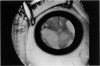
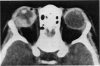
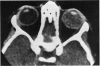
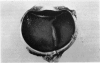
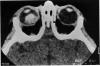
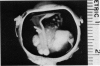
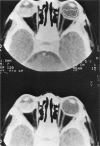
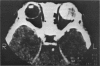
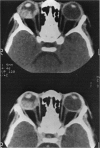
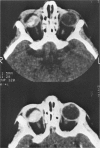
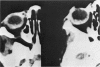
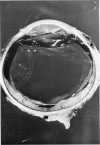
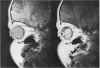
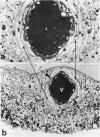
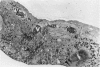
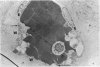
Abstract
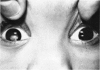
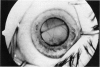
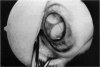
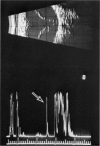
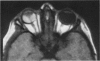
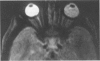
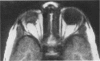
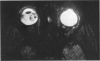
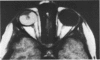
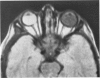
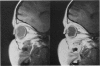
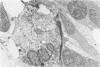
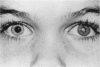
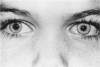
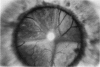
Advanced Coats' disease and retinoblastoma can both present with the triad of a retinal detachment, the appearance of a subretinal mass, and dilated retinal vessels. Thus, even the most experienced observer may not be able to differentiate these entities on ophthalmoscopic findings alone. Coats' disease is the most common reason for which eyes are enucleated with the misdiagnosis of retinoblastoma. Ultrasonography is the auxiliary diagnostic test most easily incorporated into the clinical examination, and can be utilized repeatedly without biologic tissue hazard. Ultrasonically identifiable features allowing differentiation between Coats' disease and retinoblastoma include the topography and character of retinal detachment and presence or absence of subretinal calcifications. Ultrasonography is of lesser use in poorly calcified retinoblastoma and in detecting optic nerve or extraocular extension in heavily calcified retinoblastoma. CT is perhaps the single most valuable test because of its ability to: (a) delineate intraocular morphology, (b) quantify subretinal densities, (c) identify vascularities within the subretinal space through the use of contrast enhancement, and (d) detected associated orbital or intracranial abnormalities. Optimal computed tomographic studies, however, require multiple thin slices both before and after contrast introduction and expose the child to low levels of radiation if studies are repeated periodically. MR imaging is valuable for its multiplanar imaging capabilities, its superior contrast resolution, and its ability to provide insights into the biochemical structure and composition of tissues. It is limited in its ability to detect calcium, which is the mainstay of ultrasonic and CT differentiation. Aqueous LDH and isoenzyme levels were not valuable in distinguishing between Coats' disease and retinoblastoma. The value of aqueous NSE levels in the differentiation of advanced Coats' disease and exophytic retinoblastoma deserves further study. Specimens from patients with intraocular hemorrhage should be viewed cautiously, since erythrocytes contain high levels of enolase. Analysis of subretinal aspirates is an extremely accurate method of confirming the diagnosis of Coats' disease. The key diagnostic findings are the presence of cholesterol crystals and pigment-laden macrophages and the absence of tumor cells on fresh preparations. The technique should be reserved for patients where retinoblastoma has been ruled out by all noninvasive means and massive subretinal drainage is anticipated. The natural progression in advanced Coats' disease is toward the development of a blind, painful eye. Spontaneous regression does rarely occur, and some eyes quietly progress to a phthisical state.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF













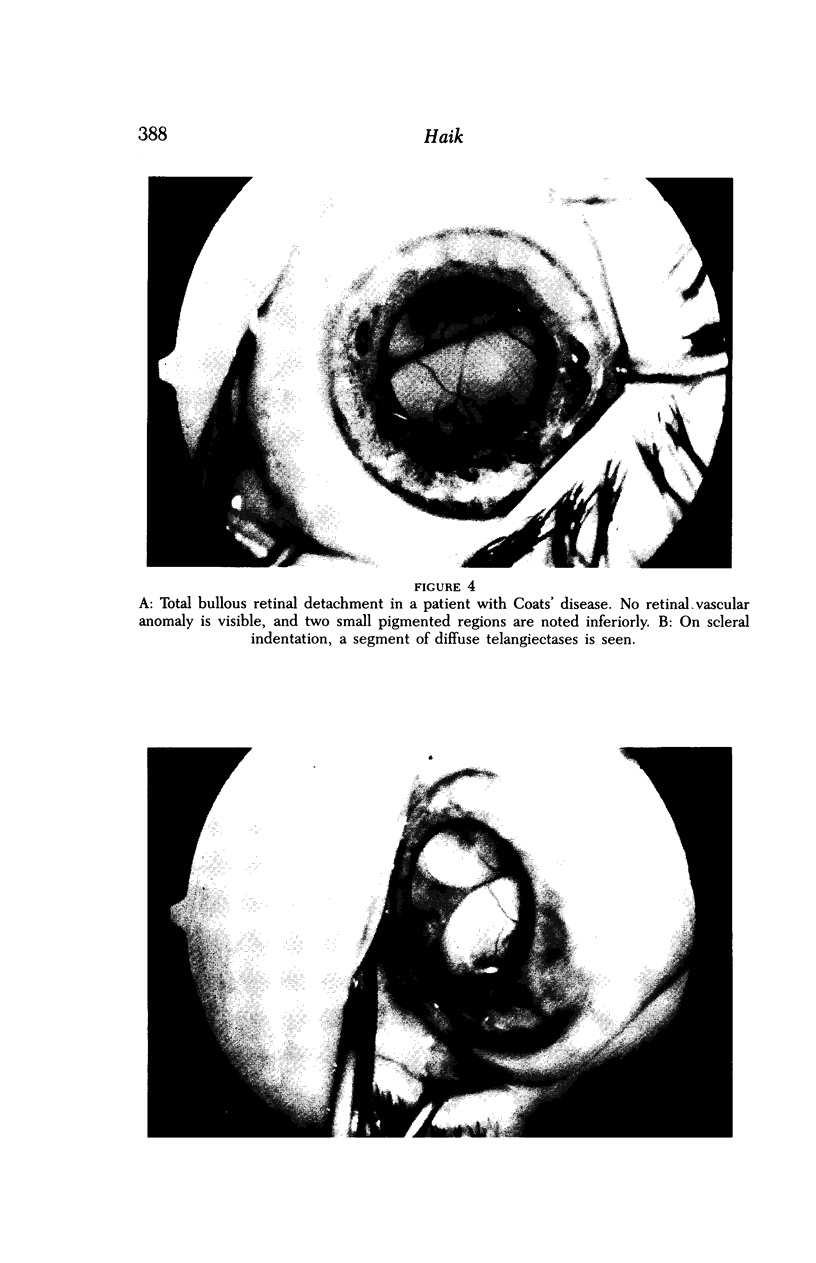




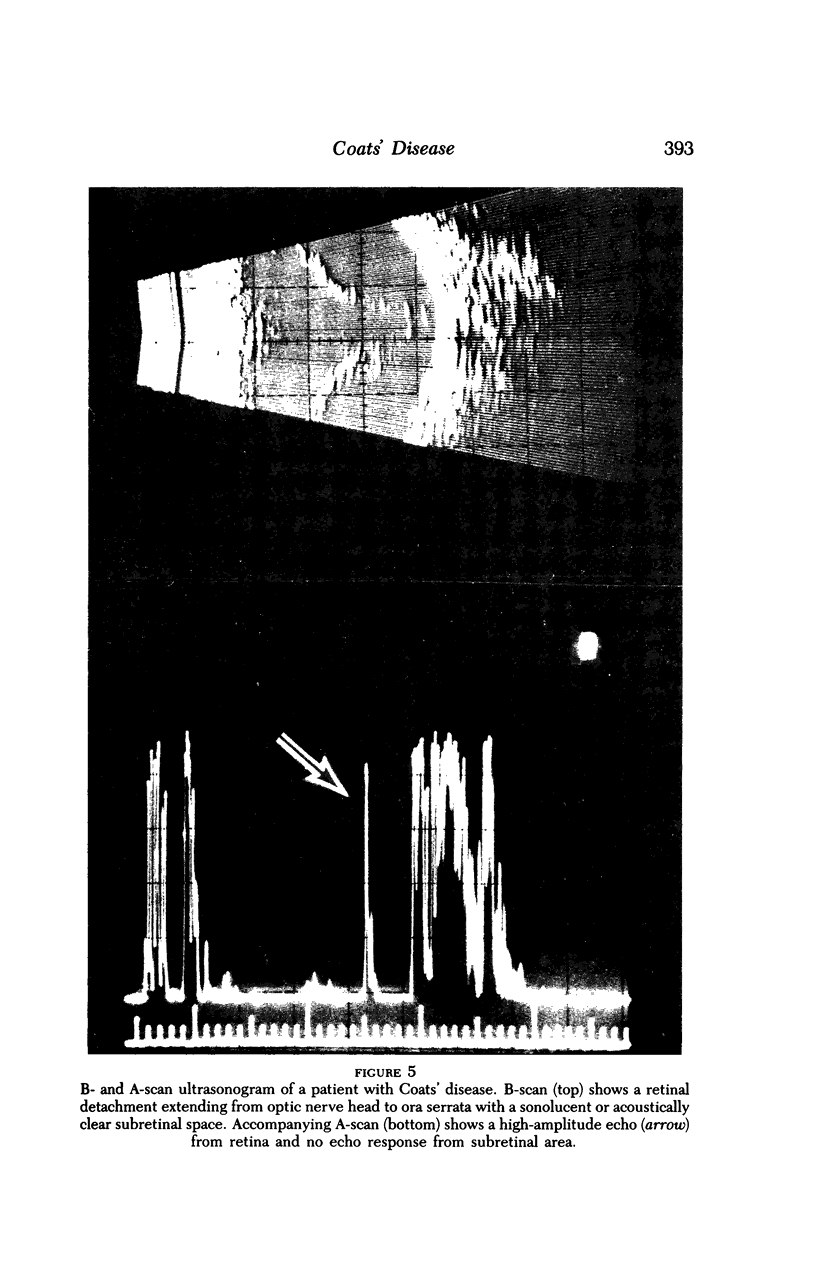
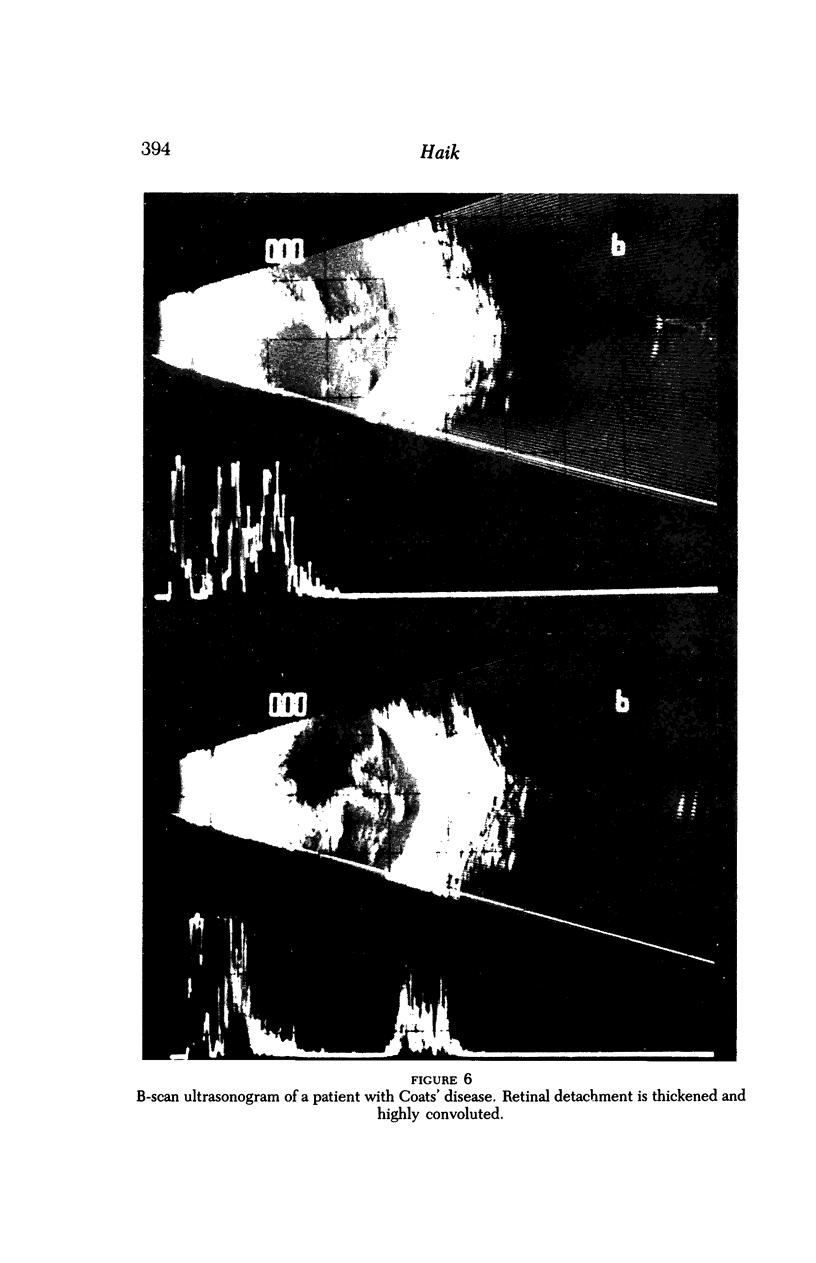

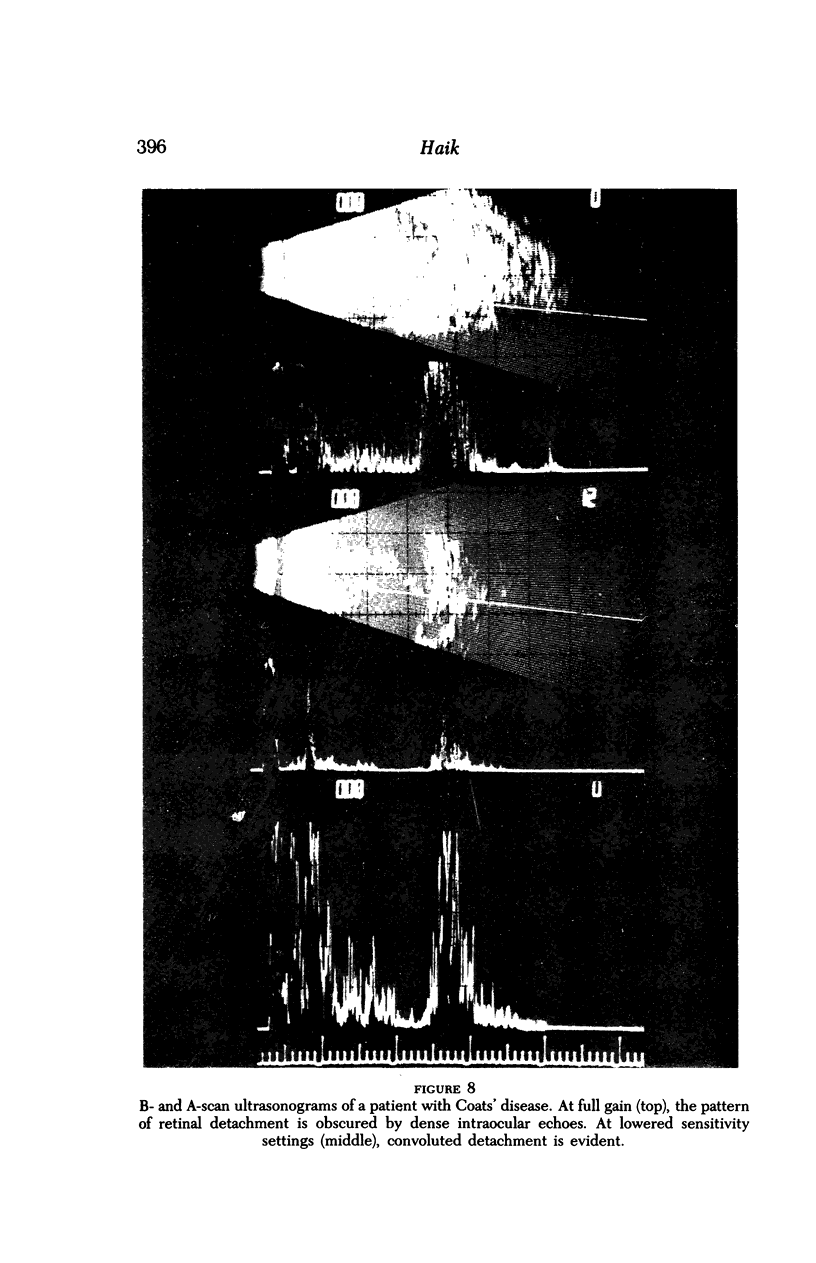

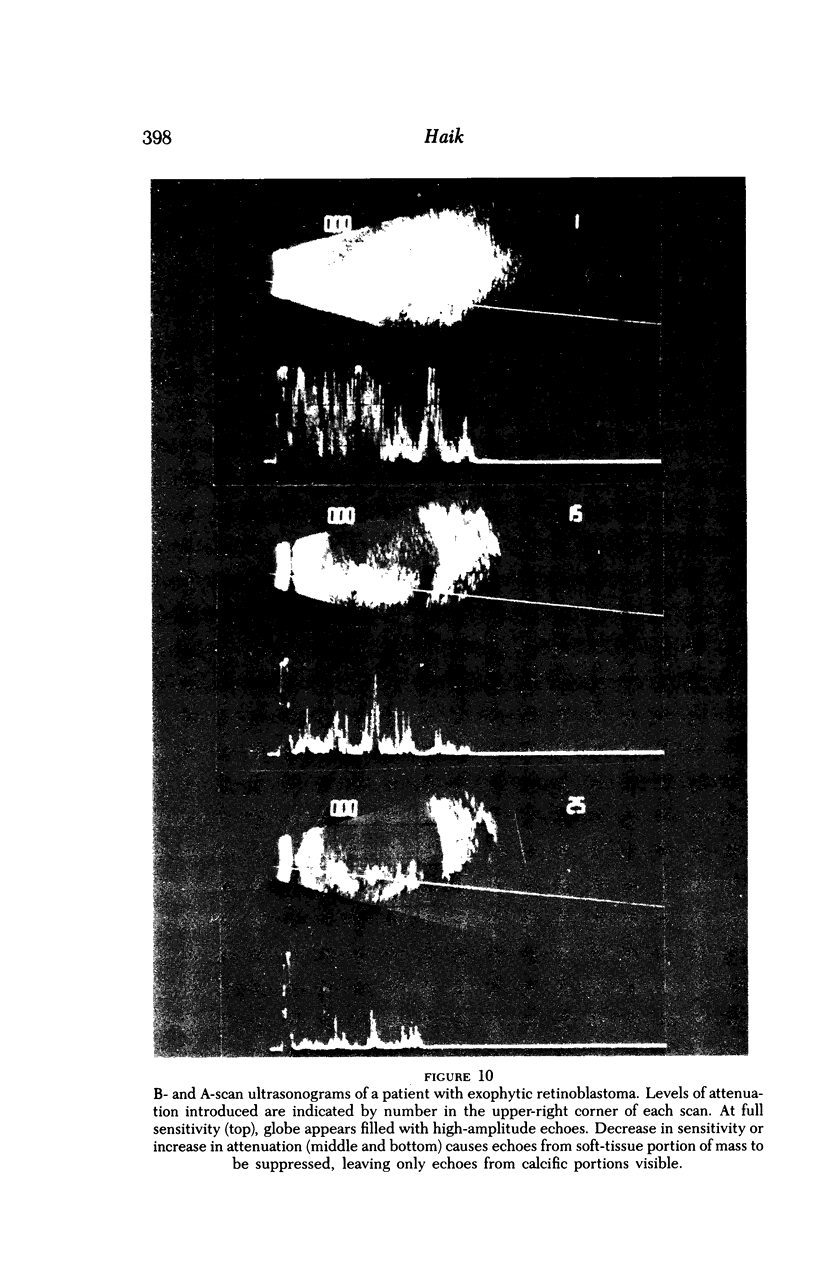

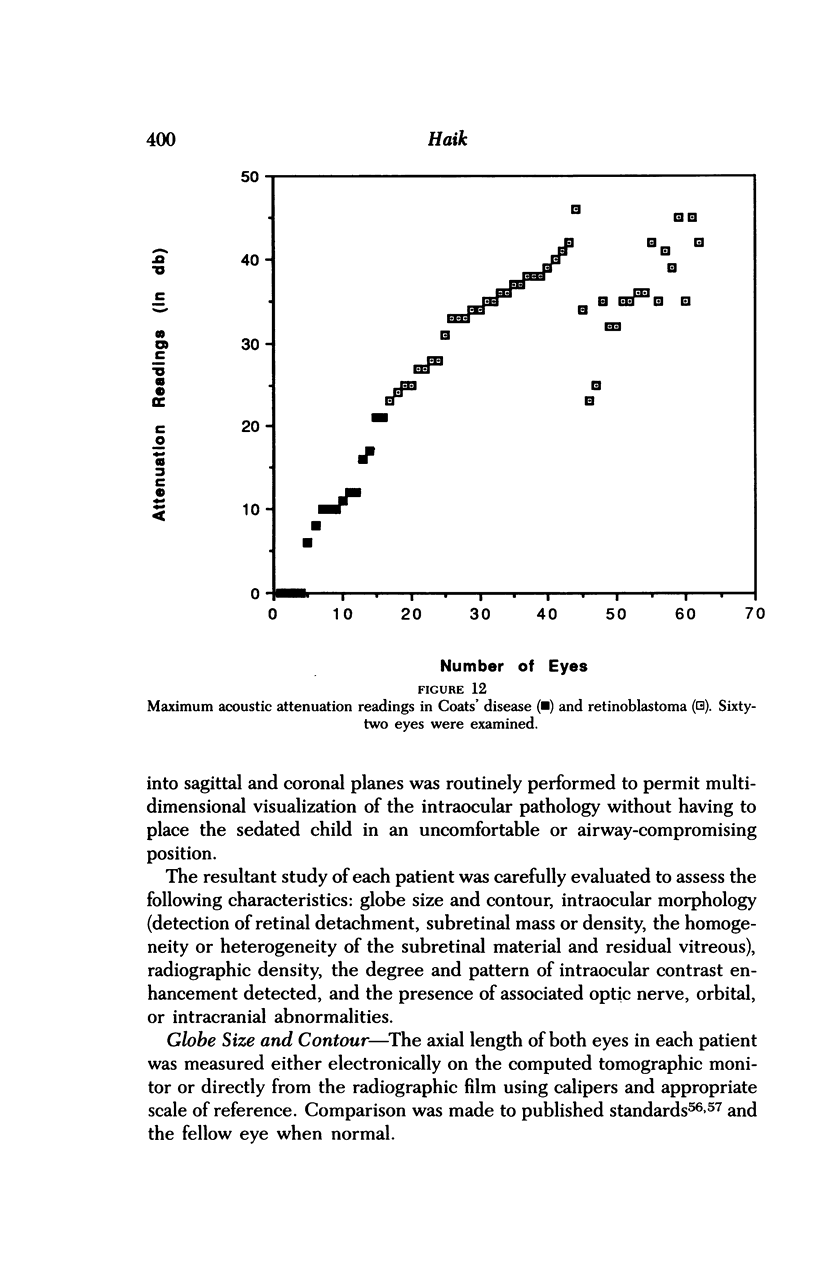

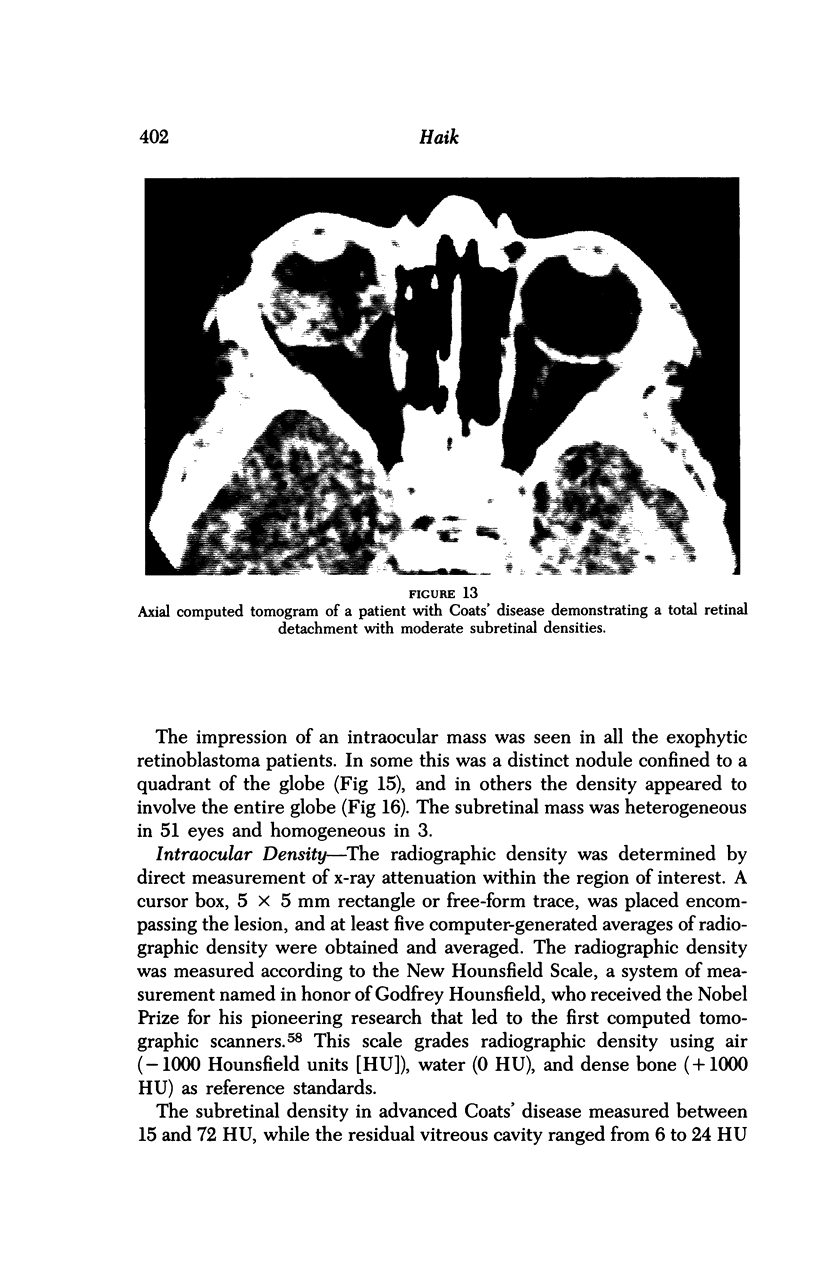
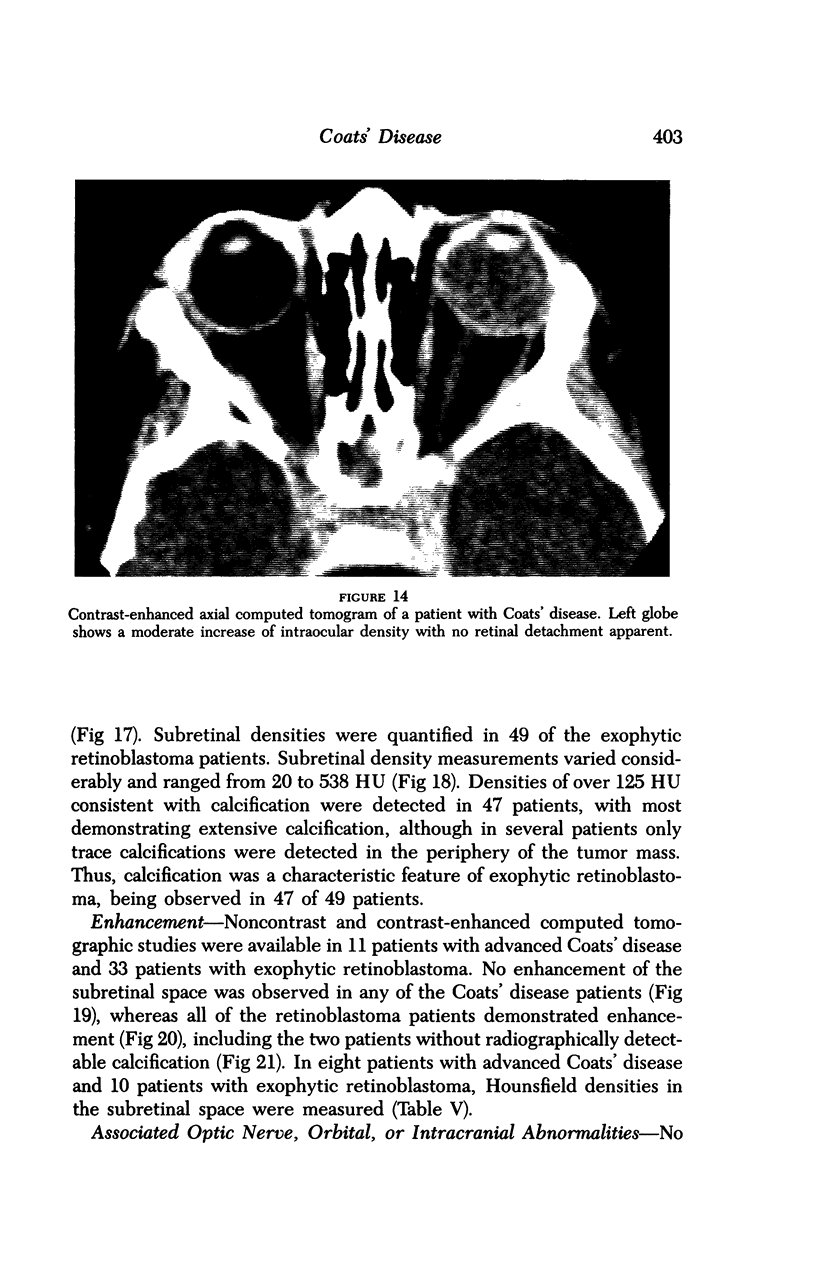

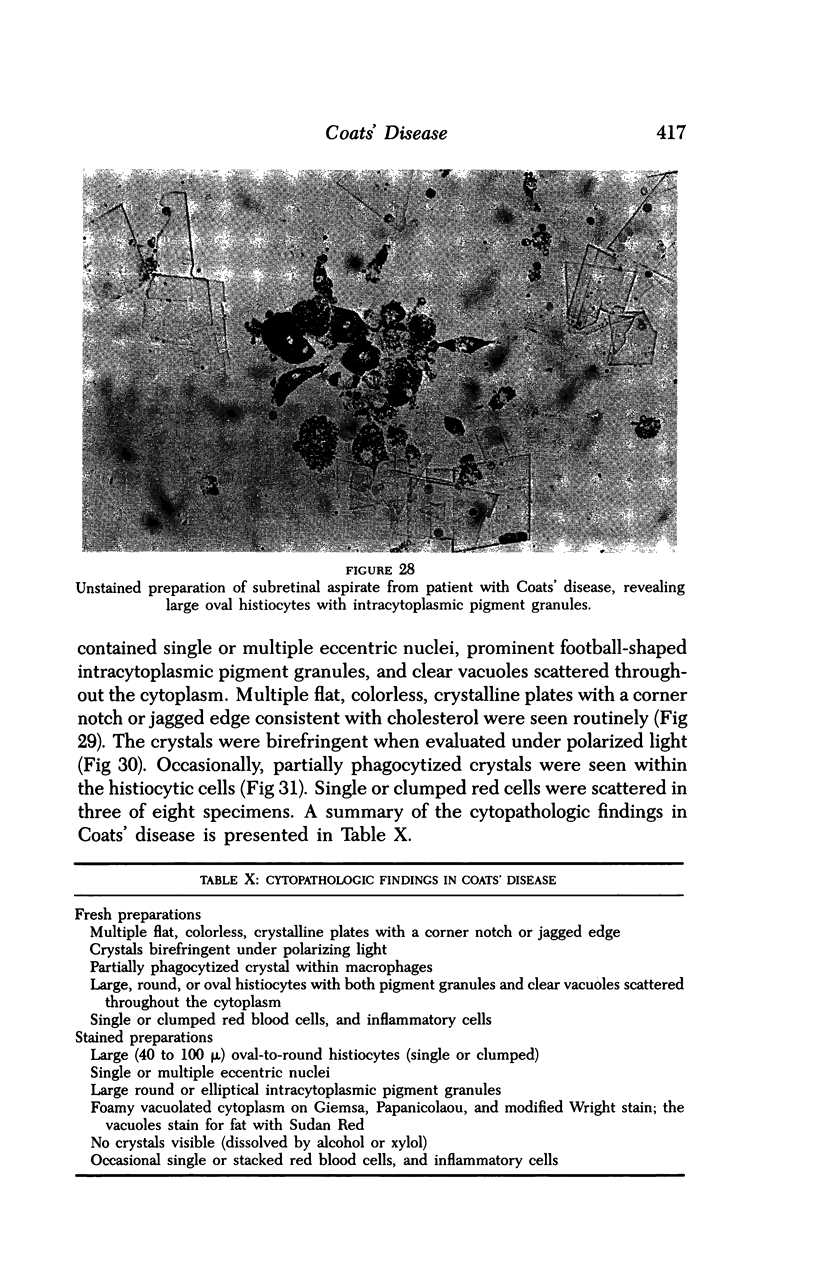

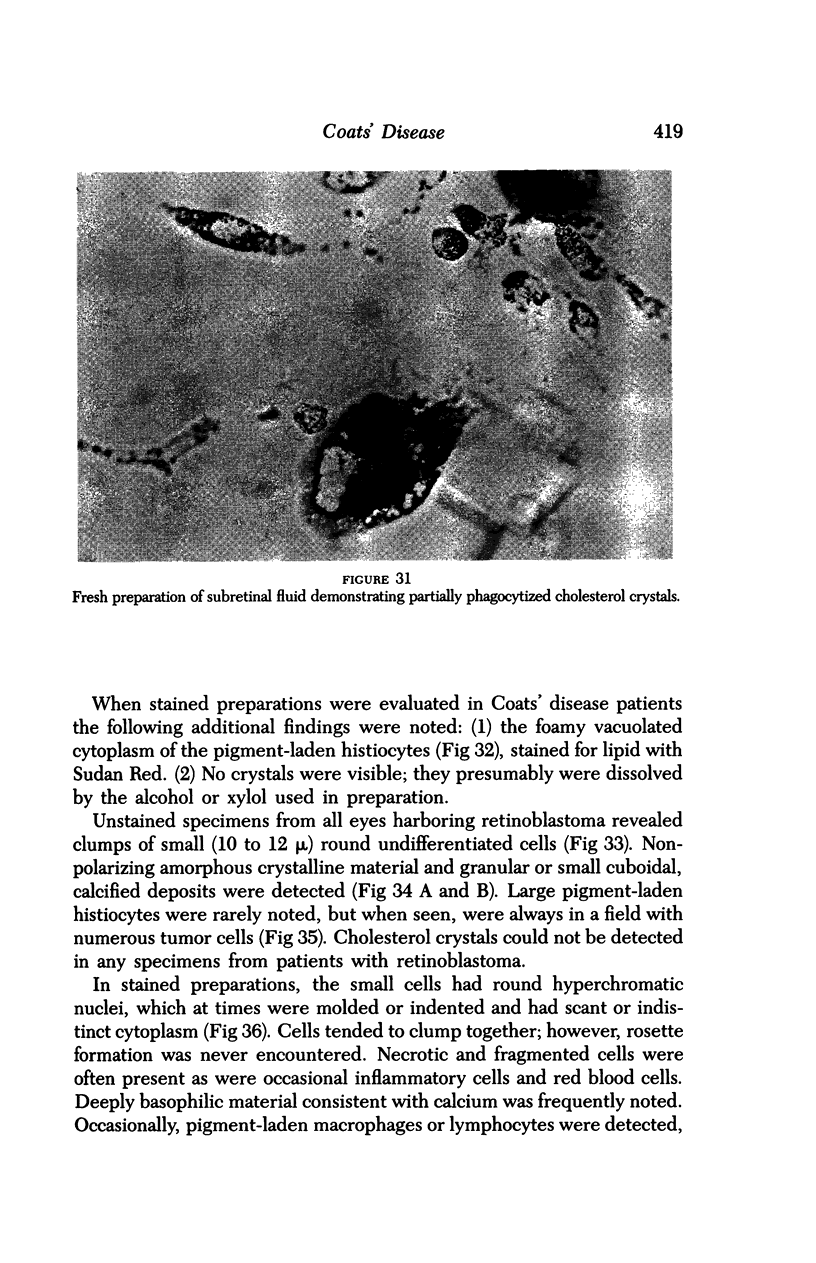
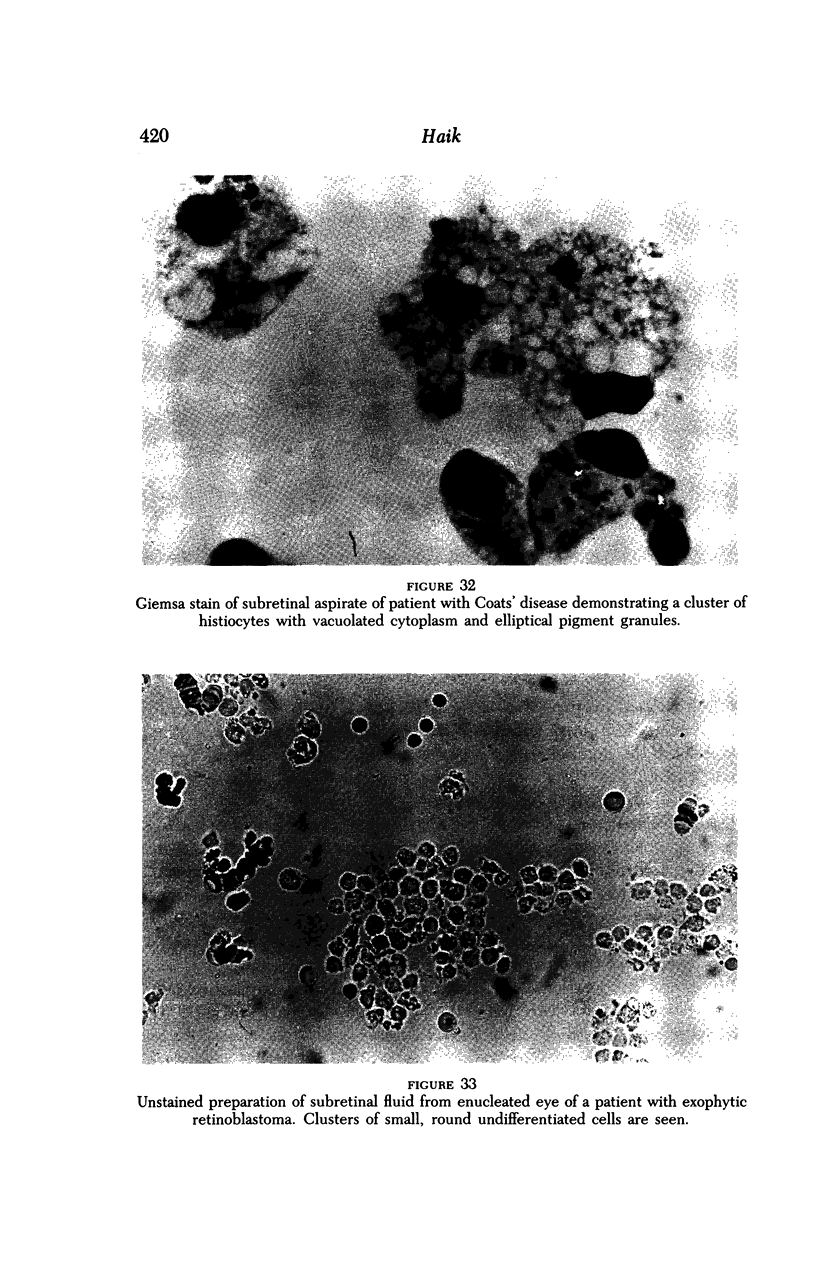
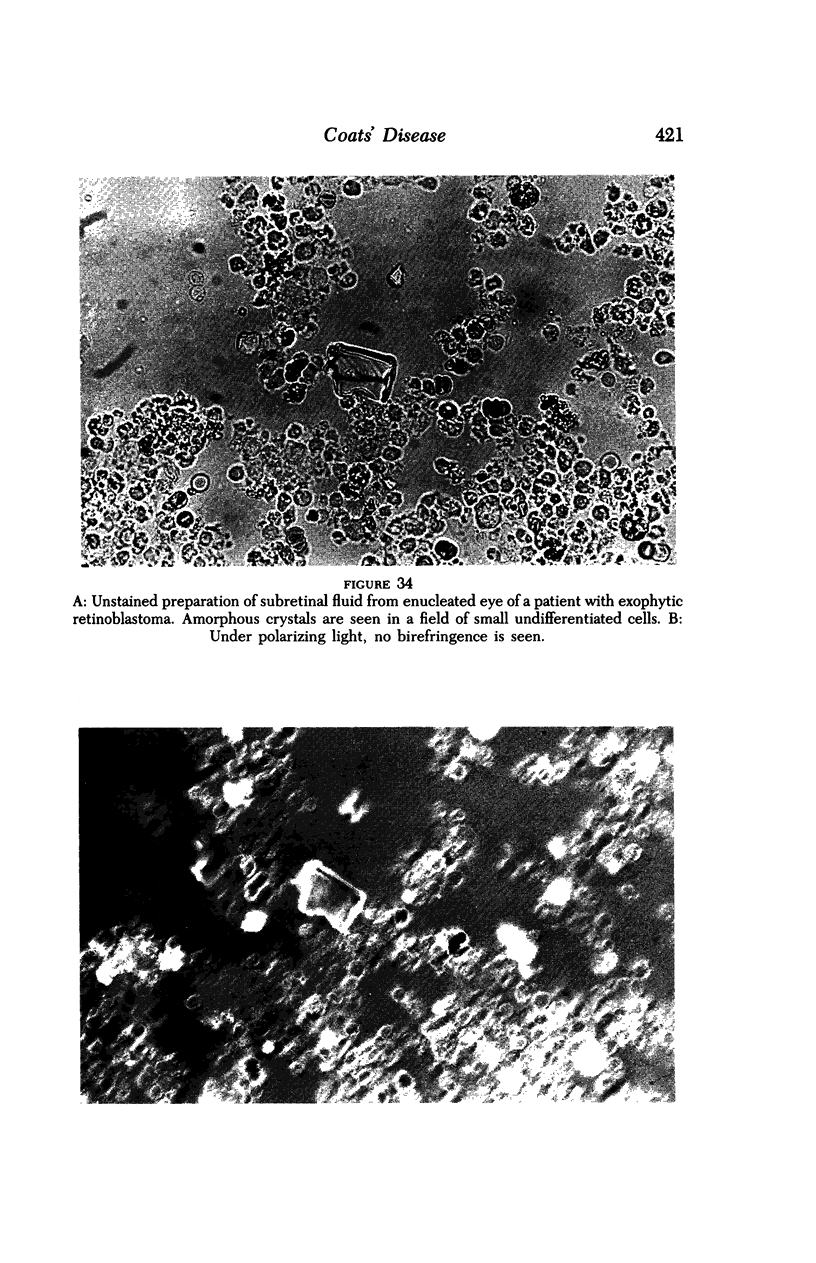
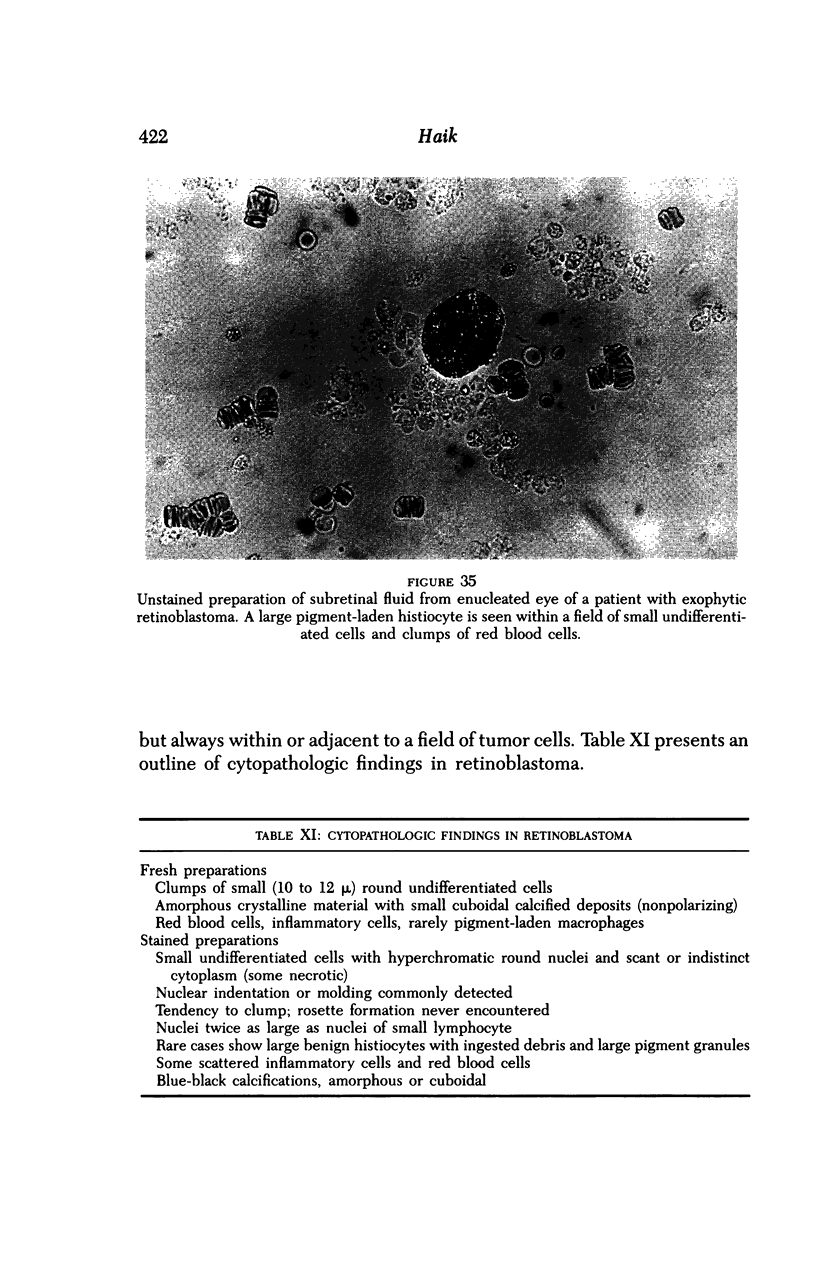





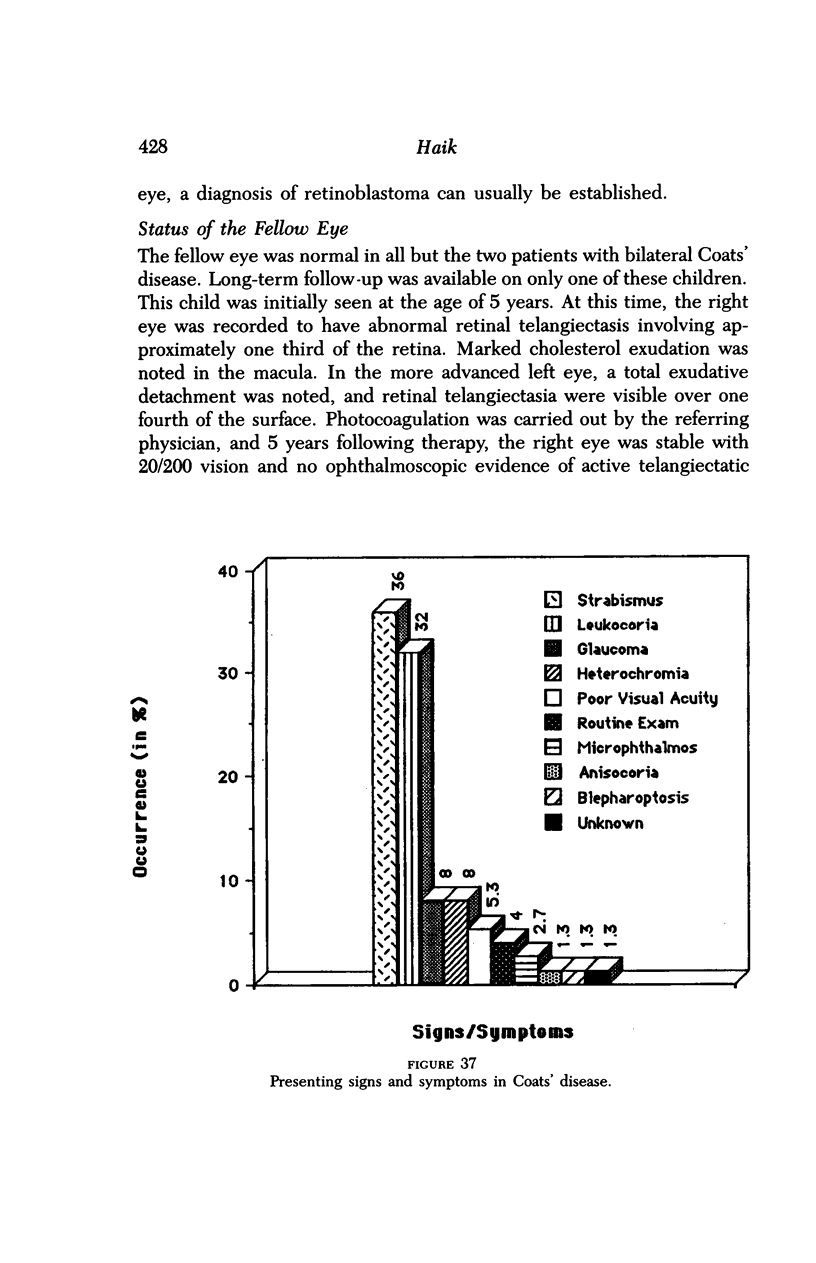


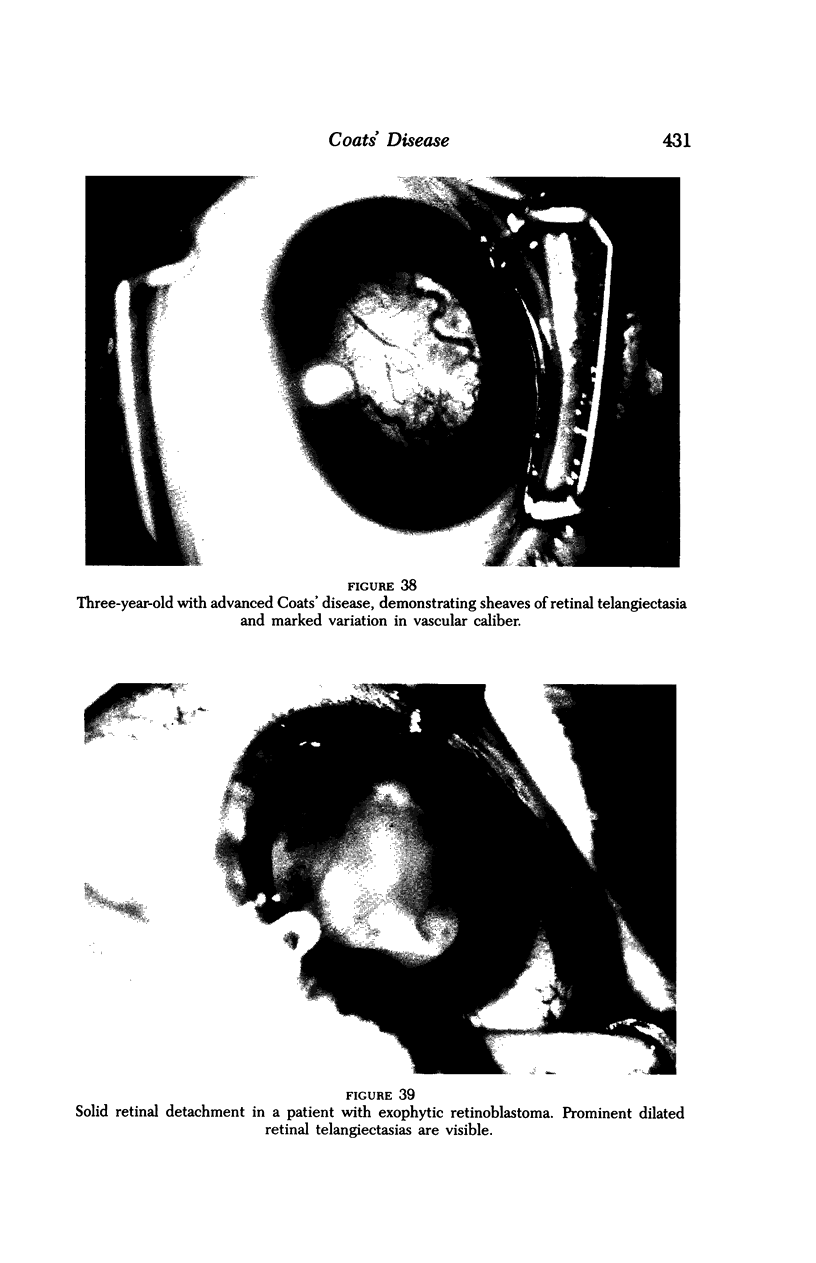
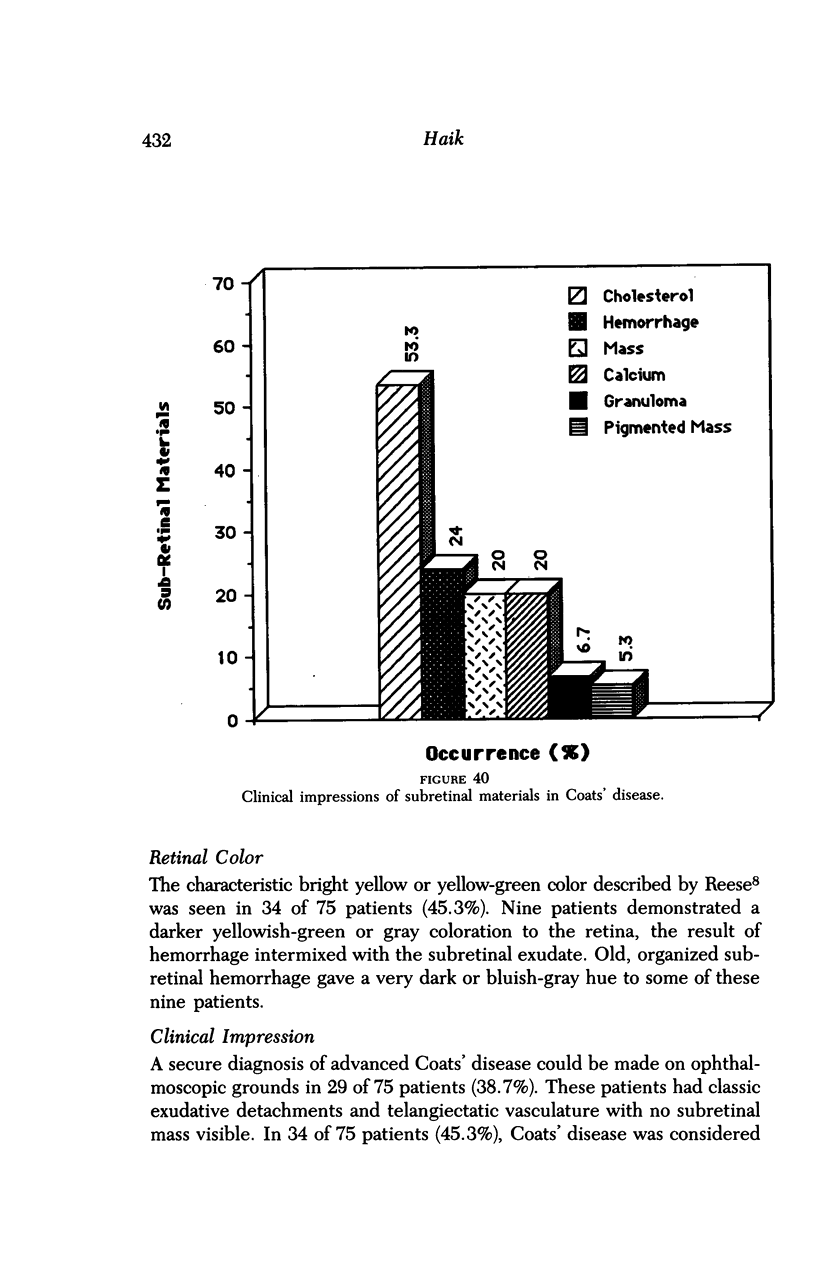




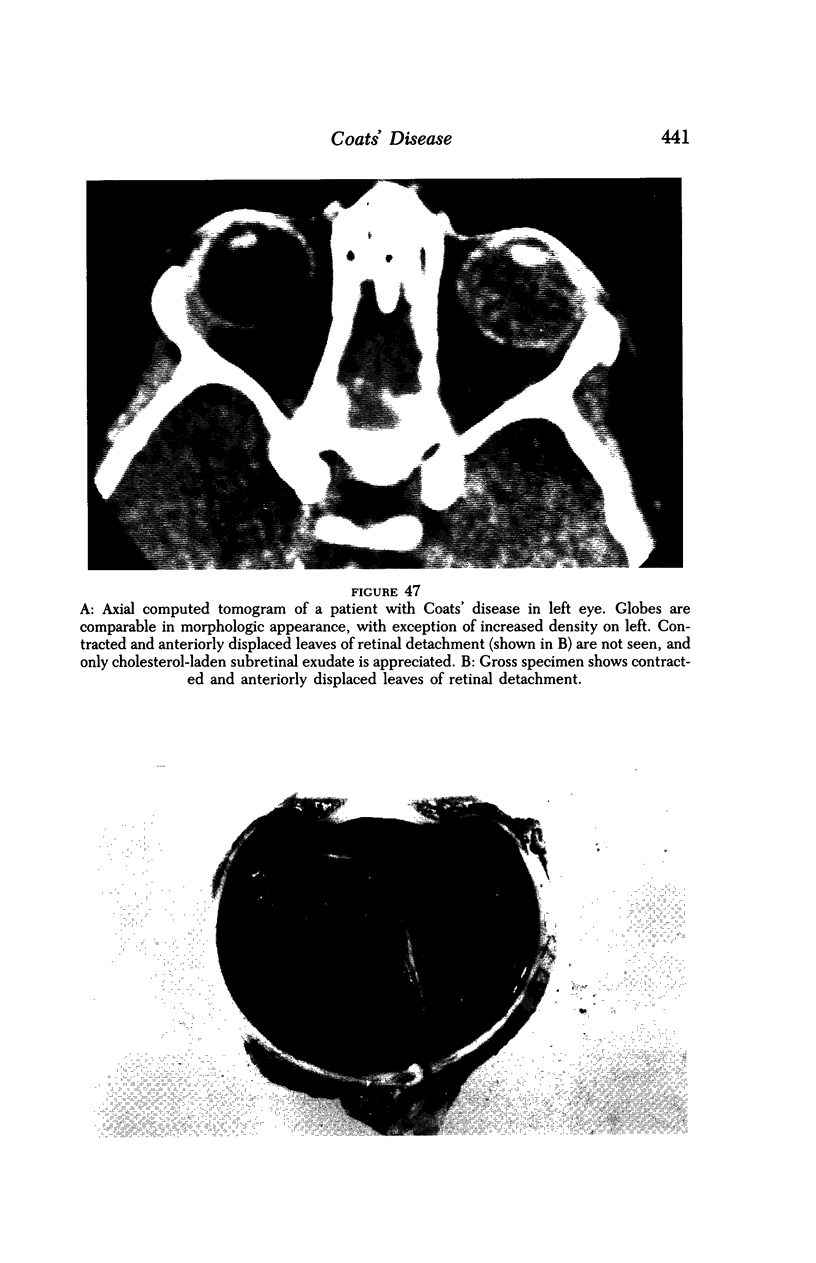

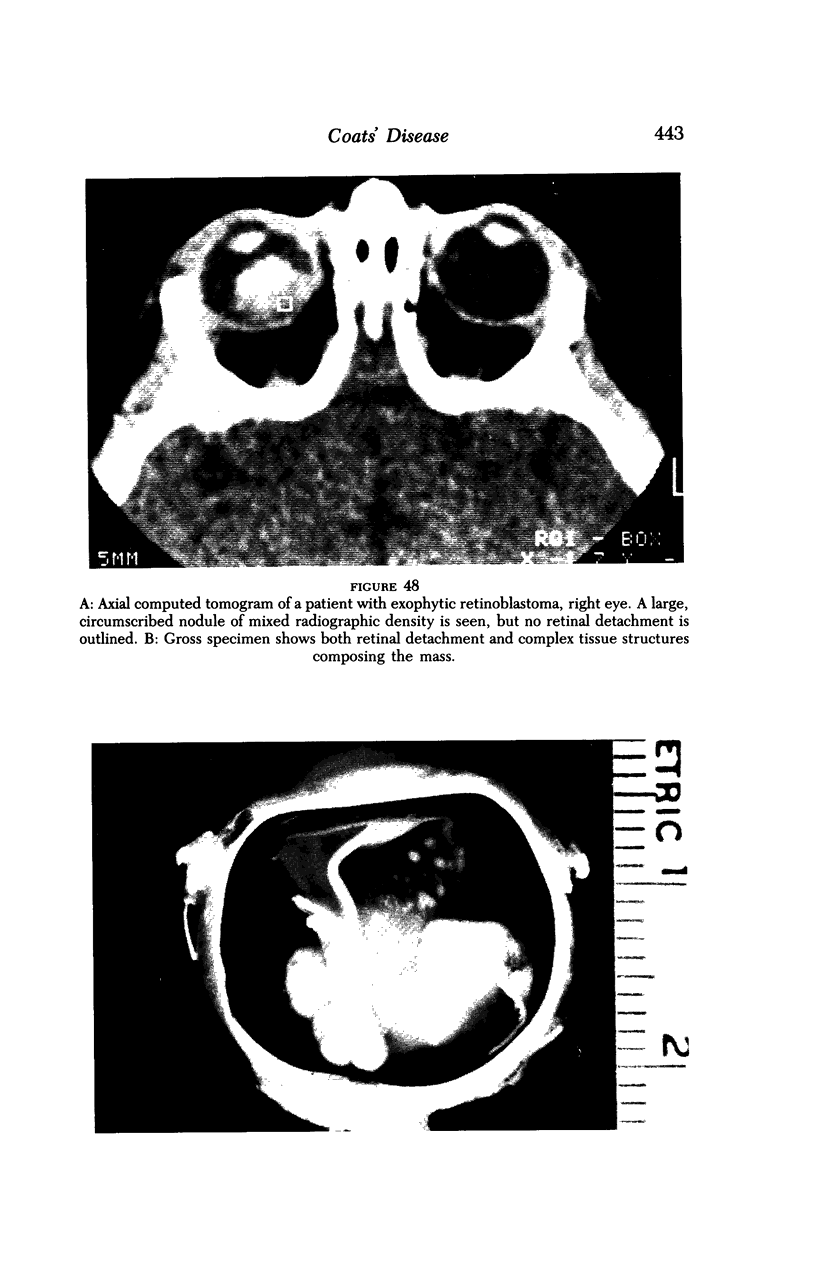
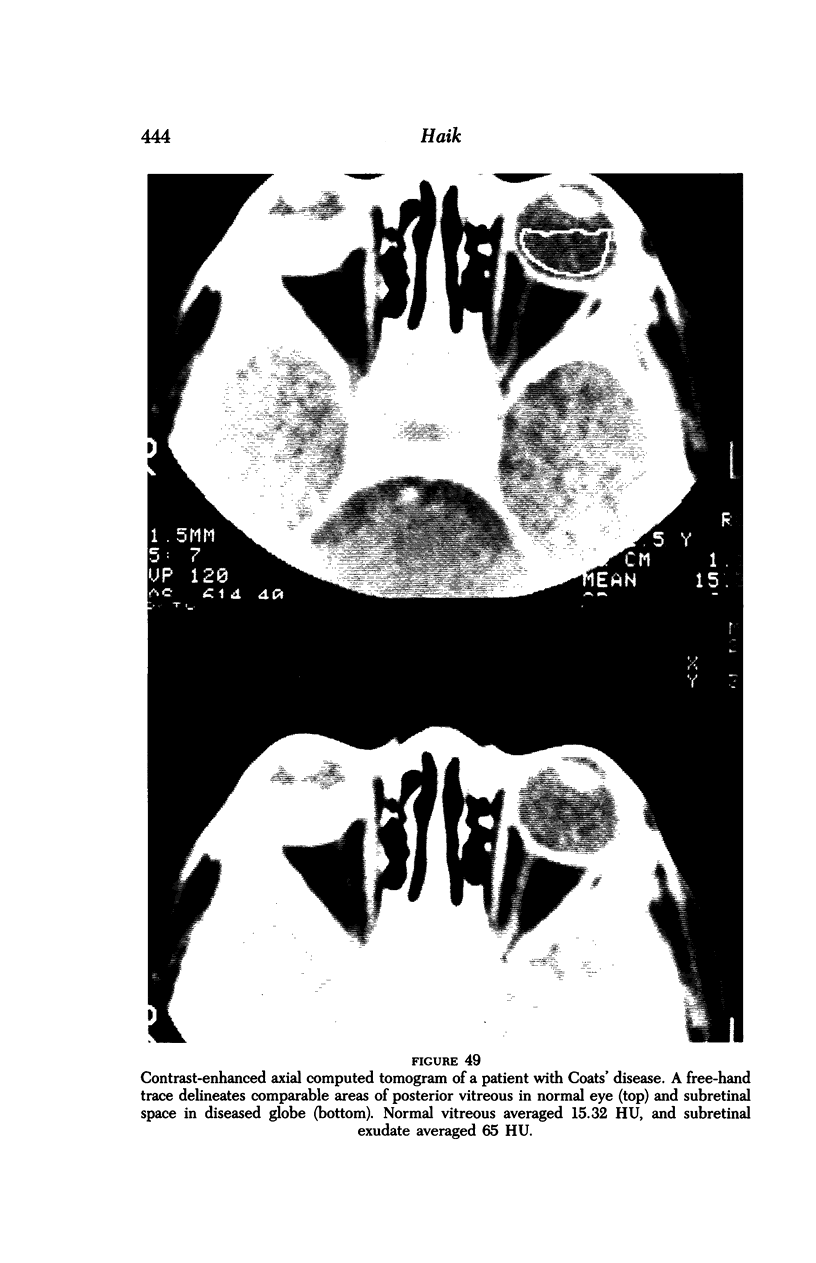


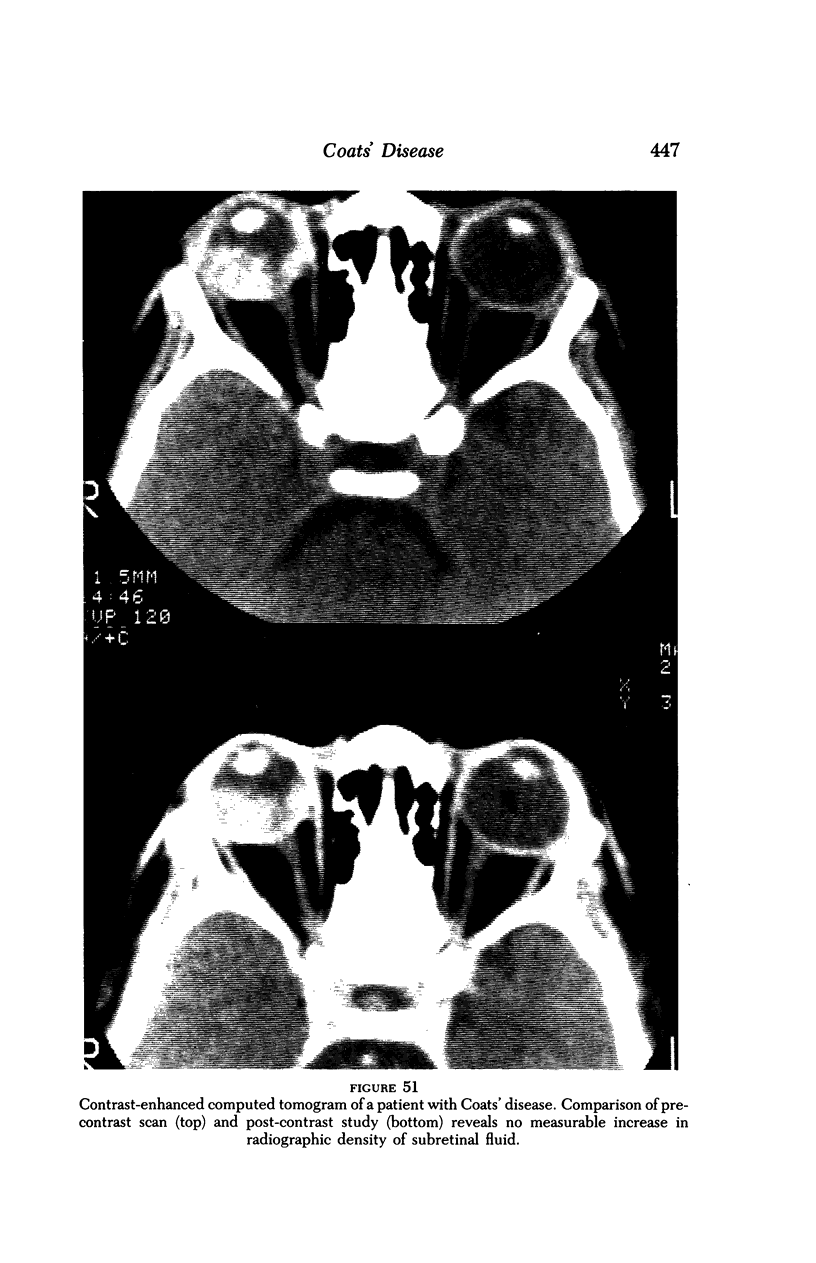






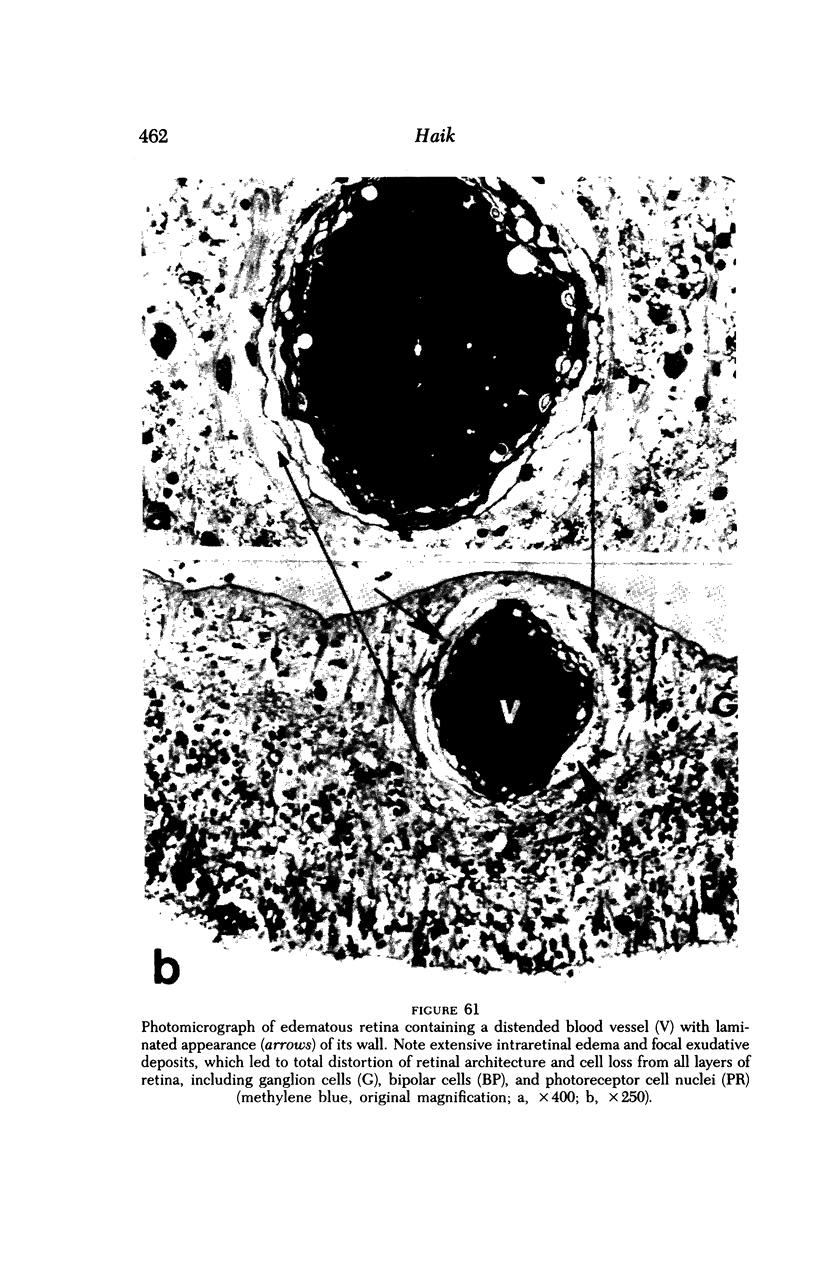

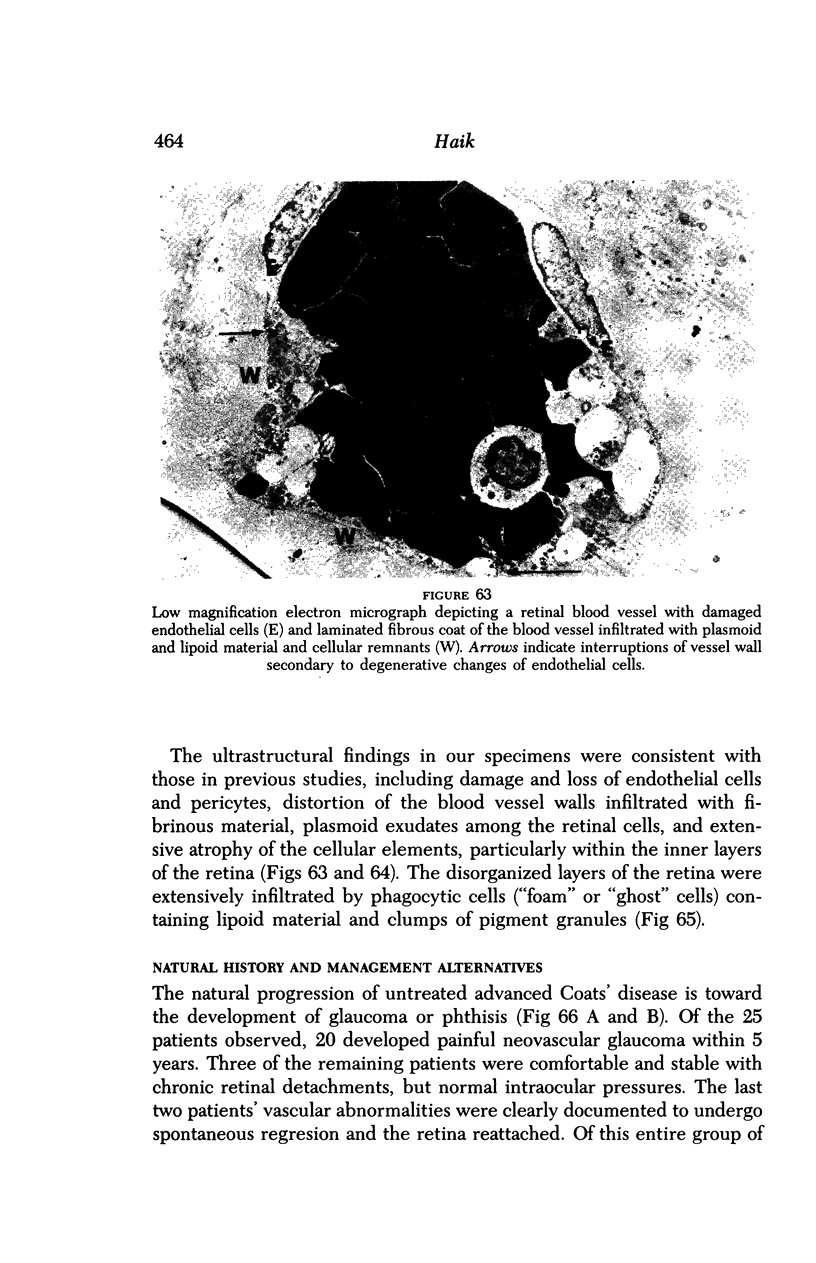
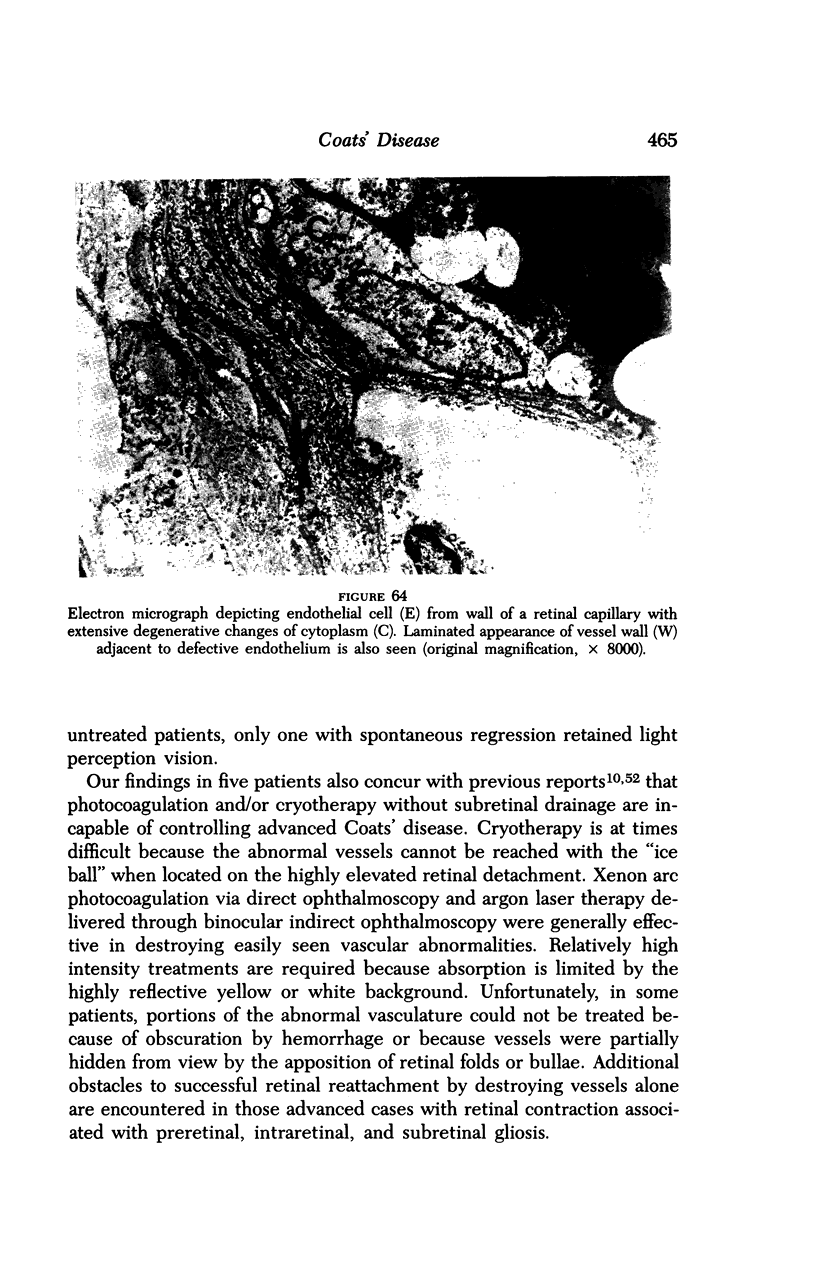
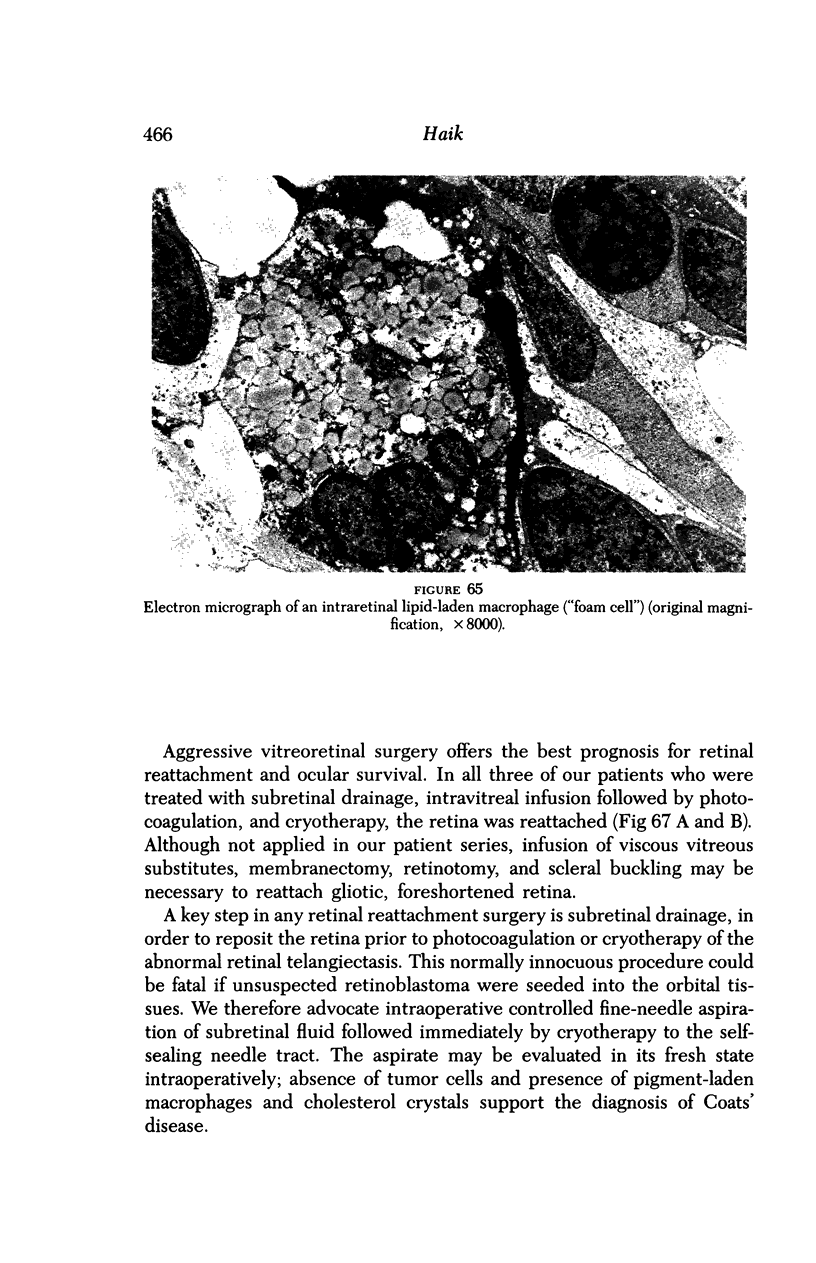
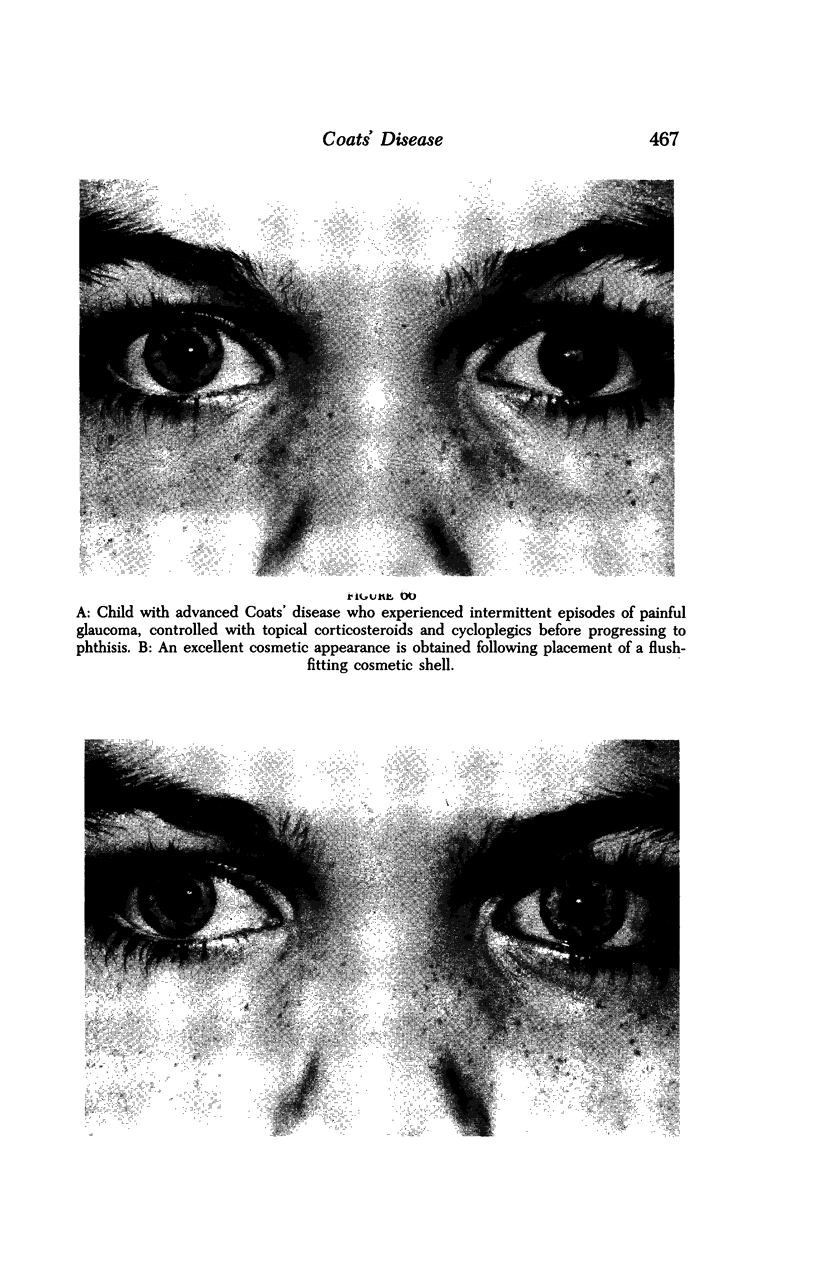
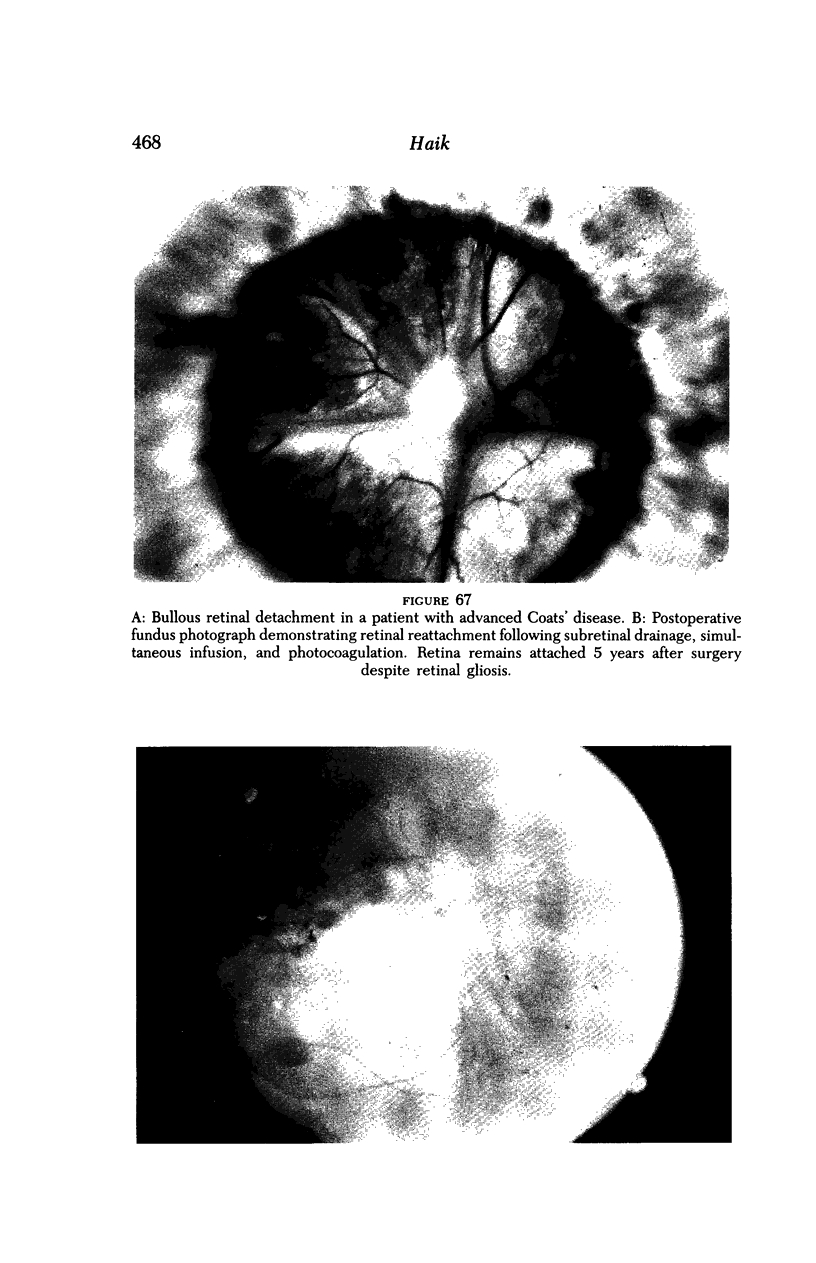








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramson D. H., Greenfield D. S., Ellsworth R. M., Fleisher M., Weiss R., Haik B., Schwartz M. K., Bhalla R. Neuron-specific enolase and retinoblastoma. Clinicopathologic correlations. Retina. 1989;9(2):148–152. doi: 10.1097/00006982-198909020-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abramson D. H., Piro P. A., Ellsworth R. M., Kitchin F. D., McDonald M. Lactate dehydrogenase levels and isozyme patterns. Measurements in the aqueous humor and serum of retinoblastoma patients. Arch Ophthalmol. 1979 May;97(5):870–871. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1979.01020010428004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen H. B., Parlette H. L. Coats disease. A condition that may mimic the Sturge-Weber syndrome. Arch Dermatol. 1973 Sep;108(3):413–415. doi: 10.1001/archderm.108.3.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrigg P. G., Lahav M., Hutchins R. K., Weiter J. J. Pigmentary retinal degeneration and Coats' disease: a case study. Ophthalmic Surg. 1988 Jun;19(6):432–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augsburger J. J., Shields J. A., Folberg R., Lang W., O'Hara B. J., Claricci J. D. Fine needle aspiration biopsy in the diagnosis of intraocular cancer. Cytologic-histologic correlations. Ophthalmology. 1985 Jan;92(1):39–49. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(85)34068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayesh I., Sanders M. D., Friedmann A. I. Retinitis pigmentosa and Coats's disease. Br J Ophthalmol. 1976 Nov;60(11):775–777. doi: 10.1136/bjo.60.11.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRINI A. Maladie de Coats; arguments en faveur de la thèse vasculaire. Bull Soc Ophtalmol Fr. 1957 Feb;(2):148–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks Anderson W., Jr, Wadsworth J. A., Landers M. B. Retinitis pigmentosa and a retinal vasculopathy of the Coats type. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1977;77:37–42. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4899-5010-9_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger M., Lieberman K. V., Schoeneman M. J., Schuman J. S., Friedman A. H. Coats' disease in a renal transplant recipient. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1987;2(2):120–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch J. V., Leveille A. S., Morse P. H. Ichthyosis hystrix (epidermal nevus syndrome) and Coats' disease. Am J Ophthalmol. 1980 Jan;89(1):25–30. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(80)90225-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron J. D., Yanoff M., Frayer W. C. Coats' disease and turner's syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol. 1974 Nov;78(5):852–854. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(74)90310-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell F. P. Coats' disease and congenital vascular retinopathy. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1976;74:365–424. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M. M., McLean I. W., Merritt J. C. Coats' disease: a study of 62 histologically confirmed cases. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1984 Sep-Oct;21(5):163–168. doi: 10.3928/0191-3913-19840901-03. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Char D. H., Hedges T. R., 3rd, Norman D. Retinoblastoma. CT diagnosis. Ophthalmology. 1984 Nov;91(11):1347–1350. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(84)34143-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Char D. H., Miller T. R. Fine needle biopsy in retinoblastoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 1984 Jun;97(6):686–690. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(84)90498-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUKE J. R., WOODS A. C. COATS'S DISEASE. II. STUDIES ON THE IDENTITY OF THE LIPIDS CONCERNED, AND THE PROBABLE ROLE OF MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDES IN ITS PATHOGENESIS. Br J Ophthalmol. 1963 Jul;47:413–434. doi: 10.1136/bjo.47.7.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danziger A., Price H. I. CT findings in retinoblastoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1979 Oct;133(4):695–697. doi: 10.2214/ajr.133.4.695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai U. R., Sabates F. N. Long-term follow-up of facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy and Coats' disease. Am J Ophthalmol. 1990 Nov 15;110(5):568–569. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)77885-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch T. A., Rabb M. F., Jampol L. M. Spontaneous regression of retinal lesions in Coats' disease. Can J Ophthalmol. 1982 Aug;17(4):169–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dias P. L., Shanmuganathan S. S., Rajaratnam M. Lactic dehydrogenase activity of aqueous humour in retinoblastoma. Br J Ophthalmol. 1971 Feb;55(2):130–132. doi: 10.1136/bjo.55.2.130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duke J. R. The Role of Cholesterol in the Pathogenesis of Coats' Disease. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1963;61:492–544. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egbert P. R., Chan C. C., Winter F. C. Flat preparations of the retinal vessels in Coats' disease. J Pediatr Ophthalmol. 1976 Nov-Dec;13(6):336–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egerer I., Tasman W., Tomer T. T. Coats disease. Arch Ophthalmol. 1974 Aug;92(2):109–112. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1974.01010010115006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellsworth R. M. The practical management of retinoblastoma. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1969;67:462–534. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farkas T. G., Potts A. M., Boone C. Some pathologic and biochemical aspects of Coats' disease. Am J Ophthalmol. 1973 Feb;75(2):289–301. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(73)91025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felberg N. T., McFall R., Shields J. A. Aqueous humor enzyme patterns in retinoblastoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1977 Nov;16(11):1039–1046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogle J. A., Welch R. B., Green W. R. Retinitis pigmentosa and exudative vasculopathy. Arch Ophthalmol. 1978 Apr;96(4):696–702. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1978.03910050386018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk J. C., Genovese F. N., Biglan A. W. Coats' disease in a patient with Cornelia de Lange syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol. 1981 May;91(5):607–610. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(81)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K. R. Coats' disease. Metab Pediatr Ophthalmol. 1980;4(3):121–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedenwald H., Friedenwald J. S. Terminal Stage in a Case of Retinitis with Massive Exudation. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1929;27:188–194. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedenwald H. Retinitis with Massive Exudation. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1914;13(Pt 3):819–850. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genkova P., Toncheva D., Tzoneva M., Konstantinov I. Deletion of 13q12.1 in a child with Coats disease. Acta Paediatr Hung. 1986;27(2):141–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitter K. A., Meyer D., White R. H., Jr, Ortolan G., Sarin L. K. Ultrasonic aid in the evaluation of leukocoria. Am J Ophthalmol. 1968 Feb;65(2):190–195. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(68)93586-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez Morales A. Coats' disease. Natural history and results of treatment. Am J Ophthalmol. 1965 Nov;60(5):855–865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon R. A., Donzis P. B. Myopia associated with retinopathy of prematurity. Ophthalmology. 1986 Dec;93(12):1593–1598. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(86)33523-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green W. R. Bilateral Coats' disease. Massive gliosis of the retina. Arch Ophthalmol. 1967 Mar;77(3):378–383. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1967.00980020380016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haik B. G., Koizumi J., Smith M. E., Ellsworth R. M. Fresh preparation of subretinal fluid aspirations in Coats' disease. Am J Ophthalmol. 1985 Aug 15;100(2):327–328. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(85)90803-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haik B. G., Saint Louis L., Smith M. E., Abramson D. H., Ellsworth R. M. Computed tomography of the nonrhegmatogenous retinal detachment in the pediatric patient. Ophthalmology. 1985 Aug;92(8):1133–1142. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(85)33920-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haik B. G., Saint Louis L., Smith M. E., Ellsworth R. M., Abramson D. H., Cahill P., Deck M., Coleman D. J. Magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of leukocoria. Ophthalmology. 1985 Aug;92(8):1143–1152. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(85)33915-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haik B. G., Zimmerman R., Saint Louis L. Gadolinium-DTPA enhancement of an optic nerve and chiasmal meningioma. J Clin Neuroophthalmol. 1989 Jun;9(2):122–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris G. J., Williams A. L., Reeser F. H., Abrams G. W. Intraocular evaluation by computed tomography. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 1982 Winter;22(4):197–217. doi: 10.1097/00004397-198202240-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris G. S. Coats' disease, diagnosis and treatment. Can J Ophthalmol. 1970 Oct;5(4):311–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckenlively J. Retinitis pigmentosa, unilateral Coats's disease, and thalassemia minor--a case report. Metab Pediatr Ophthalmol. 1981;5(2):67–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkind P., Morgan G. Peripheral retinal angioma with exudative retinopathy in adults (coats's lesion). Br J Ophthalmol. 1966 Jan;50(1):2–11. doi: 10.1136/bjo.50.1.2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper K. D., Haas D. K., Sherman J. L. The radiologic evaluation of congenital and pediatric lesions of the orbit. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 1988 Dec;9(6):413–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard G. M., Ellsworth R. M. Differential diagnosis of retinoblastoma. A statistical survey of 500 children. I. Relative frequency of the lesions which simulate retinoblastoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 1965 Oct;60(4):610–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höpping W. Erfahrungen mit der Lichtkoagulation bei Angiomatosis retinae, Miliaraneurysmenretinitis (Leber), Morbus Coats und ähnlichen Veränderungen. Bibl Ophthalmol. 1966;70:24–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe M. S., Shields J. A., Canny C. L., Eagle R. C., Jr, Fry R. L. Retinoblastoma simulating Coats' disease: a clinicopathologic report. Ann Ophthalmol. 1977 Jul;9(7):863–868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe M. S., Shields J. A., Canny C. L., Eagle R. C., Jr, Fry R. L. Retinoblastoma simulating Coats' disease: a clinicopathologic report. Ann Ophthalmol. 1977 Jul;9(7):863–868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobiec F. A., Abramson D., Scher R. Increased aqueous lactate dehydrogenase in Coats' disease. Am J Ophthalmol. 1978 May;85(5 Pt 1):686–689. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)77106-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabak J., Romano P. E. Aqueous humour lactic dehydrogenase isoenzymes in retinoblastoma. Br J Ophthalmol. 1975 May;59(5):268–269. doi: 10.1136/bjo.59.5.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko A., Suzuki H. [Lactic acid dehydrogenase activity and isozyme in the retinoblastoma]. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 1972 Aug;76(8):672–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karcioglu Z. A., Gordon R. A., Karcioglu G. L. Tumor seeding in ocular fine needle aspiration biopsy. Ophthalmology. 1985 Dec;92(12):1763–1767. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(85)34105-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato K., Asai R., Shimizu A., Suzuki F., Ariyoshi Y. Immunoassay of three enolase isozymes in human serum and in blood cells. Clin Chim Acta. 1983 Feb 7;127(3):353–363. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(83)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz N. N., Margo C. E., Dorwart R. H. Computed tomography with histopathologic correlation in children with leukokoria. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1984 Mar-Apr;21(2):50–56. doi: 10.3928/0191-3913-19840301-04. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan J. A., Ide C. H., Strickland M. P. Coats'-type retinitis pigmentosa. Surv Ophthalmol. 1988 Mar-Apr;32(5):317–332. doi: 10.1016/0039-6257(88)90094-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kivelä T. Neuron-specific enolase in retinoblastoma. An immunohistochemical study. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1986 Feb;64(1):19–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1986.tb06866.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremer I., Cohen S., Izhak R. B., Ben-Sira I. An unusual case of congenital unilateral Coats's disease associated with morning glory optic disc anomaly. Br J Ophthalmol. 1985 Jan;69(1):32–37. doi: 10.1136/bjo.69.1.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremer I., Nissenkorn I., Ben-Sira I. Cytologic and biochemical examination of the subretinal fluid in diagnosis of Coats' disease. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1989 Jun;67(3):342–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1989.tb01885.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier J. D., McCrary J. A., 3rd, Justice J. Autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa and Coats disease: a presumed familial incidence. Arch Ophthalmol. 1976 Oct;94(10):1737–1742. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1976.03910040511009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifshitz T., Tessler Z., Maor E., Yassur Y. Increased aqueous lactic dehydrogenase in Coat's disease. Ann Ophthalmol. 1987 Mar;19(3):116–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mafee M. F., Goldberg M. F., Cohen S. B., Gotsis E. D., Safran M., Chekuri L., Raofi B. Magnetic resonance imaging versus computed tomography of leukocoric eyes and use of in vitro proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of retinoblastoma. Ophthalmology. 1989 Jul;96(7):965–976. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(89)32773-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mafee M. F., Goldberg M. F., Greenwald M. J., Schulman J., Malmed A., Flanders A. E. Retinoblastoma and simulating lesions: role of CT and MR imaging. Radiol Clin North Am. 1987 Jul;25(4):667–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manschot W. A., de Bruijn W. C. Coats's disease: definition and pathogenesis. Br J Ophthalmol. 1967 Mar;51(3):145–157. doi: 10.1136/bjo.51.3.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margo C. E., Zimmerman L. E. Retinoblastoma: the accuracy of clinical diagnosis in children treated by enucleation. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1983 Nov-Dec;20(6):227–229. doi: 10.3928/0191-3913-19831101-02. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCrohan J. L., Patterson J. F., Gagne R. M., Goldstein H. A. Average radiation doses in a standard head examination for 250 CT systems. Radiology. 1987 Apr;163(1):263–268. doi: 10.1148/radiology.163.1.3823446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald M. B., Abramson D. H., Ellsworth R. M., Kitchin F. D. Lactate dehydrogenase levels and isoenzyme patterns in the serum and aqueous humor of adult cataract patients. Arch Ophthalmol. 1977 Nov;95(11):2068–2069. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1977.04450110162023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGettrick P. M., Loeffler K. U. Bilateral Coats' disease in an infant (a clinical, angiographic, light and electron microscopic study). Eye (Lond) 1987;1(Pt 1):136–145. doi: 10.1038/eye.1987.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrand J. C. Photocoagulation in Coats' disease. Trans Ophthalmol Soc U K. 1970;90:47–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyashita S., Nisyake Y. THE PATHOLOGICAL ANATOMY OF RETINAL DEGENERATION WITH MULTIPLE ANEURYSMS. Br J Ophthalmol. 1921 Oct;5(10):448–453. doi: 10.1136/bjo.5.10.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondon H., Hamard H., Girard P., Brégeat P. A propos d'un cas de gliose rétinienne au cours d'une maladie de Coats. Bull Soc Ophtalmol Fr. 1970 Sep-Oct;70(9):881–883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. E., 3rd, Crawford J. B. Retinitis pigmentosa and Coats' disease. Arch Ophthalmol. 1968 Feb;79(2):146–149. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1968.03850040148006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouillac-Gambarelli N., Hervé Fey B., Vila J. P. Toxoplasmose et maladie de Coats. Un cas chez une jeune fille de 20 ans. Bull Mem Soc Fr Ophtalmol. 1982;94:429–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima T., Kato K., Kaneko A., Tsumuraya M., Morinaga S., Shimosato Y. High concentrations of enolase, alpha- and gamma-subunits, in the aqueous humor in cases of retinoblastoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 1986 Jan 15;101(1):102–106. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(86)90471-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAUFIQUE L., CHARLEUX J. [Leber's retinal angiomatosis (treatment by photocoagulation)]. Bull Soc Ophtalmol Fr. 1961 May-Jun;5:479–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parma A. M., Marangos P. J., Goodwin F. K. A more sensitive radioimmunoassay for neuron-specific enolase suitable for cerebrospinal fluid determinations. J Neurochem. 1981 Mar;36(3):1093–1096. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb01704.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pe'er J. Calcifications in Coats' disease. Am J Ophthalmol. 1988 Dec 15;106(6):742–743. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(88)90714-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piro P. A., Jr, Abramson D. H., Ellsworth R. M., Kitchin D. Aqueous humor lactate dehydrogenase in retinoblastoma patients. Clinicopathologic correlations. Arch Ophthalmol. 1978 Oct;96(10):1823–1825. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1978.03910060335007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REESE A. B. Telangiectasis of the retina and Coats' disease. Am J Ophthalmol. 1956 Jul;42(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(56)90002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley M. E., Shields J. A., Brown G. C., Tasman W. Coats' disease. Evaluation of management. Ophthalmology. 1982 Dec;89(12):1381–1387. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(82)34634-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUGAR H. S. Coats' disease: telangiectatic or multiple vascular origin. Am J Ophthalmol. 1958 Apr;45(4 Pt 1):508–517. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(58)90520-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt D., Faulborn J. Retinopathia pigmentosa mit Coats-Syndrom. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 1970 Nov;157(5):643–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuman J. S., Lieberman K. V., Friedman A. H., Berger M., Schoeneman M. J. Senior-Loken syndrome (familial renal-retinal dystrophy) and Coats' disease. Am J Ophthalmol. 1985 Dec 15;100(6):822–827. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)73374-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman J. L., McLean I. W., Brallier D. R. Coats' disease: CT-pathologic correlation in two cases. Radiology. 1983 Jan;146(1):77–78. doi: 10.1148/radiology.146.1.6849070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields J. A., Augsburger J. J. Current approaches to the diagnosis and management of retinoblastoma. Surv Ophthalmol. 1981 May-Jun;25(6):347–372. doi: 10.1016/0039-6257(81)90072-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine B. S., Hungerford J., Vaghela B., Sheraidah G. A. Electrophoretic assessment of aqueous and serum neurone-specific enolase in retinoblastoma and ocular malignant melanoma. Br J Ophthalmol. 1990 Jul;74(7):427–430. doi: 10.1136/bjo.74.7.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silodor S. W., Augsburger J. J., Shields J. A., Tasman W. Natural history and management of advanced Coats' disease. Ophthalmic Surg. 1988 Feb;19(2):89–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skuta G. L., France T. D., Stevens T. S., Laxova R. Apparent Coats' disease and pericentric inversion of chromosome 3. Am J Ophthalmol. 1987 Jul 15;104(1):84–86. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(87)90299-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small R. G. Coats' disease and muscular dystrophy. Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1968 Mar-Apr;72(2):225–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spallone A., Carlevaro G., Ridling P. Autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa and Coats'-like disease. Int Ophthalmol. 1985 Sep;8(3):147–151. doi: 10.1007/BF00136491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spallone A. Exudative retinitis pigmentosa. Ophthalmologica. 1988;197(4):185–192. doi: 10.1159/000309942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitznas M., Joussen F., Wessing A., Meyer-Schwickerath G. Coat's disease. An epidemiologic and Fluorescein angiographic study. Albrecht Von Graefes Arch Klin Exp Ophthalmol. 1975 Jul 4;195(4):241–250. doi: 10.1007/BF00414937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterns G. K., Coleman D. J., Ellsworth R. M. The ultrasonographic characteristics of retinoblastoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 1974 Oct;78(4):606–611. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)76297-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartz M., Herbst R. W., Goldberg M. F. Aqueous humor lactic acid dehydrogenase in retinoblastoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 1974 Oct;78(4):612–617. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)76298-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takei Y. Origin of ghost cell in Coats' disease. Invest Ophthalmol. 1976 Aug;15(8):677–681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarkkanen A., Laatikainen L. Coat's disease: clinical, angiographic, histopathological findings and clinical management. Br J Ophthalmol. 1983 Nov;67(11):766–776. doi: 10.1136/bjo.67.11.766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodossiadis G. P. Some clinical, fluorescein-angiographic, and therapeutic-aspects of Coats' disease. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1979 Jul-Aug;16(4):257–262. doi: 10.3928/0191-3913-19790701-12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolmie J. L., Browne B. H., McGettrick P. M., Stephenson J. B. A familial syndrome with coats' reaction retinal angiomas, hair and nail defects and intracranial calcification. Eye (Lond) 1988;2(Pt 3):297–303. doi: 10.1038/eye.1988.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi R., Ashton N. Electron microscopical study of Coat's disease. Br J Ophthalmol. 1971 May;55(5):289–301. doi: 10.1136/bjo.55.5.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Törnquist R. The treatment of Coats' disease. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1966;44(3):457–459. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1966.tb08059.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WISE G. N. Coats' disease. AMA Arch Ophthalmol. 1957 Nov;58(5):735–746. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1957.00940010757013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOODS A. C., DUKE J. R. COATS'S DISEASE. I. REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE, DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA, CLINICAL FINDINGS, AND PLASMA LIPID STUDIES. Br J Ophthalmol. 1963 Jul;47:385–412. doi: 10.1136/bjo.47.7.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilensky J. T., Goldberg M. F., Ziyai F., Wong P. W. Infantile cataracts, Coats' disease, and ketotic hypoglycemia. J Pediatr Ophthalmol. 1976 Mar;13(2):75–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuguchi M., Majima A. A case of retinitis pigmentosa associated with Coats' syndrome. Ophthalmic Paediatr Genet. 1984 Dec;4(3):177–182. doi: 10.3109/13816818409006118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeltzer P. M., Marangos P. J., Evans A. E., Schneider S. L. Serum neuron-specific enolase in children with neuroblastoma. Relationship to stage and disease course. Cancer. 1986 Mar 15;57(6):1230–1234. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19860315)57:6<1230::aid-cncr2820570628>3.0.co;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman C. F., Schatz N. J., Glaser J. S. Magnetic resonance imaging of optic nerve meningiomas. Enhancement with gadolinium-DTPA. Ophthalmology. 1990 May;97(5):585–591. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(90)32538-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman R. A., Bilaniuk L. T. Computed tomography in the evaluation of patients with bilateral retinoblastomas. J Comput Tomogr. 1979 Dec;3(4):251–257. doi: 10.1016/0149-936x(79)90028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]