Abstract
Estrogens induce cell proliferation in target tissues by stimulating progression through the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Activation of cyclin D1 gene expression is a critical feature of this hormonal action. The existence of rapid/nongenomic estradiol-regulated protein kinase C (PKC-α) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signal transduction pathways, their cross talk, and role played in DNA synthesis and cyclin D1 gene transcription have been studied herein in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. 17β-Estradiol was found to rapidly activate PKC-α translocation and ERK-2/mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylation in this cell line. These actions were independent of each other, preceding the increase of thymidine incorporation into DNA and cyclin D1 expression, and did not involve DNA binding by estrogen receptor. The results obtained with specific inhibitors indicated that PKC-α pathway is necessary to mediate the estradiol-induced G1-S progression of HepG2 cells, but it does not exert any effect(s) on cyclin D1 gene expression. On the contrary, ERK-2 cascade was strongly involved in both G1-S progression and cyclin D1 gene transcription. Deletion of its activating protein-1 responsive element motif resulted in attenuation of cyclin D1 promoter responsiveness to estrogen. These results indicate that estrogen-induced cyclin D1 transcription can occur in HepG2 cells independently of the transcriptional activity of estrogen receptor, sustaining the pivotal role played by nongenomic pathways of estrogen action in hormone-induced proliferation.
INTRODUCTION
17β-Estradiol (E2) is strongly connected with liver development (Fisher et al., 1984), the regulation of hepatic metabolic pathways (Di Croce et al., 1996, 1997, 1999; Distefano et al., 2002) as well as with the progression of hepatocarcinogenesis (Yager et al., 1986; Chen et al., 1999). The E2 action mechanism to induce carcinogenesis has been the object of extensive studies in mammary carcinoma cells, which revealed an increased proportion of DNA-synthesizing cells by the recruitment of noncycling cells into the cell cycle and by a reduction of G1 phase duration in the already cycling cells (Sutherland et al., 1983; Foster et al., 2001). There is considerable evidence that cyclin D1, important for progression of cells through the G1 phase of the cell cycle, is a well-defined target for E2 action in mammary carcinoma cells (Altucci et al., 1996; Foster and Wimalasena, 1996; Prall et al., 1997), although no detectable estrogen-responsive element (ERE)-like sequence in the cyclin D1 gene promoter has been reported (Herber et al., 1994). The cyclin D1 activation mechanisms identified in different mammary carcinoma cells (i.e., up-regulation of c-jun and direct interaction estrogen receptor [ER]α/stimulating protein 1, SP1, or ERα/activating protein-1, AP-1) underlined the strict cell context dependence (Foster et al., 2001).
Recently, rapid/nongenomic effects of estradiol, potentially able to regulate cell proliferation, have been reported (McEwen and Alves, 1999); in particular, in the human hepatoma cell line HepG2, the inositol trisphosphate/protein kinase C-α (IP3/PKC-α) signal transduction pathway is induced just 1 min after E2 addition (Marino et al., 1998). The E2-induced activation of this signal pathway is sufficient to drive HepG2 cells into the S phase of the cell cycle, although the presence of ER in these cells is very low and insufficient to induce transactivation of ERE-containing synthetic target genes (Marino et al., 2001). As far we know, the presence of other signal pathways described in mammary carcinoma cells (i.e., mitogen-activated protein [MAP] kinase pathway) (Castoria et al., 1999), their cross talk with IP3/PKC-α signal transduction, and their relationship with E2-induced G1-S transition are completely unknown in hepatoma cells.
In this work, the ability of E2 to stimulate both PKC-α translocation from cytosol to membrane and extracellular signal regulated kinase-2 (ERK-2) phosphorylation, as well as the cross talk and involvement in DNA synthesis and cyclin D1 gene transcription, has been determined in the hepatoma cell line; moreover, the role of ERα domains also has been studied and compared with HeLa cells that do not express detectable levels of either ERα or ERβ. Herein, we demonstrated the rapid and specific activation of PKC-α translocation and ERK-2 phosphorylation by E2. Such activation preceded the increase of thymidine incorporation into DNA and cyclin D1 gene expression and did not require the DNA-binding domain of ERα. The requirement of a PKC-α pathway for G1-S progression, but not for cyclin D1 gene expression, the involvement of MAP kinase pathway in both processes and the strict relationship between AP-1–responsive element motif (TRE) of the promoter and cyclin induction have been also assessed.
These results indicate that E2-induced cyclin D1 transcription can occur in HepG2 cells independently of the transcriptional activity of ER, sustaining the new model of E2 modulation in the cell cycle progression via nongenomic signaling pathways.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Reagents
17β-Estradiol, gentamicin, penicillin, RPMI-1640, and DMEM (with or without phenol red), fetal calf serum, and charcoal-stripped fetal calf serum were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO). The MAP kinase cascade inhibitors PD98059 and U0126, the PKC inhibitor Ro31-8220, the phospholipase C (PLC) inhibitor U73122, and phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) were obtained from Calbiochem (San Diego, CA). The estrogen receptor inhibitor ICI 182,780 was obtained from Tocris Cookson (Ballwin, MO). Methyl-1-[3H]thymidine (specific activity, 81 Ci/mmol) and [32P]dCTP were purchased from Amersham Biosciences (Little Chalfont, Buckinghamshire, United Kingdom). TRIzol reagent and LipofectAMINE reagent were obtained from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA). The luciferase kit was obtained from Promega (Madison, WI). GenElute plasmid maxiprep kit was obtained from Sigma-Aldrich. Bradford protein assay was obtained from Bio-Rad (Hercules, CA). The monoclonal and policlonal anti-phospho-ERK-2, anti-ERK-1 and -2, anti-β-actin, and anti-PKC isoform antibodies were obtained from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA). CDP-Star, chemiluminescence reagent for Western blot, was obtained from PerkinElmer Life Sciences (Boston, MA).
All the other products were from Sigma-Aldrich. Analytical or reagent grade products, without further purification, were used.
Cell Culture
HepG2 and HeLa cells were routinely grown in 5% CO2 in air in modified, phenol red-free RPMI-1640 and DMEM, respectively, containing 10% (vol/vol) charcoal-stripped fetal calf serum, l-glutamine (2 mM), gentamicin (10 μg/ml), and penicillin (100 U/ml). Cells were passaged every 4 d and media changed every 2 d.
DNA Synthesis
DNA synthesis was assayed by incubating subconfluent cells (70–80%) with methyl-1-[3H]thymidine (final concentration, 1 μCi/ml). Cells were contemporary treated with E2 (final concentration, 10 nM) or vehicle (ethanol/phosphate-buffered saline, 1:10 vol/vol). Ro31-8220 (final concentration, 1 μM), or PD98059 (final concentration, 10 μM), or U0126 (final concentration, 10 μM), or ICI 182,780 (final concentration, 1 μM) 15 min before E2 and methyl-1-[3H]thymidine. Thymidine incorporation was assayed 1 h after E2 administration as reported previously (Marino et al., 2001a).
Plasmids
The gene reporter plasmids pC3-luciferase (pC3), p3-ERE-TATA-luciferase (p3-ERE), pXP2-D1-2966-luciferase (pD1), pXP2-D1Δ-944-luciferase (-944), pXP2-D1Δ-848-luciferase (-848), pXP2-D1Δ-254-luciferase (-254), and the plasmids containing the vector expression for pCR3.1-β-galactosidase, pCMV5-hERα, pCMV5-empty, pKCR2-HE14 (N-terminal deletion mutant of HE0 lacking A/B- and DNA-binding domains, amino acids 1–281) have been described previously (Herber et al., 1994; Marino et al., 2001). Plasmids were purified for transfection by using a plasmid preparation kit according to manufacturer's instructions. A luciferase dose-response curve showed that the maximum effect was present when 1 μg of plasmids was transfected together with 1 μg of pCR3.1-β-galactosidase to normalize for transfection efficiency (∼55–65%).
Transfection and Luciferase Assay
Cells were grown to ∼70% confluence and transfected using LipofectAMINE reagent according to the manufacturer's instructions. Six hours after transfection the medium was changed and 24 h thereafter cells were stimulated with 10 nM E2 for 6 h. In some experiments, HepG2 were treated with estradiol-bovine serum albumin (BSA) conjugate [β-estradiol 6-(o-carboxy-methyl)oxime:BSA, E2-BSA]. This form of macromolecular-bound estrogen does not pass through plasma membrane and is much more water soluble than free E2 (Zheng et al., 1996). To ensure the absence of free E2 in these preparations, aliquots were preabsorbed with dextran-coated charcoal to remove >99% of free steroid hormone (Dembinski et al., 1985; Russell et al., 2000). No difference in activity was found between noncharcoal-treated and charcoal-treated aliquots. When indicated 1 μM of the PKC inhibitor Ro31-8220 or 1 μM of the PLC inhibitor U73122 or 10 μM PD98059 or 10 μM U0126 (MAP kinase cascade inhibitors) was added, and reporter plasmid expression was evaluated 6 h thereafter. The cell lysis procedure as well as the subsequent measurement of luciferase gene expression was performed using the luciferase kit according to the manufacturer's instructions with an EC & G Berthold luminometer.
Electrophoresis and Immunoblotting
After treatment with inhibitors and hormone, cells were lysed as described previously (Marino et al., 2001) and solubilized in 0.125 M Tris-HCl, pH 6.8, containing 10% SDS (wt/vol), 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, and 5 μg/ml leupeptin and boiled for 2 min. Total proteins were quantified using the Bradford protein assay (Bradford, 1976). Solubilized proteins (20 μg) were resolved by 7.5% (for PKC-α) and 10% (for ERK) SDS-PAGE at 100 V for 1 h. The proteins were then electrophoretically transferred to nitrocellulose for 45 min at 150 V at 4°C. The nitrocellulose was treated with 1% bovine serum albumin in 138 mM NaCl, 25 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, and then probed at room temperature for 1 h with anti-phospho-ERK-2. The nitrocellulose was stripped by Restore Western blot stripping buffer (Pierce Chemical, Rockford, IL) for 10 min at room temperature and then probed with anti-ERK-1 and -2 and anti-β-actin antibodies (1 μg/ml). Anti-β-actin antibody was used to normalize the sample loading. The PKC-α translocation from cytosol to membrane was assessed as reported previously (Marino et al., 2001). In brief, subconfluent cells were stimulated with E2 10 nM or, in some samples, pretreated with signal transduction pathway inhibitor or treated 24 h with 10 μM PMA before E2 stimulation, and, after sonication, soluble and particulate fractions were obtained by centrifuging samples at 100,000 × g for 1 h. Proteins were solubilized, separated by SDS-PAGE, and then transferred to nitrocellulose filters as described above. Filters were then probed at room temperature for 1 h with PKC-α, -β, -ε, and -δ antibodies (1 μg/ml). Antibody reaction was visualized with chemiluminescence reagent for Western blot.
RNA Extraction and Northern Blot Analysis
Isolation of RNA from stimulated cells was performed using TRIzol reagent according to the manufacturer's instructions and quantified by spectrophotometry (260 nm). The RNA was stored as a precipitate in 70% ethanol containing 0.3 M sodium acetate, pH 5.2, at −80°C. RNA was denatured and applied (20 μg/lane) to 1.2% agarose gels containing 2.2 M formaldehyde and electrophoresis was performed (4 V). RNA was transferred to a nylon membrane (Amersham Biosciences). Northern hybridization was performed using Quickhyb solution (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA). cDNA probes of human cyclin D1 (1.3-kb fragment of EcoRI-BgIII) and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) (0.5-kb XbaI-HindIII fragment of pHcGAP) were labeled with [32P]dCTP. The amounts of RNA were quantified by densitometry and normalized by comparison with GAPDH.
RESULTS
Estradiol Activates Cyclin D1 Gene/Gene Promoter Construct in HepG2 Cells
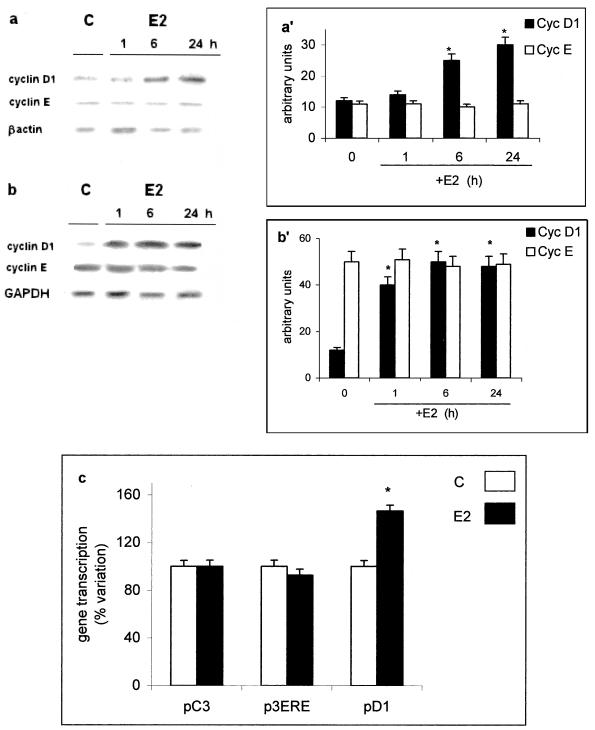
Treatment of HepG2 cells with 10 nM E2 resulted in the induction of cyclin D1 mRNA levels within 1 h (Figure 1, b and b′) and cyclin D1 protein in 6 h (Figure 1, a and a′). No E2 effect on cyclin E mRNA and protein was observed. This result, comparable with those previously reported in ER-positive breast cancer cells (Castro-Rivera et al., 2001), was surprising in hepatoma cells that contain an ER unable to transactivate ERE-containing reporter genes. Transient transfection studies with pD1 showed that treatment with E2 resulted in a significant increase in reporter cyclin D1 gene activity (Figure 1c) comparable with those reported previously (Watanabe et al., 1996). On the contrary, E2 treatment was unable to induce E2-responsive constructs containing consensus ERE (i.e., promoter of complement 3 gene, pC3, construct of three ERE repeats, p3ERE); E2-induced transactivation of these genes was observed only after cotransfection with an ERα-expression plasmid (our unpublished data).
Figure 1.
Estradiol-induced gene expression in HepG2 cells. Western (a) and Northern (b) blot analysis of cyclin D1 and cyclin E were performed, as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS, on control (C) and estradiol-treated HepG2 cells (E2) (10 nM) at different times. The amounts of protein and mRNA levels were normalized by comparison with β-actin expression or with GAPDH (a′ and b′, densitometric analysis). Data are the means ± SD of three independent experiments. (c) Luciferase assay detection on HepG2 cells transfected with pC3-luciferase (pC3), p3xERE-TATA-luciferase (p3ERE), and pXP2-D1-2966-luciferase (pD1) and those treated 6 h with vehicle (C) or estradiol (E2) (10 nM). Data are the means ± SD of four independent experiments. *P < 0.001, compared with respective control values (C).
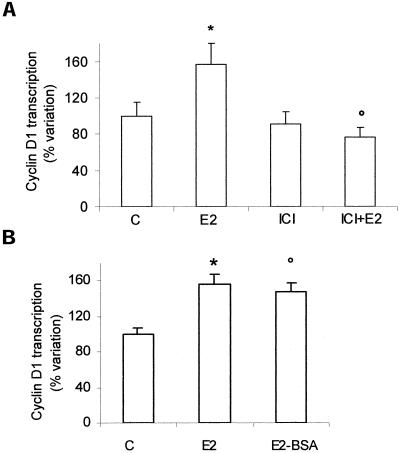
Induction of Cyclin D1 Promoter by Estradiol Can Be Selectively Blocked by Antagonist, Is Mimicked by E2-BSA, and Does Not Require DNA-binding Domain of ER
To determine the ER involvement in the E2 induction of the cyclin D1 promoter, the estrogen antagonist ICI 182,780 was tested as a possible inhibitor of this response. When added alone, it did not affect the cyclin D1 promoter activity, whereas its addition before E2 completely blocked the estrogen-induced stimulation (Figure 2a).
Figure 2.
Involvement of estrogen receptor on cyclin D1 promoter activity in HepG2 cells. Luciferase assay detection on HepG2 cells transfected with pXP2-D1–2966-luciferase, and respectively pretreated 15 min with ICI 182,870 (1 μM) (ICI) (a) and then stimulated 6 h with vehicle (C), estradiol (E2) (10 nM), or E2-BSA (10 nM) (b). Data are expressed as percentage variation with respect to the controls and are the means ± SD of four independent experiments. *P < 0.001, compared with respective control values (C), determined using Student's t test. °P < 0.001, compared with respective E2 values, determined using Student's t test.
To test whether the induction of cyclin D1 promoter transcription by E2 can be mediated by the binding of E2 to cell surface receptors, HepG2 cells were treated with E2-BSA conjugate, which does not pass through the plasma membrane. As shown in Figure 2b, after E2-BSA stimulation the increase of cyclin D1 promoter transcription was similar to that induced by free E2, suggesting a probable involvement of a membrane ER in cyclin D1 promoter induction.
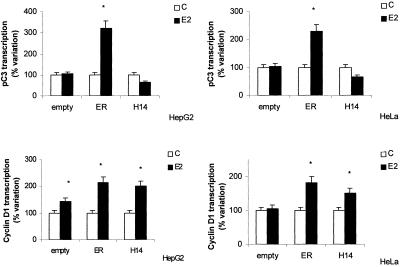
To determine the role of DNA-binding domain of ER in the induction of the cyclin D1 promoter, HepG2 cells were transiently cotransfected with the promoter of cyclin D1 or with the ERE-containing promoter pC3 together with the expression vector for human ERα or the ERα mutant HE14 lacking A/B- and DNA-binding domains of receptor as N-terminal deletions. To avoid interference due to the presence of endogenous ER (Marino et al., 2001a), a similar experiment was performed in ER-lacking HeLa cells. In either cell line considered, E2-induced pC3 gene transcription is observed only after cotransfection with ERα-expression plasmid (Figure 3, top). On the contrary, hormone-induced cyclin D1 promoter transcription was observed, in both cell lines, even after the cotransfection with ERα mutant HE14 (Figure 3, bottom). Thus, it seems that neither DBD nor activation function-1 domain of ERα are required for the full estradiol induction of cyclin D1 promoter activity in HepG2 cells.
Figure 3.
C3 and cyclin D1 gene promoter activity in HepG2 and HeLa cells. Luciferase assay detection on HepG2 and HeLa cells cotransfected with pXP2-D1-2966-luciferase (bottom) or pC3-luciferase (pC3) (top) and pCMV5-empty vector (empty), pCMV5-hERα (ER), or pKCR2-HE14 (H14) and then treated 6 h with vehicle (C) or E2 (10 nM). Data are expressed as percentage of variation with respect to the controls and are the means ± SD of four independent experiments. *P < 0.001, compared with respective control values (C), determined using Student's t test.
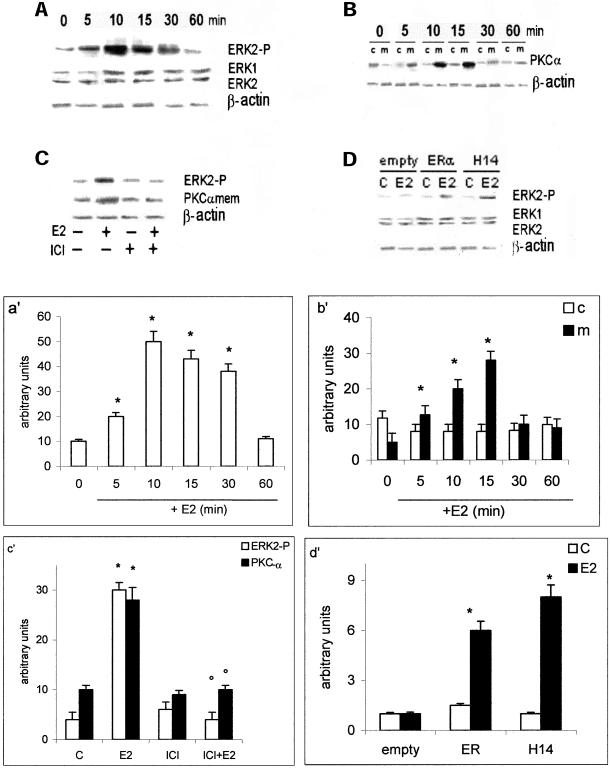
Estradiol Stimulation of HepG2 Cells Rapidly Activates PKC-α Translocation and ERK-2 Phosphorylation
The presence of E2-induced activation of signal transduction pathways was studied in HepG2 cells. Figure 4, a and a′, show E2-induced ERK-2 phosphorylation 5 min after hormone treatment, the stimulation reached a peak after 10 min and decreased toward the basal level after 60 min. No estradiol effect was present on the total level of ERK-1 and -2 proteins. The similar time-course activation was present on PKC-α translocation from cytosol to the membrane of E2-stimulated cells (Figure 4, b and b′). Both PKC-α translocation and ERK-2 phosphorylation were prevented by pretreating cells with the complete anti-ER ICI 182,780 (Figure 4, c and c′). To evaluate the ability of ERα mutant HE14 to mediate rapid activation of MAP kinase pathway, HeLa cells were transfected with ERα- or ERα HE14-expression plasmids and stimulated for 10 min with E2. Figure 4, d and d′, show that E2 induces ERK-2 phosphorylation only in the presence of ERα even when the DBD domain is lacking, confirming the inessentiality of this ER domain in E2-induced rapid signal transduction pathway.
Figure 4.
MAP kinase and PKC-α pathways activation in HepG2 and HeLa cells. Time course of ERK-2 phosphorylation (a) and PKC-α translocation to the membranes (b) in HepG2 cells were performed by Western blot analysis, as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS, on control (0) and on estradiol-treated cells (E2) (10 nM) at different times. The amounts of protein were normalized by comparison with ERK-1 and ERK-2 or β-actin level expression (a′ and b′, densitometric analysis). Western blot analysis both of ERK-2 phosphorylation and PKC-α levels on membranes after pretreating 15 min with ICI 182,870 (1 μM) (ICI) on control (−) and on 10-min estradiol-treated HepG2 cells (E2) (10 nM) (c) and of ERK-2 phosphorylation on control (C) and on 10-min estradiol-treated HeLa cells (E2) (10 nM) (d) were performed as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS. The amounts of protein were normalized by comparison with ERK-1 and ERK-2 or β-actin level expression (c′ and d′, densitometric analysis). Data are the means ± SD of three independent experiments. *P < 0.001, compared with respective control values (C), determined using Student's t test. °P < 0.001, compared with respective E2 values, determined using Student's t test.
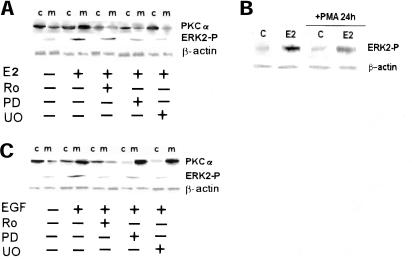
The presence of a cross talk between ERK and PKC-α signaling pathways in HepG2 cells was analyzed by using specific inhibitors. Figure 5a shows that the PKC-α inhibitor used (Ro31-8220) blocked the E2-induced PKC-α translocation on membranes and decreased the ERK-2 phosphorylation (∼50% ± 4.5). Because Ro31-8220 is an inhibitor of all PKC isoforms, we treated cells 24 h with PMA, which caused the complete and selective down-regulation of PKC-α isoform (Marino et al., 2000, 2001). The results shown in Figure 5b confirm that ERK-2 phosphorylation is only partially mediated by PKC-α. The pretreatment of cells with two MAP kinase cascade inhibitors (PD98059 or U0126) caused the block of ERK-2 phosphorylation and a decrease of PKC-α translocation from cytosol to the membrane (Figure 5a), suggesting that E2-activated PKC-α and MAP kinase are two parallel signals cross talking each other. The result obtained with MAP kinase inhibitors is E2 specific. In fact EGF, one of the well-known mitogens for HepG2 cells, activates both PKC-α and ERK-2, but the block of PKC-α prevented the MAP kinase activation being the MAP kinase downstream to the PKC-α (Figure 5c).
Figure 5.
Cross talk between MAP kinase and PKC-α pathways in HepG2. Western blot analysis both of ERK-2 phosphorylation and PKC-α translocation to the membranes (a) in HepG2 cells were performed as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS on control (−) and on stimulated cells for 10 min with E2 (10 nM) or epidermal growth factor (EGF) (10 nM) after 15 min of pretreatment with the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase inhibitors PD98059 (PD) and U0126 (U0) (10 μM) or with the PKC inhibitor Ro31-8220 (Ro) (1 μM) (c) and of ERK-2 phosphorylation were performed on control (C) and on 10-min estradiol-treated HepG2 cells (E2) (10 nM), after 24 h of pretreatment with PMA (10 μM) (b). The amounts of protein were normalized by comparison β-actin level expression. Shown are typical Western blots of three independent experiments.
Induction of Cyclin D1 Promoter by Estradiol Is Mediated by MAP Kinase but Not by PKC-α
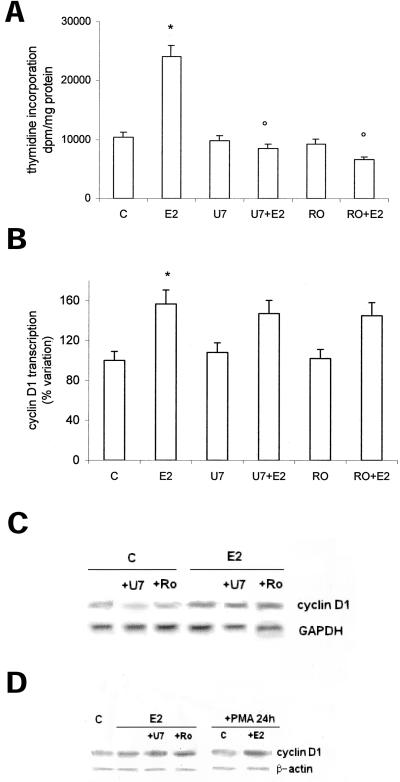
The role of estradiol-induced PKC-α activation on both DNA synthesis and cyclin D1 promoter transcription was evaluated in HepG2 cells. We described previously that PKC-α is downstream to the estradiol-induced PLC activation (Marino et al., 1998). To assess the involvement of PLC/PKC-α pathway, we treated cells with both PLC inhibitor U73122 and PKC-α inhibitor Ro31-8220. Figure 6a confirms that both inhibitors prevented the E2-induced increase of labeled thymidine into DNA, whereas they were ineffective to block cyclin D1 promoter activity, mRNA, and protein accumulation 1 and 6 h after E2 stimulation, respectively (Figure 6, b and c). To further exclude this pathway in post-transcriptional events the cells were treated for 24 h with PMA to obtain the PKC-α down-regulation or with PLC and PKC inhibitors (Figure 6d) before stimulation with E2. The data show that E2 still induces cyclin D1 protein accumulation 6 h after E2 administration.
Figure 6.
Role of PKC-α in cyclin D1 gene transcription and DNA synthesis in HepG2 cells. Tymidine incorporation into DNA has been evaluated as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS on HepG2 cells pretreated 15 min with the PKC inhibitor Ro31-8220 (Ro) (1 μM) and then stimulated 6 h with vehicle (C) or E2 (10 nM) (a). Luciferase assay detection on HepG2 cells transfected with pXP2-D1-2966-luciferase and then stimulated 6 h with vehicle (C) or E2 (10 nM), after 15 min of pretreatment with the PKC inhibitor Ro31-8220 (Ro) (1 μM) or PLC inhibitor U73122 (U7) (1 μM) (b). Data are expressed as disintegrations per minute per total protein extracted and as percentage variation with respect to the controls and are the means ± SD of four independent experiments. *P < 0.001, compared with respective control values (C), determined using Student's t test. °P < 0.001, compared with respective E2 values, determined using Student's t test. Northern (c) and Western (d) blot analysis of cyclin D1 were performed as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS on control (C) and on E2-stimulated HepG2 cells (10 nM) pretreated with the PKC inhibitor Ro31-8220 (Ro) (1 μM) or PLC inhibitor U73122 (U7) (1 μM) and PMA (10 μM), respectively. The amounts of mRNA and protein levels were normalized by comparison with GAPDH and β-actin expression. Shown are typical blots of three independent experiments.
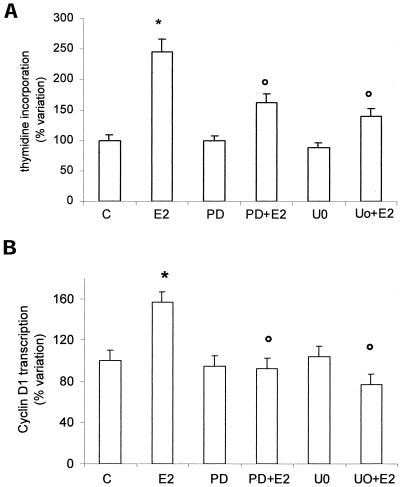
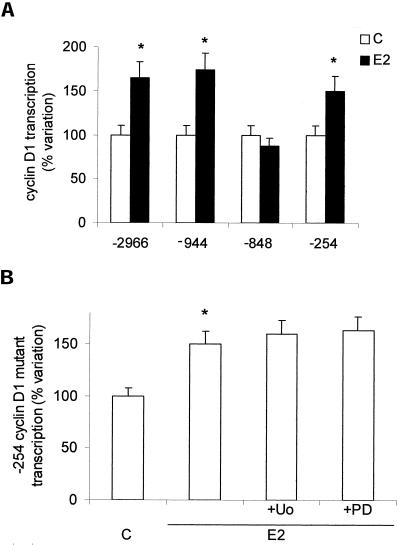
On the contrary, E2-induced ERK-2 phosphorylation is strongly involved in both DNA synthesis and cyclin D1 promoter activity. In fact, both inhibitors used (PD98059 and U0126) strongly prevented thymidine incorporation and cyclin D1 transcription (Figure 7, a and b). To investigate the involvement of the AP-1, one of the MAP kinase pathway targets, the role of TRE motif in the E2-induced cyclin D1 promoter activation in HepG2 cells has been checked. The activity of the complete cyclin D1 promoter construct (-2966) has been compared with that of deletion mutants -944, -848, and -254 (Figure 8a). Destruction of the motif -848 caused complete loss of estrogen responsiveness. Surprisingly, the cells transiently transfected with deletion mutant -254 still showed the enhancing effects of E2, which were not prevented by MAP kinase pathway inhibitors (Figure 8b). These data further support an essential role of ERK-2 and TRE motif in mediating estradiol effects.
Figure 7.
Role of ERK in cyclin D1 gene promoter activity and DNA synthesis in HepG2 cells. Tymidine incorporation into DNA has been evaluated as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS on HepG2 cells pretreated 15 min with the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase inhibitors PD98059 (PD) and U0126 (U0) (10 μM) and then stimulated 6 h with vehicle (C) or E2 (10 nM) (a). Luciferase assay detection on HepG2 cells transfected with pXP2-D1–2966-luciferase and than stimulated 6 h with vehicle (C) or E2 (10 nM) after 15 min of pretreatment with the MAP kinase pathway inhibitors PD98059 (PD) and U0126 (U0) (10 μM) (b). Data are expressed as percentage of variation with respect to the controls and are the means ± SD of four independent experiments. *P < 0.001, compared with respective control values (C), determined using Student's t test. °P < 0.001, compared with respective E2 values, determined using Student's t test.
Figure 8.
Cyclin D1 gene promoter regulation by estradiol in HepG2 cells. Luciferase assay detection on HepG2 cells transfected with pXP2-D1-2966-luciferase (-2966), pXP2-D1Δ-944-luciferase (-944), pXP2-D1Δ-848-luciferase (-848), and then treated 6 h with vehicle (C) or estradiol (E2) (10 nM) (a). Luciferase assay detection on cells transfected with pXP2-D1Δ-254-luciferase (-254) and treated 6 h with vehicle (C) or E2 (10 nM) after 15 min of pretreatment with the MAP kinase pathway inhibitors PD98059 (PD) and U0126 (U0) (10 μM) (b). Data are expressed as percentage of variation with respect to the controls and are the means ± SD of four independent experiments. *P < 0.001, compared with respective control values (C), determined using Student's t test.
DISCUSSION
The mechanism by which estradiol alters cellular function and, in particular, cell growth has been largely investigated focusing mainly on mammary gland cells. Less attention was given to cell lines derived from the liver, a well-known estrogen target organ. The human hepatoma HepG2 cell line has been shown to retain many of the differentiated characteristics of quiescent hepatocytes, including estradiol responsiveness: mitochondrial superoxide production (Chen et al., 1999), up-regulation of the class B scavenger receptor (Graf et al., 2001), apolipoprotein synthesis (Archer et al., 1985; 1986), thymidine incorporation into DNA (Marino et al., 2001a), IP3 production, and PKC-α activation (Marino et al., 1998, 2001a) were reported. HepG2 cells, cultured in medium not supplemented with estrogen, maintain ER expression (Tam et al., 1986; Farsetti et al., 1998), although at levels insufficient to induce a ligand-dependent transactivation of synthetic ERE-containing target genes (Marino et al., 2001). These characteristics make these cells a useful experimental model for studying the role played by estradiol-induced nongenomic actions on hepatic cell proliferation. Therefore, the putative role of E2-induced rapid signal transduction pathways on DNA synthesis and on cyclin D1 expression in HepG2 cells was investigated.
Cyclin D1, important for the progression of cells through the G1 phase of the cell cycle, is a well-defined target for E2 action in mammary carcinoma cells (Foster et al., 2001), even though no ERE-like sequence in the promoter of cyclin D1 gene has been detected (Herber et al., 1994). Recent evidence suggests that cyclin D1 is deeply involved in the regulation of cyclin E/Cdk2 complexes, mainly responsible for G1/S transition through the Cdk-inhibitor sequestration (Roberts, 1999). Our data showing that E2 selectively induces cyclin D1 gene expression and protein without affecting cyclin E, reinforces the concept that cyclin D1 is, even in liver-derived cells, the upstream sensor of estrogen-induced proliferative signals.
That E2 activation of cyclin D1 promoter is ER dependent, despite HepG2 cells containing low levels of ER unable to transactivate ERE-containing reporter genes, suggests a DNA-binding–independent effect of ER. This is confirmed by the estradiol-induced cyclin D1 promoter activity observed in both HepG2 and HeLa cells even if cotransfected with the mutant ER lacking both A/B- and DNA-binding domains. It is interesting to note that cotransfection of HepG2 with ERα-expression plasmid, with respect to the endogenous ER, increased the E2-induced cyclin D1 promoter activity; this could be due to the high copy number of the ER in the plasmid-transfected cells (Augereau et al., 1994; Castro-Rivera et al., 2001). Furthermore, the result obtained with E2-BSA indicates that the induction of the cyclin D1 promoter probably requires a membrane ER. Moreover, the absence in cyclin D1 promoter of any ERE sequence supports the role of rapid signal transduction pathways in E2-induced cyclin D1 gene induction in HepG2 cells.
Rapid/nongenomic effects of E2, potentially able to regulate cell proliferation, have been reported previously (Castoria et al., 2001; Coleman and Smith, 2001). In particular, in the HepG2 cells the PLC/PKC-α signal transduction pathway was induced just 1 min after the E2 addition. Herein, we confirm the E2-induced activation of PKC-α and demonstrate the parallel and synergic activation of ERK/MAP kinase pathway 10 min after E2 administration. The effects of specific inhibitors showed a decreased level of activation of both proteins. The short E2 treatment required inducing PKC-α and ERK-2 phosphorylation further supports the presence of a membrane receptor for E2 in the cell. Because the putative receptor has not been isolated and biochemically characterized, its derivation or its structural and functional characteristics are unknown; however, recently, different categories of putative membrane estrogen receptors have been reported (Norfleet et al., 2000; Kelly and Levin, 2001). The data presented herein showing that ERK-2 is rapidly phosphorylated in HeLa cells transiently transfected with expression vector for soluble ERα or with ERα mutant HE14 are consistent with previous data showing that ERα, as well as ERβ, can elicit a variety of rapid signal transduction events in transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells (Razandi et al., 1999) and that an anti-ERα antibody is able to cross-link with both nuclear and membrane receptors (Norfleet et al., 2000). These results together with recent confocal microscopy studies (Song et al., 2002) suggest that the effect on ERK-2 activation is mediated by a fraction of the classical receptor associated with the plasma membrane.
The E2-induced signaling pathways play different roles in cell proliferation. In fact, the E2-induced PKC-α is strongly related to DNA synthesis, but is not involved in cyclin D1 induction, suggesting that its role is focused on the steps after cyclin D1 induction. On the contrary, E2-induced ERK-2 phosphorylation is strongly involved in both DNA synthesis and cyclin D1 promoter activity as confirmed by the effects of the inhibitors used. Together, these data support that estradiol-induced cyclin D1 transcription is independent of ER-DBD domain and dependent on rapid/nongenomic effects.
The biological effects of the ER, independent of its transcriptional activity in the nucleus, have been reported recently (Simoncini et al., 2000; Kousteni et al., 2001; Marino et al., 2001). At present, it is well known that ERα and ERβ can also modulate the expression of genes without direct binding to DNA (Nilsson et al., 2001). Interaction between ERα and c-rel subunit of nuclear factor-κB, SP1, and AP-1 transduction factors are good examples of such modulation (Nilsson et al., 2001), but ERα-stimulated gene expression mechanism is controversial (Webb et al., 1999; Jakacka et al., 2001). Our results support the idea that neither DBD nor AF1 domain of ER is required for the estradiol induction of cyclin D1 promoter activity in HepG2 cells. Furthermore, destruction of the TRE motif -848 caused complete loss of estrogen responsiveness, indicating an essential role of the TRE motif in mediating nongenomic estradiol effects on cyclin D1 transcription.
Several cyclin D1 activation mechanisms have been identified in mammary carcinoma cells (Sabbah et al., 1999; Castoria et al., 2001; Castro-Rivera et al., 2001; Nagata et al., 2001). In particular, it has been suggested that the three GC-rich SP1 sites at −143 to −110 and the CRE motif at −96 regions of the promoter are the major mediators for the induction of the cyclin D1 promoter by E2 (Sabbah et al., 1999; Castro-Rivera et al., 2001). These investigators transfected mammary carcinoma cells with a deleted cyclin D1 promoters lacking of TRE motif: −163 and −96, respectively. It is noteworthy that the enhanced effect of E2 on cyclin D1 promoter is present with the mutant −254, which contains the Oct/Sp1 and CRE motifs but lacks E2F and the E-box (Herber et al., 1994), suggesting a negative role for these two motifs in the regulation of cyclin D1 promoter by E2. Moreover, the inability of MAP kinase pathway inhibitors to prevent such an increase further sustains that the TRE motif of cyclin D1 promoter is the target of this E2-induced signal transduction pathway.
In conclusion, our data indicate that in HepG2 cells, E2, via a likely membrane-associated ER, induces different and parallel signal transduction pathways, which may modulate distinct steps in the G1/S phase transition. The MAP kinase cascade is involved in the regulation of the cyclin D1 transcription and PKC-α pathway in the subsequent steps that lead to DNA synthesis (i.e., Cdk activation). Finally, the E2-dependent activation of cyclin D1 is a multifactorial process involving different regulatory elements present in cyclin D1 promoter: AP1, STAT5, nuclear factor-κB, E2F, Oct1, SP1, and CRE are good examples of such activation (Liu et al., 2002, and references therein). Rapid/nongenomic mechanisms represent a new model of E2-induced cyclin D1 activation.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The generous gift of cyclin D1 and cyclin E cDNA probes and antibodies from Dr. Liz Musgrove (Garvan Institute, Sidney, Australia), of human cyclin D1-luciferase reporter genes from Prof. M. Beato (IMT, Marburg, Germany), of human ERα mutant expression vector from Prof. P. Chambon (Institut de Genetique et de Biologie Moleculaire et Cellulaire, Strasbourg, France), and of ERE-containing promoter constructs from Prof. D. McDonnell (Department of Pharmacology and Cancer Biology, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, NC) are gratefully acknowledged. This work was supported by grants from MIUR (PRIN 2001-02) and 2001 Università “Roma Tre” to M.M., from MIUR (PRIN 2001-02) (to F.B.) and from Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (to A.W.).
Footnotes
Article published online ahead of print. Mol. Biol. Cell 10.1091/mbc.E02–03–0153. Article and publication date are at www.molbiolcell.org/cgi/doi/10.1091/mbc.E02–03–0153.
REFERENCES
- Altucci L, Addeo R, Citatiello L, Davois S, Parker MG, Truss M, Beato M, Sica V, Bresciani F, Weisz A. 17β-Estradiol induces cyclin D1 gene transcription, p36D1-p34cdk4 complex activation and p105Rb phosphorylation during mitogenic stimulation of G1-arrested human breast cancer cell. Oncogene. 1996;12:2315–2324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer TK, Tam SP, Deeley RG. Kinetics of estrogen-dependent modulation of apolipoprotein A-I synthesis in human hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1986;261:5067–5074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer TK, Tam SP, Deugau KV, Deeley RG. Apolipoprotein C-II mRNA levels in primate liver. Induction by estrogen in the human hepatocarcinoma cell line, HepG2. J Biol Chem. 1985;260:1676–1681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augereau P, Miralles F, Cavailles V, Gaudelet C, Parker M, Rochefort H. Characterization of the proximal estrogen-responsive element of human cathepsin D gene. Mol Endocrinol. 1994;8:693–703. doi: 10.1210/mend.8.6.7935485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Ann Biochem. 1976;772:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castoria G, Barone MV, Di Domenico M, Bilancio A, Ametrano D, Migliaccio A, Auricchio F. Non-transcriptional action of estradiol and progestin triggers DNA synthesis. EMBO J. 1999;18:2500–2510. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.9.2500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castoria G, Migliaccio A, Bilancio A, Di Domenico M, de Falco A, Lombardi M, Fiorentino R, Varricchio L, Barone MV, Auricchio F. PI3-kinase in concert with Src promotes the S-phase entry of estradiol-stimulated MCF-7 cells. EMBO J. 2001;20:6050–6059. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.21.6050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro-Rivera E, Samudio I, Safe S. Estrogen regulation of cyclin D1 gene expression in ZR-75 breast cancer cells involves multiple enhancer elements J. Biol Chem. 2001;276:30853–30861. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M103339200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J, Lavigne JA, Trush MA, Yager JD. Increased mitochondrial superoxide production in rat liver mitochondria, rat hepatocytes, and HepG2 cells following ethinyl-estradiol treatment. Toxicol Sci. 1999;51:224–235. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/51.2.224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman KM, Smith CL. Intracellular signaling pathways. nongenomic actions of estrogens and ligand-independent activation of estrogen receptors. Frontiers Biosci. 2001;6:d1379–d1391. doi: 10.2741/coleman. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dembinski TC, Leung CK, Shiu RP. Evidence for a novel pituitary factor that potentiates the mitogenic effect of estrogen in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1985;45:3083–3089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Croce L, Bruscalupi G, Trentalance A. Independent behavior of rat liver LDL receptor and HMGCoA reductase under estrogen treatment. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996;16:345–350. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1996.1031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Croce L, Bruscalupi G, Trentalance A. Independent responsiveness of frog liver low-density lipoprotein receptor and HMGCoA reductase to estrogen treatment. Pfluger Arch. 1997;435:107–111. doi: 10.1007/s004240050489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Croce L, Vicent GP, Pecci A, Bruscalupi G, Trentalance A, Beato M. The promoter of the rat 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase gene contains a tissue-specific estrogen-responsive region. Mol Endocrinol. 1999;13:29–43. doi: 10.1210/mend.13.8.0333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Distefano E, Marino M, Gillette JA, Hanstein B, Pallottini V, Brüning J, Krone W, Trentalance A. Role of tyrosine kinase-signaling in estrogen-induced LDL-receptor gene expression in HepG2 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002;1580:145–149. doi: 10.1016/s1388-1981(01)00197-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farsetti A, Moretti F, Narducci M, Misiti S, Nanni S, Andreoli M, Sacchi A, Pontecorvi A. Orphan receptor hepatocyte nuclear factor-4 antagonises estrogen receptor α-mediated induction of human coagulation factor XII gene. Endocrinology. 1998;139:4581–4589. doi: 10.1210/endo.139.11.6299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher B, Gunduz N, Saffer EA, Zheng S. Relation of estrogen and its receptor to rat liver growth and regeneration. Cancer Res. 1984;44:2410–2415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster JS, Wimalasena J. Estrogen regulates activity of cyclin-dependent kinases and retinoblastoma protein phosphorylation in breast cancer cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1996;10:488–498. doi: 10.1210/mend.10.5.8732680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster JS, Henley DC, Ahamed S. Estrogens, and cell-cycle regulation in breast cancer. Trends Endocrinol Metabol. 2001;12:320–327. doi: 10.1016/s1043-2760(01)00436-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf GA, Roswell KL, Smart EJ. 17β-Estradiol promotes the up-regulation of SR-BII in HepG2 cells, and in rat liver. J Lipid Res. 2001;42:1444–1449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herber B, Truss M, Beato M, Müller R. Inducibile regulatory elements in the human cyclin D1 promoter. Oncogene. 1994;9:1295–1304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakacka M, Ito M, Weiss J, Chien PY, Gehm BD, Jameson JL. Estrogen receptor binding to DNA is not required for its activity through the nonclassical AP-1 pathway. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:13615–13621. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M008384200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly MJ, Levin ER. Rapid actions of plasma membrane estrogen receptors. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2001;12:152–156. doi: 10.1016/s1043-2760(01)00377-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kousteni S, et al. Nongenotropic, sex-nonspecific signaling through the estrogen or androgen receptors: dissociation from transcriptional activity. Cell. 2001;104:719–790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.-M., Albanese, C., Anderson, C.M., Hilty, K., Webb, P., Uht, R.M., Price, R.H. Jr., Pestell, R.G., and Kushner, P.J. (2002) Opposing action of estrogen receptors α, and β on cyclin D1 gene expression. J. Biol. Chem., in press. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Marino M, Distefano E, Trentalance A, Smith CL. Estradiol-induced IP3 mediate the estrogen receptor activity expressed in human cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2001;182:19–26. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(01)00556-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marino M, Distefano E, Pallottini V, Caporali S, Ceracchi G, Trentalance A. β-Estradiol stimulation of DNA synthesis requires different PKC isoforms in HepG2, and MCF7 cells. J Cell Physiol. 2001a;188:170–177. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marino M, Mele R, Spagnuolo S, Pulcinelli FM, Mangiantini MT, Leoni S. EGF regulates aminoacid transport in chick embryo hepatocytes via protein kinase C-ε. Exp Physiol. 2000;85:363–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-445x.2000.01959.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marino M, Pallottini V, Trentalance A. Estrogens cause rapid activation of IP3-PKC-α signal transduction in HepG2 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;245:254–258. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1998.8413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEwen BS, Alves SE. Estrogen actions in the central nervous system. Endocrinol Rev. 1999;20:279–307. doi: 10.1210/edrv.20.3.0365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata D, Suzuki E, Nishimatsu H, Satonaka H, Goto A, Omata M, Hirata Y. Transcriptional activation of the cyclin D1 gene is mediated by multiple cis-elements, including SP1 sites, and a cAMP-responsive element in vascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:662–669. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M005522200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson S, Makela S, Treuter E, Tujague M, Thomsen J, Andersson G, Enmark E, Pettersson K, Warner M, Gustafsson JA. Mechanisms of estrogen action. Physiol Rev. 2001;81:1535–1565. doi: 10.1152/physrev.2001.81.4.1535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norfleet AM, Clarke CH, Gametchu B, Watson C. Antibodies to the estrogen receptor-α modulate rapid prolactin release from rat pituitary tumor cells through plasma membrane estrogen receptor. FASEB J. 2000;14:157–165. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.14.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prall OW, Sarcevic B, Musgrove EA, Watts CKW, Sutherland RL. Estrogen induced activation of Cdk4 and Cdk2 during G1-S phase progression is accompanied by increased cyclin D1 expression and decreased cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor association with cyclin E-Cdk2. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:10882–10894. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.16.10882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razandi M, Pedream A, Greene G, Levin ER. Cell membrane and nuclear estrogen receptors (ERs) originate from a single transcript: studies of ERα and ERβ expressed in Chinese Hamster ovary cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1999;13:307–319. doi: 10.1210/mend.13.2.0239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts JM. Evolving ideas about cyclins. Cell. 1999;98:129–132. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell KS, Haynes MP, Sinha D, Clerisme E, Bender JR. Human vascular endothelial cells contain membrane binding sites for estradiol, which mediate rapid intracellular signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97:5930–5935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.11.5930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabbah M, Courilleau D, Mester J, Redeuilh G. Estrogen induction of the cyclin D1 promoter: involvement of a camp response-like element. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:11217–11222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.20.11217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoncini T, Hafezi-Moghadam A, Brazil DP, Ley K, Chin WW, Liso JK. Interaction of oestrogen receptor with the regulatory subunit of phosphathidylinositol-3-OH kinase. Nature. 2000;407:538–451. doi: 10.1038/35035131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song RX-D, McPherson RA, Adam L, Bao Y, Shupnik M, Kumar R, Santen R. Linkage of rapid estrogen action to MAPK activation by ERα-Shc pathway activation. Mol Endocrinol. 2002;16:116–127. doi: 10.1210/mend.16.1.0748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland RL, Reddel RR, Green MD. Effects of estrogens on cell proliferation and cell cycle kinetics: a hypothesis on the cell cycle effects of antiestrogens. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1983;19:307–318. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(83)90127-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam SP, Hachè RJG, Deeley RG. Estrogen memory effect in human hepatocytes during repeated cell division without hormone. Science. 1986;234:1234–1237. doi: 10.1126/science.3022381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe G, Lee RJ, Albanese C, Rainey WE, Balle D, Pestell RG. Angiotensin II activation of cyclin D1-dependent kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:22570–22577. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.37.22570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb P, et al. The estrogen receptor enhances AP-1 activity by two distinct mechanisms with different requirements for receptor transactivation functions. Mol Endocrinol. 1999;13:1672–1685. doi: 10.1210/mend.13.10.0357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yager JD, Roebuck BD, Paluszcyk TL, Memoli VA. Effects of etinyl estradiol and tamoxifen on liver DNA turnover and new synthesis and appearance of gamma glutamyl transpeptidase-positive foci in female rats. Carcinogenesis. 1986;7:2007–2014. doi: 10.1093/carcin/7.12.2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng J, Ali A, Ramirez VD. Steroids conjugated to bovine serum albumin as tools to demonstrate specific steroid neuronal membrane binding sites. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 1996;21:187–197. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]